Seriously Useful Communication Skills!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Are Communication Skills, Really?
Superficially, communication is “conveying an idea to someone else”. But then again…
Superficially, painting is “covering some kind of surface in paint”, and yet, for some reason, the ceiling you painted at home is not regarded as equally “good painting skills” as Michaelangelo’s, with regard to the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel.
All kinds of “Dark Psychology” enthusiasts on YouTube, authors of “Office Machiavelli” handbooks, etc, tell us that good communication skills are really a matter of persuasive speaking (or writing). And let’s not even get started on “pick-up artist” guides. Bleugh.
Not to get too philosophical, but here at 10almonds, we think that having good communication skills means being able to communicate ideas simply and clearly, and in a way that will benefit as many people as possible.
The implications of this for education are obvious, but what of other situations?
Conflict Resolution
Whether at work or at home or amongst friends or out in public, conflict will happen at some point. Even the most well-intentioned and conscientious partners, family, friends, colleagues, will eventually tread on our toes—or we, on theirs. Often because of misunderstandings, so much precious time will be lost needlessly. It’s good for neither schedule nor soul.
So, how to fix those situations?
I’m OK; You’re OK
In the category of “bestselling books that should have been an article at most”, a top-tier candidate is Thomas Harris’s “I’m OK; You’re OK”.
The (very good) premise of this (rather padded) book is that when seeking to resolve a conflict or potential conflict, we should look for a win-win:
- I’m not OK; you’re not OK ❌
- For example: “Yes, I screwed up and did this bad thing, but you too do bad things all the time”
- I’m OK; you’re not OK ❌
- For example: “It is not I who screwed up; this is actually all your fault”
- I’m not OK; you’re OK ❌
- For example: “I screwed up and am utterly beyond redemption; you should immediately divorce/disown/dismiss/defenestrate me”
- I’m OK; you’re OK ✅
- For example: “I did do this thing which turned out to be incorrect; in my defence it was because you said xyz, but I can understand why you said that, because…” and generally finding a win-win outcome.
So far, so simple.
“I”-Messages
In a conflict, it’s easy to get caught up in “you did this, you did that”, often rushing to assumptions about intent or meaning. And, the closer we are to the person in question, the more emotionally charged, and the more likely we are to do this as a knee-jerk response.
“How could you treat me this way?!” if we are talking to our spouse in a heated moment, perhaps, or “How can you treat a customer this way?!” if it’s a worker at Home Depot.
But the reality is that almost certainly neither our spouse nor the worker wanted to upset us.
Going on the attack will merely put them on the defensive, and they may even launch their own counterattack. It’s not good for anyone.
Instead, what really happened? Express it starting with the word “I”, rather than immediately putting it on the other person. Often our emotions require a little interrogation before they’ll tell us the truth, but it may be something like:
“I expected x, so when you did/said y instead, I was confused and hurt/frustrated/angry/etc”
Bonus: if your partner also understands this kind of communication situation, so much the better! Dark psychology be damned, everything is best when everyone knows the playbook and everyone is seeking the best outcome for all sides.
The Most Powerful “I”-Message Of All
Statements that start with “I” will, unless you are rules-lawyering in bad faith, tend to be less aggressive and thus prompt less defensiveness. An important tool for the toolbox, is:
“I need…”
Softly spoken, firmly if necessary, but gentle. If you do not express your needs, how can you expect anyone to fulfil them? Be that person a partner or a retail worker or anyone else. Probably they want to end the conflict too, so throw them a life-ring and they will (if they can, and are at least halfway sensible) grab it.
- “I need an apology”
- “I need a moment to cool down”
- “I need a refund”
- “I need some reassurance about…” (and detail)
Help the other person to help you!
Everything’s best when it’s you (plural) vs the problem, rather than you (plural) vs each other.
Apology Checklist
Does anyone else remember being forced to write an insincere letter of apology as a child, and the literary disaster that probably followed? As adults, we (hopefully) apologize when and if we mean it, and we want our apology to convey that.
What follows will seem very formal, but honestly, we recommend it in personal life as much as professional. It’s a ten-step apology, and you will forget these steps, so we recommend to copy and paste them into a Notes app or something, because this is of immeasurable value.
It’s good not just for when you want to apologize, but also, for when it’s you who needs an apology and needs to feel it’s sincere. Give your partner (if applicable) a copy of the checklist too!
- Statement of apology—say “I’m sorry”
- Name the offense—say what you did wrong
- Take responsibility for the offense—understand your part in the problem
- Attempt to explain the offense (not to excuse it)—how did it happen and why
- Convey emotions; show remorse
- Address the emotions/damage to the other person—show that you understand or even ask them how it affected them
- Admit fault—understand that you got it wrong and like other human beings you make mistakes
- Promise to be better—let them realize you’re trying to change
- Tell them how you will try to do it different next time and finally
- Request acceptance of the apology
Note: just because you request acceptance of the apology doesn’t mean they must give it. Maybe they won’t, or maybe they need time first. If they’re playing from this same playbook, they might say “I need some time to process this first” or such.
Want to really superpower your relationship? Read this together with your partner:
Hold Me Tight: Seven Conversations for a Lifetime of Love, and, as a bonus:
The Hold Me Tight Workbook: A Couple’s Guide for a Lifetime of Love
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Cure – by Dr. Jo Marchant
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The subtitle here, “a journey into the science of mind over body”, prompts an immediate question: is this book actually about science?
And yes, yes it is. It’s not about “positive energy” or “tapping into your divine essence” or anysuch. It’s about science, and scientific studies.
The author’s PhD is in genetics and medical microbiology, not metaphysics or something.
For those of us who read a lot of clinical studies about a lot of things (hi, regular researcher/writer here), we’re very used to placebo being used as a control in medical science.
“This drug performed no better than placebo” is generally considered a disappointing statement… But what if the placebo was already having a profound effect? Shouldn’t that be worthy of note too?
Dr. Marchant looks at more than just drugs, though, and also looks into the science (complete with EEGs and such) of hypnosis and virtual reality.
The writing style here is very accessible without skimping on science. This is to be expected; Dr. Marchant also has an MSc in science communication, and spent a time as senior editor of New Scientist magazine.
This isn’t a how-to book, but there are some practical takeaways too, specific things we can do to augment (or avoid sabotaging) any medications we take, for example.
Bottom line: placebo effect (and its evil twin, the nocebo effect) has a profound impact on all of us whether we want it or not, so we might as well learn about how it works and how to leverage it. This book gives a very good, hard science grounding.
Click here to check out “Cure” and get the most out of whatever you take (or do) for your health!
Share This Post

Why Some People Get Sick More (And How To Not Be One Of Them)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some people have never yet had COVID (so far so good, this writer included); others are on their third bout already; others have not been so lucky and are no longer with us to share their stories.
Obviously, even the healthiest and/or most careful person can get sick, and it would be folly to be complacent and think “I’m not a person who gets sick; that happens to other people”.
Nor is COVID the only thing out there to worry about; there’s always the latest outbreak-du-jour of something, and there are always the perennials such as cold and flu—which are also not to be underestimated, because both weaken us to other things, and flu has killed very many, from the 50,000,000+ in the 1918 pandemic, to the 700,000ish that it kills each year nowadays.
And then there are the combination viruses:
Move over, COVID and Flu! We Have “Hybrid Viruses” To Contend With Now
So, why are some people more susceptible?
Firstly, some people are simply immunocompromised. This means for example that:
- perhaps they have an inflammatory/autoimmune disease of some kind (e.g. lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes), or…
- perhaps they are taking immunosuppressants for some reason (e.g. because they had an organ transplant), or…
- perhaps they have a primary infection that leaves them vulnerable to secondary infections. Most infections will do this to some degree or another, but some are worse for it than others; untreated HIV is a clear example. The HIV itself may not kill people, but (if untreated) the resultant AIDS will leave a person open to being killed by almost any passing opportunistic pathogen. Pneumonia of various kinds being high on the list, but it could even be something as simple as the common cold, without a working immune system to fight it.
See also: How To Prevent (Or Reduce) Inflammation
And for that matter, since pneumonia is a very common last-nail-in-the-coffin secondary infection (especially: older people going into hospital with one thing, getting a secondary infection and ultimately dying as a result), it’s particularly important to avoid that, so…
See also: Pneumonia: What We Can & Can’t Do About It
Secondly, some people are not immunocompromised per the usual definition of the word, but their immune system is, arguably, compromised.
Cortisol, the stress hormone, is an immunosuppressant. We need cortisol to live, but we only need it in small bursts here and there (such as when we are waking up the morning). When high cortisol levels become chronic, so too does cortisol’s immunosuppressant effect.
Top things that cause elevated cortisol levels include:
- Stress
- Alcohol
- Smoking
Thus, the keys here are to 1) not smoke 2) not drink, ideally, or at least keep consumption low, but honestly even one drink will elevate cortisol levels, so it’s better not to, and 3) manage stress.
See also: Lower Your Cortisol! (Here’s Why & How)
Other modifiable factors
Being aware of infection risk and taking steps to reduce it (e.g. avoiding being with many people in confined indoor places, masking as appropriate, handwashing frequently) is a good preventative strategy, along with of course getting any recommended vaccines as they come available.
What if they fail? How can we boost the immune system?
We talked about not sabotaging the immune system, but what about actively boosting it? The answer is yes, we certainly can (barring serious medical reasons why not), as there are some very important lifestyle factors too:
Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
One final last-line thing…
Since if we do get an infection, it’s better to know sooner rather than later… A recent study shows that wearable activity trackers can (if we pay attention to the right things) help predict disease, including highlighting COVID status (positive or negative) about as accurately (88% accuracy) as rapid screening tests. Here’s a pop-science article about it:
Wearable activity trackers show promise in detecting early signals of disease
Take care!
Share This Post

Ice Baths: To Dip Or Not To Dip?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many Are Cold, But Few Are Frozen

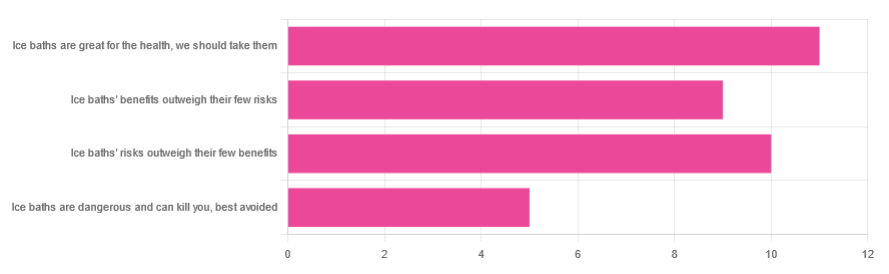
We asked you for your (health-related) view of ice baths, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 31% said “ice baths are great for the health; we should take them”
- About 29% said “ice baths’ risks outweigh their few benefits”
- About 26% said “ice baths’ benefits outweigh their few risks”
- About 14% said “ice baths are dangerous and can kill you; best avoided”
So what does the science say?
Freezing water is very dangerous: True or False?
True! Water close to freezing point is indeed very dangerous, and can most certainly kill you.
Fun fact, though: many such people are still saveable with timely medical intervention, in part because the same hypothermia that is killing them also slows down the process* of death
Source (and science) for both parts of that:
Cold water immersion: sudden death and prolonged survival
*and biologically speaking, death is a process, not an event, by the way. But we don’t have room for that today!
(unless you die in some sudden violent way, such as a powerful explosion that destroys your brain instantly; then it’s an event)
Ice baths are thus also very dangerous: True or False?
False! Assuming that they are undertaken responsibly and you have no chronic diseases that make it more dangerous for you.
What does “undertaken responsibly” mean?
Firstly, the temperature should not be near freezing. It should be 10–15℃, which for Americans is 50–59℉.
You can get a bath thermometer to check this, by the way. Here’s an example product on Amazon.
Secondly, your ice bath should last no more than 10–15 minutes. This is not a place to go to sleep.
What chronic diseases would make it dangerous?
Do check with your doctor if you have any doubts, as no list we make can be exhaustive and we don’t know your personal medical history, but the main culprits are:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Hypertension
- Diabetes (any type)
The first two are for heart attack risk; the latter is because diabetes can affect core temperature regulation.
Ice baths are good for the heart: True or False?
True or False depending on how they’re done, and your health before starting.
For most people, undertaking ice baths responsibly, repeated ice bath use causes the cardiovascular system to adapt to better maintain homeostasis when subjected to thermal shock (i.e. sudden rapid changes in temperature).
For example: Respiratory and cardiovascular responses to cold stress following repeated cold water immersion
And because that was a small study, here’s a big research review with a lot of data; just scroll to where it has the heading“Specific thermoregulative adaptations to regular exposure to cold air and/or cold water exposure“ for many examples and much discussion:
Health effects of voluntary exposure to cold water: a continuing subject of debate
Ice baths are good against inflammation: True or False?
True! Here’s one example:
Uric acid and glutathione levels (important markers of chronic inflammation) are also significantly affected:
Uric acid and glutathione levels during short-term whole body cold exposure
Want to know more?
That’s all we have room for today, but check out our previous “Expert Insights” main feature looking at Wim Hof’s work in cryotherapy:
A Cold Shower A Day Keeps The Doctor Away?
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts

Blue Cheese vs Brunost – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing blue cheese to brunost, we picked the brunost.
Why?
First, for the unfamiliar, as brunost isn’t necessarily as popular as blue cheese in N. America where most of our readers are:
Brunost, literally “brown cheese” is a traditional Norwegian affair made from aggressively boiling milk, cream, and whey in an iron cauldron. Whereas the blue in blue cheese comes from mold, the brown in brown cheese comes from caramelizing the milk sugars in the cauldron. When we say “cauldron”, yes, there is nowadays mass-produced brunost that is no longer made in something that could be mistaken for a witch’s brew, but the use of cast iron is actually important to the process, and has been the subject of regulatory controversy in Norway; first the cast iron was abandoned, then because that changed the cheese they fortified the product with added iron supplementation, then that was banned, then they reversed it because it affected iron levels in the general population. Nowadays, it is usually made with iron, one way or another.
Ok, so let’s see how they stack up against each other:
In terms of macronutrients, the two cheeses are comparable in fat, but brunost has more carbs—because whereas bacteria (and to a lesser extent, the mold) ate nearly all the carbs in the blue cheese, the caramelization of the milk sugars in brunost meant the result stayed higher in carbs. Both are considered “low GI” foods, but this category is still at least a moderate win for blue cheese.
When it comes to vitamins, brunost is higher in vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, and B12, while blue cheese is higher in vitamin B9. In other words, a clear and easy win for brunost.
In the category of minerals, brunost has more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium. Meanwhile, blue cheese contains more zinc, although we can also mention that blue cheese has about 2x the sodium, which is generally not considered a benefit. The two cheeses are about equal in calcium and selenium. Adding these up makes for another clear and easy win for brunost.
In short, unless you are strongly avoiding [even low-GI foods’] carbs for some reason, brunost wins the day by virtue of its overwhelmingly better vitamin and mineral content.
Still, like most fermented dairy products, both cheeses can be enjoyed in moderation as part of a healthy diet (assuming you don’t have an allergy/intolerance).
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

What is PMDD?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) is a mood disorder that causes significant mental health changes and physical symptoms leading up to each menstrual period.
Unlike premenstrual syndrome (PMS), which affects approximately three out of four menstruating people, only 3 percent to 8 percent of menstruating people have PMDD. However, some researchers believe the condition is underdiagnosed, as it was only recently recognized as a medical diagnosis by the World Health Organization.
Read on to learn more about its symptoms, the difference between PMS and PMDD, treatment options, and more.
What are the symptoms of PMDD?
People with PMDD typically experience both mood changes and physical symptoms during each menstrual cycle’s luteal phase—the time between ovulation and menstruation. These symptoms typically last seven to 14 days and resolve when menstruation begins.
Mood symptoms may include:
- Irritability
- Anxiety and panic attacks
- Extreme or sudden mood shifts
- Difficulty concentrating
- Depression and suicidal ideation
Physical symptoms may include:
- Fatigue
- Insomnia
- Headaches
- Changes in appetite
- Body aches
- Bloating
- Abdominal cramps
- Breast swelling or tenderness
What is the difference between PMS and PMDD?
Both PMS and PMDD cause emotional and physical symptoms before menstruation. Unlike PMS, PMDD causes extreme mood changes that disrupt daily life and may lead to conflict with friends, family, partners, and coworkers. Additionally, symptoms may last longer than PMS symptoms.
In severe cases, PMDD may lead to depression or suicide. More than 70 percent of people with the condition have actively thought about suicide, and 34 percent have attempted it.
What is the history of PMDD?
PMDD wasn’t added to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders until 2013. In 2019, the World Health Organization officially recognized it as a medical diagnosis.
References to PMDD in medical literature date back to the 1960s, but defining it as a mental health and medical condition initially faced pushback from women’s rights groups. These groups were concerned that recognizing the condition could perpetuate stereotypes about women’s mental health and capabilities before and during menstruation.
Today, many women-led organizations are supportive of PMDD being an official diagnosis, as this has helped those living with the condition access care.
What causes PMDD?
Researchers don’t know exactly what causes PMDD. Many speculate that people with the condition have an abnormal response to fluctuations in hormones and serotonin—a brain chemical impacting mood— that occur throughout the menstrual cycle. Symptoms fully resolve after menopause.
People who have a family history of premenstrual symptoms and mood disorders or have a personal history of traumatic life events may be at higher risk of PMDD.
How is PMDD diagnosed?
Health care providers of many types, including mental health providers, can diagnose PMDD. Providers typically ask patients about their premenstrual symptoms and the amount of stress those symptoms are causing. Some providers may ask patients to track their periods and symptoms for one month or longer to determine whether those symptoms are linked to their menstrual cycle.
Some patients may struggle to receive a PMDD diagnosis, as some providers may lack knowledge about the condition. If your provider is unfamiliar with the condition and unwilling to explore treatment options, find a provider who can offer adequate support. The International Association for Premenstrual Disorders offers a directory of providers who treat the condition.
How is PMDD treated?
There is no cure for PMDD, but health care providers can prescribe medication to help manage symptoms. Some medication options include:
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), a class of antidepressants that regulate serotonin in the brain and may improve mood when taken daily or during the luteal phase of each menstrual cycle.
- Hormonal birth control to prevent ovulation-related hormonal changes.
- Over-the-counter pain medication like Tylenol, which can ease headaches, breast tenderness, abdominal cramping, and other physical symptoms.
Providers may also encourage patients to make lifestyle changes to improve symptoms. Those lifestyle changes may include:
- Limiting caffeine intake
- Eating meals regularly to balance blood sugar
- Exercising regularly
- Practicing stress management using breathing exercises and meditation
- Having regular therapy sessions and attending peer support groups
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
If you or anyone you know is considering suicide or self-harm or is anxious, depressed, upset, or needs to talk, call the Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988 or text the Crisis Text Line at 741-741. For international resources, here is a good place to begin.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.

Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Is cold water bad for you? The facts behind 5 water myths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We know the importance of staying hydrated, especially in hot weather. But even for something as simple as a drink of water, conflicting advice and urban myths abound.
Is cold water really bad for your health? What about hot water from the tap? And what is “raw water”? Let’s dive in and find out.
Myth 1: Cold water is bad for you
Some recent TikToks have suggested cold water causes health problems by somehow “contracting blood vessels” and “restricting digestion”. There is little evidence for this.
While a 2001 study found 51 out of 669 women tested (7.6%) got a headache after drinking cold water, most of them already suffered from migraines and the work hasn’t been repeated since.
Cold drinks were shown to cause discomfort in people with achalasia (a rare swallowing disorder) in 2012 but the study only had 12 participants.
For most people, the temperature you drink your water is down to personal preference and circumstances. Cold water after exercise in summer or hot water to relax in winter won’t make any difference to your overall health.
Myth 2: You shouldn’t drink hot tap water
This belief has a grain of scientific truth behind it. Hot water is generally a better solvent than cold water, so may dissolve metals and minerals from pipes better. Hot water is also often stored in tanks and may be heated and cooled many times. Bacteria and other disease-causing microorganisms tend to grow better in warm water and can build up over time.
It’s better to fill your cup from the cold tap and get hot water for drinks from the kettle.
Myth 3: Bottled water is better
While bottled water might be safer in certain parts of the world due to pollution of source water, there is no real advantage to drinking bottled water in Australia and similar countries.
According to University of Queensland researchers, bottled water is not safer than tap water. It may even be tap water. Most people can’t tell the difference either. Bottled water usually costs (substantially) more than turning on the tap and is worse for the environment.
What about lead in tap water? This problem hit the headlines after a public health emergency in Flint, Michigan, in the United States. But Flint used lead pipes with a corrosion inhibitor (in this case orthophosphate) to keep lead from dissolving. Then the city switched water sources to one without a corrosion inhibitor. Lead levels rose and a public emergency was declared.
Fortunately, lead pipes haven’t been used in Australia since the 1930s. While lead might be present in some old plumbing products, it is unlikely to cause problems.
Myth 4: Raw water is naturally healthier
Some people bypass bottled and tap water, going straight to the source.
The “raw water” trend emerged a few years ago, encouraging people to drink from rivers, streams and lakes. There is even a website to help you find a local source.
Supporters say our ancestors drank spring water, so we should, too. However, our ancestors also often died from dysentery and cholera and their life expectancy was low.
While it is true even highly treated drinking water can contain low levels of things like microplastics, unless you live somewhere very remote, the risks of drinking untreated water are far higher as it is more likely to contain pollutants from the surrounding area.
Myth 5: It’s OK to drink directly from hoses
Tempting as it may be, it’s probably best not to drink from the hose when watering the plants. Water might have sat in there, in the warm sun for weeks or more potentially leading to bacterial buildup.
Similarly, while drinking water fountains are generally perfectly safe to use, they can contain a variety of bacteria. It’s useful (though not essential) to run them for a few seconds before you start to drink so as to get fresh water through the system rather than what might have been sat there for a while.
We are fortunate to be able to take safe drinking water for granted. Billions of people around the world are not so lucky.
So whether you like it hot or cold, or somewhere in between, feel free to enjoy a glass of water this summer.
Just don’t drink it from the hose.

Oliver A.H. Jones, Professor of chemistry, RMIT University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: