CBD Oil
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Q&A with the 10almonds Team
Q: Very interested in this article on CBD oil in the states. hope you do another one in the future with more studies done on people and more information on what’s new as far as CBD oil goes
A: We’re glad you enjoyed it! We’ll be sure to revisit CBD in the future—partly because it was a very popular article, and partly because, as noted, there is a lot going on there, research-wise!
And yes, we prefer human studies rather than mouse/rat studies where possible, too, and try to include those where we find them. In some cases, non-human animal studies allow us to know things that we can’t know from human studies… because a research institution’s ethics board will greenlight things for mice that it’d never* greenlight for humans.
Especially: things that for non-human animals are considered “introduction of external stressors” while the same things done to humans would be unequivocally called “torture”.
Animal testing in general is of course a moral quagmire, precisely because of the suffering it causes for animals, while the research results (hopefully) can be brought to bear to reduce to suffering of humans. We’re a health and productivity newsletter, not a philosophical publication, but all this to say: we’re mindful of such too.
And yes, we agree, when studies are available on humans, they’re always going to be better than the same study done on mice and rats.
As a topical aside, did you know there’s a monument to laboratory mice and all they’ve (however unintentionally) done for us?
❝The quirky statue depicts an anthropomorphic mouse as an elderly woman, complete with glasses balanced atop its nose. Emerging from two knitting needles in its hands is the recognizable double-helix of a strand of DNA.❞
~ Smithsonian Magazine
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
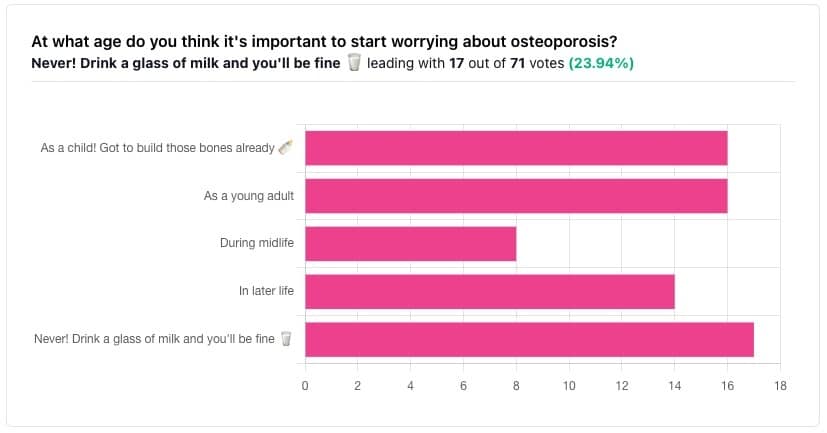
In yesterday’s issue of 10almonds, we asked you “at what age do you think it’s important to start worrying about osteoporosis?”, and here’s the spread of answers you gave us:
The Bare-bones Truth About Osteoporosis
In yesterday’s issue of 10almonds, we asked you “at what age do you think it’s important to start worrying about osteoporosis?”, and here’s the spread of answers you gave us:
At first glance it may seem shocking that a majority of respondents to a poll in a health-focused newsletter think it’ll never be an issue worth worrying about, but in fact this is partly a statistical quirk, because the vote of the strongest “early prevention” crowd was divided between “as a child” and “as a young adult”.
This poll also gave you the option to add a comment with your vote. Many subscribers chose to do so, explaining your choices… But, interestingly, not one single person who voted for “never” had any additional thoughts to add.
We loved reading your replies, by the way, and wish we had room to include them here, because they were very interesting and thought-provoking.
Let’s get to the myths and facts:
Top myth: “you will never need to worry about it; drink a glass of milk and you’ll be fine!”
The body is constantly repairing itself. Its ability to do that declines with age. Until about 35 on average, we can replace bone mineral as quickly as it is lost. After that, we lose it by up to 1% per year, and that rate climbs after 50, and climbs even more steeply for those who go through (untreated) menopause.
Losing 1% per year might not seem like a lot, but if you want to live to 100, there are some unfortunate implications!
About that menopause, by the way… Because declining estrogen levels late in life contribute significantly to osteoporosis, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be of value to many for the sake of bone health, never mind the more obvious and commonly-sought benefits.
On the topic of that glass of milk…
- Milk is a great source of calcium, which is useless to the body if you don’t also have good levels of vitamin D and magnesium.
- People’s vitamin D levels tend to directly correlate to the level of sun where they live, if supplementation isn’t undertaken.
- Plant-based milks are usually fortified with vitamin D (and calcium), by the way.
- Most people are deficient in magnesium, because green leafy things don’t form as big a part of most people’s diets as they should.
See also: An update on magnesium and bone health
Next most common myth: “bone health is all about calcium”
We spoke a little above about the importance of vitamin D and magnesium for being able to properly use that. But potassium is also critical:
Read more: The effects of potassium on bone health
While we’re on the topic…
People think of collagen as being for skin health. And it is important for that, but collagen’s benefits (and the negative effects of its absence) go much deeper, to include bone health. We’ve written about this before, so rather than take more space today, we’ll just drop the link:
We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
Want to really maximize your bone health?
You might want to check out this well-sourced LiveStrong article:
Bone Health: Best and Worst Foods
(Teaser: leafy greens are in 2nd place, topped by sardines at #1—where do you think milk ranks?)
Share This Post
-
Red Bell Peppers vs Tomatoes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing red bell peppers to tomatoes, we picked the peppers.
Why?
In terms of macronutrients, these two fruits-that-get-used-as-vegetables are similar in most respects; they’re mostly water, negligible protein and fat, similar amounts of carbs, even a similar carb breakdown (mostly fructose and glucose). One thing that does set them apart is that peppers* have about 2x the fiber, which difference results in peppers having the lower Glycemic Index—though tomatoes are quite low in GI too.
*for brevity we’re just going to write “peppers”, but we are still talking about sweet red bell peppers throughout. This is important, as different color peppers have different nutrient profiles.
In the category of vitamins, peppers have much more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, and E. In contrast, tomatoes have more vitamin K. An easy win for peppers.
When it comes to minerals, the margins are narrower, but peppers have more iron, zinc, and selenium, while tomatoes have more calcium and copper. They’re approximately equal on other minerals they both contain, making this category a slight (3:2) win for peppers.
As for phytochemical benefits, both are good sources of lycopene (both better when cooked) and other carotenes (for example lutein), and both have an array of assorted flavonoids.
All in all, a win for peppers, but both are great!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
- Bell Peppers: A Spectrum Of Specialties
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Feeding You Lies – by Vani Hari
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to advertising, we know that companies will often be as misleading as they can get away with. But just how misleading is it?
Vani Hari, of “Food Babe” fame, is here to unravel it all.
The book covers many areas of food and drink advertising and marketing, and gives particular attention to:
- Sodas (with and without sugar), and how deleterious they are to the health—as well as not even helping people lose weight, but actively hindering
- Nutritionally fortified foods, and what we may or may not actually get from them by the time the processing is done
- Organic food, and what that may or may not mean
She also covers a lot of what happens outside of supermarkets, way back in universities and corporate boardrooms. In short, who is crossing whose palms with silver for a seal of approval… And what that means for us as consumers.
A strength of this book that sets it apart from many of its genre, by the way, is that while being deeply critical of certain institutions’ practices, it doesn‘t digress into tinfoil-hat pseudoscientific scaremongering, either. Here at 10almonds we love actual science, so that was good to see too.
Bottom line: is you’d like to know “can they say that and get away with it if it’s not true?” and make decisions based on the actual nutritional value of things, this is a great book for you.
Click here to check out “Feeding You Lies” on Amazon and make your shopping healthier!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Fascinating Truth About Aspartame, Cancer, & Neurotoxicity
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is Aspartame’s Reputation Well-Deserved?
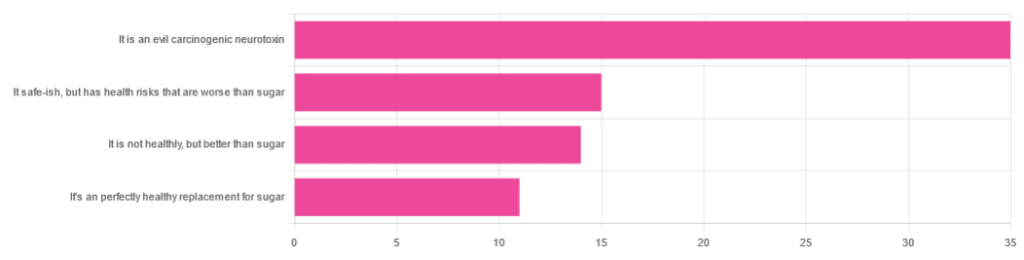
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your health-related opinions on aspartame, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 47% said “It is an evil carcinogenic neurotoxin”
- 20% said “It is safe-ish, but has health risks that are worse than sugar”
- About 19% said “It is not healthy, but better than sugar”
- About 15% said “It’s a perfectly healthy replacement for sugar”
But what does the science say?
Aspartame is carcinogenic: True or False?
False, assuming consuming it in moderation. In excess, almost anything can cause cancer (oxygen is a fine example). But for all meaningful purposes, aspartame does not appear to be carcinogenic. For example,
❝The results of these studies showed no evidence that these sweeteners cause cancer or other harms in people.❞
~ NIH | National Cancer Institute
Source: Artificial Sweeteners and Cancer
Plenty of studies and reviews have also confirmed this; here are some examples:
- Evaluation of aspartame cancer epidemiology studies based on quality appraisal criteria
- Aspartame, low-calorie sweeteners and disease: Regulatory safety and epidemiological issues
- Aspartame: A review of genotoxicity data
Why then do so many people believe it causes cancer, despite all the evidence against it?
Well, there was a small study involving giving megadoses to rats, which did increase their cancer risk. So of course, the popular press took that and ran with it.
But those results have not been achieved outside of rats, and human studies great and small have all been overwhelmingly conclusive that moderate consumption of aspartame has no effect on cancer risk.
Aspartame is a neurotoxin: True or False?
False, again assuming moderate consumption. If you’re a rat being injected with a megadose, your experience may vary. But a human enjoying a diet soda, the aspartame isn’t the part that’s doing you harm, so far as we know.
For example, the European Food Safety Agency’s scientific review panel concluded:
❝there is still no substantive evidence that aspartame can induce such effects❞
~ Dr. Atkin et al (it was a pan-European team of 21 experts in the field)
Source: Report on the Meeting on Aspartame with National Experts
See also,
❝The data from the extensive investigations into the possibility of neurotoxic effects of aspartame, in general, do not support the hypothesis that aspartame in the human diet will affect nervous system function, learning or behavior.
The weight of existing evidence is that aspartame is safe at current levels of consumption as a nonnutritive sweetener.❞
and
❝The safety testing of aspartame has gone well beyond that required to evaluate the safety of a food additive.
When all the research on aspartame, including evaluations in both the premarketing and postmarketing periods, is examined as a whole, it is clear that aspartame is safe, and there are no unresolved questions regarding its safety under conditions of intended use.❞
Source: Regulatory Toxicology & Pharmacology | Aspartame: Review of Safety
Why then do many people believe it is a neurotoxin? This one can be traced back to a chain letter hoax from about 26 years ago; you can read it here, but please be aware it is an entirely debunked hoax:
Urban Legends | Aspartame Hoax
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Currants vs Grapes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing currants to grapes, we picked the currants.
Why?
First, a note on nomenclature: when we say “currants”, we are talking about actual currants, of the Ribes genus, and in this case (as per the image) red ones. We are not talking about “currants” that are secretly tiny grapes that also get called currants in the US. So, there are important botanical differences here, beyond how they have been cultivated; they are literally entirely different plants.
So, about those differences…
In terms of macros, currants have nearly 5x the fiber, while grapes are slightly higher in carbs. So there’s an easy choice here in terms of fiber and on the glycemic index front; currants win easily.
In the category of vitamins, currants have more of vitamins B5, B9, C, and choline, while grapes have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, E, and K. So, a win for grapes in this round.
When it comes to minerals, currants have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while grapes have more manganese. A win, therefore, for currants again this time.
In terms of polyphenols, currants have a lot more in terms of total polyphenols, including (as a matter of interest) approximately 5x the resveratrol content compared to grapes—and that’s compared to black grapes, which are the “best” kind of grapes for such. Grapes really aren’t a very good source of resveratrol; people just really like the idea of red wine being a health food, so it has been talked up a lot and got a popular reputation despite its extreme paucity of nutritional value.
In any case, adding up the sections makes for a clear overall win for currants, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
21 Most Beneficial Polyphenols & What Foods Have Them
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healthy Mind In A Healthy Body
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The 8-minute piece of music “Weightless” by Marconi was created scientifically to lower the heart rate and relax the listener. How did they do it? You can read the British Academy of Sound Therapy’s explanation of the methodology here, but important results of the study were:
- “Weightless” was able to induce greater relaxation levels than a massage (increase of 6%).
- “Weightless” also induced an 11% increase in relaxation over all other relaxing music tracks in the study.
- “Weightless” was also subjectively rated as more relaxing than any other music by all the participants.
Try it for yourself!
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Isn’t that better? Whenever you’re ready, read on…
Today we’re going to share a technique for dealing with difficult emotions. The technique is used in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), and it’s called RAIN:
- Recognizing: ask yourself “what is it that I’m feeling?”, and put a name to it. It could be anger, despair, fear, frustration, anxiety, overwhelm etc.
- Accepting: “OK, so, I’m feeling ________”. There’s no point in denying it, or being defensive about it, these things won’t help you. For now, just accept it.
- Investigating: “Why am I feeling ________?” Maybe there is an obvious reason, maybe you need to dig for a reason—or dig deeper for the real reason. Most bad feelings are driven by some sort of fear or insecurity, so that can be a good avenue for examination. Important: your feelings may be rational or irrational. That’s fine. This is a time for investigating, not judging.
- Non-Identification: not making whatever it is you’re feeling into a part of you. Once you get too attached to “I am jealous”, “I am angry”, “I am sad” etc, it can be difficult to manage something that has become a part of your personality; you’ll defend your jealousy, anger, sadness etc rather than tackle it.
As a CBT tool, this is something you can do for yourself at any time. It won’t magically solve your problems, but it can stop you from spiralling into a state of crisis, and get you back on a more useful track.
As a DBT tool, to give this its full strength, ideally now you will communicate what you’re feeling, to somebody you trust, perhaps a partner or friend, for instance.
Humans are fundamentally social creatures, and we achieve our greatest strengths when we support each other—and that also means sometimes seeking and accepting support!
Do you have a good technique you’d like to share? Reply to this email and let us know!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: