Anti-Inflammatory Brownies
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Brownies are usually full of sugar, butter, and flour. These ones aren’t! Instead, they’re full of fiber (good against inflammation), healthy fats, and anti-inflammatory polyphenols:
You will need
- 1 can chickpeas (keep half the chickpea water, also called aquafaba, as we’ll be using it)
- 4 oz of your favorite nut butter (substitute with tahini if you’re allergic to nuts)
- 3 oz rolled oats
- 2 oz dark chocolate chips (or if you want the best quality: dark chocolate, chopped into very small pieces)
- 3 tbsp of your preferred plant milk (this is an anti-inflammatory recipe and unfermented dairy is inflammatory)
- 2 tbsp cocoa powder (pure cacao is best)
- 1 tbsp glycine (if unavailable, use 2 tbsp maple syrup, and skip the aquafaba)
- 2 tsp vanilla extract
- ½ tsp baking powder
- ¼ tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 350℉ / 180℃, and line a 7″ cake tin with baking paper.
2) Blend the oats in a food processor, until you have oat flour.
3) Add all the remaining ingredients except the dark chocolate chips, and process until the mixture resembles cookie dough.
3) Transfer to a bowl, and fold in the dark chocolate chips, distributing evenly.
4) Add the mixture to the cake tin, and smooth the surface down so that it’s flat and even. Bake for about 25 minutes, and let them cool in the tin for at least 10 minutes, but longer is better, as they will firm up while they cool. Cut into cubes when ready to serve:
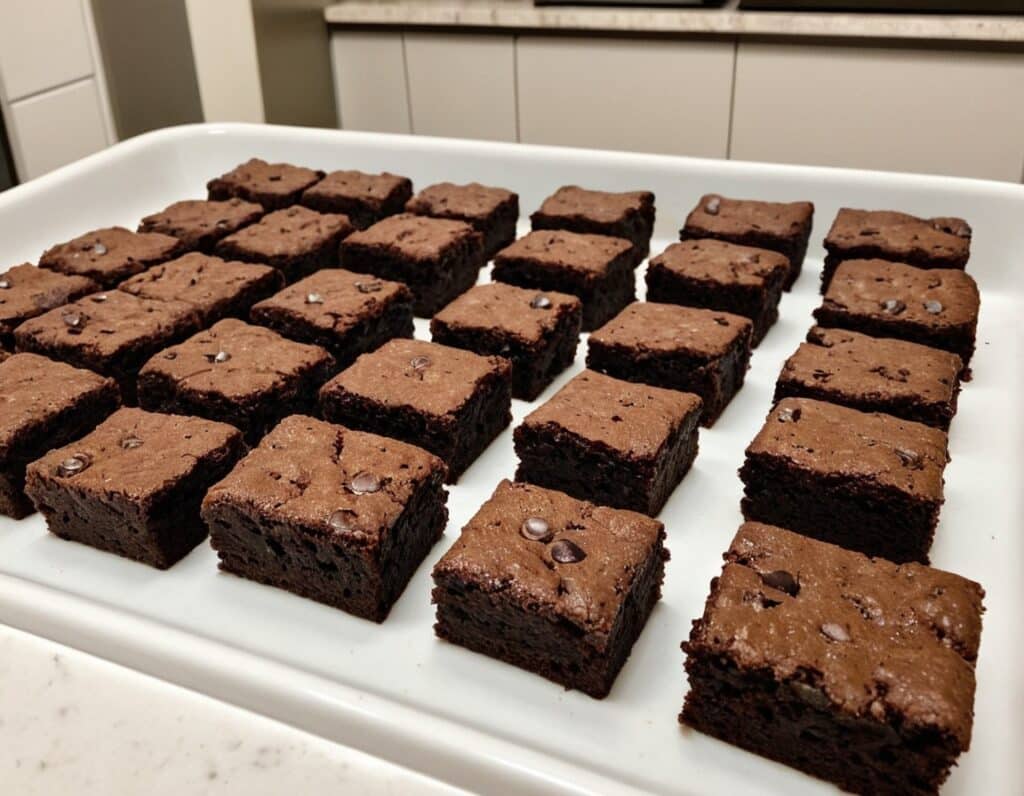

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
- Keep Inflammation At Bay
- The Sweet Truth About Glycine
- The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
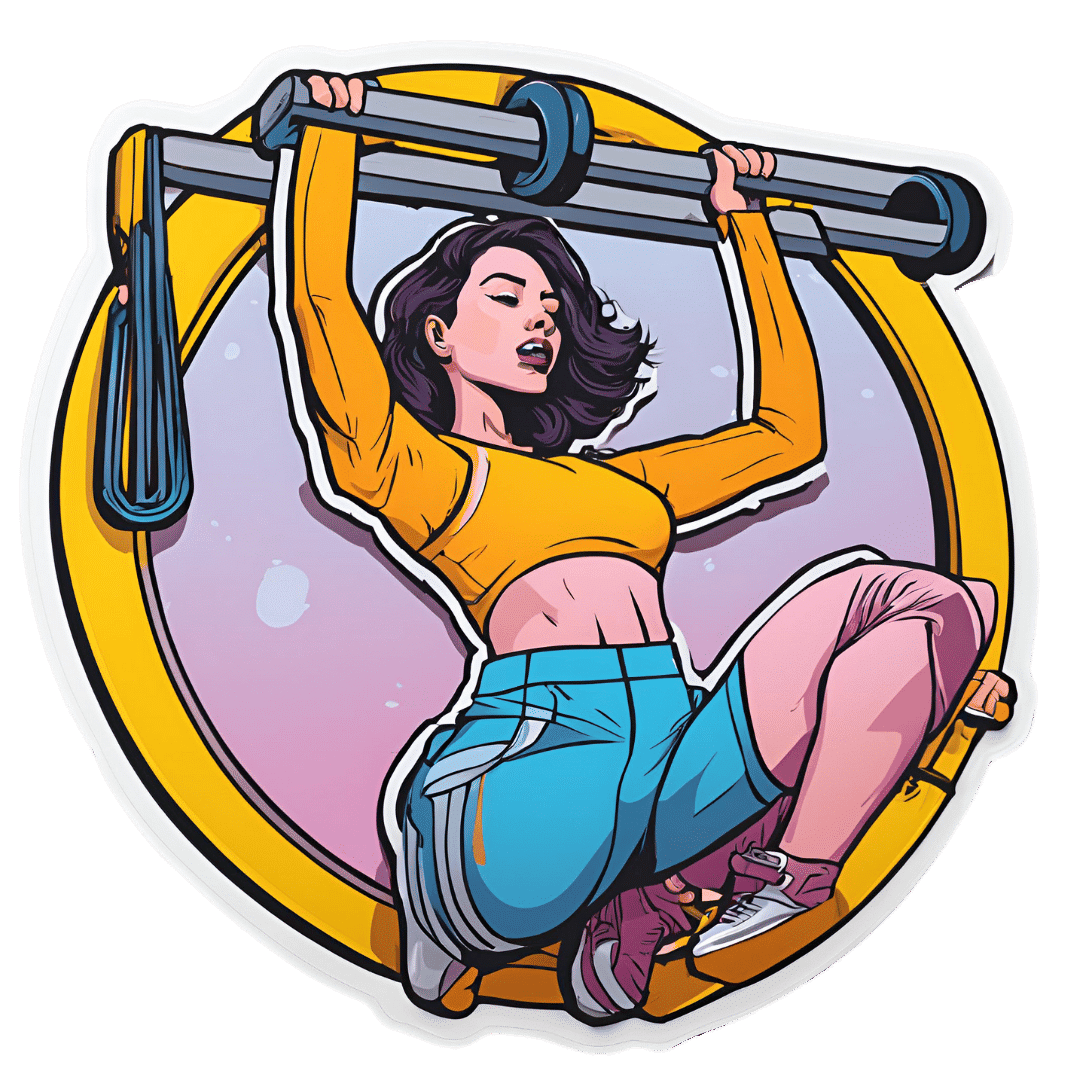
Hanging Exercises For Complete Beginners & Older Adults
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hanging (not the kind with a gallows) is great for the heath, improving not just strength and mobility, but also—critically—looking after spinal health too. Amanda Raynor explains in this video how this exercise is accessible to anyone (unless you have no arms, in which case, sorry, this one is just not for you—though hanging by your legs will also give similar spinal benefits!).
Hanging out
Hanging can be done at home or at a park, with minimal equipment (a bar, a sturdy tree branch, etc).
Note: the greater the diameter of the bar, the more it will work your grip strength, and/but the harder it will be. So, it’s recommend to start with a narrow-diameter bar first.
Getting started:
- Start with a “dead hang”: grip the bar with hands shoulder-width apart, thumb wrapped around.
- Aim to hang without pulling up; build endurance gradually (10–30 seconds is fine at first).
- Work up to holding for 60 seconds in three sets as a fitness goal.
Progression:
- If unable to hang at all initially, use a chair or stool to support some body weight.
- Gradually reduce foot support to increase duration of free hanging.
- Start with 10 seconds, progressing by small increments (e.g: 15, 20, 25 seconds) until reaching 60 seconds.
Advanced variations:
- Move the body while hanging (e.g., circles, knee lifts).
- Experiment with different grips (overhand, underhand) for varied muscle engagement.
- Try scapular pulls or one-arm hangs for additional challenge and strength-building.
For more on all of this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
13 Things Mentally Strong Couples Don’t Do – by Dr. Amy Morin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The saying “happy wife; happy life” indeed goes regardless of gender. One can have every other happiness, but if there’s relational trouble, it brings everything else down.
This book is not intended, however, only for people whose relationships are one couple’s therapy session away from divorce. Rather, it’s intended as a preventative. Because, in this as in every other aspect of health, prevention is better than cure!
It is the sign of a strong couple to be proactive about the health of the relationship, and work together to build and reinforce things along the way.
The style of this book is very accessible pop-science, but the author speaks from a strong professional background in social work, psychology, and psychotherapy, and it shows.
Bottom line: if you’d like to strengthen your relationship skills, this book gives 13 great ways to do that.
Share This Post
-
Statistical Models vs. Front-Line Workers: Who Knows Best How to Spend Opioid Settlement Cash?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
MOBILE, Ala. — In this Gulf Coast city, addiction medicine doctor Stephen Loyd announced at a January event what he called “a game-changer” for state and local governments spending billions of dollars in opioid settlement funds.
The money, which comes from companies accused of aggressively marketing and distributing prescription painkillers, is meant to tackle the addiction crisis.
But “how do you know that the money you’re spending is going to get you the result that you need?” asked Loyd, who was once hooked on prescription opioids himself and has become a nationally known figure since Michael Keaton played a character partially based on him in the Hulu series “Dopesick.”
Loyd provided an answer: Use statistical modeling and artificial intelligence to simulate the opioid crisis, predict which programs will save the most lives, and help local officials decide the best use of settlement dollars.
Loyd serves as the unpaid co-chair of the Helios Alliance, a group that hosted the event and is seeking $1.5 million to create such a simulation for Alabama.
The state is set to receive more than $500 million from opioid settlements over nearly two decades. It announced $8.5 million in grants to various community groups in early February.
Loyd’s audience that gray January morning included big players in Mobile, many of whom have known one another since their school days: the speaker pro tempore of Alabama’s legislature, representatives from the city and the local sheriff’s office, leaders from the nearby Poarch Band of Creek Indians, and dozens of addiction treatment providers and advocates for preventing youth addiction.
Many of them were excited by the proposal, saying this type of data and statistics-driven approach could reduce personal and political biases and ensure settlement dollars are directed efficiently over the next decade.
But some advocates and treatment providers say they don’t need a simulation to tell them where the needs are. They see it daily, when they try — and often fail — to get people medications, housing, and other basic services. They worry allocating $1.5 million for Helios prioritizes Big Tech promises for future success while shortchanging the urgent needs of people on the front lines today.
“Data does not save lives. Numbers on a computer do not save lives,” said Lisa Teggart, who is in recovery and runs two sober living homes in Mobile. “I’m a person in the trenches,” she said after attending the Helios event. “We don’t have a clean-needle program. We don’t have enough treatment. … And it’s like, when is the money going to get to them?”
The debate over whether to invest in technology or boots on the ground is likely to reverberate widely, as the Helios Alliance is in discussions to build similar models for other states, including West Virginia and Tennessee, where Loyd lives and leads the Opioid Abatement Council.
New Predictive Promise?
The Helios Alliance comprises nine nonprofit and for-profit organizations, with missions ranging from addiction treatment and mathematical modeling to artificial intelligence and marketing. As of mid-February, the alliance had received $750,000 to build its model for Alabama.
The largest chunk — $500,000 — came from the Poarch Band of Creek Indians, whose tribal council voted unanimously to spend most of its opioid settlement dollars to date on the Helios initiative. A state agency chipped in an additional $250,000. Ten Alabama cities and some private foundations are considering investing as well.
Stephen McNair, director of external affairs for Mobile, said the city has an obligation to use its settlement funds “in a way that is going to do the most good.” He hopes Helios will indicate how to do that, “instead of simply guessing.”
Rayford Etherton, a former attorney and consultant from Mobile who created the Helios Alliance, said he is confident his team can “predict the likely success or failure of programs before a dollar is spent.”
The Helios website features a similarly bold tagline: “Going Beyond Results to Predict Them.”
To do this, the alliance uses system dynamics, a mathematical modeling technique developed at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in the 1950s. The Helios model takes in local and national data about addiction services and the drug supply. Then it simulates the effects different policies or spending decisions can have on overdose deaths and addiction rates. New data can be added regularly and new simulations run anytime. The alliance uses that information to produce reports and recommendations.
Etherton said it can help officials compare the impact of various approaches and identify unintended consequences. For example, would it save more lives to invest in housing or treatment? Will increasing police seizures of fentanyl decrease the number of people using it or will people switch to different substances?
And yet, Etherton cautioned, the model is “not a crystal ball.” Data is often incomplete, and the real world can throw curveballs.
Another limitation is that while Helios can suggest general strategies that might be most fruitful, it typically can’t predict, for instance, which of two rehab centers will be more effective. That decision would ultimately come down to individuals in charge of awarding contracts.
Mathematical Models vs. On-the-Ground Experts
To some people, what Helios is proposing sounds similar to a cheaper approach that 39 states — including Alabama — already have in place: opioid settlement councils that provide insights on how to best use the money. These are groups of people with expertise ranging from addiction medicine and law enforcement to social services and personal experience using drugs.
Even in places without formal councils, treatment providers and recovery advocates say they can perform a similar function. Half a dozen advocates in Mobile told KFF Health News the city’s top need is low-cost housing for people who want to stop using drugs.
“I wonder how much the results” from the Helios model “are going to look like what people on the ground doing this work have been saying for years,” said Chance Shaw, director of prevention for AIDS Alabama South and a person in recovery from opioid use disorder.
But Loyd, the co-chair of the Helios board, sees the simulation platform as augmenting the work of opioid settlement councils, like the one he leads in Tennessee.
Members of his council have been trying to decide how much money to invest in prevention efforts versus treatment, “but we just kind of look at it, and we guessed,” he said — the way it’s been done for decades. “I want to know specifically where to put the money and what I can expect from outcomes.”
Jagpreet Chhatwal, an expert in mathematical modeling who directs the Institute for Technology Assessment at Massachusetts General Hospital, said models can reduce the risk of individual biases and blind spots shaping decisions.
If the inputs and assumptions used to build the model are transparent, there’s an opportunity to instill greater trust in the distribution of this money, said Chhatwal, who is not affiliated with Helios. Yet if the model is proprietary — as Helios’ marketing materials suggest its product will be — that could erode public trust, he said.
Etherton, of the Helios Alliance, told KFF Health News, “Everything we do will be available publicly for anyone who wants to look at it.”
Urgent Needs vs. Long-Term Goals
Helios’ pitch sounds simple: a small upfront cost to ensure sound future decision-making. “Spend 5% so you get the biggest impact with the other 95%,” Etherton said.
To some people working in treatment and recovery, however, the upfront cost represents not just dollars, but opportunities lost for immediate help, be it someone who couldn’t find an open bed or get a ride to the pharmacy.
“The urgency of being able to address those individual needs is vital,” said Pamela Sagness, executive director of the North Dakota Behavioral Health Division.
Her department recently awarded $7 million in opioid settlement funds to programs that provide mental health and addiction treatment, housing, and syringe service programs because that’s what residents have been demanding, she said. An additional $52 million in grant requests — including an application from the Helios Alliance — went unfunded.
Back in Mobile, advocates say they see the need for investment in direct services daily. More than 1,000 people visit the office of the nonprofit People Engaged in Recovery each month for recovery meetings, social events, and help connecting to social services. Yet the facility can’t afford to stock naloxone, a medication that can rapidly reverse overdoses.
At the two recovery homes that Mobile resident Teggart runs, people can live in a drug-free space at a low cost. She manages 18 beds but said there’s enough demand to fill 100.
Hannah Seale felt lucky to land one of those spots after leaving Mobile County jail last November.
“All I had with me was one bag of clothes and some laundry detergent and one pair of shoes,” Seale said.
Since arriving, she’s gotten her driver’s license, applied for food stamps, and attended intensive treatment. In late January, she was working two jobs and reconnecting with her 4- and 7-year-old daughters.
After 17 years of drug use, the recovery home “is the one that’s worked for me,” she said.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Aging Solo – by Ellen Dawson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many of us will face the challenge of “aging solo”, if indeed we’re not already. The premise of this book is that while it may indeed be a challenge, it can be an exciting challenge rather than a scary one.
Thus, Dawson bids us empower ourselves to tackle it head on, proactively.
To that end, she offers her “EMPOWER” framework:
- Embrace the challenge of living solo
- Manage money mindfully while welcoming desires
- Prioritize vitality and live a vibrant life
- Own your identity; build resilience and confidence
- Weave bonds: build and maintain relationships (solo doesn’t mean lacking connections!
- Energize yourself and discover new passions
- Renew yourself and create a joyful environment
Now, as listed, those may seem a little vague, but rest assured she goes into great detail in the book, with a whole chapter for each.
For example, prioritizing vitality and energizing oneself can seem like a double-up, but the former chapter is about healthy living in the context of the solo life, while the latter chapter is more about avocation lifelong learning, overcoming fear of the unknown, and making sure to actually live this one precious life, not just go through the motions.
The style is energetic and motivational, and yet backed up with 19 pages of scientific references.
Bottom line: this book is, in essence, a roadmap for aging solo and creating the future we deserve, on our own terms. An enjoyable, practical, and uplifting read!
Click here to check out Aging Solo, and thrive as a “Soloist”!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Bell Pepper vs Sweetcorn – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing bell pepper to sweetcorn, we picked the corn.
Why?
If you’re thinking “but wait, which color bell pepper, don’t they have different nutritional properties?” then firstly, well-remembered, and secondly, it doesn’t matter in this case. The main things that it affects are vitamins A and C and various polyphenols, and even the weakest bell pepper for them wins on both of those vitamins (while the strongest bell peppers for them still lose on vitamins in total) and even the strongest bell pepper for them loses on polyphenols, so the results go the same with any color.
In terms of macros, the corn has more carbs, protein, and fiber; however, both are low in glycemic index, so we’ll go with the “more food per food” option, the corn.
In the category of vitamins, even green bell peppers (the least well-endowed) have more of vitamins A, B6, C, E, and K, while sweetcorn has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B9, and choline, compared to even yellow or red bell peppers (which are the best peppers for vitamins). So, a moderate win for the corn.
When it comes to minerals, bell peppers have more calcium and copper, while sweetcorn has more iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. An easy win for sweetcorn.
In short, enjoy both, but the corn is the overall winner today!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It! ← green bell peppers are a good source of lutein, as is sweetcorn
- A Spectrum Of Specialties: Which Bell Peppers To Pick?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Falling: Is It Due To Age Or Health Issues?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝What are the signs that a senior is falling due to health issues rather than just aging?❞
Superficial answer: having an ear infection can result in a loss of balance, and is not particularly tied to age as a risk factor
More useful answer: first, let’s consider these two true statements:
- The risks of falling (both the probability and the severity of consequences) increase with age
- Health issues (in general) tend to increase with age
With this in mind, it’s difficult to disconnect the two, as neither exist in a vacuum, and each is strongly associated with the other.
So the question is easier to answer by first flipping it, to ask:
❝What are the health issues that typically increase with age, that increase the chances of falling?❞
A non-exhaustive list includes:
- Loss of strength due to sarcopenia (reduced muscle mass)
- Loss of mobility due to increased stiffness (many causes, most of which worsen with age)
- Loss of risk-awareness due to diminished senses (for example, not seeing an obstacle until too late)
- Loss of risk-awareness due to reduced mental focus (cognitive decline producing absent-mindedness)
Note that in the last example there, and to a lesser extent the third one, reminds us that falls also often do not happen in a vacuum. There is (despite how it may sometimes feel!) no actual change in our physical relationship with gravity as we get older; most falls are about falling over things, even if it’s just one’s own feet:
The 4 Bad Habits That Cause The Most Falls While Walking
Disclaimer: sometimes a person may just fall down for no external reason. An example of why this may happen is if a person’s joint (for example an ankle or a knee) has a particular weakness that means it’ll occasionally just buckle and collapse under one’s own weight. This doesn’t even have to be a lot of weight! The weakness could be due to an old injury, or Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (with its characteristic joint hypermobility symptoms), or something else entirely.
Now, notice how:
- all of these things can happen at any age
- all of these things are more likely to happen the older we get
- none of these things have to happen at any age
That last one’s important to remember! Aging is often viewed as an implacable Behemoth, but the truth is that it is many-faceted and every single one of those facets can be countered, to a greater or lesser degree.
Think of a room full of 80-year-olds, and now imagine that…
- One has the hearing of a 20-year-old
- One has the eyesight of a 20-year-old
- One has the sharp quick mind of a 20-year-old
- One has the cardiovascular fitness of a 20-year-old
…etc. Now, none of those things in isolation is unthinkable, so remember, there is no magic law of the universe saying we can’t have each of them:
Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
Which means: that goes for the things that increase the risk of falling, too. In other words, we can combat sarcopenia with protein and resistance training, maintain our mobility, look after our sensory organs as best we can, nourish our brain and keep it sharp, etc etc etc:
Train For The Event Of Your Life! (Mobility As A Long-Term “Athletic” Goal For Personal Safety)
Which doesn’t mean: that we will necessarily succeed in all areas. Your writer here, broadly in excellent health, and whose lower body is still a veritable powerhouse in athletic terms, has a right ankle and left knee that will sometimes just buckle (yay, the aforementioned hypermobility).
So, it becomes a priority to pre-empt the consequences of that, for example:
- being able to fall with minimal impact (this is a matter of knowing how, and can be learned from “soft” martial arts such as aikido), and
- ensuring the skeleton can take a knock if necessary (keeping a good balance of vitamins, minerals, protein, etc; keeping an eye on bone density).
See also:
Fall Special ← appropriate for the coming season, but it’s about avoiding falling, and reducing the damage of falling if one does fall, including some exercises to try at home.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: