Take Care Of Your Lymphatic System To Beat Cognitive Decline
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First of all, for any unfamiliar with the lymphatic system, it’s mostly the body’s clean-up system (as well as a big part of the body’s anticancer system).
See: The Lymphatic System Against Cancer & More
It may not be the most glamorous job, but it’s certainly an essential one.
There’s no lymph in the brain, but…
Because of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) that keeps the astonishingly sensitive brain as safe as it can from unwanted things, there are many aspects of our physiology that only happen inside the brain, or only happen outside of it, as the compounds in question may be too large to get through the BBB.
The lymphatic system is, in and of itself, an entirely outside-of-the-brain affair. So, how does stuff get cleaned out from the brain (such as beta-amyloid and alpha-synuclein clearance, to avoid Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, respectively)?
The glymphatic system (a portmanteau of glial cells doing the job of the lymphatic system) is the brain’s own cleanup crew, and we wrote about it here:
How To Clean Your Brain (Glymphatic Health Primer)
Why lymph still matters for the brain
Although the glymphatic system is doing a (hopefully) fine job of scrubbing up the brain, if the lymphatic system isn’t working at least as well, then this becomes the equivalent of what would happen if you at home were very attentive to taking the trash out, but the garbage disposal crews stopped doing their job, or did it much less well than they need to. Soon, you’d end up with a mountain of trash at home, even though you were doing your part correctly.
In short: the glymphatic system needs to pass the waste on somewhere, and the lymphatic system is its go-to.
You may be wondering about the role of blood in all of this, and the answer is that no part of any of the above systems can do its job without adequate oxygenation, and our blood also assists in the transport of things removed—which is one of the reasons why there are blood-based Alzheimer’s tests that can be done; they measure certain markers of neurodegeneration that become present in the blood having left the brain:
Early Dementia Screening From Your Blood & More ← the “and more” is actually quite interesting, but it’s the blood we’re interested in for this section
What can be done about it
Our first two links up above, about the lymphatic and glymphatic systems, respectively, also tell how to look after each of them, but we’ll mention a few salient pointers here.
For the lymphatic system:
- do lymphatic massage
- exercise, with a focus on maximizing movement
- eat an anti-inflammatory diet
For the glymphatic system:
- do vagal massage (Vagal! Not vaginal, which will not help! Or rather: it won’t help the glymphatic system, anyway)
- exercise, and/but also rest well (good quality sleep)
- eat omega-3 fatty acids
For more details and suggestions on each though, do check out:
Lymphatic health primer | Glymphatic health primer
How this was discovered
Until as recently as 2014, it was not known that there was any part of the lymphatic system around the brain, waiting to take things from the glymphatic system. Since then, research has slowly been done about the relationship between the two, how things work, and what affects what and how.
Most recently (the study was published two days ago, at time of writing this) it was discovered that, in mice at least, improving lymphatic function just outside of the brain (the meningeal lymphatic vessels, responsible for draining waste from the brain) improves memory.
Aged mice who underwent a process that rejuvenated the meningeal lymphatic vessels, performed better in memory tests afterwards.
How this worked, step-by-step:
- The mice were given a special protein that rejuvenated the meningeal lymphatic vessels¹
- The lymphatic vessels were then able to do their job better
- This meant that the glial cells of the glymphatic system were no longer drowning in excess stuff
- This reduced levels of a protein that says “help, too much stuff!” and starts inhibiting everything it can to try to cope²
- This meant that neural activity was no longer being suppressed, and memory improved
Technical bits for those who want it:
¹ We’re not being secretive about what this special protein was; it’s just that the special protein is called adeno-associated virus 1 cytomegalovirus murine vascular endothelial growth factor C, or “AAV1-CMV-mVEGF-C” for short, so for readability, “a special protein” does the job. Suffice it to say, a) you can’t exactly buy AAV1-CMV-mVEGF-C on Amazon, and b) you wouldn’t want it anyway, you’d want its close cousin AAV1-CMV-hVEGF-C (“m” for murine, i.e. mousey, vs “h” for human)
² This one’s just called interleukin-6 (IL-6); perhaps you’ve heard of interleukin; we’ve mentioned it sometimes before.
You can read the paper in its entirety here; if you don’t mind reading very technical stuff, it is very interesting:
Meningeal lymphatics-microglia axis regulates synaptic physiology
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We speak often about the importance of dietary diversity, and of that, especially diversity of plants in one’s diet, but we’ve never really focused on it as a main feature, so that’s what we’re going to do today.
Specifically, you may have heard the advice to “eat 30 different kinds of plants per week”. But where does that come from, and is it just a number out of a hat?
The magic number?
It is not, in fact, a number out of a hat. It’s from a big (n=11,336) study into what things affect the gut microbiome for better or for worse. It was an observational population study, championing “citizen science” in which volunteers tracked various things and collected and sent in various samples for analysis.
The most significant finding of this study was that those who consumed more than 30 different kinds of plants per week, had a much better gut microbiome than those who consumed fewer than 10 different kinds of plants per week (there is a bell curve at play, and it gets steep around 10 and 30):
American Gut: an Open Platform for Citizen Science Microbiome Research
Why do I care about having a good gut microbiome?
Gut health affects almost every other kind of health; it’s been called “the second brain” for the various neurotransmitters and other hormones it directly makes or indirectly regulates (which in turn affect every part of your body), and of course there is the vagus nerve connecting it directly to the brain, impacting everything from food cravings to mood swings to sleep habits.
See also:
Any other benefits?
Yes there are! Let’s not forget: as we see often in our “This or That” section, different foods can be strong or weak in different areas of nutrition, so unless we want to whip out a calculator and database every time we make food choices, a good way to cover everything is to simply eat a diverse diet.
And that goes not just for vitamins and minerals (which would be true of animal products also), but in the case of plants, a wide range of health-giving phytochemicals too:
Measuring Dietary Botanical Diversity as a Proxy for Phytochemical Exposure
Ok, I’m sold, but 30 is a lot!
It is, but you don’t have to do all 30 in your first week of focusing on this, if you’re not already accustomed to such diversity. You can add in one or two new ones each time you go shopping, and build it up.
As for “what counts”: we’re counting unprocessed or minimally-processed plants. So for example, an apple is an apple, as are dried apple slices, as is apple sauce. Any or all of those would count as 1 plant type.
Note also that we’re counting types, not totals. If you’re having apple slices with apple sauce, for some reason? That still only counts as 1.
However, while apple sauce still counts as apples (minimally processed), you cannot eat a cake and say “that’s 2 because there was wheat and sugar cane somewhere in its dim and distant history”.
Nor is your morning espresso a fruit (by virtue of coffee beans being the fruit of the plant, botanically speaking). However, it would count as 1 plant type if you eat actual coffee beans—this writer has been known to snack on such; they’re only healthy in very small portions though, because their saturated fat content is a little high.
You, however, count grains in general, as well as nuts and seeds, not just fruits and vegetables. As for herbs and spices, they count for ¼ each, except for salt, which might get lumped in with spices but is of course not a plant.
How to do it
There’s a reason we’re doing this in our Saturday Life Hacks edition. Here are some tips for getting in far more plants than you might think, a lot more easily than you might think:
- Buy things ready-mixed. This means buying the frozen mixed veg, the frozen mixed chopped fruit, the mixed nuts, the mixed salad greens etc. This way, when you’re reaching for one pack of something, you’re getting 3–5 different plants instead of one.
- Buy things individually, and mix them for storage. This is a more customized version of the above, but in the case of things that keep for at least a while, it can make lazy options a lot more plentiful. Suddenly, instead of rice with your salad you’re having sorghum, millet, buckwheat, and quinoa. This trick also works great for dried berries that can just be tipped into one’s morning oatmeal. Or, you know, millet, oats, rye, and barley. Suddenly, instead of 1 or 2 plants for breakfast you have maybe 7 or 8.
- Keep a well-stocked pantry of shelf-stable items. This is good practice anyway, in case of another supply-lines shutdown like at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. But for plant diversity, it means that if you’re making enchiladas, then instead using kidney beans because that’s what’s in the cupboard, you can raid your pantry for kidney beans, black beans, pinto beans, fava beans, etc etc. Yes, all of them; that’s a list, not a menu.
- Shop in the discount section of the supermarket. You don’t have shop exclusively there, but swing by that area, see what plants are available for next to nothing, and buy at least one of each. Figure out what to do with it later, but the point here is that it’s a good way to get suggestions of plants that you weren’t actively looking for—and novelty is invariably a step into diversity.
- Shop in a different store. You won’t be able to beeline the products you want on autopilot, so you’ll see other things on the way. Also, they may have things your usual store doesn’t.
- Shop in person, not online—at least as often as is practical. This is because when shopping for groceries online, the store will tend to prioritize showing you items you’ve bought before, or similar items to those (i.e. actually the same item, just a different brand). Not good for trying new things!
- Consider a meal kit delivery service. Because unlike online grocery shopping, this kind of delivery service will (usually) provide you with things you wouldn’t normally buy. Our sometimes-sponsor Purple Carrot is a fine option for this, but there are plenty of others too.
- Try new recipes, especially if they have plants you don’t normally use. Make a note of the recipe, and go out of your way to get the ingredients; if it seems like a chore, reframe it as a little adventure instead. Honestly, it’s things like this that keep us young in more ways than just what polyphenols can do!
- Hide the plants. Whether or not you like them; hide them just because it works in culinary terms. By this we mean; blend beans into that meaty sauce; thicken the soup with red lentils, blend cauliflower into the gravy. And so on.
One more “magic 30”, while we’re at it…
30g fiber per day makes a big (positive) difference to many aspects of health. Obviously, plants are where that comes from, so there’s a big degree of overlap here, but most of the tips we gave are different, so for double the effectiveness, check out:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Seriously Useful Communication Skills!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Are Communication Skills, Really?
Superficially, communication is “conveying an idea to someone else”. But then again…
Superficially, painting is “covering some kind of surface in paint”, and yet, for some reason, the ceiling you painted at home is not regarded as equally “good painting skills” as Michaelangelo’s, with regard to the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel.
All kinds of “Dark Psychology” enthusiasts on YouTube, authors of “Office Machiavelli” handbooks, etc, tell us that good communication skills are really a matter of persuasive speaking (or writing). And let’s not even get started on “pick-up artist” guides. Bleugh.
Not to get too philosophical, but here at 10almonds, we think that having good communication skills means being able to communicate ideas simply and clearly, and in a way that will benefit as many people as possible.
The implications of this for education are obvious, but what of other situations?
Conflict Resolution
Whether at work or at home or amongst friends or out in public, conflict will happen at some point. Even the most well-intentioned and conscientious partners, family, friends, colleagues, will eventually tread on our toes—or we, on theirs. Often because of misunderstandings, so much precious time will be lost needlessly. It’s good for neither schedule nor soul.
So, how to fix those situations?
I’m OK; You’re OK
In the category of “bestselling books that should have been an article at most”, a top-tier candidate is Thomas Harris’s “I’m OK; You’re OK”.
The (very good) premise of this (rather padded) book is that when seeking to resolve a conflict or potential conflict, we should look for a win-win:
- I’m not OK; you’re not OK ❌
- For example: “Yes, I screwed up and did this bad thing, but you too do bad things all the time”
- I’m OK; you’re not OK ❌
- For example: “It is not I who screwed up; this is actually all your fault”
- I’m not OK; you’re OK ❌
- For example: “I screwed up and am utterly beyond redemption; you should immediately divorce/disown/dismiss/defenestrate me”
- I’m OK; you’re OK ✅
- For example: “I did do this thing which turned out to be incorrect; in my defence it was because you said xyz, but I can understand why you said that, because…” and generally finding a win-win outcome.
So far, so simple.
“I”-Messages
In a conflict, it’s easy to get caught up in “you did this, you did that”, often rushing to assumptions about intent or meaning. And, the closer we are to the person in question, the more emotionally charged, and the more likely we are to do this as a knee-jerk response.
“How could you treat me this way?!” if we are talking to our spouse in a heated moment, perhaps, or “How can you treat a customer this way?!” if it’s a worker at Home Depot.
But the reality is that almost certainly neither our spouse nor the worker wanted to upset us.
Going on the attack will merely put them on the defensive, and they may even launch their own counterattack. It’s not good for anyone.
Instead, what really happened? Express it starting with the word “I”, rather than immediately putting it on the other person. Often our emotions require a little interrogation before they’ll tell us the truth, but it may be something like:
“I expected x, so when you did/said y instead, I was confused and hurt/frustrated/angry/etc”
Bonus: if your partner also understands this kind of communication situation, so much the better! Dark psychology be damned, everything is best when everyone knows the playbook and everyone is seeking the best outcome for all sides.
The Most Powerful “I”-Message Of All
Statements that start with “I” will, unless you are rules-lawyering in bad faith, tend to be less aggressive and thus prompt less defensiveness. An important tool for the toolbox, is:
“I need…”
Softly spoken, firmly if necessary, but gentle. If you do not express your needs, how can you expect anyone to fulfil them? Be that person a partner or a retail worker or anyone else. Probably they want to end the conflict too, so throw them a life-ring and they will (if they can, and are at least halfway sensible) grab it.
- “I need an apology”
- “I need a moment to cool down”
- “I need a refund”
- “I need some reassurance about…” (and detail)
Help the other person to help you!
Everything’s best when it’s you (plural) vs the problem, rather than you (plural) vs each other.
Apology Checklist
Does anyone else remember being forced to write an insincere letter of apology as a child, and the literary disaster that probably followed? As adults, we (hopefully) apologize when and if we mean it, and we want our apology to convey that.
What follows will seem very formal, but honestly, we recommend it in personal life as much as professional. It’s a ten-step apology, and you will forget these steps, so we recommend to copy and paste them into a Notes app or something, because this is of immeasurable value.
It’s good not just for when you want to apologize, but also, for when it’s you who needs an apology and needs to feel it’s sincere. Give your partner (if applicable) a copy of the checklist too!
- Statement of apology—say “I’m sorry”
- Name the offense—say what you did wrong
- Take responsibility for the offense—understand your part in the problem
- Attempt to explain the offense (not to excuse it)—how did it happen and why
- Convey emotions; show remorse
- Address the emotions/damage to the other person—show that you understand or even ask them how it affected them
- Admit fault—understand that you got it wrong and like other human beings you make mistakes
- Promise to be better—let them realize you’re trying to change
- Tell them how you will try to do it different next time and finally
- Request acceptance of the apology
Note: just because you request acceptance of the apology doesn’t mean they must give it. Maybe they won’t, or maybe they need time first. If they’re playing from this same playbook, they might say “I need some time to process this first” or such.
Want to really superpower your relationship? Read this together with your partner:
Hold Me Tight: Seven Conversations for a Lifetime of Love, and, as a bonus:
The Hold Me Tight Workbook: A Couple’s Guide for a Lifetime of Love
Share This Post
- I’m not OK; you’re not OK ❌
-
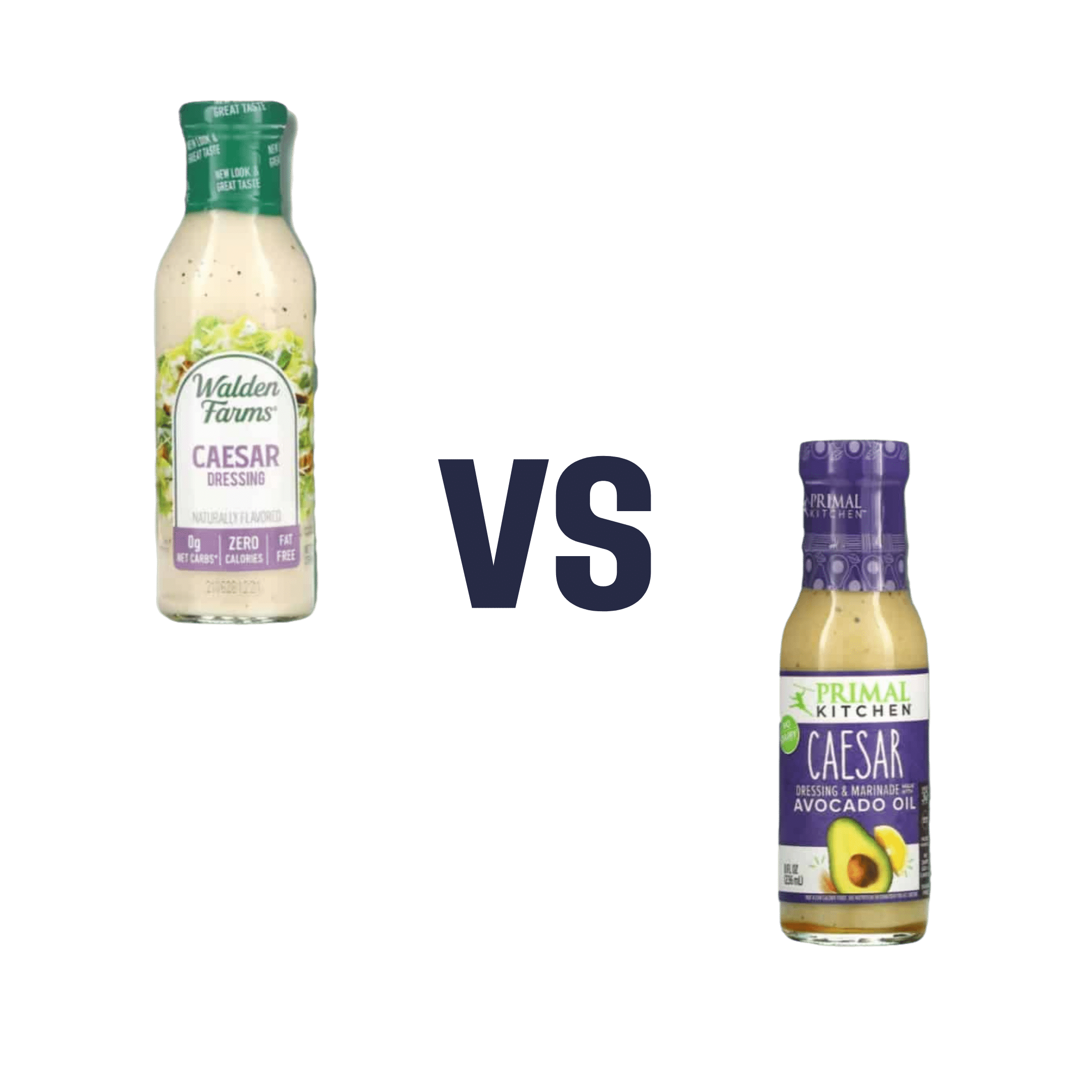
Walden Farms Caesar Dressing vs. Primal Kitchen Caesar Dressing – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Walden Farms Caesar Dressing to Primal Kitchen Caesar Dressing, we picked the Primal Kitchen.
Why?
As you can see from the front label, the Walden Farms product has 0 net carbs, 0 calories, and 0 fat. In fact, its ingredients list begins:
Water, white distilled vinegar, erythritol, corn fiber, salt, microcrystalline cellulose, xanthan gum, titanium dioxide (color)
…before it gets to something interesting (garlic purée), by which point the amount must be miniscule.
The Primal Kitchen product, meanwhile, has 140 calories per serving and 15g fat (of which, 1.5g is saturated). However! The ingredients list this time begins:
Avocado oil, water, organic coconut aminos (organic coconut sap, sea salt), organic apple cider vinegar, organic distilled vinegar, mushroom extract, organic gum acacia, organic guar gum
…before it too gets to garlic, which this time, by the way, is organic roasted garlic.
In case you’re wondering about the salt content in both, they add up to 190mg for the Walden Farms product, and 240mg for the Primal Kitchen product. We don’t think that the extra 50mg (out of a daily allowance of 2300–5000mg, depending on whom you ask) is worthy of note.
In short, the Walden Farms product is made of mostly additives of various kinds, whereas the Primal Kitchen product is made of mostly healthful ingredients.
So, the calories and fat are nothing to fear.
For this reason, we chose the product with more healthful ingredients—but we acknowledge that if you are specifically trying to keep your calories down, then the Walden Farms product may be a valid choice.
Read more:
• Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
• Caloric Restriction with Optimal NutritionShare This Post
Related Posts
-
Mind Gym – by Gary Mack and David Casstevens
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
While this book seems to be mostly popular amongst young American college athletes and those around them (coaches, parents, etc) its applicability is a lot wider than that.
The thing is, as this book details, we don’t have to settle for less than optimal in our training—whatever “optimal” means for us, at any stage of life.
The style is largely narrative, and conveys a lot of ideas through anecdotes. They are probably true, but whether they occured entirely as-written or have been polished or embellished is not so important, as to to give food for thought, and reflection on how we can hone what we’re doing to work the best for us.
Nor is it just a long pep-talk, though it certainly has a motivational aspect. But rather, it covers also such things as the seven critical areas that we need to excel at if we want to be mentally robust, and—counterintuitively—the value of slowing down sometimes. The authors also talk about the importance of love, labor, and ongoing learning if we want a fulfilled life.
Bottom line: if you are engaged with any sport or sport-like endeavor that you’d like to be better at, this book will sharpen your training and development.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to be kind to yourself (without going to a day spa)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“I have to be hard on myself,” Sarah told me in a recent telehealth psychology session. “I would never reach my potential if I was kind and let myself off the hook.”
I could empathise with this fear of self-compassion from clients such as Sarah (not her real name). From a young age, we are taught to be kind to others, but self-kindness is never mentioned.
Instead, we are taught success hinges on self-sacrifice. And we need a healthy inner critic to bully us forward into becoming increasingly better versions of ourselves.
But research shows there doesn’t have to be a trade-off between self-compassion and success.
Self-compassion can help you reach your potential, while supporting you to face the inevitable stumbles and setbacks along the way.
What is self-compassion?
Self-compassion has three key ingredients.
1. Self-kindness
This involves treating yourself with the same kindness you would extend towards a good friend – via your thoughts, feelings and actions – especially during life’s difficult moments.
For instance, if you find yourself fixating on a minor mistake you made at work, self-kindness might involve taking a ten-minute walk to shift focus, and reminding yourself it is OK to make mistakes sometimes, before moving on with your day.
2. Mindfulness
In this context, mindfulness involves being aware of your own experience of stress or suffering, rather than repressing or avoiding your feelings, or over-identifying with them.
Basically, you must see your stress with a clear (mindful) perspective before you can respond with kindness. If we avoid or are consumed by our suffering, we lose perspective.
3. Common humanity
Common humanity involves recognising our own experience of suffering as something that unites us as being human.
For instance, a sleep-deprived parent waking up (for the fourth time) to feed their newborn might choose to think about all the other parents around the world doing exactly the same thing – as opposed to feeling isolated and alone.
It’s not about day spas, or booking a manicure
When Sarah voiced her fear that self-compassion would prevent her success, I explained self-compassion is distinct from self-indulgence.
“So is self-compassion just about booking in more mani/pedis?” Sarah asked.
Not really, I explained. A one-off trip to a day spa is unlikely to transform your mental health.
Instead, self-compassion is a flexible psychological resilience factor that shapes our thoughts, feelings and actions.
It’s associated with a suite of benefits to our wellbeing, relationships and health.
A one-off trip to a day spa is unlikely to transform your mental health.
baranq/ShutterstockWhat does the science say?
Over the past 20 years, we’ve learned self-compassionate people enjoy a wide range of benefits. They tend to be happier and have fewer psychological symptoms of distress.
Those high on self-compassion persevere following a failure. They say they are more motivated to overcome a personal weakness than those low on self-compassion, who are more likely to give up.
So rather than feeling trapped by your inadequacies, self-compassion encourages a growth mindset, helping you reach your potential.
However, self-compassion is not a panacea. It will not change your life circumstances or somehow make life “easy”. It is based on the premise that life is hard, and provides practical tools to cope.
It’s a factor in healthy ageing
I research menopause and healthy ageing and am especially interested in the value of self-compassion through menopause and in the second half of life.
Because self-compassion becomes important during life’s challenges, it can help people navigate physical symptoms (for instance, menopausal hot flushes), life transitions such as divorce, and promote healthy ageing.
I’ve also teamed up with researchers at Autism Spectrum Australia to explore self-compassion in autistic adults.
We found autistic adults report significantly lower levels of self-compassion than neurotypical adults. So we developed an online self-compassion training program for this at-risk population.
Three tips for self-compassion
You can learn self-compassion with these three exercises.
1. What would you say to a friend?
Think back to the last time you made a mistake. What did you say to yourself?
If you notice you’re treating yourself more like an enemy than a friend, don’t beat yourself up about it. Instead, try to think about what you might tell a friend, and direct that same friendly language towards yourself.
2. Harness the power of touch
Soothing human touch activates the parasympathetic “relaxation” branch of our nervous system and counteracts the fight or flight response.
Specifically, self-soothing touch (for instance, by placing both hands on your heart, stroking your forearm or giving yourself a hug) reduces cortisol responses to psychosocial stress.
Yes, hugging yourself can help.
http://krakenimages.com/Shutterstock3. What do I need right now?
Sometimes, it can be hard to figure out exactly what self-compassion looks like in a given moment. The question “what do I need right now” helps clarify your true needs.
For example, when I was 37 weeks pregnant, I woke up bolt awake one morning at 3am.
Rather than beating myself up about it, or fretting about not getting enough sleep, I gently placed my hands on my heart and took a few deep breaths. By asking myself “what do I need right now?” it became clear that listening to a gentle podcast/meditation fitted the bill (even though I wanted to addictively scroll my phone).
Lydia Brown, Senior Lecturer in Psychology, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Live Life in Crescendo – by Stephen Covey and Cynthia Covey-Haller
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Stephen Covey is of course best known for his “7 Habits of Highly Effective People“, while the dozen books he wrote afterwards, not including this one, did not get the same acclaim.
Not including this one, because this one was published posthumously and, notwithstanding the order of the names on the cover, in all likelihood his daughter wrote most of.
And yet! The very spirit of this book is in defiance of 7 Habits being his “early career” magnum opus. We say “early career”, because he was 57 already when that was published, but it was one of his earlier books.
In this work the authors lay out the case for how “your most important work is always ahead of you“, and that it is perfectly possible to “live life in crescendo“, and keep on giving whatever it is that we want to give to the world.
We also learn, mostly through storytelling, of how people are infinitely more important than things, and that it is there that we should put our investments. And that while adversity may not make us stronger, it just means we may need to change our approach, to continue to be productive in whatever way is meaningful to us.
Bottom line: if ever you wonder how your future could live up to your past (in a good way), this is the book to get you thinking.
Click here to check out Live Life in Crescendo, and figure out what your next great work will be!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: