Test For Whether You Will Be Able To Achieve The Splits
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some people stretch for years without being able to do the splits; others do it easily after a short while. Are there people for whom it is impossible, and is there a way to know in advance whether our efforts will be fruitful? Liv (of “LivInLeggings” fame) has the answer:
One side of the story
There are several factors that affect whether we can do the splits, including:
- arrangement of the joint itself
- length of tendons and muscles
- “stretchiness” of tendons and muscles
The latter two things, we can readily train to improve. Yes, even the basic length can be changed over time, because the body adapts.
The former thing, however (arrangement of the joint itself) is near-impossible, because skeletal changes happen more slowly than any other changes in the body. In a battle of muscle vs bone, muscle will always win eventually, and even the bone itself can be rebuilt (as the body fixes itself, or in the case of some diseases, messes itself up). However, changing the arrangement of your joint itself is far beyond the auspices of “do some stretches each day”. So, for practical purposes, without making it the single most important thing in your life, it’s impossible.
How do we know if the arrangement of our hip joint will accommodate the splits? We can test it, one side at a time. Liv uses the middle splits, also called the side splits or box splits, as an example, but the same science and the same method goes for the front splits.
Stand next to a stable elevated-to-hip-height surface. You want to be able to raise your near-side leg laterally, and rest it on the surface, such that your raised leg is now perfectly perpendicular to your body.
There’s a catch: not only do you need to still be stood straight while your leg is elevated 90° to the side, but also, your hips still need to remain parallel to the floor—not tilted up to one side.
If you can do this (on both sides, even if not both simultaneously right now), then your hip joint itself definitely has the range of motion to allow you to do the side splits; you just need to work up to it. Technically, you could do it right now: if you can do this on both sides, then since there’s no tendon or similar running between your two legs to make it impossible to do both at once, you could do that. But, without training, your nerves will stop you; it’s an in-built self-defense mechanism that’s just firing unnecessarily in this case, and needs training to get past.
If you can’t do this, then there are two main possibilities:
- Your joint is not arranged in a way that facilitates this range of motion, and you will not achieve this without devoting your life to it and still taking a very long time.
- Your tendons and muscles are simply too tight at the moment to allow you even the half-split, so you are getting a false negative.
This means that, despite the slightly clickbaity title on YouTube, this test cannot actually confirm that you can never do the middle splits; it can only confirm that you can. In other words, this test gives two possible results:
- “Yes, you can do it!”
- “We don’t know whether you can do it”
For more on the anatomy of this plus a visual demonstration of the test, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Stretching Scientifically – by Thomas Kurz ← this is our review of the book she’s working from in this video; this book has this test!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Circadian Rhythm: Far More Than Most People Know
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Circadian Rhythm: Far More Than Most People Know
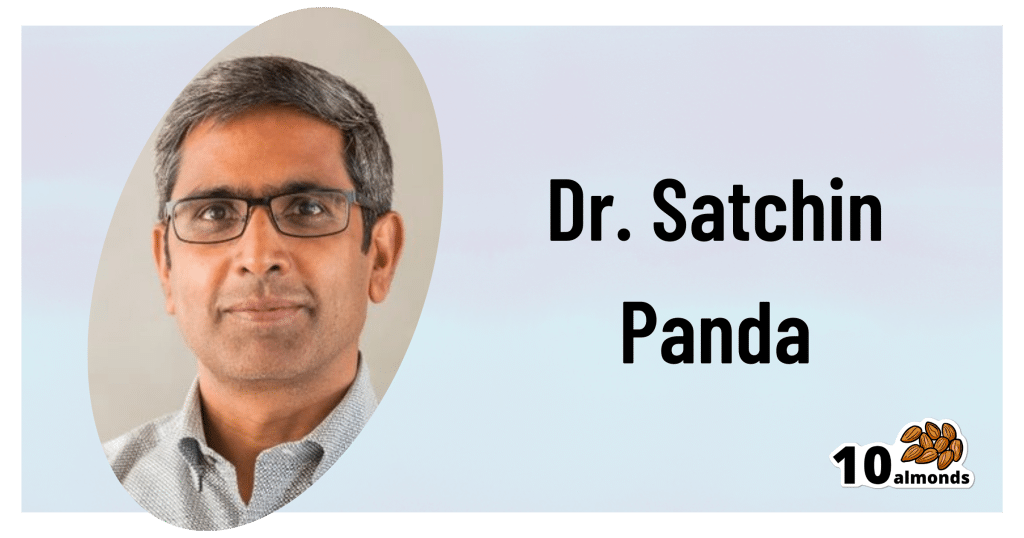
This is Dr. Satchidananda (Satchin) Panda, the scientist behind the discovery of the blue-light sensing cell type in the retina, and the many things it affects. But, he’s discovered more…
First, what you probably know (with a little more science)
Dr. Panda discovered that melanopsin, a photopigment, is “the primary candidate for photoreceptor-mediated entrainment”.
To put that in lay terms, it’s the brain’s go-to for knowing approximately what time of day or night it is, according to how much light there is (or isn’t), and how long it has (or hasn’t) been there.
But… the brain’s “go-to” isn’t the only method. By creating mice without melanopsin, he was able to find that they still keep a circadian rhythm, even in complete darkness:
Melanopsin (Opn4) Requirement for Normal Light-Induced Circadian Phase Shifting
In other words, it was a helpful, but not completely necessary, means of keeping a circadian rhythm.
So… What else is going on?
Dr. Panda and his team did a lot of science that is well beyond the scope of this main feature, but to give you an idea:
- With jargon: it explored the mechanisms and transcription translation negative feedback loops that regulate chronobiological processes, such as a histone lysine demathlyase 1a (JARID1a) that enhances Clock-Bmal1 transcription, and then used assorted genomic techniques to develop a model for how JARID1a works to moderate the level of Per transcription by regulating the transition between its repression and activation, and discovered that this heavily centered on hepatic gluconeogenesis and glucose homeostasis, facilitated by the protein cryptochrome regulating the fasting signal that occurs when glucagon binds to a G-protein coupled receptor, triggering CREB activation.
- Without jargon: a special protein tells our body how to respond to eating/fasting at different times of day—and conversely, certain physiological responses triggered by eating/fasting help us know what time of day it is.
- Simplest: our body keeps on its best cycle if we eat at the same time every day
This is important, because our circadian rhythm matters for a lot more than sleeping/waking! Take hormones, for example:
- Obvious hormones: testosterone and estrogen peak in the mornings around 9am, progesterone peaks between 10pm and 2am
- Forgotten hormones: cortisol peaks in the morning around 8:30am, melatonin peaks between 10pm and 2am
- More hormones: ghrelin (hunger hormone) peaks around 10am, leptin (satiety hormone) peaks 20 minutes after eating a certain amount of satiety-triggering food (protein does this most quickly), insulin is heavily tied to carbohydrate intake, but will still peak and trough according to when the body expects food.
What does this mean for us in practical terms?
For a start, it means that intermittent fasting can help guard against metabolic and related diseases (including inflammation, and thus also cancer, diabetes, arthritis, and more) a lot more if we practice it with our circadian rhythm in mind.
So that “8-hour window” for eating, that many intermittent fasting practitioners adhere to, is going to do much, much better if it’s 10am to 6pm, rather than, say, 4pm to midnight.
Additionally, Dr. Panda and his team found that a 12-hour eating window wasn’t sufficient to help significantly.
Some other take-aways:
- For reasons beyond the scope of this article, it’s good to exercise a) early b) before eating, so getting in some exercise between 8.30am and 10am is ideal
- It also means it’s beneficial to “front-load” eating, so a large breakfast at 10am, and smaller meals/snacks afterwards, is best.
- It also means that getting sunlight (even if cloud-covered) around 8.30am helps guard against metabolic disorders a lot, since the light remains the body’s go-to way of knowing the time.
- We realize that sunlight is not available at 8.30am at all latitudes at all times of year. Artificial is next-best.
- It also means sexual desire will typically peak in men in the mornings (per testosterone) and women in the evenings (per progesterone), but this is just an interesting bit of trivia, and not so relevant to metabolic health
What to do next…
Want to stabilize your own circadian rhythm in the best way, and also help Dr. Panda with his research?
His team’s (free!) app, “My Circadian Clock”, can help you track and organize all of the body’s measurable-by-you circadian events, and, if you give permission, will contribute to what will be the largest-yet human study into the topics covered today, to refine the conclusions and learn more about what works best.
Share This Post
-
Nine Pints – by Rose George
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Rose George is not a scientist, but an investigative journalist. As such, she’s a leave-no-stone-unturned researcher, and that shows here.
The style throughout is, as one might expect, journalistic. But, she’s unafraid of diving into the science of it, interviewing many medical professionals as part of her work. She also looks to people living with various blood-related conditions, ranging from hemophilia to HIV.
Speakling of highly-stigmatized yet very manageable conditions, there’s also a fair section devoted to menstruation, menstrual blood, and societies’ responses to such, from shunning to active support.
We also learn about the industrialization of blood—from blood banks to plasma labs to leech farms. You probably knew leeches are still used as a medical tool in even the most high-tech of hospitals, but you’ll doubtlessly learn a fascinating thing or two from the “insider views” along the way.
Bottom line: if you’d like to know more about the red stuff in all its marvelous aspects, with neither sensationalization nor sanitization (the topic needs neither!), this is the book for you.
Click here to check out Nine Pints, and learn more about yours!
Share This Post
-
What You Should Have Been Told About The Menopause Beforehand
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What You Should Have Been Told About Menopause Beforehand
This is Dr. Jen Gunter. She’s a gynecologist, specializing in chronic pain and vulvovaginal disorders. She’s also a woman on a mission to demystify things that popular culture, especially in the US, would rather not talk about.
When was the last time you remember the menopause being referenced in a movie or TV show? If you can think of one at all, was it just played for laughs?
And of course, the human body can be funny, so that’s not necessarily the problem, but it sure would be nice if that weren’t all that there is!
So, what does Dr. Gunter want us to know?
It’s a time of changes, not an end
The name “menopause” is misleading. It’s not a “pause”, and those menses aren’t coming back.
And yet, to call it a “menostop” would be differently misleading, because there’s a lot more going on than a simple cessation of menstruation.
Estrogen levels will drop a lot, testosterone levels may rise slightly, mood and sleep and appetite and sex drive will probably be affected (progesterone can improve all these things!) and
not to mention butwe’re going to mention: vaginal atrophy, which is very normal and very treatable with a topical estrogen cream. Untreated menopause can also bring a whole lot of increased health risks (for example, heart disease, osteoporosis, and, counterintuitively given the lower estrogen levels, breast cancer).However, with a little awareness and appropriate management, all these things can usually be navigated with minimal adverse health outcomes.
Dr Gunter, for this reason, refers to it interchangeably as “the menopausal transition”. She describes it as being less like a cliff edge we fall off, and more like a bridge we cross.
Bridges can be dangerous to cross! But they can also get us safely where we’re going.
Ok, so how do we manage those things?
Dr. Gunter is a big fan of evidence-based medicine, so we’ll not be seeing any yonic crystals or jade eggs. Or “goop”.
See also: Meet Goop’s Number One Enemy
For most people, she recommends Menopausal Hormone Therapy (MHT), which falls under the more general category of Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT).
This is the most well-evidenced, science-based way to avoid most of the risks associated with menopause.
Nevertheless, there are scare-stories out there, ranging from painful recommencement of bleeding, to (once again) increased risk of breast cancer. However, most of these are either misunderstandings, or unrelated to menopause and MHT, and are rather signs of other problems that should not be ignored.
To get a good grounding in this, you might want to read her Hormone Therapy Guide, freely available as a standalone section on her website. This series of posts is dedicated to hormone therapy. It starts with some basics and builds on that knowledge with each post:
Dr. Gunter’s Guide To The Hormone Menoverse
What about natural therapies?
There are some non-hormonal things that work, but these are mostly things that:
- give a statistically significant reduction in symptoms
- give the same statistically significant reduction in symptoms as placebo
As Dr. Gunter puts it:
❝While most of the studies of prescription medications for hot flashes have an appropriate placebo arm, this is rarely the case with so-called alternative therapies.
In fact, the studies here are almost always low quality, so it’s often not possible to conclude much.
Many reviews that look at these studies often end with a line that goes something like, “Randomized trials with a placebo arm, a low risk of bias, and adequate sample sizes are urgently needed.”
You should interpret this kind of conclusion as the polite way of saying, “We need studies that aren’t BS to say something constructive.”❞
However, if it works, it works, whatever its mechanism. It’s just good, when making medical decisions, to do so with the full facts!
For that matter, even Dr. Gunter acknowledges that while MHT can be lifechanging (in a positive way) for many, it’s not for everyone:
Informed Decisions: When Menopause Hormone Therapy Isn’t Recommended
Want to know more?
Dr. Gunter also has an assortment of books available, including The Menopause Manifesto (which we’ve reviewed previously), and some others that we haven’t, such as “Blood” and “The Vagina Bible”.
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What’s the difference between burnout and depression?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If your summer holiday already feels like a distant memory, you’re not alone. Burnout – a state of emotional, physical and mental exhaustion following prolonged stress – has been described in workplaces since a 5th century monastery in Egypt.
Burnout and depression can look similar and are relatively common conditions. It’s estimated that 30% of the Australian workforce is feeling some level of burnout, while almost 20% of Australians are diagnosed with depression at some point in their lives.
So what’s the difference between burnout and depression?
Burnout is marked by helplessness and depression by hopelessness. They can have different causes and should also be managed differently.
Yuri A/Shutterstock What is burnout?
The World Health Organization defines burnout as an “occupational phenomenon” resulting from excessively demanding workload pressures. While it is typically associated with the workplace, carers of children or elderly parents with demanding needs are also at risk.
Our research created a set of burnout symptoms we captured in the Sydney Burnout Measure to assist self-diagnosis and clinicians undertaking assessments. They include:
- exhaustion as the primary symptom
- brain fog (poor concentration and memory)
- difficulty finding pleasure in anything
- social withdrawal
- an unsettled mood (feeling anxious and irritable)
- impaired work performance (this may be result of other symptoms such as fatigue).
People can develop a “burning out” phase after intense work demands over only a week or two. A “burnout” stage usually follows years of unrelenting work pressure.
What is depression?
A depressive episode involves a drop in self-worth, increase in self-criticism and feelings of wanting to give up. Not everyone with these symptoms will have clinical depression, which requires a diagnosis and has an additional set of symptoms.
Clinically diagnosed depression can vary by mood, how long it lasts and whether it comes back. There are two types of clinical depression:
- melancholic depression has genetic causes, with episodes largely coming “out of the blue”
- non-melancholic depression is caused by environmental factors, often triggered by significant life events which cause a drop in self-worth.
When we created our burnout measure, we compared burnout symptoms with these two types of depression.
Burnout shares some features with melancholic depression, but they tend to be general symptoms, such as feeling a loss of pleasure, energy and concentration skills.
We found there were more similarities between burnout and non-melancholic (environmental) depression. This included a lack of motivation and difficulties sleeping or being cheered up, perhaps reflecting the fact both have environmental causes.
Looking for the root cause
The differences between burnout and depression become clearer when we look at why they happen.
Personality comes into play. Our work suggests a trait like perfectionism puts people at a much higher risk of burnout. But they may be less likely to become depressed as they tend to avoid stressful events and keep things under control.
Excessive workloads can contribute to burnout. tartanparty/Shutterstock Those with burnout generally feel overwhelmed by demands or deadlines they can’t meet, creating a sense of helplessness.
On the other hand, those with depression report lowered self-esteem. So rather than helpless they feel that they and their future is hopeless.
However it is not uncommon for someone to experience both burnout and depression at once. For example, a boss may place excessive work demands on an employee, putting them at risk of burnout. At the same time, the employer may also humiliate that employee and contribute to an episode of non-melancholic depression.
What can you do?
A principal strategy in managing burnout is identifying the contributing stressors. For many people, this is the workplace. Taking a break, even a short one, or scheduling some time off can help.
Australians now have the right to disconnect, meaning they don’t have to answer work phone calls or emails after hours. Setting boundaries can help separate home and work life.
Burnout can be also be caused by compromised work roles, work insecurity or inequity. More broadly, a dictatorial organisational structure can make employees feel devalued. In the workplace, environmental factors, such as excessive noise, can be a contributor. Addressing these factors can help prevent burnout.
As for managing symptoms, the monks had the right idea. Strenuous exercise, meditation and mindfulness are effective ways to deal with everyday stress.
Regular exercise can help manage symptoms of burnout. alexei_tm/Shutterstock Deeper contributing factors, including traits such as perfectionism, should be managed by a skilled clinical psychologist.
For melancholic depression, clinicians will often recommend antidepressant medication.
For non-melancholic depression, clinicians will help address and manage triggers that are the root cause. Others will benefit from antidepressants or formal psychotherapy.
While misdiagnosis between depression and burnout can occur, burnout can mimic other medical conditions such as anemia or hypothyroidism.
For the right diagnosis, it’s best to speak to your doctor or clinician who should seek to obtain a sense of “the whole picture”. Only then, once a burnout diagnosis has been affirmed and other possible causes ruled out, should effective support strategies be put in place.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14.
Correction: This article originally stated that depression is marked by helplessness and burnout by hopelessness, when in fact it is vice versa. This has been amended.
Gordon Parker, Scientia Professor of Psychiatry, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Professional-Style Dental Cleaning At Home?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You know the scene: your dentist is rummaging around inside your mouth with an implement that looks like a medieval torture device; you wince at a sudden sharp pain, only to be told “if you flossed, you wouldn’t be bleeding now”.
For most of us, going to the dentist isn’t near the top of our “favorite things to do” list, but it is of course a necessity of (healthy) life.
So, what can we do to minimize suffering in the dentist’s chair?
First, the basics
Of course, good oral hygiene is the absolute baseline, but with so many choices out there, which is best? We examined an array of options in this three-part series:
- Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
- Flossing Without Flossing?
- Less Common Oral Hygiene Options ← we recommend the miswak! Not only does it clean the teeth as well as or better than traditional brushing, but also it changes the composition of saliva to improve the oral microbiome, effectively turning your saliva into a biological mouthwash that kills unwanted microbes and is comfortable for the ones that should be there.
In fact, caring for the composition of one’s saliva, and thus one’s oral microbiome, is so important that we did a main feature on that, a little later:
Make Your Saliva Better For Your Teeth ← this is especially important if you take any meds that affect the composition of your saliva (scroll down to the table of meds). Your medications’ leaflets won’t tell you that it does that directly, but they will list “dry mouth” as one of the potential side effects (and you’ll probably know if you have a medication that gives you a dry mouth).
Next, level up
For this one, we’ll drop some links to some videos we’ve featured (for those who prefer text, worry not, your faithful writer has added text-based overviews):
- How To Regrow Receding Gums
- Tooth Remineralization: How To Heal Your Teeth Naturally
- Tartar Removal At Home & How To Prevent Tartar
Now, that last one sounds slightly more exciting than it is—it is about using chemical processes to gradually lessen the tartar over time, with a six-month timeframe.
So, what if you want to do one better than that?
Finally… Buckle up, this one’s fun
Ok, so “fun” and “dental care” don’t usually go hand-in-hand, and maybe your sense of fun differs from this writer’s, but hey. The thing is, we’re going to get hands-on with dental tools.
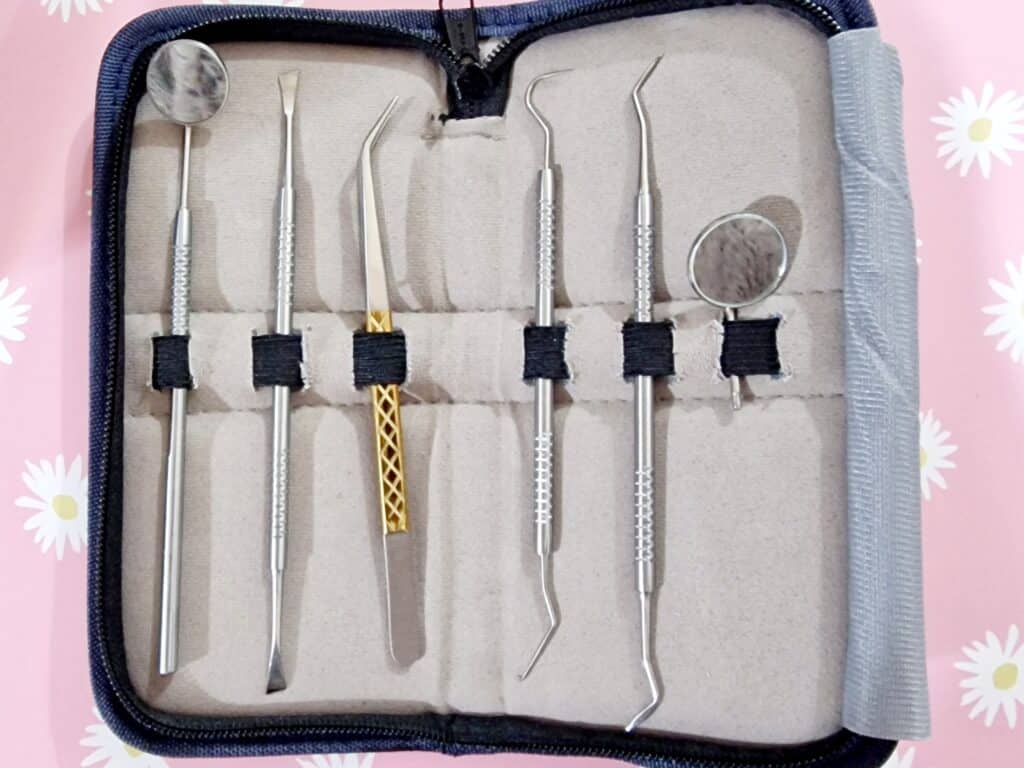
Specifically, these dental tools:
👆 these are literally the tools this writer has; if you look in the specula (the round mirror bits), you can see the reflection of the fluffy gray bathrobe I was wearing when I took the picture!
You can get tools like these easily online; here’s an example product on Amazon; do also shop around of course, and we recommend checking the reviews to ensure good quality.
Writer’s story on why I have these: once upon a time, a wisdom tooth came through at 45°, ploughing through the molar next to it, which then needed removing.
However, my teeth have the interesting anatomical quirk that I have hooked/barbed roots, which does not make tooth extraction easy; it had to come out sidewise, and the process was somewhat bungled by an inexperienced dental surgeon.
When the anesthetic wore off, it was the most pain I’ve ever been in in my life.
After that, I wasn’t a very regular returner to the dentist, and in 2013, I fell into a very deep depression for unrelated reasons, and during that period, I got some plaque/tartar buildup on some of my teeth due to lack of care, that then just stayed until I decided to take care of it more recently, which I am happy to say, I’ve now done (my teeth are the happiest and healthiest they’ve ever been), and I’m going to share how, with you.
So, here’s how to do it… First, you’ll need those tools, of course.
You will also want a good quality backlit magnifying mirror. Again, here’s an example product on Amazon ← this is the exact kind this writer has, and it’s very good.
You may be thinking: “wait a minute, this is scary, those are dangerous and I’m not a dentist!”
If so, then a few quick things to bear in mind:
- If you’re not comfortable doing it, don’t do it. As ever, our medical/legal disclaimer applies, and we share information for your interest only, and not as an exhortation to take any particular action. By all means confer with your dentist, too, and see whether they support the idea.
- These things do look scarier than they are once you get used to them. Do you use metal silverware when eating? Technically you could stab yourself with a fork any time, or damage your teeth with it, but when was the last time you did that?
- With regard to manual dexterity, if you have the manual dexterity required to paint your nails, floss your teeth, sew by hand, or write with a pen, then you have the manual dexterity to do this, too.
Now, about the tools:
- Speculum / magnifying speculum: the one with the mirror. This is useful for looking at the backs of teeth.
- Tweezers: the one with the gold grip in the photo above. You probably won’t need to use these, but we’re sure you know how to use tweezers in general.
- Dental explorer: the one with the big wicked-looking hook on one end, and a tiny (almost invisible in the photo) hook on the other end. This is for examining cavities, not for manipulating things. Best leave that to your dentist if you have cavities.
- Dental pick: this is the one to the right of the dental explorer, and it is for cleaning in the crevices between teeth. One end is quite blunt; the other is pointier, and you can choose which end to use depending on what fits into the shape of the crevice between your teeth.
- Dental scraper: this is the one with chisel ends. One end curves very slightly to the left, the other, very slightly to the right. This is for ergonomics depending on which hand you’re using, and which side you’re scraping (you’ll become very aware that your teeth, even if they look straight, curve very slightly at the edges.
You’ll be using these last two for the actual tartar removal, selecting the tool appropriate to cleaning the flat surface of a tooth, or the crevice where the teeth meet (not like flossing! That part, yes, but under no circumstances is this thing going all the way through to the other side, it’s just for getting into to nook that the scraper can’t so easily clean, that’s all).
A word on using metal against your teeth: a scary prospect, initially! However…
While steel is indeed harder than the enamel of your teeth, the enamel of your teeth is much harder than the plaque/tartar/calculus that you will be removing. Therefore, the technique to use is very gently scrape, starting as gently as humanly possible until you get a feel for it.
Unlike the dentist, you will have an advantage here in that you have biofeedback, and bone conduction of the sounds in your mouth, so you can exercise much more restraint than your dentist can. With the correct minimum of pressure, the tool should glide smoothly down enamel, but when it’s scraping tartar, it should make a very fine sandpapery noise.
This is why “or write with a pen” was one of the skills we mentioned earlier; it’s the same thing; you don’t press with a pen so hard that it goes through the paper, so don’t press so hard with the tool that it damages your enamel, that’s all.
Because of the differential in hardness between the tartar and the enamel, it’s really very easy to remove the tartar without harming the enamel, provided one is gentle.
Final word of warning; we’ll repeat: If you’re not comfortable doing it, don’t do it. As ever, our medical/legal disclaimer applies, and we share information for your interest only, and not as an exhortation to take any particular action. By all means confer with your dentist, too, and see whether they support the idea.
Also, while this kind of cleaning can be done safely at home, we recommend against doing anything more complicated than that.
See for example: Can You Repair Your Own Teeth At Home? ← the short answer is “no”, or not beyond tooth remineralization, anyway, and kits that say otherwise are potentially misleading, or stop-gap solutions at best.
One last time: always consult with a professional and get their advice (ours is not advice; it’s just information).
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why Fibromyalgia Is Not An Acceptable Diagnosis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Efrat Lamandre makes the case that fibromyalgia is less of a useful diagnosis and more of a rubber stamp, much like the role historically often fulfilled by “heart failure” as an official cause of death (because certainly, that heart sure did stop beating). It’s a way of answering the question without answering the question.
…and what to look for instead
Fibromyalgia is characterized by chronic pain, tenderness, sleep disturbances, fatigue, and other symptoms. It’s often considered an “invisible” illness, because it’s the kind that’s easy to dismiss if you’re not the one carrying it. A broken leg, one can point at and see it’s broken; a respiratory infection, one can see its effects and even test for presence of the pathogen and/or its antigens. But fibromyalgia? “It hurts and I’m tired” doesn’t quite cut it.
Much like “heart failure” as a cause of death when nothing else is implicated, fibromyalgia is a diagnosis that gets applied when known causes of chronic pain have been ruled out.
Dr. Lamandre advocates for functional medicine and seeking the underlying causes of the symptoms, rather than the industry standard approach, which is to just manage the symptoms themselves with medications (of course, managing the symptoms with medications has its place; there is no need to suffer needlessly if pain relief can be used; it’s just not a sufficient response).
She notes that potential triggers for fibromyalgia include microbiome imbalances, food sensitivities, thyroid issues, nutrient deficiencies, adrenal fatigue, mitochondrial dysfunction, mold toxicity, Lyme disease, and more. Is this really just one illness? Maybe, but quite possibly not.
In short… If you are given a diagnosis of fibromyalgia, she advises that you insist doctors keep on looking, because that’s not an answer.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
- How To Eat To Beat Chronic Fatigue ← yes, including how to do so when you are chronically fatigued. In other words, this isn’t just dietary advice, but rather practical advice too
- When Painkillers Aren’t Helping, These Things Might
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: