Your Brain on Art – by Susan Magsamen & Ivy Ross
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The notion of art therapy is popularly considered a little wishy-washy. As it turns out, however, there are thousands of studies showing its effectiveness.
Nor is this just a matter of self-expression. As authors Magsamen and Ross explore, different kinds of engagement with art can convey different benefits.
That’s one of the greatest strengths of this book: “this form of engagement with art will give these benefits, according to these studies”
With benefits ranging from reducing stress and anxiety, to overcoming psychological trauma or physical pain, there’s a lot to be said for art!
And because the book covers many kinds of art, if you can’t imagine yourself taking paintbrush to canvas, that’s fine too. We learn of the very specific cognitive benefits of coloring in mandalas (yes, really), of sculpting something terrible in clay, or even just of repainting the kitchen, and more. Each thing has its set of benefits.
The book’s main goal is to encourage the reader to cultivate what the authors call an aesthetic mindset, which involves four key attributes:
- a high level of curiosity
- a love of playful, open-ended exploration
- a keen sensory awareness
- a drive to engage in creative activities
And, that latter? It’s as a maker and/or a beholder. We learn about what we can gain just by engaging with art that someone else made, too.
Bottom line: come for the evidence-based cognitive benefits; stay for the childlike wonder of the universe. If you already love art, or have thought it’s just “not for you”, then this book is for you.
Click here to check out Your Brain On Art, and open up whole new worlds of experience!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
‘Tis To Season To Be SAD-Savvy
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Seasonal Affective Disorder & SAD Lamps
For those of us in the Northern Hemisphere, it’s that time of the year; especially after the clocks recently went back and the nights themselves are getting longer. So, what to do in the season of 3pm darkness?
First: the problem
The problem is twofold:
- Our circadian rhythm gets confused
- We don’t make enough serotonin
The latter is because serotonin production is largely regulated by sunlight.
People tend to focus on item 2, but item 1 is important too—both as problem, and as means of remedy.
Circadian rhythm is about more than just light
We did a main feature on this a little while back, talking about:
- What light/dark does for us, and how it’s important, but not completely necessary
- How our body knows what time it is even in perpetual darkness
- The many peaks and troughs of many physiological functions over the course of a day/night
- What that means for us in terms of such things as diet and exercise
- Practical take-aways from the above
Read: The Circadian Rhythm: Far More Than Most People Know
With that in mind, the same methodology can be applied as part of treating Seasonal Affective Disorder.
Serotonin is also about more than just light
Our brain is a) an unbelievably powerful organ, and the greatest of any animal on the planet b) a wobbly wet mass that gets easily confused.
In the case of serotonin, we can have problems:
- knowing when to synthesize it or not
- synthesizing it
- using it
- knowing when to scrub it or not
- scrubbing it
- etc
Selective Serotonin Re-uptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of antidepressants that, as the name suggests, inhibit the re-uptake (scrubbing) of serotonin. So, they won’t add more serotonin to your brain, but they’ll cause your brain to get more mileage out of the serotonin that’s there, using it for longer.
So, whether or not they help will depend on you and your brain:
Read: Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
How useful are artificial sunlight lamps?
Artificial sunlight lamps (also called SAD lamps), or blue light lamps, are used in an effort to “replace” daylight.
Does it work? According to the science, generally yes, though everyone would like more and better studies:
- The Efficacy of Light Therapy in the Treatment of Seasonal Affective Disorder: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Blue-Light Therapy for Seasonal and Non-Seasonal Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Interestingly, it does still work in cases of visual impairment and blindness:
How much artificial sunlight is needed?
According to Wirz-Justice and Terman (2022), the best parameters are:
- 10,000 lux
- full spectrum (white light)
- 30–60 minutes exposure
- in the morning
Source: Light Therapy: Why, What, for Whom, How, and When (And a Postscript about Darkness)
That one’s a fascinating read, by the way, if you have time.
Can you recommend one?
For your convenience, here’s an example product on Amazon that meets the above specifications, and is also very similar to the one this writer has
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Debate over tongue tie procedures in babies continues. Here’s why it can be beneficial for some infants
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There is increasing media interest about surgical procedures on new babies for tongue tie. Some hail it as a miracle cure, others view it as barbaric treatment, though adverse outcomes are rare.
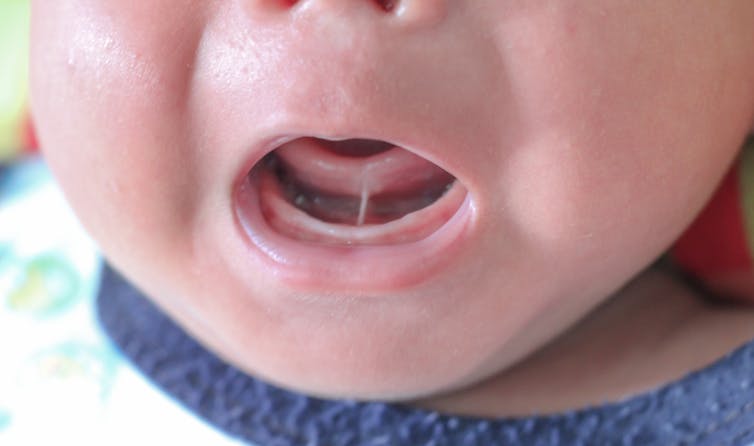
Tongue tie occurs when the tissue under the tongue is attached to the lower gum or floor of the mouth in a way that can restrict the movement or range of the tongue. This can impact early breastfeeding in babies. It affects an estimated 8% of children under one year of age.
While there has been an increase in tongue tie releases (also called division or frenotomy), it’s important to keep this in perspective relative to the increase in breastfeeding rates.
The World Health Organization recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life, with breastfeeding recommended into the second year of life and beyond for the health of mother and baby as well as optimal growth. Global rates of breastfeeding infants for the first six months have increased from 38% to 48% over the past decade. So, it is not surprising there is also an increase in the number of babies being referred globally with breastfeeding challenges and potential tongue tie.
An Australian study published in 2023 showed that despite a 25% increase in referrals for tongue tie division between 2014 and 2018, there was no increase in the number of tongue tie divisions performed. Tongue tie surgery rates increased in Australia in the decade from 2006 to 2016 (from 1.22 per 1,000 population to 6.35) for 0 to 4 year olds. There is no data on surgery rates in Australia over the last eight years.
Tongue tie division isn’t always appropriate but it can make a big difference to the babies who need it. More referrals doesn’t necessarily mean more procedures are performed.
chomplearn/Shutterstock How tongue tie can affect babies
When tongue tie (ankyloglossia) restricts the movement of the tongue, it can make it more difficult for a baby to latch onto the mother’s breast and painlessly breastfeed.
Earlier this month, the International Consortium of oral Ankylofrenula Professionals released a tongue tie position statement and practice guideline. Written by a range of health professionals, the guidelines define tongue tie as a functional diagnosis that can impact breastfeeding, eating, drinking and speech. The guidelines provide health professionals and families with information on the assessment and management of tongue tie.
Tongue tie release has been shown to improve latch during breastfeeding, reduce nipple pain and improve breast and bottle feeding. Early assessment and treatment are important to help mothers breastfeed for longer and address any potential functional problems.
The frenulum is a band of tissue under the tongue that is attached to the gumline base of the mouth. Akkalak Aiempradit/Shutterstock Where to get advice
If feeding isn’t going well, it may cause pain for the mother or there may be signs the baby isn’t attaching properly to the breast or not getting enough milk. Parents can seek skilled help and assessment from a certified lactation consultant or International Board-Certified Lactation Consultant who can be found via online registry.
Alternatively, a health professional with training and skills in tongue tie assessment and division can assist families. This may include a doctor, midwife, speech pathologist or dentist with extended skills, training and experience in treating babies with tongue tie.
When access to advice or treatment is delayed, it can lead to unnecessary supplementation with bottle feeds, early weaning from breastfeeding and increased parental anxiety.
Getting a tongue tie assessment
During assessment, a qualified health professional will collect a thorough case history, including pregnancy and birth details, do a structural and functional assessment, and conduct a comprehensive breastfeeding or feeding assessment.
They will view and thoroughly examine the mouth, including the tongue’s movement and lift. The appearance of where the tissue attaches to the underside of the tongue, the ability of the tongue to move and how the baby can suck also needs to be properly assessed.
Treatment decisions should focus on the concerns of the mother and baby and the impact of current feeding issues. Tongue tie division as a baby is not recommended for the sole purpose of avoiding speech problems in later life if there are no feeding concerns for the baby.
A properly qualified lactation consultant can help with positioning and attachment. HarryKiiM Stock/Shutterstock Treatment options
The Australian Dental Association’s 2020 guidelines provide a management pathway for babies diagnosed with tongue tie.
Once feeding issues are identified and if a tongue tie is diagnosed, non-surgical management to optimise positioning, latch and education for parents should be the first-line approach.
If feeding issues persist during follow-up assessment after non-surgical management, a tongue tie division may be considered. Tongue tie release may be one option to address functional challenges associated with breastfeeding problems in babies.
There are risks associated with any procedure, including tongue tie release, such as bleeding. These risks should be discussed with the treating practitioner before conducting any laser, scissor or scalpel tongue tie procedure.
Post-release support by a certified lactation consultant or feeding specialist is necessary after a tongue tie division. A post-release treatment plan should be developed by a team of health professionals including advice and support for breastfeeding to address both the mother and baby’s individual needs.
We would like to acknowledge the contribution of Raymond J. Tseng, DDS, PhD, (Paediatric Dentist) to the writing of this article.
Sharon Smart, Lecturer and Researcher (Speech Pathology) – School of Allied Health, Curtin University; David Todd, Associate Professor, Neonatology, ANU Medical School, Australian National University, and Monica J. Hogan, PhD student, ANU School of Medicine and Psychology, Australian National University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Does Eating Shellfish Contribute To Gout?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝I have a question about seafood as healthy, doesn’t eating shellfish contribute to gout?❞
It can do! Gout (a kind of inflammatory arthritis characterized by the depositing of uric acid crystals in joints) has many risk factors, and diet is one component, albeit certainly the most talked-about one.
First, you may be wondering: isn’t all arthritis inflammatory? Since arthritis is by definition the inflammation of joints, this is a reasonable question, but when it comes to classifying the kinds, “inflammatory” arthritis is caused by inflammation, while “non-inflammatory” arthritis (a slightly confusing name) merely has inflammation as one of its symptoms (and is caused by physical wear-and-tear). For more information, see:
- Tips For Avoiding/Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis ←inflammatory
- Tips For Avoiding/Managing Osteoarthritis ← “non-inflammatory”
As for gout specifically, top risk factors include:
- Increasing age: risk increases with age
- Being male: women do get gout, but much less often
- Hypertension: all-cause hypertension is the biggest reasonably controllable factor
There’s not a lot we can do about age (but of course, looking after our general health will tend to slow biological aging, and after all, diseases only care about the state of our body, not what the date on the calendar is).
As for sex, this risk factor is hormones, and specifically has to do with estrogen and testosterone’s very different effects on the immune system (bearing in mind that chronic inflammation is a disorder of the immune system). However, few if any men would take up feminizing hormone therapy just to lower their gout risk!
That leaves hypertension, which happily is something that we can all (barring extreme personal circumstances) do quite a bit about. Here’s a good starting point:
Hypertension: Factors Far More Relevant Than Salt
…and for further pointers:
How To Lower Your Blood Pressure (Cardiologists Explain)
As for diet specifically (and yes, shellfish):
The largest study into this (and thus, one of the top ones cited in a lot of other literature) looked at 47,150 men with no history of gout at the baseline.
So, with the caveat that their findings could have been different for women, they found:
- Eating meat in general increased gout risk
- Narrowing down specific meats: beef, pork, and lamb were the worst offenders
- Eating seafood in general increased gout risk
- Narrowing down specific seafoods: all seafoods increased gout risk within a similar range
- As a specific quirk of seafoods: the risk was increased if the man had a BMI under 25
- Eating dairy in general was not associated with an increased risk of gout
- Narrowing down specific dairy foods: low-fat dairy products such as yogurt were associated with a decreased risk of gout
- Eating purine-rich vegetables in general was not associated with an increased risk of gout
- Narrowing down to specific purine-rich vegetables: no purine-rich vegetable was associated with an increase in the risk of gout
Dairy products were included in the study, as dairy products in general and non-fermented dairy products in particular are often associated with increased inflammation. However, the association was simply not found to exist when it came to gout risk.
Purine-rich vegetables were included in the study, as animal products highest in purines have typically been found to have the worst effect on gout. However, the association was simply not found to exist when it came to plants with purines.
You can read the full study here:
Purine-Rich Foods, Dairy and Protein Intake, and the Risk of Gout in Men
So, the short answer to your question of “doesn’t eating shellfish contribute to the risk of gout” is:
Yes, it can, but occasional consumption probably won’t result in gout unless you have other risk factors going against you.
If you’re a slim male 80-year-old alcoholic smoker with hypertension, then definitely do consider skipping the lobster, but honestly, there may be bigger issues to tackle there.
And similarly, obviously skip it if you have a shellfish allergy, and if you’re vegan or vegetarian or abstain from shellfish for religious reasons, then you can certainly live very healthily without ever having any.
See also: Do We Need Animal Products, To Be Healthy?
For most people most of the time, a moderate consumption of seafood, including shellfish if you so desire, is considered healthy.
As ever, do speak with your own doctor to know for sure, as your individual case may vary.
For reference, this question was surely prompted by the article:
Lobster vs Crab – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Could the shingles vaccine lower your risk of dementia?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A recent study has suggested Shingrix, a relatively new vaccine given to protect older adults against shingles, may delay the onset of dementia.
This might seem like a bizarre link, but actually, research has previously shown an older version of the shingles vaccine, Zostavax, reduced the risk of dementia.
In this new study, published last week in the journal Nature Medicine, researchers from the United Kingdom found Shingrix delayed dementia onset by 17% compared with Zostavax.
So how did the researchers work this out, and how could a shingles vaccine affect dementia risk?
Melinda Nagy/Shutterstock From Zostavax to Shingrix
Shingles is a viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It causes painful rashes, and affects older people in particular.
Previously, Zostavax was used to vaccinate against shingles. It was administered as a single shot and provided good protection for about five years.
Shingrix has been developed based on a newer vaccine technology, and is thought to offer stronger and longer-lasting protection. Given in two doses, it’s now the preferred option for shingles vaccination in Australia and elsewhere.
In November 2023, Shingrix replaced Zostavax on the National Immunisation Program, making it available for free to those at highest risk of complications from shingles. This includes all adults aged 65 and over, First Nations people aged 50 and older, and younger adults with certain medical conditions that affect their immune systems.
What the study found
Shingrix was approved by the US Food and Drugs Administration in October 2017. The researchers in the new study used the transition from Zostavax to Shingrix in the United States as an opportunity for research.
They selected 103,837 people who received Zostavax (between October 2014 and September 2017) and compared them with 103,837 people who received Shingrix (between November 2017 and October 2020).
By analysing data from electronic health records, they found people who received Shingrix had a 17% increase in “diagnosis-free time” during the follow-up period (up to six years after vaccination) compared with those who received Zostavax. This was equivalent to an average of 164 extra days without a dementia diagnosis.
The researchers also compared the shingles vaccines to other vaccines: influenza, and a combined vaccine for tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis. Shingrix and Zostavax performed around 14–27% better in lowering the risk of a dementia diagnosis, with Shingrix associated with a greater improvement.
The benefits of Shingrix in terms of dementia risk were significant for both sexes, but more pronounced for women. This is not entirely surprising, because we know women have a higher risk of developing dementia due to interplay of biological factors. These include being more sensitive to certain genetic mutations associated with dementia and hormonal differences.
Why the link?
The idea that vaccination against viral infection can lower the risk of dementia has been around for more than two decades. Associations have been observed between vaccines, such as those for diphtheria, tetanus, polio and influenza, and subsequent dementia risk.
Research has shown Zostavax vaccination can reduce the risk of developing dementia by 20% compared with people who are unvaccinated.
But it may not be that the vaccines themselves protect against dementia. Rather, it may be the resulting lack of viral infection creating this effect. Research indicates bacterial infections in the gut, as well as viral infections, are associated with a higher risk of dementia.
Notably, untreated infections with herpes simplex (herpes) virus – closely related to the varicella-zoster virus that causes shingles – can significantly increase the risk of developing dementia. Research has also shown shingles increases the risk of a later dementia diagnosis.
This isn’t the first time research has suggested a vaccine could reduce dementia risk. ben bryant/Shutterstock The mechanism is not entirely clear. But there are two potential pathways which may help us understand why infections could increase the risk of dementia.
First, certain molecules are produced when a baby is developing in the womb to help with the body’s development. These molecules have the potential to cause inflammation and accelerate ageing, so the production of these molecules is silenced around birth. However, viral infections such as shingles can reactivate the production of these molecules in adult life which could hypothetically lead to dementia.
Second, in Alzheimer’s disease, a specific protein called Amyloid-β go rogue and kill brain cells. Certain proteins produced by viruses such as COVID and bad gut bacteria have the potential to support Amyloid-β in its toxic form. In laboratory conditions, these proteins have been shown to accelerate the onset of dementia.
What does this all mean?
With an ageing population, the burden of dementia is only likely to become greater in the years to come. There’s a lot more we have to learn about the causes of the disease and what we can potentially do to prevent and treat it.
This new study has some limitations. For example, time without a diagnosis doesn’t necessarily mean time without disease. Some people may have underlying disease with delayed diagnosis.
This research indicates Shingrix could have a silent benefit, but it’s too early to suggest we can use antiviral vaccines to prevent dementia.
Overall, we need more research exploring in greater detail how infections are linked with dementia. This will help us understand the root causes of dementia and design potential therapies.
Ibrahim Javed, Enterprise and NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow, UniSA Clinical & Health Sciences, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Human, Bird, or Dog Waste? Scientists Parsing Poop To Aid DC’s Forgotten River
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
KFF Health News Peggy Girshman reporting fellow Jackie Fortiér joined a boat tour to spotlight a review of microbes in the Anacostia River, a step toward making the river healthier and swimmable. The story was featured on WAMU’s “Health Hub” on Feb. 26.
On a bright October day, high schoolers from Francis L. Cardozo Education Campus piled into a boat on the Anacostia River in Washington, D.C. Most had never been on the water before.
Their guide, Trey Sherard of the Anacostia Riverkeeper, started the tour with a well-rehearsed safety talk. The nonprofit advocates for the protection of the river.
A boy with tousled black hair casually dipped his fingers in the water.
“Don’t touch it!” Sherard yelled.
Why was Sherard being so stern? Was it dangerously cold? Were there biting fish?
Because of the sewage.
“We get less sewage than we used to. Sewage is a code word for what?” Sherard asked the teenagers.
“Poop!” one student piped up.
“Human poop,” Sherard said. “Notice I didn’t say we get none. I said we get what? Less.”
Tours like this are designed to get young people interested in the river’s ecology, but it’s a fine line to tread — interacting with the water can make people sick. Because of the health risks, swimming hasn’t been legal in the Anacostia for more than half a century. The polluted water can cause gastrointestinal and respiratory illnesses, as well as eye, nose, and skin infections.
The river is the cleanest it’s been in years, according to environmental experts, but they still advise you not to take a dip in the Anacostia — not yet, at least.
About 40 million people in the U.S. live in a community with a combined sewer system, where wastewater and stormwater flow through the same pipes. When pipe capacities are reached after heavy rains, the overflow sends raw wastewater into the rivers instead of to a treatment plant.
Federal regulations, including sections of the Clean Water Act, require municipalities such as Washington to reduce at least 85% of this pollution or face steep fines.
To achieve compliance, Washington launched a $2.6 billion infrastructure project in 2011. DC Water’s Clean Rivers Project will eventually build multiple miles-long underground storage basins to capture stormwater and wastewater and pump it to treatment plants once heavy rains have subsided.
The Anacostia tunnel is the first of these storage basins to be completed. It can collect 190 million gallons of bacteria-laden wastewater for later treatment, said Moussa Wone, vice president of the Clean Rivers Project.
Climate change is causing more intense rainstorms in Washington, so even after construction is complete in 2030, Wone said, untreated stormwater will be discharged into the river, though much less frequently.
“On the Anacostia, we’re going to be reducing the frequency of overflows from 82 to two in an average year,” Wone said.
But while the Anacostia sewershed covers 176 square miles, he noted, only 17% is in Washington.
“The other 83% is outside the district,” Wone said. “We can do our part, but everybody else has to do their part also.”
Upstream in Maryland’s Montgomery and Prince George’s counties, miles of sewer lines are in the process of being upgraded to divert raw sewage to a treatment plant instead of the river.
The data shows that poop is a problem for river health — but knowing what kind of poop it is matters. Scientists monitor E. coli to indicate the presence of feces in river water, but since the bacteria live in the guts of most warm-blooded animals, the source is difficult to determine.
“Is it human feces? Or is it deer? Is it gulls’? Is it dogs’?” said Amy Sapkota, a professor of environmental and occupational health at the University of Maryland.
Bacterial levels can fluctuate across the river even without rainstorms. An Anacostia Riverkeeper report found that in 2023 just three of nine sites sampled along the Washington portion of the watershed had consistently low E. coli levels throughout the summer season.
Sapkota is heading a new bacterial monitoring program measuring the amount of E. coli that different animal species deposit along the river.
The team uses microbial source tracking to analyze samples of river water taken from different locations each month by volunteers. The molecular approach enables scientists to target specific gene sequences associated with fecal bacteria and determine whether the bacteria come from humans or wildlife. Microbial source tracking also measures fecal pollution levels by source.
“We can quantify the levels of different bacterial targets that may be coming from a human fecal source or an animal fecal source,” Sapkota said.
Her team expects to have preliminary results this year.
The health risk to humans from river water will never be zero, Sapkota said, but based on her team’s research, smart city planning and retooled infrastructure could lessen the level of harmful bacteria in the water.
“Let’s say that we’re finding that actually there’s a lot of deer fecal signatures in our results,” Sapkota said. “Maybe this points to the fact that we need more green buffers along the river that can help prevent fecal contaminants from wildlife from entering the river during stormwater events.”
Washington is hoping to recoup some of the cost of building green spaces and other river cleanup. In January, the office of D.C. Attorney General Brian Schwalb filed a lawsuit seeking unspecified damages from the federal government over decades of alleged pollution of the Anacostia River.
Brenda Lee Richardson, coordinator of the Anacostia Parks & Community Collaborative, said the efforts to cut down on trash and sewage are paying off. She sees a river on the mend, with more plant and animal life sprouting up.
“The ecosystem seems a lot greener,” she said. “There’s stuff in the river now that wasn’t there before.”
But any changes to the waterfront need to be done with residents of both sides of the river in mind, she said.
“We want there to be some sense of equity as it relates to who has access,” she said. “When I look at who is recreating, it’s not people who look like me.”
Richardson has lived for 40 years in Ward 8 — a predominantly Black area on the east side of the river whose residents are generally less affluent than those on the west side. She and her neighbors don’t consider the Anacostia a place to get out and play, she said.
As the water quality slowly improves, Richardson said, she hopes the Anacostia’s reputation is also rehabilitated. Even if it’s not safe to swim in, Richardson enjoys boating trips like the one with the Anacostia Riverkeeper.
“To see all those creatures along the way and the greenery. It was comforting,” she said. “So rather than take a pill to settle my nerves, I can just go down the river.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Better Sex = Longer Life (Here’s How)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Dr. Candice Hargons. She’s a professor of psychology, and has served on the Kentucky Psychological Association Board, the Society of Counseling Psychology Executive Board, and the American Psychological Association (APA)’s Council of Representatives. She also served on the APA Board of Directors, after receiving the APA’s Presidential Citation award for her research and leadership.
She leads the Study of Mental And Sexual Health Equity in Relationships (SMASHER Lab), with a predominant focus on promoting good sex, sexual wellness, and liberation among couples and communities.
In her own words:
❝Sex is one of the most common and normal human behaviors, and yet it remains relatively taboo as a topic. Many people worry about being judged, either for being perceived as too sexual or not sexual enough, and a major focus of my work is to normalize talking and learning about sex to improve sexual functioning across the adult lifespan.❞
~ Dr. Candice Hargons
So, let’s do that!
What does good sex do for health?
We’ve written previously about the health aspects of orgasms specifically:
“Early To Bed…” (Mythbusting Orgasms) ← including resources pertaining to anorgasmia, the inability to orgasm
…but orgasms are not the be-all-and-end-all of sex; see for example:
A Urologist Explains Edging: What, Why, & Is It Safe? ← when the journey is genuinely more of a focus than the destination
And certainly, good sex is simply a very good way to relax and de-stress, which is important, given how important stress management is to general health in very many ways (affecting things ranging from inflammation to heart health and more).
Plus, while the level of athleticism deployed may vary, sex is a physical activity, and physical activity is, as a rule, good.
There’s more to it than that though! It also can help us bind closely to our loved ones, in a positive way, which—critically—has a very positive impact on healthy longevity:
Only One Kind Of Relationship Promotes Longevity This Much! ← this is about the seriousness of the relationship, not the sex, but for most people, a strong and fulfilling relationship will include having good sex.
The scientific relationship between sex and longevity also got a whole chapter in this excellent book that we reviewed all so recently:
Age Proof: The New Science of Living a Longer and Healthier Life – by Dr. Rose Anne Kenny
What makes it “good”?
Dr. Hargons considers (and her opinion is backed by extensive research in the SMASHER Lab, if you’ll pardon the mental image that that might conjure) that first and foremost… It has to feel good to all parties involved.
In contrast, oftentimes, one partner’s pleasure is prioritized over another’s, and that becomes a problem.*
*assuming that’s not part of an established kink dynamic with enthusiastic affirmative consent, such as if the partner whose pleasure is being deprioritized is enthusiastically requesting to be denied orgasms, for example. Yes, that’s a real kink and even a popular one, but it’s not what’s happening in most sexually uneven relationships.
This kind of unplanned disparity often goes undiscussed by the couple in question—especially in heterosexual couples if the man is getting what he wants/needs and the woman isn’t, because there’s a rather lop-sided societal expectation in that regard. And even a loving, well-intentioned man can simply not know how to do better and be afraid to ask. And for that matter, it’s also entirely possible for his partner to not know either.
Dr. Hargons lists the four main keys as:
- Communication
- Intimacy
- Passion
- Pleasure
And communication indeed comes first, so to speak. For example, she advises:
❝Begin by identifying what you like and don’t like sexually. An easy way to do this is to create a “Yes, No, Maybe So” list. You can use paper or a Notes app on your phone.
Create three columns: one for Yes, No, and Maybe So sections. In the Yes section, write all the things you enjoy and want to keep doing sexually, as well as things you have not tried yet that you want to try. In the No section, write all the things you don’t enjoy and do not want to do anymore. It can also include things you haven’t tried that you’re uninterested in trying. Finally, in your Maybe So list, write all the things you’re curious about and/or are only willing to try in specific settings or circumstances.
You can share this list with your partner, but even if you are not ready to do that, you will already have enhanced your sexual self-awareness and be better positioned to talk with your sexual partner about what you want.❞
This represents an important shift from “whatever” to taking an active role in your sex life at your own pace.
And from there, it’s just a matter of exploring, together, and learning as you go. Could anything be more exciting than that?
“What if I’m single?”
We talked about this a little previously, more relationally than sexually specifically, though:
Now, a single person can of course still have an active sex life if you so choose, in which case, the above advice still applies, just, it’ll be conversations with your partner-of-the-moment rather than with a life partner. And that’s important too! Just because something is casual, doesn’t mean it need not be entered into mindfully and with a sense of what you want out of it, and communicating that effectively (while encouraging the same from others, and of course actually listening to, and caring about, what they say too).
And if you are, perchance, single and decided on a life of celibacy now, you can and (if you are sexual at all) should still figure out what you like and don’t like sexually, because even if it’s going to be you-on-you action, it will be good for you to love yourself enough to do it right.
Seriously, treat yourself at least as well as you would any other lover.
On which note, corded wand-style vibrators like the famous “Magic Wand” kind are much more powerful than the battery kind, and you will feel the difference, in a good way.
And if you really want to invest in your sexual wellness and you like the idea, saddle-style vibrators like this one will rock your socks off in ways handheld vibrators couldn’t dream of.
Want to know more?
You might want to check out Dr. Hargons’ book:
Good Sex: Stories, Science, and Strategies for Sexual Liberation – by Dr. Candice Hargons ← this covers so many important areas, more than we have room to here. Just check out the table of contents, and you’ll see what we mean.
…which we haven’t reviewed yet, but here are some excellent related books that we have:
- Come Together: The Science (and Art) of Creating Lasting Sexual Connections – by Dr. Emily Nagoski
- Better Sex Through Mindfulness: How Women Can Cultivate Desire – by Dr. Lori Brotto
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: