The Painkilling Power Of Opioids, Without The Harm?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to painkilling medications, they can generally be categorized into two kinds:
- non-opioids (e.g. ibuprofen, paracetamol/acetaminophen, aspirin)
- ones that actually work for something more serious than a headache
That’s an oversimplification, but broadly speaking, when there is serious painkilling to be done, that’s when doctors consider it’s time to break out the opioids.
Nor are all opioids created equal—there’s a noteworthy difference between codeine and morphine, for instance—but the problems of opioids are typically the same (tolerance, addiction, and eventual likelihood of overdose when one tries to take enough to make it work after developing a tolerance), and it becomes simply a matter of degree.
See also: I’ve been given opioids after surgery to take at home. What do I need to know?
So, what’s the new development?
A team of researchers have found that the body can effectively produce its own targetted painkilling peptides, similar in function to benzodiazepines (an opioid drug), but—and which is a big difference—confined to the peripheral nervous system (PNS), meaning that it doesn’t enter the brain.
- The peptides killing the pain before it can reach the brain is obviously good because that means the pain is simply not experienced
- The peptides not having any effect on the brain, however, means that the mechanism of addiction of opioids simply does not apply here
- The peptides not having any effect on the brain also means that the CNS can’t be “put to sleep” by these peptides in the same way it can if a high dose of opioids is taken (this is what typically causes death in opioid overdoses; the heart simply beats too slowly to maintain life)
The hope, therefore, is to now create medications that target the spinal ganglia that produce these peptides, to “switch them on” at will.
Obviously, this won’t happen overnight; there will need to be first a lot of research to find a drug that does that (likely this will involve a lot of trial and error and so many mice/rats), and then multiple rounds of testing to ascertain that the drug is safe and effective for humans, before it can then be rolled out commercially.
But, this is still a big breakthrough; there arguably hasn’t been a breakthrough this big in pain research since various opioid-related breakthroughs in the 70s and 80s.
You can see a pop-science article about it here:
And you can see the previous research (from earlier this year) that this is now building from, about the glial cells in the spinal ganglia, here:
Peripheral gating of mechanosensation by glial diazepam binding inhibitor
But wait, there’s more!
Remember what we said about affecting the PNS without affecting the CNS, to kill the pain without killing the brain?
More researchers are already approaching the same idea to deal with the same problem, but from the angle of gene therapy, and have already had some very promising results with mice:
Structure-guided design of a peripherally restricted chemogenetic system
…which you can read about in pop-science terms (with diagrams!) here:
New gene therapy could alleviate chronic pain, researchers find
While you’re waiting…
In the meantime, approaches that are already available include:
- The 7 Approaches To Pain Management
- Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
- Science-Based Alternative Pain Relief ← when painkillers aren’t helping, these things might!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Rose Hips vs Blueberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing rose hips to blueberries, we picked the rose hips.
Why?
Both of these fruits are abundant sources of antioxidants and other polyphenols, but one of them stands out for overall nutritional density:
In terms of macros, rose hips have about 2x the carbohydrates, and/but about 10x the fiber. That’s an easy calculation and a clear win for rose hips.
When it comes to vitamins, rose hips have a lot more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B5, B6, C, E, K, and choline. On the other hand, blueberries boast more of vitamins B1 and B9. That’s a 9:2 lead for rose hips, even before we consider rose hips’ much greater margins of difference (kicking off with 80x the vitamin A, for instance, and many multiples of many of the others).
In the category of minerals, rose hips have a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. Meanwhile, blueberries are not higher in any minerals.
In short: as ever, enjoy both, but if you’re looking for nutritional density, there’s a clear winner here and it’s rose hips.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
It’s In The Hips: Rosehip’s Benefits, Inside & Out
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Younger For Life – by Dr. Anthony Youn
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed anti-aging books before, so what makes this one different? Mostly, it’s the very practical focus.
Which is not to say there’s not also good science in here; there is. But the focus is on what everything means for the reader, not what happened with a certain cohort of lab mice. Instead, he looks at the causes of aging, the process of aging, and what interventions to implement to address those, and reverse many of them.
Some parts are more general lifestyle interventions that 10almonds readers will know well already, but other parts are very specific advices, protocols, and regimes; in particular his skincare section is well worth reading. As for nutrition, there’s even a respectable recipes section, so this book does have it all!
The final section of the book is dedicated to plastic surgeries (the author is a plastic surgeon who believes that most people should not need those, and would do well to stick to the advices in the rest of the book). We suspect this last part of the book will be of least interest to 10almonds readers.
Bottom line: if you’re of the view that getting older should come with as little as possible physical deterioration along the way, then this book can help a lot with that.
Share This Post
-
Never Too Old?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Age Limits On Exercise?
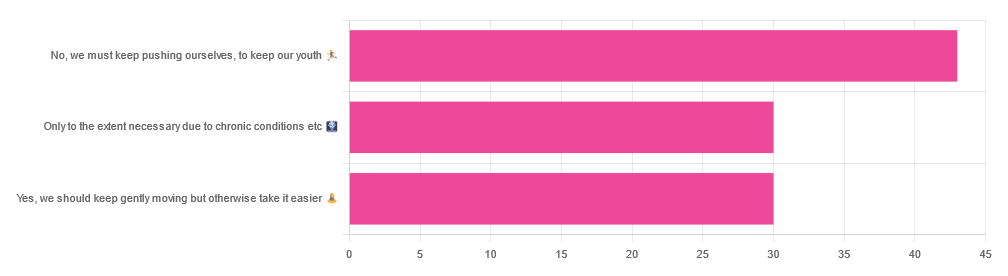
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your opinion on whether we should exercise less as we get older, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 42% said “No, we must keep pushing ourselves, to keep our youth“
- About 29% said “Only to the extent necessary due to chronic conditions etc”
- About 29% said “Yes, we should keep gently moving but otherwise take it easier”
One subscriber who voted for “No, we must keep pushing ourselves, to keep our youth“ wrote to add:
❝I’m 71 and I push myself. I’m not as fast or strong as I used to be but, I feel great when I push myself instead of going through the motions. I listen to my body!❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
One subscriber who voted for “Only to the extent necessary due to chronic conditions etc” wrote to add:
❝It’s never too late to get stronger. Important to keep your strength and balance. I am a Silver Sneakers instructor and I see first hand how helpful regular exercise is for seniors.❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
One subscriber who voted to say “Yes, we should keep gently moving but otherwise take it easier” wrote to add:
❝Keep moving but be considerate and respectful of your aging body. It’s a time to find balance in life and not put yourself into a positon to damage youself by competing with decades younger folks (unless you want to) – it will take much longer to bounce back.❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
These will be important, because we’ll come back to them at the end.
So what does the science say?
Endurance exercise is for young people only: True or False?
False! With proper training, age is no barrier to serious endurance exercise.
Here’s a study that looked at marathon-runners of various ages, and found that…
- the majority of middle-aged and elderly athletes have training histories of less than seven years of running
- there are virtually no relevant running time differences (p<0.01) per age in marathon finishers from 20 to 55 years
- after 55 years, running times did increase on average, but not consistently (i.e. there were still older runners with comparable times to the younger age bracket)
The researchers took this as evidence of aging being indeed a biological process that can be sped up or slowed down by various lifestyle factors.
See also:
Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
this covers the many aspects of biological aging (it’s not one number, but many!) and how our various different biological ages are often not in sync with each other, and how we can optimize each of them that can be optimized
Resistance training is for young people only: True or False?
False! In fact, it’s not only possible for older people, but is also associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality.
Specifically, those who reported strength-training at least once per week enjoyed longer lives than those who did not.
You may be thinking “is this just the horse-riding thing again, where correlation is not causation and it’s just that healthier people (for other reasons) were able to do strength-training more, rather than the other way around?“
…which is a good think to think of, so well-spotted if you were thinking that!
But in this case no; the benefits remained when other things were controlled for:
❝Adjusted for demographic variables, health behaviors and health conditions, a statistically significant effect on mortality remained.
Although the effects on cardiac and cancer mortality were no longer statistically significant, the data still pointed to a benefit.
Importantly, after the physical activity level was controlled for, people who reported strength exercises appeared to see a greater mortality benefit than those who reported physical activity alone.❞
See the study: Is strength training associated with mortality benefits? A 15 year cohort study of US older adults
And a pop-sci article about it: Strength training helps older adults live longer
Closing thoughts
As it happens… All three of the subscribers we quoted all had excellent points!
Because in this case it’s less a matter of “should”, and more a selection of options:
- We (most of us, at least) can gain/regain/maintain the kind of strength and fitness associated with much younger people, and we need not be afraid of exercising accordingly (assuming having worked up to such, not just going straight from couch to marathon, say).
- We must nevertheless be mindful of chronic conditions or even passing illnesses/injuries, but that goes for people of any age
- We also can’t argue against a “safety first” cautious approach to exercise. After all, sure, maybe we can run marathons at any age, but that doesn’t mean we have to. And sure, maybe we can train to lift heavy weights, but if we’re content to be able to carry the groceries or perhaps take our partner’s weight in the dance hall (or the bedroom!), then (if we’re also at least maintaining our bones and muscles at a healthy level) that’s good enough already.
Which prompts the question, what do you want to be able to do, now and years from now? What’s important to you?
For inspiration, check out: Train For The Event Of Your Life!
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Feminist narratives are being hijacked to market medical tests not backed by evidence
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Corporations have used feminist language to promote their products for decades. In the 1980s, companies co-opted messaging about female autonomy to encourage women’s consumption of unhealthy commodities, such as tobacco and alcohol.
Today, feminist narratives around empowerment and women’s rights are being co-opted to market interventions that are not backed by evidence across many areas of women’s health. This includes by commercial companies, industry, mass media and well-intentioned advocacy groups.
Some of these health technologies, tests and treatments are useful in certain situations and can be very beneficial to some women.
However, promoting them to a large group of asymptomatic healthy women that are unlikely to benefit, or without being transparent about the limitations, runs the risk of causing more harm than good. This includes inappropriate medicalisation, overdiagnosis and overtreatment.
In our analysis published today in the BMJ, we examine this phenomenon in two current examples: the anti-mullerian hormone (AMH) test and breast density notification.
The AMH test
The AMH test is a blood test associated with the number of eggs in a woman’s ovaries and is sometimes referred to as the “egg timer” test.
Although often used in fertility treatment, the AMH test cannot reliably predict the likelihood of pregnancy, timing to pregnancy or specific age of menopause. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists therefore strongly discourages testing for women not seeking fertility treatment.
The AMH test can’t predict your chance of getting pregnant.
Anastasia Vityukova/UnsplashDespite this, several fertility clinics and online companies market the AMH test to women not even trying to get pregnant. Some use feminist rhetoric promising empowerment, selling the test as a way to gain personalised insights into your fertility. For example, “you deserve to know your reproductive potential”, “be proactive about your fertility” and “knowing your numbers will empower you to make the best decisions when family planning”.
The use of feminist marketing makes these companies appear socially progressive and champions of female health. But they are selling a test that has no proven benefit outside of IVF and cannot inform women about their current or future fertility.
Our recent study found around 30% of women having an AMH test in Australia may be having it for these reasons.
Misleading women to believe that the test can reliably predict fertility can create a false sense of security about delaying pregnancy. It can also create unnecessary anxiety, pressure to freeze eggs, conceive earlier than desired, or start fertility treatment when it may not be needed.
While some companies mention the test’s limitations if you read on, they are glossed over and contradicted by the calls to be proactive and messages of empowerment.
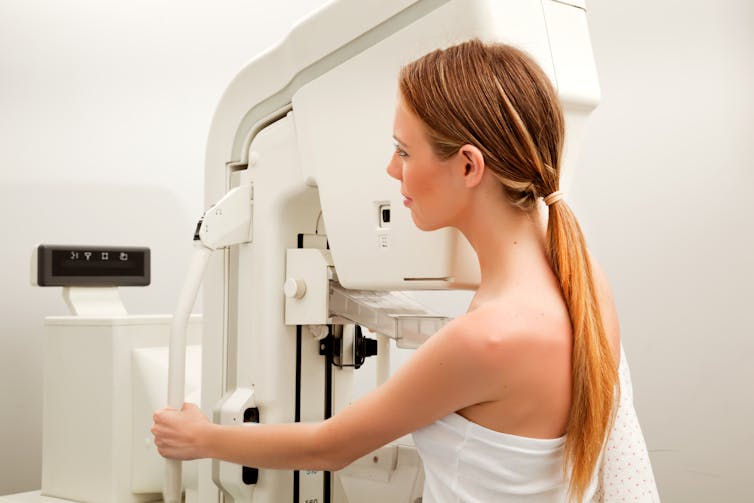
Breast density notification
Breast density is one of several independent risk factors for breast cancer. It’s also harder to see cancer on a mammogram image of breasts with high amounts of dense tissue than breasts with a greater proportion of fatty tissue.
While estimates vary, approximately 25–50% of women in the breast screening population have dense breasts.
Dense breasts can make it harder to detect cancer.
Tyler Olsen/ShutterstockStemming from valid concerns about the increased risk of cancer, advocacy efforts have used feminist language around women’s right to know such as “women need to know the truth” and “women can handle the truth” to argue for widespread breast density notification.
However, this simplistic messaging overlooks that this is a complex issue and that more data is still needed on whether the benefits of notifying and providing additional screening or tests to women with dense breasts outweigh the harms.
Additional tests (ultrasound or MRI) are now being recommended for women with dense breasts as they have the ability to detect more cancer. Yet, there is no or little mention of the lack of robust evidence showing that it prevents breast cancer deaths. These extra tests also have out-of-pocket costs and high rates of false-positive results.
Large international advocacy groups are also sponsored by companies that will financially benefit from women being notified.
While stronger patient autonomy is vital, campaigning for breast density notification without stating the limitations or unclear evidence of benefit may go against the empowerment being sought.
Ensuring feminism isn’t hijacked
Increased awareness and advocacy in women’s health are key to overcoming sex inequalities in health care.
But we need to ensure the goals of feminist health advocacy aren’t undermined through commercially driven use of feminist language pushing care that isn’t based on evidence. This includes more transparency about the risks and uncertainties of health technologies, tests and treatments and greater scrutiny of conflicts of interests.
Health professionals and governments must also ensure that easily understood, balanced information based on high quality scientific evidence is available. This will enable women to make more informed decisions about their health.
Brooke Nickel, NHMRC Emerging Leader Research Fellow, University of Sydney and Tessa Copp, NHMRC Emerging Leader Research Fellow, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Surprising Link Between Type 2 Diabetes & Alzheimer’s
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Surprising Link Between Type 2 Diabetes & Alzheimer’s
This is Dr. Rhonda Patrick. She’s a biomedical scientist with expertise in the areas of aging, cancer, and nutrition. In the past five years she has expanded her research of aging to focus more on Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, as she has a genetic predisposition to both.
What does that genetic predisposition look like? People who (like her) have the APOE-ε4 allele have a twofold increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease—and if you have two copies (i.e., one from each of two parents), the risk can be up to tenfold. Globally, 13.7% of people have at least one copy of this allele.
So while getting Alzheimer’s or not is not, per se, hereditary… The predisposition to it can be passed on.
What’s on her mind?
Dr. Patrick has noted that, while we don’t know for sure the causes of Alzheimer’s disease, and can make educated guesses only from correlations, the majority of current science seems to be focusing on just one: amyloid plaques in the brain.
This is a worthy area of research, but ignores the fact that there are many potential Alzheimer’s disease mechanisms to explore, including (to count only mainstream scientific ideas):
- The amyloid hypothesis
- The tau hypothesis
- The inflammatory hypothesis
- The cholinergic hypothesis
- The cholesterol hypothesis
- The Reelin hypothesis
- The large gene instability hypothesis
…as well as other strongly correlated factors such as glucose hypometabolism, insulin signalling, and oxidative stress.
If you lost your keys and were looking for them, and knew at least half a dozen places they might be, how often would you check the same place without paying any attention to the others?
To this end, she notes about those latter-mentioned correlated factors:
❝50–80% of people with Alzheimer’s disease have type 2 diabetes; there is definitely something going on❞
There’s another “smoking gun” for this too, because dysfunction in the blood vessels and capillaries that line the blood-brain barrier seem to be a very early event that is common between all types of dementia (including Alzheimer’s) and between type 2 diabetes and APOE-ε4.
Research is ongoing, and Dr. Patrick is at the forefront of that. However, there’s a practical take-away here meanwhile…
What can we do about it?
Dr. Patrick hypothesizes that if we can reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes, we may reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s with it.
Obviously, avoiding diabetes if possible is a good thing to do anyway, but if we’re aware of an added risk factor for Alzheimer’s, it becomes yet more important.
Of course, all the usual advices apply here, including a Mediterranean diet and regular moderate exercise.
Three other things Dr. Patrick specifically recommends (to reduce both type 2 diabetes risk and to reduce Alzheimer’s risk) include:
(links are to her blog, with lots of relevant science for each)
You can also hear more from Dr. Patrick personally, as a guest on Dr. Peter Attia’s podcast recently. She discusses these topics in much greater detail than we have room for in our newsletter:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Green Coffee Bean Extract: Coffee Benefits Without The Coffee?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Coffee is, on balance, very good for the health in moderation. We wrote about it here:
The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
Some quick facts before moving on:
- Coffee is the world’s biggest source of antioxidants
- 65% reduced risk of Alzheimer’s for coffee-drinkers
- 67% reduced risk of type 2 diabetes for coffee-drinkers
- 43% reduced risk of liver cancer for coffee-drinkers
- 53% reduced suicide risk for coffee-drinkers
Those are some compelling statistics!
But what about the caffeine content?
Assuming one doesn’t have a caffeine sensitivity, caffeine is also healthy in moderation—but it is easy to accidentally become dependent on it, so it can be good to take a “tolerance break” once in a while, and then reintroduce it with more modest moderation:
Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
We also, for that matter, have discussed its impact on the gut:
Coffee & Your Gut ← surprise, it’s a positive impact
What if I don’t like coffee?
We suspect that, having seen the title of this article, you know what the answer’s going to be here:
Green coffee bean extract is the extract from green (i.e. unroasted) coffee beans. It has one or two advantages over drinking coffee:
- For those who do not like drinking coffee, this supplement sidesteps that neatly
- Roasting coffee beans destroys a lot (sometimes almost all; it depends on the temperature and duration) of their chlorogenic acid, a highly beneficial polyphenol; using unroasted (i.e. green) coffee beans avoids that
See: Role of roasting conditions in the level of chlorogenic acid content in coffee beans
All about GCE and CGA
That’s “green coffee extract” and “chlorogenic acid”, respectively, bearing in mind that the latter is found generously in the former.
As to what it does:
❝CGA is an important and biologically active dietary polyphenol, playing several important and therapeutic roles such as antioxidant activity, antibacterial, hepatoprotective, cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, neuroprotective, anti-obesity, antiviral, anti-microbial, anti-hypertension, free radicals scavenger and a central nervous system (CNS) stimulator. Furthermore, CGA causes hepatoprotective effects.❞
👆 Those are the things we know for sure that it does. And it may do even more things:
❝In addition, it has been found that CGA could modulate lipid metabolism and glucose in both genetically and healthy metabolic related disorders. It is speculated that CGA can perform crucial roles in lipid and glucose metabolism regulation and thus help to treat many disorders such as hepatic steatosis, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity as well.❞
Read in full: Chlorogenic acid (CGA): A pharmacological review and call for further research
About lipid metabolism…
- Green coffee extract supplementation significantly reduces serum total cholesterol levels.
- Green coffee extract supplementation significantly reduces serum LDL (“bad” cholesterol) levels.
- Increases in HDL (“good” cholesterol) after green coffee bean extract consumption are significant in green coffee bean extract dosages ≥400mg/day.
About blood glucose and insulin…
- Green coffee extract supplementation significantly improved fasting blood sugar levels
- Green coffee extract supplementation at ≥400 mg/day significantly lowered postprandial insulin levels (that’s good)
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: