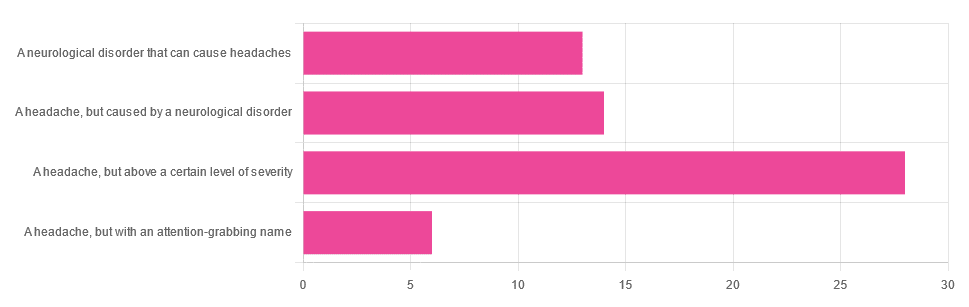
We don’t all need regular skin cancer screening – but you can know your risk and check yourself
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Australia has one of the highest skin cancer rates globally, with nearly 19,000 Australians diagnosed with invasive melanoma – the most lethal type of skin cancer – each year.
While advanced melanoma can be fatal, it is highly treatable when detected early.
But Australian clinical practice guidelines and health authorities do not recommend screening for melanoma in the general population.
Given our reputation as the skin cancer capital of the world, why isn’t there a national screening program? Australia currently screens for breast, cervical and bowel cancer and will begin lung cancer screening in 2025.
It turns out the question of whether to screen everyone for melanoma and other skin cancers is complex. Here’s why.

The current approach
On top of the 19,000 invasive melanoma diagnoses each year, around 28,000 people are diagnosed with in-situ melanoma.
In-situ melanoma refers to a very early stage melanoma where the cancerous cells are confined to the outer layer of the skin (the epidermis).
Instead of a blanket screening program, Australia promotes skin protection, skin awareness and regular skin checks (at least annually) for those at high risk.
About one in three Australian adults have had a clinical skin check within the past year.

Why not just do skin checks for everyone?
The goal of screening is to find disease early, before symptoms appear, which helps save lives and reduce morbidity.
But there are a couple of reasons a national screening program is not yet in place.
We need to ask:
1. Does it save lives?
Many researchers would argue this is the goal of universal screening. But while universal skin cancer screening would likely lead to more melanoma diagnoses, this might not necessarily save lives. It could result in indolent (slow-growing) cancers being diagnosed that might have never caused harm. This is known as “overdiagnosis”.
Screening will pick up some cancers people could have safely lived with, if they didn’t know about them. The difficulty is in recognising which cancers are slow-growing and can be safely left alone.
Receiving a diagnosis causes stress and is more likely to lead to additional medical procedures (such as surgeries), which carry their own risks.
2. Is it value for money?
Implementing a nationwide screening program involves significant investment and resources. Its value to the health system would need to be calculated, to ensure this is the best use of resources.
Narrower targets for better results
Instead of screening everyone, targeting high-risk groups has shown better results. This focuses efforts where they’re needed most. Risk factors for skin cancer include fair skin, red hair, a history of sunburns, many moles and/or a family history.
Research has shown the public would be mostly accepting of a risk-tailored approach to screening for melanoma.
There are moves underway to establish a national targeted skin cancer screening program in Australia, with the government recently pledging $10.3 million to help tackle “the most common cancer in our sunburnt country, skin cancer” by focusing on those at greater risk.
Currently, Australian clinical practice guidelines recommend doctors properly evaluate all patients for their future risk of melanoma.
Looking with new technological eyes
Technological advances are improving the accuracy of skin cancer diagnosis and risk assessment.
For example, researchers are investigating 3D total body skin imaging to monitor changes to spots and moles over time.
Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms can analyse images of skin lesions, and support doctors’ decision making.
Genetic testing can now identify risk markers for more personalised screening.
And telehealth has made remote consultations possible, increasing access to specialists, particularly in rural areas.
Check yourself – 4 things to look for
Skin cancer can affect all skin types, so it’s a good idea to become familiar with your own skin. The Skin Cancer College Australasia has introduced a guide called SCAN your skin, which tells people to look for skin spots or areas that are:
1. sore (scaly, itchy, bleeding, tender) and don’t heal within six weeks
2. changing in size, shape, colour or texture
3. abnormal for you and look different or feel different, or stand out when compared to your other spots and moles
4. new and have appeared on your skin recently. Any new moles or spots should be checked, especially if you are over 40.
If something seems different, make an appointment with your doctor.
You can self-assess your melanoma risk online via the Melanoma Institute Australia or QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute.
H. Peter Soyer, Professor of Dermatology, The University of Queensland; Anne Cust, Professor of Cancer Epidemiology, The Daffodil Centre and Melanoma Institute Australia, University of Sydney; Caitlin Horsham, Research Manager, The University of Queensland, and Monika Janda, Professor in Behavioural Science, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cashews vs Peanuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cashews to peanuts, we picked the peanuts.
Why?
Another one for “that which is more expensive is not necessarily the healthier”! Although, certainly both are good:
In terms of macros, cashews have about 2x the carbs while peanuts have a little more (healthy!) fat and more than 2x the fiber, meaning that peanuts also enjoy the lower glycemic index. All in all, a fair win for peanuts here.
When it comes to vitamins, cashews have more of vitamins B6 and K, while peanuts have a lot more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B7, B9, and E. Another easy win for peanuts.
In the category of minerals; cashews have more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, and selenium, while peanuts have more calcium, manganese, and potassium. A win for cashews, this time.
Adding up the sections makes for an overall win for peanuts, but (assuming you are not allergic) enjoy either or both! In fact, enjoying both is best; diversity is good.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Jasmine McDonald’s Ballet Stretching Routine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Why Jasmine’s Video is Useful
Jasmine McDonald is not only a professional ballerina, but is also a certified personal trainer, so when it comes to keeping her body strong and flexible, she’s a wealth of knowledge. Her video (below) is a great example of this.
In case you’re interested in learning more, she currently (privately) tutors over 30 people on a day-to-day basis. You can contact her here!
Other Stretches?
If you think that Jasmine’s stretches may be out of your league, we recommend checking out our other articles on stretching, including:
- 11 Minutes to Pain-Free Hips
- How to Permanently Loosen a Tight Psoas
- Stretching Scientifically
- Stretching & Mobility
- Stretching to Stay Young
Otherwise, let loose on these dancer stretches and exercises:
How did you find that video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Share This Post
-
Osteoporosis & Exercises: Which To Do (And Which To Avoid)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Any idea about the latest research on the most effective exercises for osteoporosis?❞
While there isn’t much new of late in this regard, there is plenty of research!
First, what you might want to avoid:
- Sit-ups, and other exercises with a lot of repeated spinal flexion
- Running, and other high-impact exercises
- Skiing, horse-riding, and other activities with a high risk of falling
- Golf and tennis (both disproportionately likely to result in injuries to wrists, elbows, and knees)
Next, what you might want to bear in mind:
While in principle resistance training is good for building strong bones, good form becomes all the more important if you have osteoporosis, so consider working with a trainer if you’re not 100% certain you know what you’re doing:
Some of the best exercises for osteoporosis are isometric exercises:
5 Isometric Exercises for Osteoporosis (with textual explanations and illustrative GIFs)
You might also like this bone-strengthening exercise routine from corrective exercise specialist Kendra Fitzgerald:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Undo The Sun’s Damage To Your Skin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s often said that our skin is our largest organ. Our brain or liver are the largest solid organs by mass (which one comes out on top will vary from person to person), our gut is the longest, and our lungs are the largest by surface area. But our skin is large, noticeable, and has a big impact on the rest of our health.
The sun is one of the main damaging factors for our skin; assorted toxins are also a major threat for many people, and once the skin barrier gets broken, it’s a field-day for bacteria.
So, what can we do about it?
Tretinoin: the skin’s rejuvenator
Tretinoin is also called retinoic acid, not to be mistaken for retinol, although they are both retinoids. Tretinoin is much stronger.
As for what it’s stronger at:
It’s usually prescribed for the treatment of sun-damage, acne, and wrinkles. Paradoxically, it works by inflaming the skin (and then making it better, and having done so, keeping it better).
In few words: it encourages your skin to speed up its life cycle, which means that cells die and are replaced sooner, which means the average age of skin cells will be considerably younger at any given time.
This is the same principle as we see at work when it comes to cellular apoptosis and autophagy in general, and specifically the same idea as we discussed when talking about senolytics, compounds that kill aging cells:
Fisetin: The Anti-Aging Assassin
About that paradoxical inflammation…
❝The topical use of tretinoin as an antiacne agent began almost a half century ago. Since that time it has been successfully used to treat comedonal and inflammatory acne.
Over the intervening years, the beneficial effects of tretinoin have grown from an understanding of its potent cornedolytie-related properties to an evolving appreciation of its antiinflammatory actions.
…
The topical use of clindamycin and tretinoin as a combination treatment modality that includes antibacterial, comedolytic, and antiinflammatoiy properties has proven to be a very effective therapy for treating the various stages of acne
…
It is now becoming increasingly clear that there may be good reasons for these observations.❞
~ Drs. Schmidt & Gans, lightly edited here for brevity
Read in full: Tretinoin: A Review of Its Anti-inflammatory Properties in the Treatment of Acne
Against damage by the sun
The older we get, the more likely sun damage is a problem than acne. And in the case of tretinoin,
❝In several well-controlled clinical trials, the proportion of patients showing improvement was significantly higher with 0.01 or 0.05% tretinoin cream than with placebo for criteria such as global assessment, fine and coarse wrinkling, pigmentation and roughness.
Improvements in the overall severity of photodamage were also significantly greater with tretinoin than with placebo.
…
Several placebo-controlled clinical studies have demonstrated that topical tretinoin has significant efficacy in the treatment of photodamaged skin. Improvements in subjective global assessment scores were recorded in:
49–100% of patients using once-daily 0.01% tretinoin,
68–100% of patients using 0.05% tretinoin, and
0–44% of patients using placebo.❞
~ Drs. Wagstaff & Noble
…which is quite compelling.
Read in full: Tretinoin: A Review of its Pharmacological Properties and Clinical Efficacy in the Topical Treatment of Photodamaged Skin
This is very well-established by now; here’s an old paper from when the mechanism of action was unknown (here in the current day, 17 mechanisms of action have been identified; beyond the scope of this article as we only have so much room, but it’s nice to see science building on science):
❝Tretinoin cream has been used extensively to reverse the changes of photoaging. It is the first topical therapy to undergo controlled clinical testing and proved to be efficacious. These results have been substantiated with photography, histopathologie examination, and skin surface replicas.
…
Tretinoin cream has an excellent safety record; a local cutaneous hypervitaminosis A reaction is the only common problem.❞
~ Dr. Goldfarb et al.
Read in full: Topical tretinoin therapy: Its use in photoaged skin
Is it safe?
For most people, when used as directed*, yes. However, it’s likely to irritate your skin at first, and that’s normal. If this persists more than a few weeks, or seems unduly severe, then you might want to stop and talk to your doctor again.
*See also: Scarring following inappropriate use of 0.05% tretinoin gel
(in the case of a young woman who used it 4x daily instead of 1x daily)
Want to try some?
Tretinoin is prescription-only, so speak with your doctor/pharmacist about that. Alternatively, retinal (not retinol) is the strongest natural alternative that works on the same principles; here’s an example product on Amazon 😎
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Do we really need to burp babies? Here’s what the research says
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Parents are often advised to burp their babies after feeding them. Some people think burping after feeding is important to reduce or prevent discomfort crying, or to reduce how much a baby regurgitates milk after a feed.
It is true babies, like adults, swallow air when they eat. Burping releases this air from the top part of our digestive tracts. So when a baby cries after a feed, many assume it’s because the child needs to “be burped”. However, this is not necessarily true.
Why do babies cry or ‘spit up’ after a feed?
Babies cry for a whole host of reasons that have nothing to do with “trapped air”.
They cry when they are hungry, cold, hot, scared, tired, lonely, overwhelmed, needing adult help to calm, in discomfort or pain, or for no identifiable reason. In fact, we have a name for crying with no known cause; it’s called “colic”.
“Spitting up” – where a baby gently regurgitates a bit of milk after a feed – is common because the muscle at the top of a newborn baby’s stomach is not fully mature. This means what goes down can all too easily go back up.
Spitting up frequently happens when a baby’s stomach is very full, there is pressure on their tummy or they are picked up after lying down.
Spitting up after feeding decreases as babies get older. Three-quarters of babies one month old spit up after feeding at least once a day. Only half of babies still spit up at five months and almost all (96%) stop by their first birthdays.
There’s not much research out there on ‘burping’ babies. antoniodiaz/Shutterstock Does burping help reduce crying or spitting up?
Despite parents being advised to burp their babies, there’s not much research evidence on the topic.
One study conducted in India encouraged caregivers of 35 newborns to burp their babies, while caregivers of 36 newborns were not given any information about burping.
For the next three months, mothers and caregivers recorded whether their baby would spit up after feeding and whether they showed signs of intense crying.
This study found burping did not reduce crying and actually increased spitting up.
When should I be concerned about spitting up or crying?
Most crying and spitting up is normal. However, these behaviours are not:
- refusing to feed
- vomiting so much milk weight gain is slow
- coughing or wheezing distress while feeding
- bloody vomit.
If your baby has any of these symptoms, see a doctor or child health nurse.
If your baby seems unbothered by vomiting and does not have any other symptoms it is a laundry problem rather than something that needs medical attention.
It is also normal for babies to cry and fuss quite a lot; two hours a day, for about the first six weeks is the average.
This has usually reduced to about one hour a day by the time they are three months of age.
Crying more than this doesn’t necessarily mean there is something wrong. The intense, inconsolable crying of colic is experienced by up to one-quarter of young babies but goes away with time on its own .
If your baby is crying more than average or if you are worried there might be something wrong, you should see your doctor or child health nurse.
If your baby likes being ‘burped’, then it’s OK to do it. But don’t stress if you skip it. Miljan Zivkovic/Shutterstock Not everyone burps their baby
Burping babies seems to be traditional practice in some parts of the world and not in others.
For example, research in Indonesia found most breastfeeding mothers rarely or never burped their babies after feeding.
One factor that may influence whether a culture encourages burping babies may be related to another aspect of infant care: how much babies are carried.
Carrying a baby in a sling or baby carrier can reduce the amount of time babies cry.
Babies who are carried upright on their mother or another caregiver’s front undoubtedly find comfort in that closeness and movement.
Babies in slings are also being held firmly and upright, which would help any swallowed air to rise up and escape via a burp if needed.
Using slings can make caring for a baby easier. Studies (including randomised controlled trials) have also shown women have lower rates of post-natal depression and breastfeed for longer when they use a baby sling.
It is important baby carriers and slings are used safely, so make sure you’re up to date on the latest advice on how to do it.
So, should I burp my baby?
The bottom line is: it’s up to you.
Gently burping a baby is not harmful. If you feel burping is helpful to your baby, then keep doing what you’re doing.
If trying to burp your baby after every feed is stressing you or your baby out, then you don’t have to keep doing it.
Karleen Gribble, Adjunct Associate Professor, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Western Sydney University and Nina Jane Chad, Research Fellow, University of Sydney School of Public Health, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Migraine Mythbusting
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Migraine: When Headaches Are The Tip Of The Neurological Iceberg
Yesterday, we asked you “What is a migraine?” and got the above-depicted, below-described spread of responses:
- Just under 46% said “a headache, but above a certain level of severity”
- Just under 23% said “a headache, but caused by a neurological disorder”
- Just over 21% said “a neurological disorder that can cause headaches”
- Just under 10% said “a headache, but with an attention-grabbing name”
So… What does the science say?
A migraine is a headache, but above a certain level of severity: True or False?
While that’s usually a very noticeable part of it… That’s only one part of it, and not a required diagnostic criterion. So, in terms of defining what a migraine is, False.
Indeed, migraine may occur without any headache, let alone a severe one, for example: Abdominal Migraine—though this is much less well-researched than the more common with-headache varieties.
Here are the defining characteristics of a migraine, with the handy mnemonic 5-4-3-2-1:
- 5 or more attacks
- 4 hours to 3 days in duration
- 2 or more of the following:
- Unilateral (affects only one side of the head)
- Pulsating
- Moderate or severe pain intensity
- Worsened by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity
- 1 or more of the following:
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Sensitivity to both light and sound
Source: Cephalalgia | ICHD-II Classification: Parts 1–3: Primary, Secondary and Other
As one of our subscribers wrote:
❝I have chronic migraine, and it is NOT fun. It takes away from my enjoyment of family activities, time with friends, and even enjoying alone time. Anyone who says a migraine is just a bad headache has not had to deal with vertigo, nausea, loss of balance, photophobia, light sensitivity, or a host of other symptoms.❞
Migraine is a neurological disorder: True or False?
True! While the underlying causes aren’t known, what is known is that there are genetic and neurological factors at play.
❝Migraine is a recurrent, disabling neurological disorder. The World Health Organization ranks migraine as the most prevalent, disabling, long-term neurological condition when taking into account years lost due to disability.
Considerable progress has been made in elucidating the pathophysiological mechanisms of migraine, associated genetic factors that may influence susceptibility to the disease❞
Source: JHP | Mechanisms of migraine as a chronic evolutive condition
Migraine is just a headache with a more attention-grabbing name: True or False?
Clearly, False.
As we’ve already covered why above, we’ll just close today with a nod to an old joke amongst people with chronic illnesses in general:
“Are you just saying that because you want attention?”
“Yes… Medical attention!”
Want to learn more?
You can find a lot of resources at…
NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders & Stroke | Migraine
and…
The Migraine Trust ← helpfully, this one has a “Calm mode” to tone down the colorscheme of the website!
Particularly useful from the above site are its pages:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: