10,000 Steps, 30 Days, 4 Changes
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ariel wasn’t the most active person, and took on a “30 day challenge” to do the commonly-prescribed 10,000 steps per day—without adjusting her diet or doing any other exercise. How much of a difference does it make, really?
Stepping onwards
The 4 main things that she found changed for her weren’t all what she expected:
- Weight loss yes, but only marginally: she lost 3 lbs in a month, which did nevertheless make a visible difference. We might hypothesize that part of the reason for the small weight loss and yet visible difference is that she gained a little muscle, and the weight loss was specifically shifting away from a cortisol-based fat distribution, to a more healthy fat distribution.
- Different eating habits: she felt less hungry and craved less sugar. This likely has less to do with calorie consumption, and more to do with better insulin signalling.
- Increased energy and improved mood: these are going together in one item, because she said “4 things”, but really they are two related things. So, consider one of them a bonus item! In any case, she felt more energized and productive, and less reliant on caffeine.
- Improved sleep: or rather, at first, disrupted sleep, and then slept better and stayed better. A good reminder that changes for the better don’t always feel better in the first instance!
To hear about it in her own words, and see the before and after pictures, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Wakefulness, Cognitive Enhancement, AND Improved Mood?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Old Drug, New Tricks?
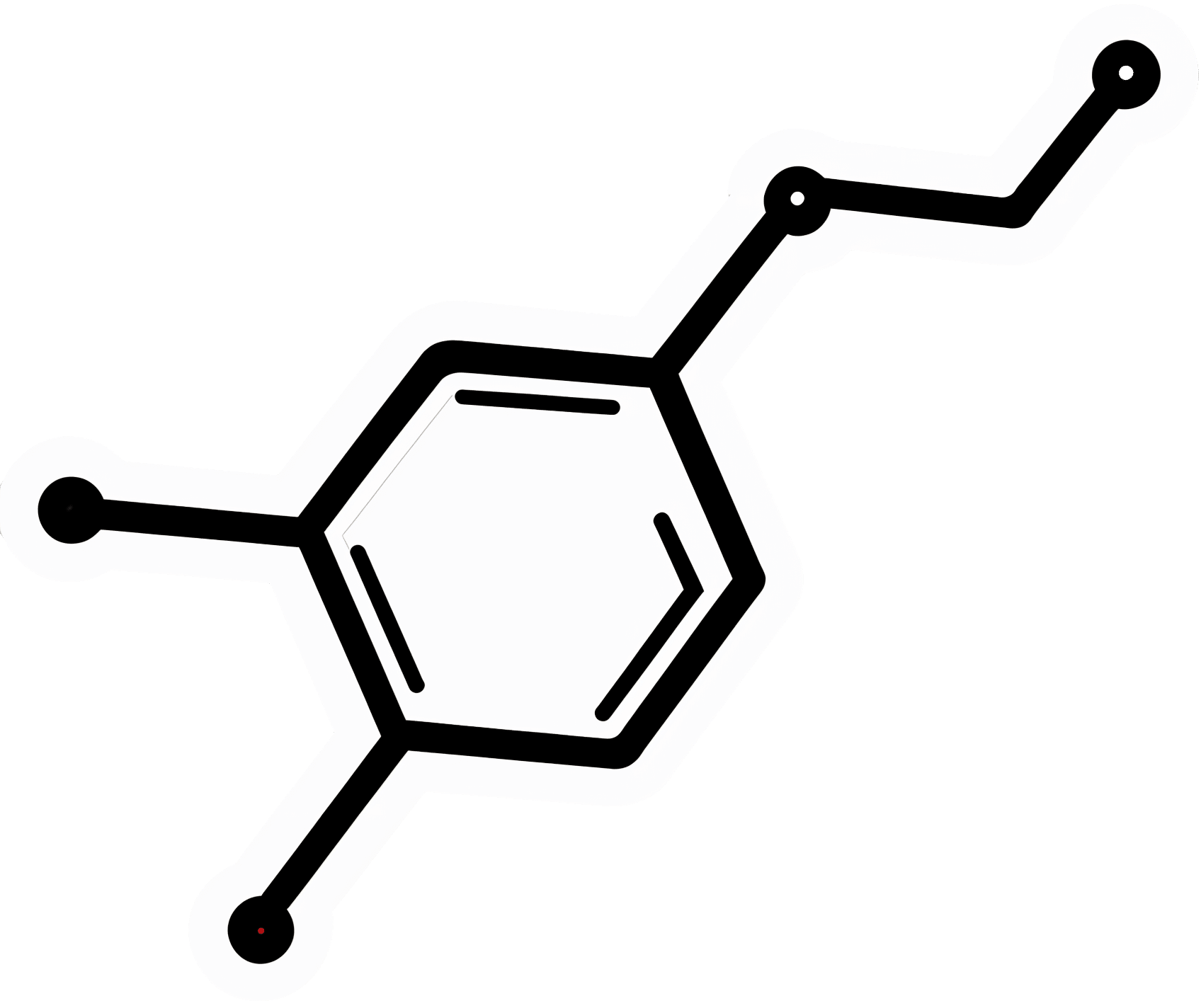
Modafinil (also known by brand names including Modalert and Provigil) is a dopamine uptake inhibitor.
What does that mean? It means it won’t put any extra dopamine in your brain, but it will slow down the rate at which your brain removes naturally-occuring dopamine.
The result is that your brain will get to make more use of the dopamine it does have.
(dopamine is a neutrotransmitter that allows you to feel wakeful and happy, and perform complex cognitive tasks)
Modafinil is prescribed for treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness. Often that’s caused by shift work sleep disorder, sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, or narcolepsy.
Read: Overview of the Clinical Uses, Pharmacology, and Safety of Modafinil
Many studies done on humans (rather than rats) have been military experiments to reduce the effects of sleep deprivation:
Click Here To See A Military Study On Modafinil!
They’ve found modafinil to be helpful, and more effective and more long-lasting than caffeine, without the same “crash” later. This is for two reasons:
1) while caffeine works by blocking adenosine (so you don’t feel how tired you are) and by constricting blood vessels (so you feel more ready-for-action), modafinil works by allowing your brain to accumulate more dopamine (so you’re genuinely more wakeful, and you get to keep the dopamine)
2) the biological half-life of modafinil is 12–15 hours, as opposed to 4–8 hours* for caffeine.
*Note: a lot of sources quote 5–6 hours for caffeine, but this average is misleading. In reality, we are each genetically predetermined to be either a fast caffeine metabolizer (nearer 4 hours) or a slow caffeine metabolizer (nearer 8 hours).
What’s a biological half-life (also called: elimination half-life)?
A substance’s biological half-life is the time it takes for the amount in the body to be reduced by exactly half.
For example: Let’s say you’re a fast caffeine metabolizer and you have a double-espresso (containing 100mg caffeine) at 8am.
By midday, you’ll have 50mg of caffeine left in your body. So far, so simple.
By 4pm you might expect it to be gone, but instead you have 25mg remaining (because the amount halves every four hours).
By 8pm, you have 12.5mg remaining.
When midnight comes and you’re tucking yourself into bed, you still have 6.25mg of caffeine remaining from your morning coffee!
Use as a nootropic
Many healthy people who are not sleep-deprived use modafinil “off-label” as a nootropic (i.e., a cognitive enhancer).
Read: Modafinil for cognitive neuroenhancement in healthy non-sleep-deprived subjects: A systematic review
Important Note: modafinil is prescription-controlled, and only FDA-approved for sleep disorders.
To get around this, a lot of perfectly healthy biohackers describe the symptoms of sleep pattern disorder to their doctor, to get a prescription.
We do not recommend lying to your healthcare provider, and nor do we recommend turning to the online “grey market”.
Such websites often use anonymized private doctors to prescribe on an “informed consent” basis, rather than making a full examination. Those websites then dispense the prescribed medicines directly to the patient with no further questions asked (i.e. very questionable practices).
Caveat emptor!
A new mood-brightener?
Modafinil was recently tested head-to-head against Citalapram for the treatment of depression, and scored well:
See its head-to-head scores here!
How does it work? Modafinil does for dopamine what a lot of anti-depressants do for serotonin. Both dopamine and serotonin promote happiness and wakefulness.
This is very promising, especially as modafinil (in most people, at least) has fewer unwanted side-effects than a lot of common anti-depressant medications.
Share This Post
-
How we can prepare for future public health emergencies
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The U.S. is experiencing an increasing number of disease outbreaks and extreme weather events. While state and national preparedness for public health emergencies has improved in some areas, dangerous gaps remain, says a recent report from Trust for America’s Health.
Titled, “Ready or Not 2024: Protecting the Public’s Health from Diseases, Disasters, and Bioterrorism,” the report identifies gaps in national and state preparedness for public health emergencies and provides recommendations for improvement.
Using nine key indicators, the report categorizes all U.S. states and the District of Columbia into three readiness levels: high, medium, and low. The writers hope the report will help policymakers in under-performing states improve public health infrastructure.
Read on to learn more about what the research found and how we can individually prepare for future public health emergencies.
There’s work to be done
The report highlights areas with strong performance as well as those that need improvement.
Some areas with strong performance:
- State public health funding: Most states and the District of Columbia either maintained or increased their public health funding during the 2023 fiscal year.
- Health care labor force preparedness: Most states have started expanding the health care labor force for improved emergency response. As of 2023, 39 states participated in the Nurse Licensure Compact, which allows nurses to work in multiple member states without the need for additional state licenses.
Some areas that need improvement:
- Hospital safety scores: Only 25 percent of acute care hospitals earned the highest patient safety grade in fall 2023. These scores measure health care-associated infection rates, intensive care unit capacity, and other metrics. More high-scoring hospitals would improve preparedness for future public health emergencies.
- Access to paid time off: From March 2018 to March 2023, only 55 percent of U.S. workers used paid time off. Access to paid time off is important for reducing the spread of infectious diseases.
We can all do our part by staying up to date on vaccines
While the report focuses on policy changes that would improve emergency preparedness, Trust for America’s Health’s research identifies one way that we can individually prepare for future public health emergencies: staying up to date on vaccines.
The report found that during the 2022-2023 flu season, only 49 percent of those eligible for the flu vaccine received it. Public health experts are concerned that false claims about COVID-19 vaccines have resulted in overall vaccine hesitancy.
A decline in vaccination rates has led to an uptick in life-threatening, vaccine-preventable diseases, such as measles. Increasing vaccine uptake would prevent the spread of vaccine-preventable diseases and reduce strain on hospital systems during public health crises.
Make sure that you and your children have received all recommended vaccines to prevent severe illness, hospitalization, and death. Learn more about recommended vaccines for adults and children from the CDC.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
The Circadian Code – by Dr. Satchin Panda
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s a lot more to circadian rhythm than “sleep during these hours”. And there’s a lot more to bear in mind than “don’t have blue/white light at night”.
In fact, Dr. Satchin Panda explains, there’s a whole daily symphony of movements in our body as different biochemical processes wax and wane according to what time of day it is.
There are several important things he wants us to know about this:
- Our body needs to know what time it is, for those processes to work correctly
- Because of these daily peaks and troughs of various physiological functions, we get “correct” times for things we do every day. Not just sleeping/waking, but also:
- The best time to eat
- The best time to exercise
- The best time to do mental work
- The best times to take different kinds of supplements/medications
Dr. Panda also looks at what things empower, or disempower, our body to keep track of what time it is.
Bottom line: if you’d like to optimize your days and your health, this book has a lot of very valuable practicable tips.
Click here to check out The Circadian Code, and make the most of yours!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Microplastics are in our brains. How worried should I be?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Plastic is in our clothes, cars, mobile phones, water bottles and food containers. But recent research adds to growing concerns about the impact of tiny plastic fragments on our health.
A study from the United States has, for the first time, found microplastics in human brains. The study, which has yet to be independently verified by other scientists, has been described in the media as scary, shocking and alarming.
But what exactly are microplastics? What do they mean for our health? Should we be concerned?
Daniel Megias/Shutterstock What are microplastics? Can you see them?
We often consider plastic items to be indestructible. But plastic breaks down into smaller particles. Definitions vary but generally microplastics are smaller than five millimetres.
This makes some too small to be seen with the naked eye. So, many of the images the media uses to illustrate articles about microplastics are misleading, as some show much larger, clearly visible pieces.
Microplastics have been reported in many sources of drinking water and everyday food items. This means we are constantly exposed to them in our diet.
Such widespread, chronic (long-term) exposure makes this a serious concern for human health. While research investigating the potential risk microplastics pose to our health is limited, it is growing.
How about this latest study?
The study looked at concentrations of microplastics in 51 samples from men and women set aside from routine autopsies in Albuquerque, New Mexico. Samples were from the liver, kidney and brain.
These tiny particles are difficult to study due to their size, even with a high-powered microscope. So rather than trying to see them, researchers are beginning to use complex instruments that identify the chemical composition of microplastics in a sample. This is the technique used in this study.
The researchers were surprised to find up to 30 times more microplastics in brain samples than in the liver and kidney.
They hypothesised this could be due to high blood flow to the brain (carrying plastic particles with it). Alternatively, the liver and kidneys might be better suited to dealing with external toxins and particles. We also know the brain does not undergo the same amount of cellular renewal as other organs in the body, which could make the plastics linger here.
The researchers also found the amount of plastics in brain samples increased by about 50% between 2016 and 2024. This may reflect the rise in environmental plastic pollution and increased human exposure.
The microplastics found in this study were mostly composed of polyethylene. This is the most commonly produced plastic in the world and is used for many everyday products, such as bottle caps and plastic bags.
This is the first time microplastics have been found in human brains, which is important. However, this study is a “pre-print”, so other independent microplastics researchers haven’t yet reviewed or validated the study.
The most common plastic found was polyethylene, which is used to make plastic bags and bottle caps. Maciej Bledowski/Shutterstock How do microplastics end up in the brain?
Microplastics typically enter the body through contaminated food and water. This can disrupt the gut microbiome (the community of microbes in your gut) and cause inflammation. This leads to effects in the whole body via the immune system and the complex, two-way communication system between the gut and the brain. This so-called gut-brain axis is implicated in many aspects of health and disease.
We can also breathe in airborne microplastics. Once these particles are in the gut or lungs, they can move into the bloodstream and then travel around the body into various organs.
Studies have found microplastics in human faeces, joints, livers, reproductive organs, blood, vessels and hearts.
Microplastics also migrate to the brains of wild fish. In mouse studies, ingested microplastics are absorbed from the gut into the blood and can enter the brain, becoming lodged in other organs along the way.
To get into brain tissue, microplastics must cross the blood-brain-barrier, an intricate layer of cells that is supposed to keep things in the blood from entering the brain.
Although concerning, this is not surprising, as microplastics must cross similar cell barriers to enter the urine, testes and placenta, where they have already been found in humans.
Is this a health concern?
We don’t yet know the effects of microplastics in the human brain. Some laboratory experiments suggest microplastics increase brain inflammation and cell damage, alter gene expression and change brain structure.
Aside from the effects of the microplastic particles themselves, microplastics might also pose risks if they carry environmental toxins or bacteria into and around the body.
Various plastic chemicals could also leach out of the microplastics into the body. These include the famous hormone-disrupting chemicals known as BPAs.
But microplastics and their effects are difficult to study. In addition to their small size, there are so many different types of plastics in the environment. More than 13,000 different chemicals have been identified in plastic products, with more being developed every year.
Microplastics are also weathered by the environment and digestive processes, and this is hard to reproduce in the lab.
A goal of our research is to understand how these factors change the way microplastics behave in the body. We plan to investigate if improving the integrity of the gut barrier through diet or probiotics can prevent the uptake of microplastics from the gut into the bloodstream. This may effectively stop the particles from circulating around the body and lodging into organs.
How do I minimise my exposure?
Microplastics are widespread in the environment, and it’s difficult to avoid exposure. We are just beginning to understand how microplastics can affect our health.
Until we have more scientific evidence, the best thing we can do is reduce our exposure to plastics where we can and produce less plastic waste, so less ends up in the environment.
An easy place to start is to avoid foods and drinks packaged in single-use plastic or reheated in plastic containers. We can also minimise exposure to synthetic fibres in our home and clothing.
Sarah Hellewell, Senior Research Fellow, The Perron Institute for Neurological and Translational Science, and Research Fellow, Faculty of Health Sciences, Curtin University; Anastazja Gorecki, Teaching & Research Scholar, School of Health Sciences, University of Notre Dame Australia, and Charlotte Sofield, PhD Candidate, studying microplastics and gut/brain health, University of Notre Dame Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
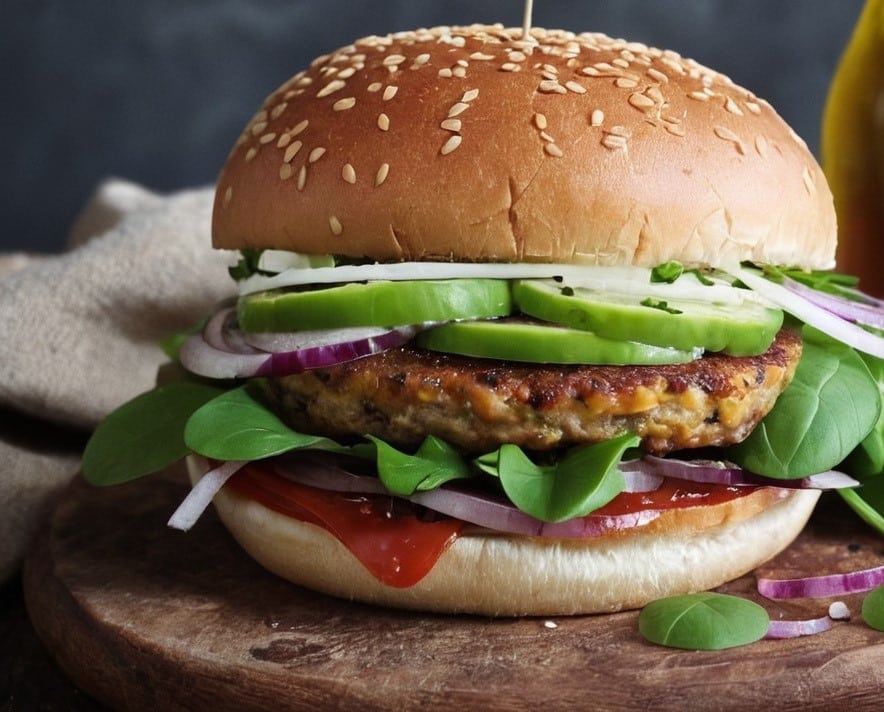
Sunflower Corn Burger
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Burgers are rarely a health food, but in this case, everything in the patty is healthy, and it’s packed with protein, fiber, and healthy fats.
You will need
- 1 can chickpeas
- ¾ cup frozen corn
- ½ cup chopped fresh parsley
- ⅓ cup sunflower seeds
- ⅓ cup cornichon pickles
- ⅓ cup wholegrain bread crumbs (gluten-free, if desired/required)
- ¼ bulb garlic (or more if you want a stronger flavor)
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil, plus more for frying
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast (or 1 tsp yeast extract)
- 2 tsp ground cumin
- 2 tsp red pepper flakes
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp Dijon mustard
- To serve: 4 burger buns; these are not usually healthy, so making your own is best, but if you don’t have the means/time, then getting similarly shaped wholegrain bread buns works just fine.
- Optional: your preferred burger toppings, e.g. greenery, red onion, tomato slices, avocado, jalapeños, whatever does it for you
Note: there is no need to add salt; there is enough already in the pickles.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine all the ingredients except the buns (and any optional toppings) in a food processor, pulsing a few times for a coarse texture (not a purée).
2) Shape the mixture into 4 burger patties, and let them chill in the fridge for at least 30 minutes.
3) Heat a skillet over a medium-high heat with some olive oil, and fry the burgers on both sides until they develop a nice golden crust; this will probably take about 4 minutes per side.
4) Assemble in the buns with any toppings you want, and serve:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Sunflower Seeds vs Pumpkin Seeds – Which is Healthier? ← pumpkin seeds have more micronutrients; sunflower seeds have more healthy fats; feel free to use either or both in this recipe
- What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
No-Exercise Exercise!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Do you love to go to the gym?
If so, today’s article might not be for you so much. Or maybe it will, because let’s face it, exercise is fun!
At least… It can be, and should be 😎
So without further ado, here’s a slew of no-exercise exercise ideas; we’re willing to bet that somewhere in the list there’s at least some you haven’t tried before, and probably some you haven’t done in a while but might enjoy making a reprise!
Walking
No surprises here: walking is great. Hopefully you have some green spaces near you, but if you don’t, [almost] any walking is better than no walking. So unless there’s some sort of environmental disaster going on outside, lace up and get stepping.
If you struggle to “walk for walking’s sake” give yourself a little mission. Walk to the shop to buy one item. Walk to the park and find a flower to photograph. Walk to the library and take out a book. Whatever works for you!
See also: The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, And Move More
Take the stairs
This one doesn’t need many words, just: make it a habit.
Treat the elevators as though they aren’t there!
See also: How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
Dance
Dance is amazing! Any kind of dance, whatever suits your tastes. This writer loves salsa and tango, but no matter whether for you it’s zouk or zumba, breakdancing or line dancing, whatever gets you moving is going to be great for you.
If you don’t know how, online tutorials abound, and best of all is to attend local classes if you can, because they’re always a fun social experience too.
Make music
Not something often thought of as an exercise, but it is! Most instruments require that we be standing or siting with good posture, focusing intently on our movements, and often as not, breathing very mindfully too. And yes, it’s great for the brain as well!
Check out: This Is Your Brain on Music: The Science of a Human Obsession – by Dr. Daniel Levitin
Take a stand
If you spend a lot of time at a desk, please consider investing in a standing desk; they can be truly life-changing. Not only is it so much better for your back, hips, neck, and internal organs, but also it burns hundreds more calories than sitting, due to the no-exercise exercise that is keeping your body constantly stabilized while on your feet.
(or, if you’re like this writer: on your foot. I do have two feet, I just spend an inordinate amount of time at my desk standing on one leg at a time; I’m a bit of a flamingo like that)
See also: Deskbound: Standing Up to a Sitting World – by Kelly Starrett and Glen Cordoza
Sit, but…
Sit in a sitting squat! Sometimes called a Slav squat, or an Asian squat, or a resting squat, or various other names:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Alternatively, sitting in seiza (the traditional Japanese sitting position) is also excellent, but watch out! While it’s great once your body is accustomed to it, if you haven’t previously sat this way much, you may cut off your own circulation, hurt your knees, and (temporarily) lose feeling in your feet. So if you don’t already sit in seiza often, gradually work up the time period you spend sitting in seiza, so that your vasculature can adapt and improve, which honestly, is a very good thing for your legs and feet to have.
Breathe
Perhaps the absolute most “no-exercise exercise” there is. And yes, of course you are (hopefully) breathing all the time, but how you are breathing matters a lot:
The Inside Job Of Fixing Our Breathing: Exercises That Can Fix Sinus Problems (And More)
Clean
This doesn’t have to mean scrubbing floors like a sailor—even merely giving your house the Marie Kondo treatment counts, because while you’re distracted with all the objects, you’re going to be going back and forth, getting up and down, etc, clocking up lots of exercise that you barely even notice!
PS, check out: The Life-Changing Manga Of Tidying Up – by Marie Kondo
Garden
As with the above, it’s lots of activity that doesn’t necessarily feel like it (assuming you’re doing more pruning and weeding etc, and less digging ditches etc), and as a bonus, there are a stack of mental health benefits to being in a green natural environment and interacting with soil:
Read more: The Antidepressant In Your Garden
Climb
Depending on where you live, this might mean an indoor climbing wall, but give it a go! They have color-coded climbs from beginner to advanced, so don’t worry about being out of your depth.
And the best thing is, the beginner climbs will be as much a workout to a beginner as the advanced climbs will be to an advanced climber, because at the end of the day, you’re still clinging on for dear life, no matter whether it’s a sizeable handhold not far from the ground, or the impression of a fingernail crack in an overhang 100ft in the air.
Video games (but…)
Less in the category of Stardew Valley, and more in the category of Wii Fit.
So, dust off that old controller (or treat yourself to one if you didn’t have one already), and get doing a hundred sports and other physical activities in the comfort of your living room, with a surprisingly addictive gaming system!
Sex!
You probably don’t need instructions here, and if you do, well honestly, we’re running out of space today. But the answer to “does xyz count?” is “did it get your heart racing?” because if so, it counts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: