The Comfort Zone – by Kristen Butler
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are you sitting comfortably? Then we’ll begin. Funny, how being comfortable can be a good starting point, then we are advised “You have to get out of your comfort zone”.
And yet, when we think of our personal greatest moments in life, they were rarely uncomfortable moments. Why is that?
Kristen Butler wants us to resolve this paradox, with a reframe:
The comfort zone? That’s actually the “flow” zone.
Just as “slow and steady wins the race”, we can—like the proverbial tortoise—take our comfort with us as we go.
The discomfort zone? That’s the stress zone, the survival zone, the “putting out fires” zone. From the outside, it looks like we’re making a Herculean effort, and perhaps we are, but is it actually so much better than peaceful consistent productivity?
Butler writes in a way that will be relatable for many, and may be a welcome life-ring if you feel like you’ve been playing catch-up for a while.
Is she advocating for complacency, then? No, and she discusses this too. That “complacency zone” is really the “burnout zone” after being in the “survival zone” for too long.
She lays out for us, therefore, a guide for growing in comfort, expanding the comfort zone yes, but by securely pushing it from the inside, not by making a mad dash out and hoping it follows us.
Bottom line: if you’ve been (perhaps quietly) uncomfortable for a little too long for comfort, this book can reframe your approach to get you to a position of sustainable, stress-free growth.
Click here to check out The Comfort Zone, and start building yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is white rice bad for me? Can I make it lower GI or healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Rice is a culinary staple in Australia and around the world.
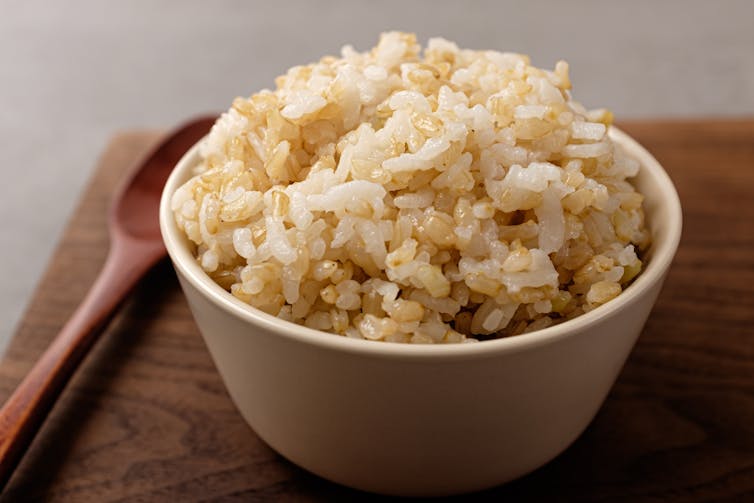
It might seem like a given that brown rice is healthier than white and official public health resources often recommend brown rice instead of white as a “healthy swap”.
But Australians definitely prefer white rice over brown. So, what’s the difference, and what do we need to know when choosing rice?
Dragne Marius/Unsplash What makes rice white or brown?
Rice “grains” are technically seeds. A complete, whole rice seed is called a “paddy”, which has multiple parts:
- the “hull” is the hard outer layer which protects the seed
- the “bran”, which is a softer protective layer containing the seed coat
- the “germ” or the embryo, which is the part of the seed that would develop into a new plant if was germinated
- the “endosperm”, which makes up most of the seed and is essentially the store of nutrients that feeds the developing plant as a seed grows into a plant.
Rice needs to be processed for humans to eat it.
Along with cleaning and drying, the hard hulls are removed since we can’t digest them. This is how brown rice is made, with the other three parts of the rice remaining intact. This means brown rice is regarded as a “wholegrain”.
White rice, however, is a “refined” grain, as it is further polished to remove the bran and germ, leaving just the endosperm. This is a mechanical and not a chemical process.
What’s the difference, nutritionally?
Keeping the bran and the germ means brown rice has more magnesium, phosphorus, potassium B vitamins (niacin, folate, riboflavin and pyridoxine), iron, zinc and fibre.
The germ and the bran also contain more bioactives (compounds in foods that aren’t essential nutrients but have health benefits), like oryzanols and phenolic compounds which have antioxidant effects.
Brown rice is cleaned and dried and the hard hulls are removed. Sung Min/Shutterstock But that doesn’t mean white rice is just empty calories. It still contains vitamins, minerals and some fibre, and is low in fat and salt, and is naturally gluten-free.
White and brown rice actually have similar amounts of calories (or kilojoules) and total carbohydrates.
There are studies that show eating more white rice is linked to a higher risk of type 2 diabetes. But it is difficult to know if this is down to the rice itself, or other related factors such as socioeconomic variables or other dietary patterns.
What about the glycaemic index?
The higher fibre means brown rice has a lower glycaemic index (GI), meaning it raises blood sugar levels more slowly. But this is highly variable between different rices within the white and brown categories.
The GI system uses low (less than 55), medium (55–70) and high (above 70) categories. Brown rices fall into the low and medium categories. White rices fall in the medium and high.
There are specific low-GI types available for both white and brown types. You can also lower the GI of rice by heating and then cooling it. This process converts some of the “available carbohydrates” into “resistant starch”, which then functions like dietary fibre.
Are there any benefits to white rice?
The taste and textural qualities of white and brown rices differ. White rice tends to have a softer texture and more mild or neutral flavour. Brown rice has a chewier texture and nuttier flavour.
So, while you can technically substitute brown rice into most recipes, the experience will be different. Or other ingredients may need to be added or changed to create the desired texture.
Removing more of the outer layers may also reduce the levels of contaminants such as pesticides.
We don’t just eat rice
You’ll likely have vegetables and protein with your rice. Chay_Tee/Shutterstock Comparing white and brown rice seems like an easy way to boost nutritional value. But just because one food (brown rice) is more nutrient-dense doesn’t make the other food (white rice) “bad”.
Ultimately, it’s not often that we eat just rice, so we don’t need the rice we choose to be the perfect one. Rice is typically the staple base of a more complex dish. So, it’s probably more important to think about what we eat with rice.
Adding vegetables and lean proteins to rice-based dishes can easily add the micronutrients, bioactives and fibre that white rice is comparatively lacking, and this can likely do more to contribute to diet quality than eating brown rice instead.
Emma Beckett, Adjunct Senior Lecturer, Nutrition, Dietetics & Food Innovation – School of Health Sciences, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Psychology Sunday: Family Estrangement & How To Fix It
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Estrangement, And How To Heal It
We’ve written before about how deleterious to the health loneliness and isolation can be, and what things can be done about it. Today, we’re tackling a related but different topic.
We recently had a request to write about…
❝Reconciliation of relationships in particular estrangement mother adult daughter❞
And, this is not only an interesting topic, but a very specific one that affects more people than is commonly realized!
In fact, a recent 800-person study found that more than 43% of people experienced family estrangement of one sort or another, and a more specific study of more than 2,000 mother-child pairs found that more than 11% of mothers were estranged from at least one adult child.
So, if you think of the ten or so houses nearest to you, probably at least one of them contains a parent estranged from at least one adult child. Maybe it’s yours. Either way, we hope this article will give you some pause for thought.
Which way around?
It makes a difference to the usefulness of this article whether any given reader experiencing estrangement is the parent or the adult child. We’re going to assume the reader is the parent. It also makes a difference who did the estranging. That’s usually the adult child.
So, we’re broadly going to write with that expectation.
Why does it happen?
When our kids are small, we as parents hold all the cards. It may not always feel that way, but we do. We control our kids’ environment, we influence their learning, we buy the food they eat and the clothes they wear. If they want to go somewhere, we probably have to take them. We can even set and enforce rules on a whim.
As they grow, so too does their independence, and it can be difficult for us as parents to relinquish control, but we’re going to have to at some point. Assuming we are good parents, we just hope we’ve prepared them well enough for the world.
Once they’ve flown the nest and are living their own adult lives, there’s an element of inversion. They used to be dependent on us; now, not only do they not need us (this is a feature not a bug! If we have been good parents, they will be strong without us, and in all likelihood one day, they’re going to have to be), but also…
We’re more likely to need them, now. Not just in the “oh if we have kids they can look after us when we’re old” sense, but in that their social lives are growing as ours are often shrinking, their family growing, while ours, well, it’s the same family but they’re the gatekeepers to that now.
If we have a good relationship, this goes fine. However, it might only take one big argument, one big transgression, or one “final straw”, when the adult child decides the parent is more trouble than they’re worth.
And, obviously, that’s going to hurt. But it’s pretty much how it pans out, according to studies:
Here be science: Tensions in the Parent and Adult Child Relationship: Links to Solidarity and Ambivalence
How to fix it, step one
First, figure out what went wrong.
Resist any urge to protect your own feelings with a defensive knee-jerk “I don’t know; I was a good, loving parent”. That’s a very natural and reasonable urge and you’re quite possibly correct, but it won’t help you here.
Something pushed them away. And, it will almost certainly have been a push factor from you, not a pull factor from whoever is in their life now. It’s easy to put the blame externally, but that won’t fix anything.
And, be honest with yourself; this isn’t a job interview where we have to present a strength dressed up as a “greatest weakness” for show.
You can start there, though! If you think “I was too loving”, then ok, how did you show that love? Could it have felt stifling to them? Controlling? Were you critical of their decisions?
It doesn’t matter who was right or wrong, or even whether or not their response was reasonable. It matters that you know what pushed them away.
How to fix it, step two
Take responsibility, and apologize. We’re going to assume that your estrangement is such that you can, at least, still get a letter to them, for example. Resist the urge to argue your case.
Here’s a very good format for an apology; please consider using this template:
The 10-step (!) apology that’s so good, you’ll want to make a note of it
You may have to do some soul-searching to find how you will avoid making the same mistake in the future, that you did in the past.
If you feel it’s something you “can’t change”, then you must decide what is more important to you. Only you can make that choice, but you cannot expect them to meet you halfway. They already made their choice. In the category of negotiation, they hold all the cards now.
How to fix it, step three
Now, just wait.
Maybe they will reply, forgiving you. If they do, celebrate!
Just be aware that once you reconnect is not the time to now get around to arguing your case from before. It will never be the time to get around to arguing your case from before. Let it go.
Nor should you try to exact any sort of apology from them for estranging you, or they will at best feel resentful, wonder if they made a mistake in reconnecting, and withdraw.
Instead, just enjoy what you have. Many people don’t get that.
If they reply with anger, maybe it will be a chance to reopen a dialogue. If so, family therapy could be an approach useful for all concerned, if they are willing. Chances are, you all have things that you’d all benefit from talking about in a calm, professional, moderated, neutral environment.
You might also benefit from a book we reviewed previously, “Parent Effectiveness Training”. This may seem like “shutting the stable door after the horse has bolted”, but in fact it’s a very good guide to relationship dynamics in general, and extensively covers relations between parents and adult children.
If they don’t reply, then, you did your part. Take solace in knowing that much.
Some final thoughts:
At the end of the day, as parents, our kids living well is (hopefully) testament to that we prepared them well for life, and sometimes, being a parent is a thankless task.
But, we (hopefully) didn’t become parents for the plaudits, after all.
Share This Post
-
Cucumber vs Lychee – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cucumber to lychee, we picked the lychee.
Why?
In terms of macros, the lychee has more carbs and more fiber, but both are low glycemic index foods. Functionally a tie, though we could consider it a nominal win for cucumber.
In the category of vitamins, cucumber has more of vitamins A, B1, B5, and K, while lychee has more of vitamins B2, B3, B6, B9, C, E, and choline. In particular, cucumber has a lot more vitamin K and lychee has a lot more vitamin C. Nevertheless, in terms of overall vitamin coverage, lychee is the clear winner here.
Looking at minerals, cucumber has more calcium, magnesium, manganese, and zinc, while lychee has more copper (especially rich in this), iron, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium. Another clear win for lychee.
Both have an abundance of anti-inflammatory polyphenols, but we could find no strong argument for one being better than the other in this category, just different.
In short, both are fine options, but the more nutritionally dense is the lychee, so that’s our choice!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Cucumber Extract Beats Glucosamine & Chondroitin… At 1/135th Of The Dose?!
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Exercising With Less Soreness!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
An Ancient Sports Drink & Healing Potion, Now With Modern Science?
Ginseng has many health benefits, we talked about 8 of them in this previous edition of 10almonds:
…but we’ve somehow never yet done a Monday’s Research Review for it! We must do one, one of these days. For now though, it’s Saturday’s Life Hacks, and we’re here with…
Speeding up recovery after muscle damage
We talked about this topic before too:
Overdone It? How To Speed Up Recovery After Exercise
…which gives very good advice (including some supplements that help), but was published before the latest science that we’re going to talk about today:
A team of researchers all so very recently found that ginseng also reduces muscular fatigue and, importantly, hastens recovery of muscle damage caused by exercise.
And that’s not all…
❝It should also be noted that, by reducing fatigue, taking ginseng on a regular basis may also help reduce the risk of injury, particularly in the case of muscles or ligaments, which can in turn improve athletic performance.❞
This means that it can be taken regularly and prophylactically, as they found:
❝taking ginseng systematically for a long time can mitigate the response of the biological markers, mainly creatine kinase (CK) and interleukin 6 (IL-6), responsible for exercise-induced muscle damage and inflammation.❞
You may be thinking “isn’t creatine good?” and yes, yes it is:
Creatine: Very Different For Young & Old People
…however, creatine kinase is not creatine. Creatine kinase (CK) is an enzyme that affects the creatine (to put it in few words, without getting into the fascinating biochemistry of this). Now, it’s necessary for us to have some CK (or else we wouldn’t be able to do what we need to with the creatine), but elevated levels often indicate some sort of problem going on:
Approach to asymptomatic creatine kinase elevation
…so ginseng keeping those things balanced is a good thing.
The study
We’ve talked a lot about the findings and what they mean, but if you’d like to read the paper for yourself, you can read it here:
Effect of Ginseng Intake on Muscle Damage Induced by Exercise in Healthy Adults
Where to get ginseng
If you’d like to take ginseng as a supplement, then there are many ways to do so, with the most common being capsules or ginseng tea, which has an interesting and distinctive taste, and is very refreshing. Here are examples on Amazon, for your convenience:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Toothpastes and mouthwashes: which kinds help, and which kinds harm?
You almost certainly brush your teeth. You might use mouthwash. A lot of people floss for three weeks at a time, often in January.
There are a lot of options for oral hygiene; variations of the above, and many alternatives too. This is a big topic, so rather than try to squeeze it all in one, this will be a several-part series.
For today, let’s look at toothpastes and mouthwashes, to start!
Toothpaste options
Toothpastes may contain one, some, or all of the following, so here are some notes on those:
Fluoride
Most toothpastes contain fluoride; this is generally recognized as safe though is not without its controversies. The fluoride content is the reason it’s recommended not to swallow toothpaste, though.
The fluoride in toothpaste can cause some small problems if overused; if you see unusually white patches on your teeth (your teeth are supposed to be ivory-colored, not truly white), that is probably a case of localized overcalcification because of the fluoride, and yes, you can have too much of a good thing.
Overall, the benefits are considered to far outweigh the risks, though.
Baking soda
Whether by itself or as part of a toothpaste, baking soda is a safe and effective choice, not just for cosmetic purposes, but for boosting genuine oral hygiene too:
- Enhanced plaque removal to improve gingival health: 3-month randomized clinical study of the effects of baking soda toothpaste on plaque and gingivitis
- The effects of two baking-soda toothpastes in enhancing mechanical plaque removal and improving gingival health: A 6-month randomized clinical study
- The efficacy of baking soda dentifrice in controlling plaque and gingivitis: A systematic review
Activated charcoal
Activated charcoal is great at removing many chemicals from things it touches. That includes the kind you might see on your teeth in the form of stains.
A topical aside on safety: activated charcoal is a common ingredient in a lot of black-colored Halloween-themed foods and drinks around this time of year. Beware, if you ingest these, there’s a good chance of it also cleaning out any meds you are taking. Ask your pharmacist about your own personal meds, but meds that (ingested) activated charcoal will usually remove include:
- Oral HRT / contraceptives
- Antidepressants (many kinds)
- Heart medications (at least several major kinds)
Toothpaste, assuming you are spitting-not-swallowing, won’t remove your medications though. Nor, in case you were worrying, will it strip tooth enamel, even if you have extant tooth enamel erosion:
Source: Activated charcoal toothpastes do not increase erosive tooth wear
However, it’s of no special extra help when it comes to oral hygiene itself, just removing stains.
So, if you’d like to use it for cosmetic reasons, go right ahead. If not, no need.
Hydrogen peroxide
This is generally not a good idea, speaking for the health. For whitening, yes, it works. But for health, not so much:
To be clear, when they say “alter”, they mean “in a bad way”. It increases inflammation and tissue damage.
If buying commercially-available whitening toothpaste made with hydrogen peroxide, the academic answer is that it’s a lottery, because brands’ proprietorial compounding processes vary widely and constantly with little oversight and even less transparency:
Is whitening toothpaste safe for dental health?: RDA-PE method
Mouthwash options
In the case of fluoride and hydrogen peroxide, the same advice (for and against) goes as per toothpaste.
Alcohol
There has been some concern about the potential carcinogenic effect of alcohol-based mouthwashes. According to the best current science, this one’s not an easy yes-or-no, but rather:
- If there are no other cancer risk factors, it does not seem to increase cancer risk
- If there are other cancer risk factors, it does make the risk worse
Read more:
- Does the use of alcohol mouthwash increase the risk of developing oral cancer?
- Alcohol-based mouthwash as a risk factor of oral cancer: A systematic review
Non-Alcohol
Non-alcoholic mouthwashes are not without their concerns either. In this case, the potential problem is changing the oral microbiome (we are supposed to have one!), and specifically, that the spread of what it kills and what it doesn’t may result in an imbalance that causes a lowering of the pH of the mouth.
Put differently: it makes your saliva more acidic.
Needless to say, that can cause its own problems for teeth. The research on this is still emerging, with regard to whether the benefits outweigh the problems, but the fact that it has this effect seems to be a consensus. Here’s an example paper; there are others:
Effects of Chlorhexidine mouthwash on the oral microbiome
Flossing, scraping, and alternatives
These are important (and varied, and interesting) enough to merit their own main feature, rather than squeezing them in at the end.
So, watch this space for a main feature on these soon!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Nori vs Wakame – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing nori to wakame, we picked the nori.
Why?
It was close, and both of these seaweed options are great!
In terms of macros, nori has more protein while wakame has more carbs; they’re about equal on fiber. While the difference in protein and carbs isn’t big, out of the two we’ll prioritize protein, and thus say nori gets a notional win here—but as it’s so close, one could just as easily call it a tie.
In the category of vitamins both are very rich in many minerals, but nori has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, B12*, and C, while wakame has more of vitamins B5, B9, K, and choline. Thus, a 6:4 victory for nori.
*Yes, nori is one of those rare vegan foods that naturally contain vitamin B12; it’s because of the composition of the algae that this seaweed is made of, which includes some beneficial B12-making bacteria. Meanwhile, wakame is “just” a kelp, so it doesn’t have B12.
When it comes to minerals, nori has more potassium and zinc, while wakame has more calcium and magnesium. They’re equal on other minerals, except: it’s worth noting that wakame is moderately high in sodium, while nori has very little sodium. So, either a tie-breaking win for nori, or just a tie.
Adding up the sections gives nori the overall win; it’s only the margin of the win that’s reasonably debatable. Still, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- A Deeper Dive Into Seaweed
- Spirulina vs Nori – Which is Healthier? ← guess which won!
- 21% Stronger Bones in a Year at 62? Yes, It’s Possible (No Calcium Supplements Needed!) ← nori and wakame both feature (very favorably) in this case study
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: