Water Fluoridation, Atheroma, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝I watched a documentary recently on Fluoride in our drinking water & the dangers of it. Why are we poisoning our water?❞
This is a great question, and it certainly is controversial. It sounds like the documentary you watched was predominantly or entirely negative, but there’s a lot of science to back both sides of this, and it’s not even that the science is contradictory (it’s not). It’s that what differs is people’s opinions about whether benefiting one thing is worth creating a risk to another, and that means looking at:
- What is the risk associated with taking no action (error of omission)?
- What is the risk associated with taking an action (error of commission)?
The whole topic is worth a main feature, but to summarize a few key points:
- Water fluoridation is considered good for the prevention of dental cavities
- Water fluoridation aims to deliver fluoride and doses far below dangerous levels
- This requires working on consumer averages, though
- ”Where do we put the safety margins?” is to some extent a subjective question, in terms of trading off one aspect of health for another
- Too much fluoride can also be bad for the teeth (at least cosmetically, creating little white* spots)
- Detractors of fluoride tend to mostly be worried about neurological harm
- However, the doses in public water supplies are almost certainly far below the levels required to cause this harm.
- That said, again this is working on consumer averages, though.
- However, the doses in public water supplies are almost certainly far below the levels required to cause this harm.
- A good guide is: watch your teeth! Those white* spots will be “the canary in the coal mine” of more serious harm that could potentially come from higher levels due to overconsumption of fluorine.
*Teeth are not supposed to be pure white. The “Hollywood smile” is a lie. Teeth are supposed to be a slightly off-white, ivory color. Anything whiter than that is adding something else that shouldn’t be there, or stripping something off that should be there.
❝How does your diet change clean out your arteries of the bad cholesterol?❞
There’s good news and bad news here, and they can both be delivered with a one-word reply:
Slowly.
Or rather: what’s being cleaned out is mostly not the LDL (bad) cholesterol, but rather, the result of that.
When our diet is bad for cardiovascular health, our arteries get fatty deposits on their walls. Cholesterol gets stuck here too, but that’s not the main physical problem.
Our body’s natural defenses come into action and try to clean it up, but they (for example macrophages, a kind of white blood cell that consumes invaders and then dies, before being recycled by the next part of the system) often get stuck and become part of the buildup (called atheroma), which can lead to atherosclerosis and (if calcium levels are high) hardening of the arteries, which is the worst end of this.
This can then require medical attention, precisely because the body can’t remove it very well—especially if you are still maintaining a heart-unhealthy diet, thus continuing to add to the mess.
However, if it is not too bad yet, yes, a dietary change alone will reverse this process. Without new material being added to the arterial walls, the body’s continual process of rejuvenation will eventually fix it, given time (free from things making it worse) and resources.
In fact, your arteries can be one of the quickest places for your body to make something better or worse, because the blood is the means by which the body moves most things (good or bad) around the body.
All the more reason to take extra care of it, since everything else depends on it!
You might also like our previous main feature:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healing Back Pain – by Dr. John Sarno
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Often when we review books with titles like this one, we preface it with a “what it’s not: a think-yourself-better book”.
In this case… It is, in fact, a think-yourself-better book. However, its many essay-length rave reviews caught our attention, and upon reading, we can report: its ideas are worth reading.
The focus of this book is on TMS, or “Tension Myoneural Syndrome”, to give it its full name. The author asserts (we cannot comment on the accuracy) that many cases of TMS are misdiagnosed as other things, from sciatica to lupus. When other treatments fail, or are simply not available (no cure for lupus yet, for example) or are unenticing (risky surgeries, for example), he offers an alternative approach.
Dr. Sarno lays out the case for TMS being internally fixable, since our muscles and nerves are all at the command of our brain. Rather than taking a physical-first approach, he takes a psychological-first approach, before building into a more holistic model.
The writing style is… A little dated and salesey and unnecessarily padded, to be honest, but the content makes it worthwhile.
Bottom line: if you have back pain, then the advice of this book, priced not much more than a box of top brand painkillers, seems a very reasonable thing to try.
Click here to check out Healing Back Pain, and see if it works for you!
Share This Post
-
The Keys to Good Mental Wellbeing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Nine Keys To Good Mental Wellbeing
Today’s main feature is a bit “pop psychology”, but it has its underpinnings in actual psychology, and is especially useful if approached from that angle.
What it’s most popularly enjoyed as:
- A personality-typing system.
- People love little quizzes and identifiers and such.
What it’s actually really useful as:
- A tool for understanding why people (including ourselves) are the way we are
- A foundational knowledge for living better ourselves, and helping others too
This stems from the fairly simple principle, uncontroversial in psychology:
- We have needs, desires, and aversions
- We act in a way that tries to get our needs met and avoid suffering
- Thus: Need/Fear → Motivation → Action
The Enneagram
The Enneagram (ἐννέα = “nine” in Ancient Greek) system posits that we each have one fundamental need/fear (from a list of nine) that’s strongest for us. A deep-seated insecurity/longing, that we’ll go to almost any lengths to try to meet. Sometimes, in good ways, sometimes, bad.
The Nine Basic Fears/Insecurities, And Their Corresponding Needs/Desires:
- Fear of being a fundamentally bad, wrong person / Need to be good and correct
- Fear of being fundamentally unloveable / Need to be loved
- Fear of being fundamentally worthless / Need to be valued
- Fear of being like everyone else / Need to be different
- Fear of being useless / Need to be useful
- Fear of being outcast / Need to have a set place in the group
- Fear of missing out / Need to experience things
- Fear of being hurt or controlled / Need to be in control
- Fear of conflict / Need to be at peace
Of course, most of us have most of these fears/needs to some extent, though usually one will stand out—especially if we aren’t managing it well. The less healthy our coping mechanisms, the more obvious it is how we’re trying to overcompensate in some fashion. For example:
- A person who fears being wrong and so becomes a perfectionist rules-abider to a fault
- A person who fears being unloveable, and so exaggerates problems to get pity, as the next best thing
- A person who fears being worthless, and so exaggerates their accomplishments in order to be admired and valued
- A person who fears being like everyone else, and so descends into a “nobody could ever possibly understand me” black hole of pathos.
- A person who fears being useless, so burns themself out trying to be an omnicompetent Leonardo da Vinci without ever actually taking the time to stop and smell the flowers as Leonardo did.
- A person who fears being outcast, so becomes clingy, passive-aggressive, and suspicious
- A person who fears missing out, so tries to experience all the things all the time, ruining their health with dizzying highs and crushing lows.
- A person who fears being hurt or controlled, so becomes aggressive and domineering
- A person who fears conflict, so shuts down at the slightest hint of it
If we have healthier coping mechanisms, these same nine people can look a lot different, but in much more subtle ways because we’re not trying to overcompensate so badly:
- A person who lives their life rationally by principles that can be adapted as they learn
- A person who loves and is loved, as perhaps the most notable part of their character
- A person who sets reasonable goals and accomplishes them, and seeks to uplift others
- A person who creates and innovates, enriching their own life and the lives of others
- A person who is simply very competent and knowledgeable, without overstretching
- A person who is dependable and loyal, and a reliable part of something bigger than themself
- A person who is fun to be around and loves trying new things, while also knowing how to relax
- A person who develops their leadership skills and is a tower of strength for others
- A person who knows how to make peace and does so—by themself, and with others
By being aware of our own fears/insecurities that may drive our motivations and thus underpin our behaviors, we can usually manage them in a much more mindful fashion. Same goes when it comes to managing interactions with other people, too:
- Letting the Type 3 know you value them, not their accomplishments or what they can do for you.
- Appreciating the Type 5’s (varied or specialist) skills and knowledge.
- Giving love to a Type 2 unprompted, but on your own terms, with your own boundaries.
- And so on for other types
Or for yourself…
- As a Type 8, remembering that you can let go sometimes and let someone else be in charge.
- As a Type 1, catching yourself holding yourself (or others) to impossible standards, and then easing up on that a little.
- As a Type 9, remembering to stand up for yourself and others, however gently, but firmly.
- And so on for other types
If you’re unsure what to focus on, ask yourself: what’s your worst nightmare or greatest daydream? Then work out what it is about that, that makes it feel so bad or good.
Then, approach things mindfully. Catch yourself in your unhealthy coping mechanisms, and find healthy ones instead.
What if I get my type wrong? Or I get someone else’s type wrong?
Obviously it’s better to get them right for maximum effect, but you can never go too far wrong anyway… because we all have all nine of those qualities in us, it’s just a matter of how strong a factor each is for us. So in the worst case scenario, you’ll make someone feel more secure about something that was only a very minor insecurity for them, for example.
Or in the case of your own type, you may mistakenly think you’re acing being the world’s healthiest Type 5, until you realize you’re actually a Type 3 who thought learning all those things would make you more worthy (spoiler: those things are great, but you’re worthy already). Again, not the end of the world! No matter what, you’re learning and growing, and that’s good.
Want to delve further?
Read: The Nine Enneagram Type Descriptions (Basic, but more detailed descriptions than the above)
Read: How The Enneagram System Works (More complex. Now we’re getting into the more arcane stuff we didn’t have time for today—wings and lines, triads, health levels, directions of integration and disintegration, and more)
Like learning from books? Here are our top two picks, depending on your learning style:
- The Wisdom of the Enneagram – Very comprehensive textbook and guide to improving your coping mechanism and growing as a person.
- The Enneagram Made Easy – it explains it with cartoons!
We’d love to offer a quick free test here, but all the tests we could find either require paid registration or are wildly inaccurate, so we’ll not waste your time.
However, we do also think that working it out for yourself is better, as it means you have a handle on what those ideas, fears, insecurities, desires, needs, really mean to you—that way you can actually use the information!
We’ll close by repeating our previous advice: If you’re unsure what to focus on, ask yourself: what’s your worst nightmare or greatest daydream? Then work out what it is about those scenarios that make them so bad or good. That’ll help you find your real fears/needs, such that you can work on them.
Good luck!
Share This Post
-
Age Proof – by Dr. Rose Anne Kenny
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We don’t generally include an author bio, but in this case it’s worth noting that Dr. Kenny, the Chair of Medical Gerontology at Trinity College Dublin, with over 300 staff under her, has 704 peer-reviewed publications to her name, and enough awards and honors and achievements to more than fill a page on her university’s website.
In short, she knows her stuff.
A lot of the material in this book will not be completely new to regular 10almonds readers; there’s a lot about Blue Zones supercentenarians, the usual qualities associated with healthy longevity in those places (diet, lifestyle, etc), as well as genetic factors and epigenetic, and so forth.
Some items are… Not new, but not so commonly focused on in such works; for example, Dr. Kenny devotes a chapter to sleep, a chapter to laughter, a chapter to hormesis, and a chapter to sexual activity, amongst others.
Another thing she delivers that a lot of books of this kind don’t is that she has a collection of “Test Yourself” appendices, so that you can establish where you are relative to various benchmarks of aging.
Dr. Kenny also references her own work especially with TILDA (The Irish Longitudinal Study on Aging) that she has directed for many years, which has a vast amount of data and many important findings, which adds another extra strength to this book often not found in others.
The style is surprisingly personal, making it an enjoyable read as well as an educational one, and yet with a lot of hard science throughout—explained well for the layperson though, and thoroughly referenced with an extensive bibliography.
Bottom line: if you’d like to be (and continue to be!) “young for your years”, then this is an excellent book to get (and/or keep) you on the right track.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How Does Alcohol Cause Blackouts?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sometimes people who have never experienced an alcoholic blackout wonder “is it real, or is it just a convenient excuse to avoid responsibility/embarrassment with regard to things done while drunk?”
In 1969 (so, still in the era of incredibly unethical psychological experiments that ranged from the 50s into the 70s), Dr. Donald Goodwin conducted a study in which intoxicated participants were asked to recall an object they had just seen. Most succeeded initially, but half were unable to remember the object just 30 minutes later, demonstrating alcohol-induced memory blackouts.
But, is it any different from regular forgetting? And the answer is: yes, it is indeed different.
The memories that never got stored
Ethanol, the active compound in alcohol, is lipophilic, enabling it to cross the blood-brain barrier and disrupt brain function. It impairs all kinds of things, including decision-making, impulse control, motor skills, and, notably, memory networks—which is what we’re looking at today.
Memory formation (beyond “working memory”, which is the kind that enables you to have an idea of what you were just doing, and carry out simple plans like “pick up this cup, raise it to my mouth, and take a sip”, without forgetting partway through) relies on a process called long-term potentiation (LTP), which strengthens neural connections to store information. Ethanol disrupts this process, preventing memory storage and causing blackouts.
In effect, this means you didn’t just forget a memory; you never stored it in the first place. For this reason, experiences from during an alcoholic blackout cannot be retrieved in the same ways we might retrieve other memories (e.g. in regular forgetting, it’s possible that a context clue jogs our memory and then we remember the experience—because in regular forgetting, the memory was in there; we just didn’t recall it until we were reminded).
Blackouts (in which the memory is never stored in the first place) typically occur when blood alcohol concentration (BAC) exceeds 0.16, while lower levels can result in partial memory loss (brownouts) in which some things may be recalled, but not others. Factors such as dehydration, genetics, medications, food consumption, and age influence the likelihood of complete blackouts.
While alcohol’s residual effects typically subside within a day, repeated over-drinking can cause permanent neuron damage, as well as of course plenty of damage to other organs in the body (especially the liver and gut).
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
What Happens To Your Body When You Stop Drinking Alcohol
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Chocolate & Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chocolate & Health: Fact or Fiction?
“Chocolate Is Good For The Heart”
“When making chocolate chip cookies, you don’t measure using cups, you measure by heart”
…but how good is chocolate when it comes to heart health?
First, what is heart health?
A healthy heart typically has a low resting pulse rate and a strong, steady beat. This is affected strongly by exercise habits, and diet plays only a support role (can’t exercise without energy from food!).
It is also important to have blood pressure within a healthy range (with high blood pressure being a more common problem than low, so things that lower blood pressure are generally considered good).
- Flavanols, flavonoids, and polyphenols in chocolate contribute to lower blood pressure
- Dark chocolate is best for these, as milk chocolate contains much less cocoa solids and more unhelpful fats
- White chocolate contains no cocoa solids and is useless for this
- Some of the fats in most commercial chocolate can contribute to atherosclerosis which raises blood pressure and ultimately can cause heart attacks.
- If you’re diabetic, you will probably not get the usual heart-related benefits from chocolate (sorry)
The Verdict: dark chocolate, in moderation, can support good heart health.
“Chocolate Is Good For The Brain”
Chocolate has been considered a “brain food”… why?
- The brain uses more calories than any other organ (chocolate has many calories)
- The heart benefits we listed above mean improved blood flow—including to your brain
- Chocolate contains phenylethylamine, a powerful chemical that has a similar effect to amphetamines… But it’s metabolized in digestion and never makes it to the central nervous system (so basically, this one’s a miss; we had a good run with the other two, though!)
The Verdict: dark chocolate, in moderation, can support good brain health
“Chocolate Is An Aphrodisiac”
“If chocolate be the food of love, pass me that cocoa; I’m starving”
Most excitingly, chocolate contains phenylethylamine, the “molecule of love” or, more accurately, lust. It has an effect similar to amphetamines, and while we can synthesize it in the body, we can also get it from certain foods. But…
Our body is so keen to get it that most of it is metabolized directly during digestion and doesn’t make it to the brain. Also, chocolate is not as good a source as cabbage—do with that information what you will!
However!
Chocolate contains theobromine and small amounts of caffeine, both stimulants and both generally likely to improve mood; it also contains flavonoids which in turn stimulate production of nitric oxide, which is a relaxant. All in all, things that are convivial to having a good time.
On the other hand…
That relaxation comes specifically with a reduction in blood pressure—something typically considered good for the health for most people most of the time… but that means lowering blood pressure in all parts of your body, which could be the opposite of what you want in intimate moments.
Chocolate also contains zinc, which is essential for hormonal health for most people—the body uses it to produce testosterone and estrogen, respectively. Zinc supplements are popularly sold to those wishing to have more energy in general and good hormonal health in particular, and rightly so. However…
This approach requires long-term supplementation—you can’t just pop a zinc tablet / bar of chocolate / almond before bed and expect immediate results. And if your daily zinc supplementation takes the form of a 3.5oz (100g) bar of chocolate, then you may find it has more effects on your health, and not all of them good!
The Verdict: dark chocolate, in moderation, may promote “the mood”, but could be a double-edged sword when it comes to “the ability”.
“Chocolate Is Good During Menstruation”
The popular wisdom goes that chocolate is rich in iron (of which more is needed during menstruation), and indeed, if you eat 7oz (150g) of dark chocolate made with 85% cocoa, you’ll get a daily a dose of iron (…and nearly 1,000 calories).
More bang-for-buck dietary sources of iron include chickpeas and broccoli, but for some mysterious reason, these are not as commonly reported as popular cravings.
The real explanation for chocolate cravings is more likely that eating chocolate—a food high in sugar and fat along with a chemical bombardment of more specialized “hey, it’s OK, you can relax now” molecules (flavanols/flavonoids, polyphenols, phenylamines, even phenylethylamine, etc) gives a simultaneous dopamine kick (the body’s main “reward” chemical) with a whole-body physiological relaxation… so, little wonder we might crave it in times of stress and discomfort!
The Verdict: it helps, not because it serves a special nutritional purpose, but rather, because the experience of eating chocolate makes us feel good.
Fun fact: Tiramisu (this writer’s favorite dessert) is literally Italian for “pick-me-up”
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
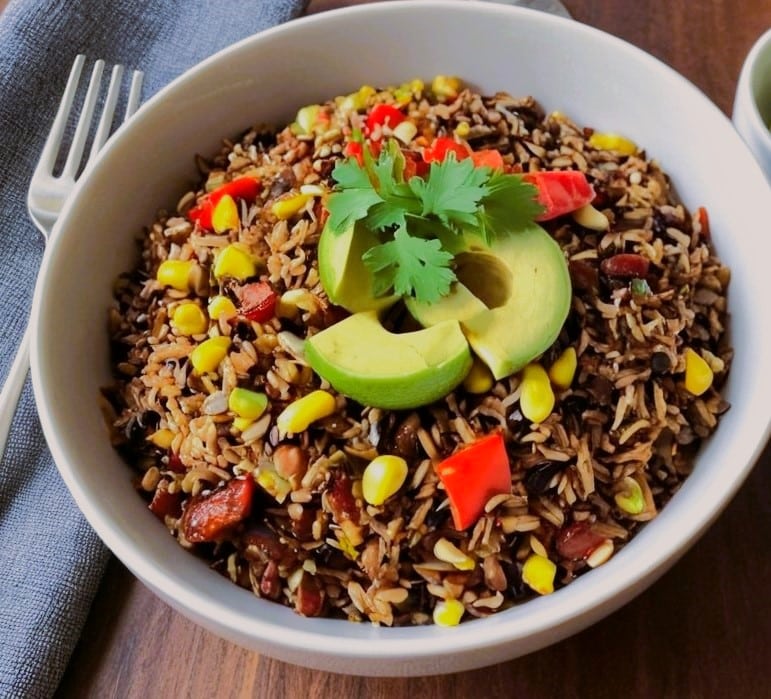
Chipotle Chili Wild Rice
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a very gut-healthy recipe that’s also tasty and filling, and packed with polyphenols too. What’s not to love?
You will need
- 1 cup cooked wild rice (we suggest cooking it with 1 tbsp chia seeds added)
- 7 oz cooked sweetcorn (can be from a tin or from frozen or cook it yourself)
- 4 oz charred jarred red peppers (these actually benefit from being from a jar—you can use fresh or frozen if necessary, but only jarred will give you the extra gut-healthy benefits from fermentation)
- 1 avocado, pitted, peeled, and cut into small chunks
- ½ red onion, thinly sliced
- 6–8 sun-dried tomatoes, chopped
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 2 tsp chipotle chili paste (adjust per your heat preferences)
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Juice of 1 lime
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Mix the cooked rice, red onion, sweetcorn, red peppers, avocado pieces, and sun-dried tomato, in a bowl. We recommend to do it gently, or you will end up with guacamole in there.
2) Mix the olive oil, lime juice, chipotle chili paste, black pepper, and MSG/salt, in another bowl. If perchance you have a conveniently small whisk, now is the time to use it. Failing that, a fork will suffice.
3) Add the contents of the second bowl to the first, tossing gently but thoroughly to combine well, and serve.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Brown Rice vs Wild Rice – Which is Healthier?
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: