Lime-Charred Cauliflower Popcorn
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Called “popcorn” for its appearance and tasty-snackness, this one otherwise bears little relation to the usual movie theater snack, and it’s both tastier and healthier. All that said, it can be eaten on its own as a snack (even with a movie, if you so wish), or served as one part of a many-dish banquet, or (this writer’s favorite) as a delicious appetizer that also puts down a healthy bed of fiber ready for the main course to follow it.
You will need
- 1 cauliflower, cut into small (popcorn-sized) florets
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp lime pickle
- 1 tsp cumin seeds
- 1 tsp smoked paprika
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp ground turmeric
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat your oven as hot as it will go
2) Mix all the ingredients in a small bowl except the cauliflower, to form a marinade
3) Drizzle the marinade over the cauliflower in a larger bowl (i.e. big enough for the cauliflower), and mix well until the cauliflower is entirely, or at least almost entirely, coated. Yes, it’s not a lot of marinade but unless you picked a truly huge cauliflower, the proportions we gave will be enough, and you want the end result to be crisp, not dripping.
4) Spread the marinaded cauliflower florets out on a baking tray lined with baking paper. Put it in the oven on the middle shelf, so it doesn’t cook unevenly, but keeping the temperature as high as it goes.
5) When it is charred and crispy golden, it’s done—this should take about 20 minutes, but we’ll say ±5 minutes depending on your oven, so do check on it periodically—and time to serve (it is best enjoyed warm).
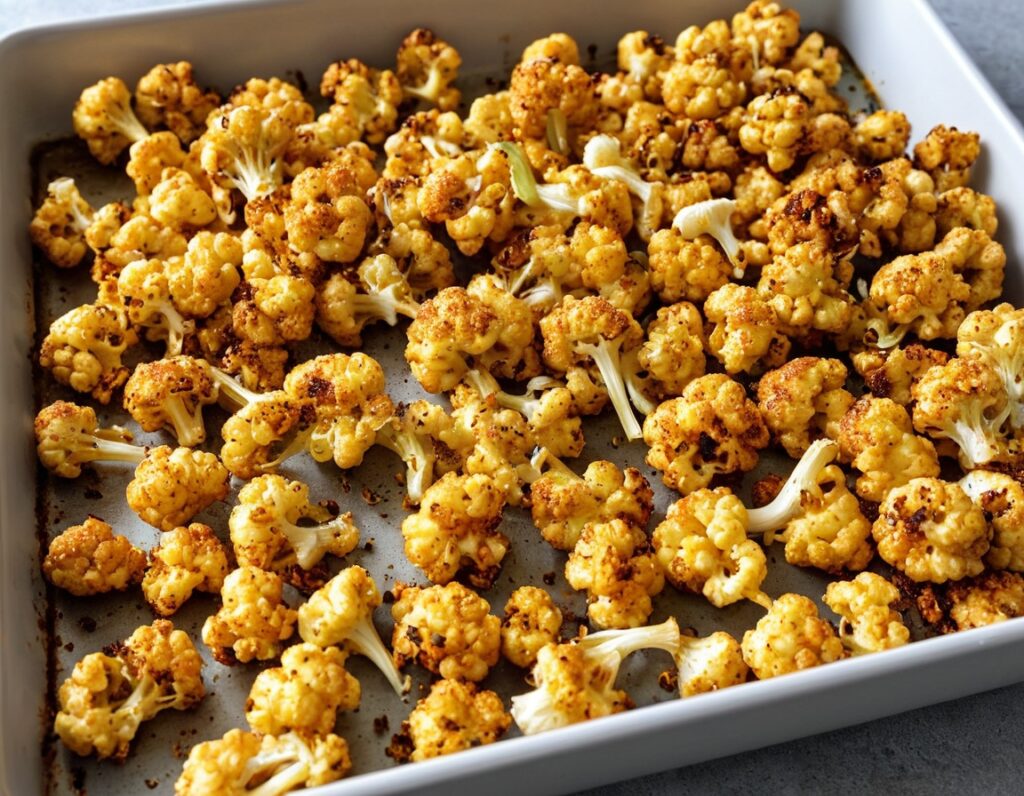

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- We must do a main feature on the merits of cruciferous vegetables! Watch this space.
- All About Olive Oils (Extra Virgin & Otherwise)
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
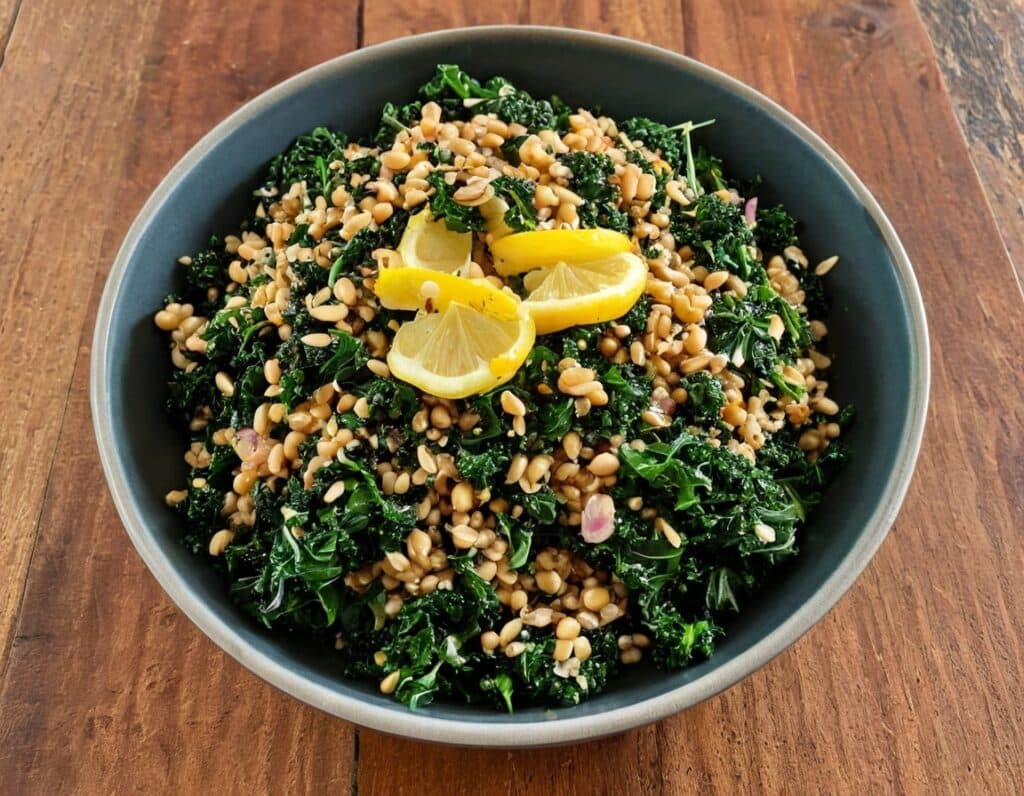
SMOL Bowl With Sautéed Greens
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Whole grains are good, and gluten is bad for some people. Today’s dish has four whole grains, and no gluten (assuming no cross-contamination, so look for the gluten-free label if that’s important to you). Breafast? Brunch? Lunch? Supper, even? This is good at any time of day, packed with nutrients and full of flavor!
You will need (per person)
- 1 cup mixed cooked grains of equal parts sorghum, millet, oats, lentils (SMOL)—these can be cooked in bulk in advance and frozen in portions, as it’s often good to used mixed grains, and these four are a great combination for many purposes.
- ½ cup low sodium vegetable stock (ideally you made this yourself from vegetable offcuts you kept in the freezer until you had enough for this purpose, but failing that, low-sodium stock cubes can be bought at most large supermarkets).
- ½ cup finely chopped red onion
- 6 oz cavolo nero, finely chopped
- 1 small carrot, finely chopped
- 3 cloves garlic, finely chopped
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp white miso paste
- To serve: 1 lemon wedge
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Add the stock to a sauté pan over a medium heat, and add the onion, garlic, and carrot. Stir frequently for about 7 minutes.
2) Add the cavolo nero and miso paste, stirring for another 4 minutes. If there is any liquid remaining, drain it off now.
3) Warm the SMOL mixture (microwave is fine) and spoon it into a bowl, topping with the nutritional yeast and black pepper. Finally, add the hot cavolo nero mixture.
4) Serve with the lemon wedge on the side, to add a dash of lemon at will.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Why are tall people more likely to get cancer? What we know, don’t know and suspect
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
People who are taller are at greater risk of developing cancer. The World Cancer Research Fund reports there is strong evidence taller people have a higher chance of of developing cancer of the:
- pancreas
- large bowel
- uterus (endometrium)
- ovary
- prostate
- kidney
- skin (melanoma) and
- breast (pre- and post-menopausal).
But why? Here’s what we know, don’t know and suspect.
Pexels/Andrea Piacquadio Height does increase your cancer risk – but only by a very small amount. Christian Vinces/Shutterstock A well established pattern
The UK Million Women Study found that for 15 of the 17 cancers they investigated, the taller you are the more likely you are to have them.
It found that overall, each ten-centimetre increase in height increased the risk of developing a cancer by about 16%. A similar increase has been found in men.
Let’s put that in perspective. If about 45 in every 10,000 women of average height (about 165 centimetres) develop cancer each year, then about 52 in each 10,000 women who are 175 centimetres tall would get cancer. That’s only an extra seven cancers.
So, it’s actually a pretty small increase in risk.
Another study found 22 of 23 cancers occurred more commonly in taller than in shorter people.
Why?
The relationship between height and cancer risk occurs across ethnicities and income levels, as well as in studies that have looked at genes that predict height.
These results suggest there is a biological reason for the link between cancer and height.
While it is not completely clear why, there are a couple of strong theories.
The first is linked to the fact a taller person will have more cells. For example, a tall person probably has a longer large bowel with more cells and thus more entries in the large bowel cancer lottery than a shorter person.
Scientists think cancer develops through an accumulation of damage to genes that can occur in a cell when it divides to create new cells.
The more times a cell divides, the more likely it is that genetic damage will occur and be passed onto the new cells.
The more damage that accumulates, the more likely it is that a cancer will develop.
A person with more cells in their body will have more cell divisions and thus potentially more chance that a cancer will develop in one of them.
Some research supports the idea having more cells is the reason tall people develop cancer more and may explain to some extent why men are more likely to get cancer than women (because they are, on average, taller than women).
However, it’s not clear height is related to the size of all organs (for example, do taller women have bigger breasts or bigger ovaries?).
One study tried to assess this. It found that while organ mass explained the height-cancer relationship in eight of 15 cancers assessed, there were seven others where organ mass did not explain the relationship with height.
It is worth noting this study was quite limited by the amount of data they had on organ mass.
Is it because tall people have more cells? Halfpoint/Shutterstock Another theory is that there is a common factor that makes people taller as well as increasing their cancer risk.
One possibility is a hormone called insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). This hormone helps children grow and then continues to have an important role in driving cell growth and cell division in adults.
This is an important function. Our bodies need to produce new cells when old ones are damaged or get old. Think of all the skin cells that come off when you use a good body scrub. Those cells need to be replaced so our skin doesn’t wear out.
However, we can get too much of a good thing. Some studies have found people who have higher IGF-1 levels than average have a higher risk of developing breast or prostate cancer.
But again, this has not been a consistent finding for all cancer types.
It is likely that both explanations (more cells and more IGF-1) play a role.
But more research is needed to really understand why taller people get cancer and whether this information could be used to prevent or even treat cancers.
I’m tall. What should I do?
If you are more LeBron James than Lionel Messi when it comes to height, what can you do?
Firstly, remember height only increases cancer risk by a very small amount.
Secondly, there are many things all of us can do to reduce our cancer risk, and those things have a much, much greater effect on cancer risk than height.
We can take a look at our lifestyle. Try to:
- eat a healthy diet
- exercise regularly
- maintain a healthy weight
- be careful in the sun
- limit alcohol consumption.
And, most importantly, don’t smoke!
If we all did these things we could vastly reduce the amount of cancer.
You can also take part in cancer screening programs that help pick up cancers of the breast, cervix and bowel early so they can be treated successfully.
Finally, take heart! Research also tells us that being taller might just reduce your chance of having a heart attack or stroke.
Susan Jordan, Associate Professor of Epidemiology, The University of Queensland and Karen Tuesley, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, School of Public Health, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Unfuck Your Brain – by Dr. Faith Harper
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book takes a trauma-informed care approach, which is relatively novel in the mental health field and it’s quickly becoming the industry standard because of its effectiveness.
The basic premise of trauma-informed care is that you had a bad experience (possibly even more than one—what a thought!) and that things that remind you of that will tend to prompt reactivity from you in a way that probably isn’t healthy. By identifying each part of that process, we can then interrupt it, much like we might with CBT (the main difference being that CBT, for all its effectiveness, tends to assume that the things that are bothering you are not true, while TIC acknowledges that they might well be, and that especially historically, they probably were).
A word of warning: if something that triggers a trauma-based reactivity response in you is people swearing, then this book will either cure you by exposure therapy or leave you a nervous wreck, because it’s not just the title; Dr. Harper barely gets through a sentence without swearing. It’s a lot, even by this (European) reviewer’s standards (we’re a lot more relaxed about swearing over here, than people tend to be in America).
On the other hand, something that Dr. Harper excels at is actually explaining stuff very well. So while it sometimes seems like she’s “trying too hard” style-wise in terms of being “not like other therapists”, in her defence she’s nevertheless a very good writer; she knows her stuff, and knows how to communicate it clearly.
Bottom line: if you don’t mind a writer who swears more than 99% of soldiers, then this book is an excellent how-to guide for self-administered trauma-informed care.
Click here to check out Unfuck Your Brain, and indeed unfuck it!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Rushing Woman’s Syndrome – by Dr. Libby Weaver
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s well-known that very many women suffer from “the triple burden” of professional work, housework, and childcare. And it’s not even necessarily that we resent any of those things or feel like they’re a burden; we (hopefully) love our professions, homes, children. But, here’s the thing: no amount of love will add extra hours to the day!
On the psychological level, a lot is about making more conscious decisions and fewer automatic reactions. For example, everyone wants everything from us right now, if not by yesterday, but when do they need it? And, is it even our responsibility? Not everything is, and many of us take on more than we should in our effort to be “enough”.
On the physical level, she covers hormones, including the menstrual/menopausal and the metabolic, as well as liver health, digestive issues, and sleep.
The style is direct and friendly, making frequent references to science but not getting deep into it.
It’s worth noting that while she acknowledges other demographics exist, she’s writing mainly for an audience of otherwise healthy straight white women with children and at least moderate financial resources, so if you fall outside of those things, there may be things that society will penalize you for and expect more from you in return for less, so that is a limitation of the book.
Bottom line: if the above describes you, you will probably get value out of this book.
Click here to check out Rushing Woman’s Syndrome, and take care of yourself too!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Buckwheat vs Oats – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing buckwheat to oats, we picked the oats.
Why?
First of all, for any thinking about the health concerns sometimes associated with wheat: buckwheat is not a kind of wheat, nor is it even in the same family; it’s not a grain, but a flowering plant. Buckwheat is to wheat as a lionfish is to lions.
That said, while these are both excellent foods, one of them is so good it makes the other one look bad in comparison:
In terms of macros, oats have more carbs, but also more protein and more fiber.
When it comes to vitamins, a clear winner emerges: oats have more of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, and B9, while buckwheat is higher in vitamin K and choline.
In the category of minerals, things are even more pronounced: oats are higher in calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. On the other hand, buckwheat is higher in selenium.
All in all: as ever, enjoy both, but if you’re picking one, oats cannot be beaten.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Behind Book Recommendations
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day!
Each Thursday, we respond to subscriber questions and requests! If it’s something small, we’ll answer it directly; if it’s something bigger, we’ll do a main feature in a follow-up day instead!
So, no question/request to big or small; they’ll just get sorted accordingly
Remember, you can always hit reply to any of our emails, or use the handy feedback widget at the bottom. We always look forward to hearing from you!
Q: What’s the process behind the books you recommend? You seem to have a limitless stream of recommendations
We do our best!
The books we recommend are books that…
- are on Amazon—it makes things tidy, consistent, and accessible. And if you end up buying one of the books, we get a small affiliate commission*.
- we have read—we would say “obviously”, but you might be surprised how many people write about books without having read them.
- pertain in at least large part to health and/or productivity.
- are written by humans—bookish people (and especially Kindle Unlimited users) may have noticed lately that there are a lot of low quality AI-written books flooding the market, sometimes with paid 5-star reviews to bolster them. It’s frustrating, but we can tell the difference and screen those out.
- are of a certain level of quality. They don’t have to be “top 5 desert-island books”, because well, there’s one every day and the days keep coming. But they do have to genuinely deliver the value that we describe, and merit a sincere recommendation.
- are varied—we try to not give a run of “samey” books one after another. We will sometimes review a book that covers a topic another previously-reviewed book did, but it must have something about it that makes it different. It may be a different angle or a different writing style, but it needs something to set it apart.
*this is from Amazon and isn’t product-specific, so this is not affecting our choice of what books to review at all—just that they will be books that are available on Amazon.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: