13 Things Mentally Strong Couples Don’t Do – by Dr. Amy Morin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The saying “happy wife; happy life” indeed goes regardless of gender. One can have every other happiness, but if there’s relational trouble, it brings everything else down.
This book is not intended, however, only for people whose relationships are one couple’s therapy session away from divorce. Rather, it’s intended as a preventative. Because, in this as in every other aspect of health, prevention is better than cure!
It is the sign of a strong couple to be proactive about the health of the relationship, and work together to build and reinforce things along the way.
The style of this book is very accessible pop-science, but the author speaks from a strong professional background in social work, psychology, and psychotherapy, and it shows.
Bottom line: if you’d like to strengthen your relationship skills, this book gives 13 great ways to do that.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
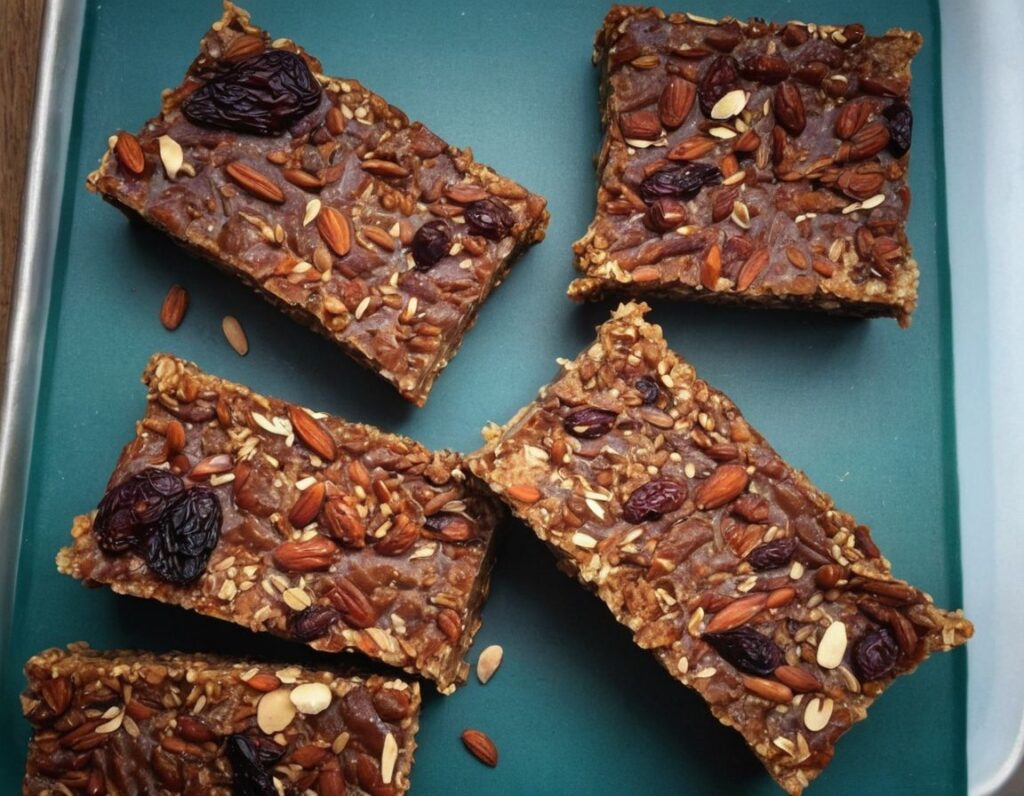
Balanced Energy Cake Bars
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Unlike a lot of commercially available products, these bars won’t spike your blood sugars in the same way. There’s technically plenty of sugar in them, mostly from the chopped dates, but they’re also full of fiber, protein, and healthy fats. This means they can give you an energy boost (along with lots of gut-healthy, heart-healthy, and brain-healthy ingredients) without any crash later. They’re also delicious, and make for a great afternoon snack!
You will need
- 1 cup oats
- 15 Medjool dates, pitted and soaked in hot water for 15 minutes
- 3 carrots, grated
- 4oz almond butter
- 2 tbsp tahini
- 2 tbsp flaxseeds, milled
- 1 tbsp sesame seeds, toasted
- Optional: your choice of dried fruit and/or chopped nuts (mix it up; diversity is good!)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Steam the grated carrots for 3–4 minutes; pat dry and allow to cool
2) Drain and pat dry the dates, roughly chop them and add them to a bowl with the carrots. Because we chopped the dates rather than blended them (as many recipes do), they keep their fiber, which is important.
3) Add the oats, seeds, almond butter, and tahini. Also add in any additional dried fruit and/or chopped nuts you selected for the optional part. Mix well; the mixture should be quite firm. If it isn’t, add more oats.
4) Press the mixture into a 10″ square baking tin lined with baking paper. Refrigerate for a few hours, before cutting into bar shapes (or squares if you prefer). These can now be eaten immediately or stored for up to a week.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Most Annoying Nutrition Tips (7 Things That Actually Work)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You can’t out-exercise a bad diet, and getting a good diet can be a challenge depending on your starting point. Here’s Cori Lefkowith’s unglamorous seven-point plan:
Step by step
Seven things to do:
- Start tracking first: track your food intake (as it is, without changing anything) without judgment to identify realistic areas for improvement.
- Add protein: add 10g of protein to three meals daily to improve satiety, aid fat loss, and retain muscle.
- Fiber swaps: swap foods for higher-fiber options where possible to improve gut health, improve heart health, support fat loss, and promote satiety.
- Hydration: take your body weight in kilograms (or half your body weight in pounds), then get that many ounces of water daily to support metabolism and reduce cravings.
- Calorie swaps: replace or reduce calorie-dense foods to create a small, modestly sustainable calorie deficit. Your body will still adjust to this after a while; that’s fine; it’s about a gradual reduction.
- Tweak and adjust: regularly reassess and adjust your diet and habits to fit your lifestyle and progress.
- Guard against complacency: track consistently, and stay on course.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
The Smartest Way To Get To 20% Body Fat (Or 10% For Men)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Comfortable with Uncertainty – by Pema Chödrön
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is exactly what the subtitle claims it to be: 108 teachings on cultivating fearlessness and compassion. They are short extracts, entire of themselves, taken from Chödrön’s wider work and arranged to offer her insights and advices on this one topic, in one place.
It is worth noting, by the way, that the author is a Buddhist nun, and as such, the principles and practices are Buddhist in origin. If that’s a problem for you, then this book will not be for you. It does not, however, require that the reader be Buddhist to benefit, simply that one has a will to be calm in the face of chaos, and yet not indifferent—rather, to take on the challenges of life with a whole heart.
And about that compassion? This is about alleviating suffering; your own, and the suffering in the world as a whole, increasingly uncertain as this world is. And being brave enough to do that, in a world that is not always gentle.
The style is idiosyncratic, and you will likely love it or hate it. If you love it, then you will find this book at once both soothing and empowering; if not, you will put the book down and pick up a book on CBT or something instead.
Bottom line: this book absolutely does deliver on its title/subtitle promises—provided you, dear reader, internalize it and practise it.
Click here to check out Comfortable with Uncertainty, and get comfortable with uncertainty!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Train For The Event Of Your Life!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mobility As A Sporting Pursuit
As we get older, it becomes increasingly important to treat life like a sporting event. By this we mean:
As an “athlete of life”, there are always events coming up for which we need to train. Many of these events will be surprise tests!
Such events/tests might include:
- Not slipping in the shower and breaking a hip (or worse)
- Reaching an item from a high shelf without tearing a ligament
- Getting out of the car at an awkward angle without popping a vertebra
- Climbing stairs without passing out light-headed at the top
- Descending stairs without making it a sled-ride-without-a-sled
…and many more.
Train for these athletic events now
Not necessarily this very second; we appreciate you finishing reading first. But, now generally in your life, not after the first time you fail such a test; it can (and if we’re not attentive: will) indeed happen to us all.
With regard to falling, you might like to revisit our…
…which covers how to not fall, and to not injure yourself if you do.
You’ll also want to be able to keep control of your legs (without them buckling) all the way between standing and being on the ground.
Slav squats or sitting squats (same exercise, different names, amongst others) are great for building and maintaining this kind of strength and suppleness:
(Click here for a refresher if you haven’t recently seen Zuzka’s excellent video explaining how to do this, especially if it’s initially difficult for you, “The Most Anti-Aging Exercise”)
this exercise is, by the way, great for pretty much everything below the waist!
You will also want to do resistance exercises to keep your body robust:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
And as for those shoulders? If it is convenient for you to go swimming, then backstroke is awesome for increasing and maintaining shoulder mobility (and strength).
If swimming isn’t a viable option for you, then doing the same motion with your arms, while standing, will build the same flexibility. If you do it while holding a small weight (even just 1kg is fine, but feel free to increase if you so wish and safely can) in each hand will build the necessary strength as you go too.
As for why even just 1kg is fine: read on
About that “and strength”, by the way…
Stretching is not everything. Stretching is great, but mobility without strength (in that joint!) is just asking for dislocation.
You don’t have to be built like the Terminator, but you do need to have the structural integrity to move your body and then a little bit more weight than that (or else any extra physical work could be enough to tip you to breaking point) without incurring damage from the strain. So, it needs to not be a strain! See again, the aforementioned resistance exercises.
That said, even very gentle exercise helps too; see for example the impact of walking on osteoporosis:
Living near green spaces linked to higher bone density and lower osteoporosis risk
and…
So you don’t have to run marathons—although you can if you want:
Marathons in Mid- and Later-Life
…to keep your hips and more in good order.
Want to test yourself now?
Check out:
Building & Maintaining Mobility
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
154 million lives saved in 50 years: 5 charts on the global success of vaccines
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We know vaccines have been a miracle for public health. Now, new research led by the World Health Organization has found vaccines have saved an estimated 154 million lives in the past 50 years from 14 different diseases. Most of these have been children under five, and around two-thirds children under one year old.
In 1974 the World Health Assembly launched the Expanded Programme on Immunization with the goal to vaccinate all children against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whooping cough), measles, polio, tuberculosis and smallpox by 1990. The program was subsequently expanded to include several other diseases.
The modelling, marking 50 years since this program was established, shows a child aged under ten has about a 40% greater chance of living until their next birthday, compared to if we didn’t have vaccines. And these positive effects can be seen well into adult life. A 50-year-old has a 16% greater chance of celebrating their next birthday thanks to vaccines.
What the study did
The researchers developed mathematical and statistical models which took in vaccine coverage data and population numbers from 194 countries for the years 1974–2024. Not all diseases were included (for example smallpox, which was eradicated in 1980, was left out).
The analysis includes vaccines for 14 diseases, with 11 of these included in the Expanded Programme on Immunization. For some countries, additional vaccines such as Japanese encephalitis, meningitis A and yellow fever were included, as these diseases contribute to major disease burden in certain settings.
The models were used to simulate how diseases would have spread from 1974 to now, as vaccines were introduced, for each country and age group, incorporating data on increasing vaccine coverage over time.
Children are the greatest beneficiaries of vaccines
Since 1974, the rates of deaths in children before their first birthday has more than halved. The researchers calculated almost 40% of this reduction is due to vaccines.
The effects have been greatest for children born in the 1980s because of the intensive efforts made globally to reduce the burden of diseases like measles, polio and whooping cough.
Some 60% of the 154 million lives saved would have been lives lost to measles. This is likely due to its ability to spread rapidly. One person with measles can spread the infection to 12–18 people.
The study also found some variation across different parts of the world. For example, vaccination programs have had a much greater impact on the probability of children living longer across low- and middle-income countries and settings with weaker health systems such as the eastern Mediterranean and African regions. These results highlight the important role vaccines play in promoting health equity.
Vaccine success is not assured
Low or declining vaccine coverage can lead to epidemics which can devastate communities and overwhelm health systems.
Notably, the COVID pandemic saw an overall decline in measles vaccine coverage, with 86% of children having received their first dose in 2019 to 83% in 2022. This is concerning because very high levels of vaccination coverage (more than 95%) are required to achieve herd immunity against measles.
In Australia, the coverage for childhood vaccines, including measles, mumps and rubella, has declined compared to before the pandemic.
This study is a reminder of why we need to continue to vaccinate – not just against measles, but against all diseases we have safe and effective vaccines for.
The results of this research don’t tell us the full story about the impact of vaccines. For example, the authors didn’t include data for some vaccines such as COVID and HPV (human papillomavirus). Also, like with all modelling studies, there are some uncertainties, as data was not available for all time periods and countries.
Nonetheless, the results show the success of global vaccination programs over time. If we want to continue to see lives saved, we need to keep investing in vaccination locally, regionally and globally.
Meru Sheel, Associate Professor and Epidemiologist, Infectious Diseases, Immunisation and Emergencies Group, Sydney School of Public Health, University of Sydney and Alexandra Hogan, Mathematical epidemiologist, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Water Water Everywhere, But Which Is Best To Drink?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Well Well Well…
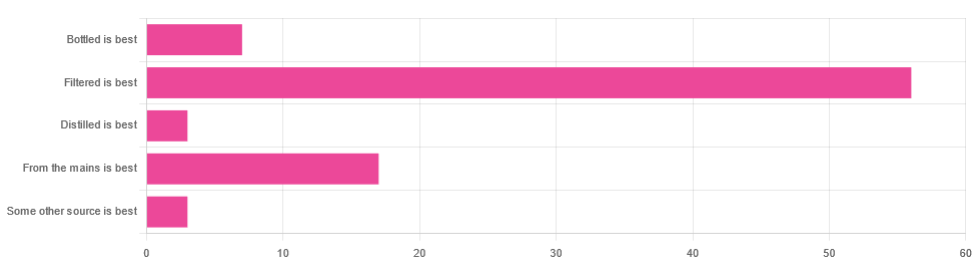
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your (health-related) opinion on drinking water—with the understanding that this may vary from place to place. We got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 65% said “Filtered is best”
- About 20% said “From the mains is best”
- About 8% said “Bottled is best”
- About 3% said “Distilled is best”
- About 3% said “Some other source is best”
Of those who said “some other source is best”, one clarified that their preferred source was well water.
So what does the science say?
Fluoridated water is bad for you: True or False?
False, assuming a normal level of consumption. Rather than take up more space today though, we’ll link to what we previously wrote on this topic:
You may be wondering: but what if my level of consumption is higher than normal?
Let’s quickly look at some stats:
- The maximum permitted safety level varies from place to place, but is (for example) 2mg/l in the US, 1.5mg/l in Canada & the UK.
- The minimum recommended amount also varies from place to place, but is (for example) 0.7mg/l in Canada and the US, and 1mg/l in the UK.
It doesn’t take grabbing a calculator to realize that if you drink twice as much water as someone else, then depending on where you are, water fluoridated to the minimum may give you more than the recommended maximum.
However… Those safety margins are set so much lower than the actual toxicity levels of fluoride, that it doesn’t make a difference.
For example: your writer here takes a medication that has the side effect of causing dryness of the mouth, and consequently she drinks at least 3l of water per day in a climate that could not be described as hot (except perhaps for about 2 weeks of the year). She weighs 72kg (that’s about 158 pounds), and the toxicity of fluoride (for ill symptoms, not death) is 0.2mg/kg. So, she’d need 14.4mg of fluoride, which even if the water fluoridation here were 2mg/l (it’s not; it’s lower here, but let’s go with the highest figure to make a point), would require drinking more than 7l of water faster than the body can process it.
For more about the numbers, check out:
Acute Fluoride Poisoning from a Public Water System
Bottled water is the best: True or False?
False, if we consider “best” to be “healthiest”, which in turn we consider to be “most nutrients, with highest safety”.
Bottled water generally does have higher levels of minerals than most local mains supply water does. That’s good!
But you know what else is generally has? Microplastics and nanoplastics. That’s bad!
We don’t like to be alarmist in tone; it’s not what we’re about here, but the stats on bottled water are simply not good; see:
We Are Such Stuff As Bottles Are Made Of
You may be wondering: “but what about bottled water that comes in glass bottles?”
Indeed, water that comes in glass bottles can be expected to have lower levels of plastic than water that comes in plastic bottles, for obvious reasons.
However, we invite you to consider how likely you believe it to be that the water wasn’t stored in plastic while being processed, shipped and stored, before being portioned into its final store-ready glass bottles for end-consumer use.
Distilled water is the best: True or False?
False, generally, with caveats:
Distilled water is surely the safest water anywhere, because you know that you’ve removed any nasties.
However, it’s also devoid of nutrients, because you also removed any minerals it contained. Indeed, if you use a still, you’ll be accustomed to the build-up of these minerals (generally simplified and referenced as “limescale”, but it’s a whole collection of minerals).
Furthermore, that loss of nutrients can be more than just a “something good is missing”, because having removed certain ions, that water could now potentially strip minerals from your teeth. In practice, however, you’d probably have to swill it excessively to cause this damage.
Nevertheless, if you have the misfortune of living somewhere like Flint, Michigan, then a water still may be a fair necessity of life. In other places, it can simply be useful to have in case of emergency, of course.
Here’s an example product on Amazon if you’d like to invest in a water still for such cases.
PS: distilled water is also tasteless, and is generally considered bad, tastewise, for making tea and coffee. So we really don’t recommend distilling your water unless you have a good reason to do so.
Filtered water is the best: True or False?
True for most people in most places.
Let’s put it this way: it can’t logically be worse than whatever source of water you put into it…
Provided you change the filter regularly, of course.
Otherwise, after overusing a filter, at best it won’t be working, and at worst it’ll be adding in bacteria that have multiplied in the filter over however long you left it there.
You may be wondering: can water filters remove microplastics, and can they remove minerals?
The answer in both cases is: sometimes.
- For microplastics it depends on the filter size and the microplastic size (see our previous article for details on that).
- For minerals, it depends on the filter type. Check out:
The H2O Chronicles | 5 Water Filters That Remove Minerals
One other thing to think about: while most water filtration jugs are made of PFAS-free BPA-free plastics for obvious reasons, for greater peace of mind, you might consider investing in a glass filtration jug, like this one ← this is just one example product on Amazon; by all means shop around and find one you like
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: