Super Gut – by Dr. William Davis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may be wondering: what sets this book apart from the other gut health books we’ve reviewed? For this one, mostly it’s depth.
This is the most scientifically dense book we’ve reviewed on gut health, so if you’re put off by that, this might not be one for you. However, you don’t need prior knowledge, as he does explain things as he goes. The advice in this book is not just the usual “gut health 101” stuff, either!
A particular strength of this book is that it looks at a wide variety of gut- and gut-related disorders, and ways certain readers may need to do different things than others, to address those problems on the path to good gut health.
The style, for all its hard science content, is quite sensationalist, and that may take some getting used to for non-Americans. However, it doesn’t affect the content!
Bottom line: if you just want simple basic advice, then probably best to skip this one. However, if you are sincerely serious about gut health (or just like reading this sort of thing because learning is satisfying), then this book is packed with relevant and detailed information.
Click here to check out Super Gut, and get to know and improve yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Small Pleasures – by Ryan Riley
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When Hippocrates said “let food be thy medicine, and let medicine be thy food”, he may or may not have had this book in mind.
In terms of healthiness, this one’s not the very most nutritionist-approved recipe book we’ve ever reviewed. It’s not bad, to be clear!
But the physical health aspect is secondary to the mental health aspects, in this one, as you’ll see. And as we say, “mental health is also just health”.
The book is divided into three sections:
- Comfort—for when you feel at your worst, for when eating is a chore, for when something familiar and reassuring will bring you solace. Here we find flavor and simplicity; pastas, eggs, stews, potato dishes, and the like.
- Restoration—for when your energy needs reawakening. Here we find flavors fresh and tangy, enlivening and bright. Things to make you feel alive.
- Pleasure—while there’s little in the way of health-food here, the author describes the dishes in this section as “a love letter to yourself; they tell you that you’re special as you ready yourself to return to the world”.
And sometimes, just sometimes, we probably all need a little of that.
Bottom line: if you’d like to bring a little more joie de vivre to your cuisine, this book can do that.
Click here to check out Small Pleasures, and rekindle joy in your kitchen!
Share This Post
-
Pine Bark’s Next-Level Antioxidant Properties
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pine Bark’s Next-Level Antioxidant Properties
Pine bark extract has been used by the indigenous peoples of N. America for a very long time, to treat a variety of ailments.
This one falls into the category of “things from traditional medicine that eventually got investigated and their scientific worth noticed by people from outside of those cultures”.
Not all pine trees!
If you happen to have pine trees near you, be aware that without sufficient botanical knowledge, you could find yourself bark-harvesting from the wrong tree—but many species of pine do have these qualities.
Useful (for this purpose) pine trees include, but are not limited to:
- Pinus banksiana
- Pinus massoniana
- Pinus pinaster
- Pinus radiata
- Pinus resinosa
- Pinus strobus
…which is already a fair list, but there are dozens more that have not been studied, and/or found lacking in medicinal qualities, and/or just didn’t make our list here today.
What does it do & How does it work?
We sneakily put those two questions together today because it’s easiest to explain in one:
The Pinus family in general has powerful antioxidant qualities, and not just like blueberries or coffee (wonderful as those are).
Rather, it has:
- Phenolic acids: these are the polyphenols found in many plant foods rich in antioxidants. These are great, but they aren’t the exciting part here.
- Catechins: these aren’t classified as antioxidants, but they are flavonoids that do the same job in a slightly different way
- Procyanidins: another class of flavonoids, and this is where pine bark really comes into its own
And yes, as ever, “those three things that always seem to come together”, it having these antioxidant properties means it is also anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer:
…and anti-aging:
Pleiotropic Effects of French Maritime Pine Bark Extract to Promote Healthy Aging
…which does of course mean that it almost certainly fights age-related cognitive decline, though studies for that have been animal studies so far, such as:
- Pine Bark Polyphenolic Extract Attenuates Amyloid-β and Tau Misfolding in a Model System of Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropathology
- Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Pinus densiflora Bark Extract in Gerbil Hippocampus Following Transient Forebrain Ischemia
- Neuroprotective Effects of Korean Red Pine ( Pinus densiflora) Bark Extract and Its Phenolics
- Pine bark treatment decelerates plaque development and improves spatial memory in Alzheimer’s disease mice
Where to get it?
As ever, we don’t sell it, but here’s an example product on Amazon for your convenience; we recommend shopping around though, as prices vary a lot!
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Half Of Americans Over 50 Have Hemorrhoids, But They Can Be Prevented!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Hello. I was hoping you could give some useful tips about how to avoid a painful ailment that has affected Ernest Hemingway, Karl Marx, David Livingstone, Napoleon, Marilyn Monroe, King Alfred, and Martin Luther, and, I confess, me from time to time … namely, hemorrhoids. Help!❞
Firstly: that list could be a lot longer! We don’t have global stats, but in the US for example, half of adults over 50 have hemorrhoids.
So, you’re certainly not alone. People just don’t talk about it.
But, there are preventative things you can do:
Fiber, fiber, fiber. See also:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Hydrate, hydrate, hydrate.
This one’s simple enough. If you are dehydrated, constipation is more likely, and with it, hemorrhoids.
Watch your meds…
Some medications can cause constipation—painkillers containing codeine are a common culprit, for example.
When you go, go!
Not only can prolonged straining promote hemorrhoids, but also (if you’ll pardon the phrasing—there’s only so delicately we can say this) simply sitting with things partway “open” down there is not good for its health; things can quickly become irritated, and that can lead to hemorrhoids.
So: when you go, go. Leave your phone in another room!
Wash—but carefully.
Beyond your normal showering/bathing routine, a bidet is a great option for keeping things happy down there, if you have that option available to you.
However, if you have hemorrhoids, don’t use soap, as this can cause irritation and make it worse.
Warm water is fine, as is a salt bath, and pat dry and/or use gentle wet-wipes rather than rougher paper.
You can follow up with a hemorrhoid cream of your choice (or hydrocortisone, unless that’s contraindicated by another condition you have)
Know when to seek help
Hemorrhoids will usually go away by themselves if not exacerbated. But if it’s getting unduly difficult, and/or you’re bleeding down there, it’s time to see a doctor.
Note on bleeding: even if you’re 100% sure you have hemorrhoids, there are still other reasons you could be bleeding, and so it needs checking out.
Hemorrhoid treatment, if needed, will vary depending on severity. Beyond creams and lotions, there are other options that are less fun but sometimes necessary, including injections, electrotherapy, banding, or surgery.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Pasteurization: What It Does And Doesn’t Do
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pasteurization’s Effect On Risks & Nutrients
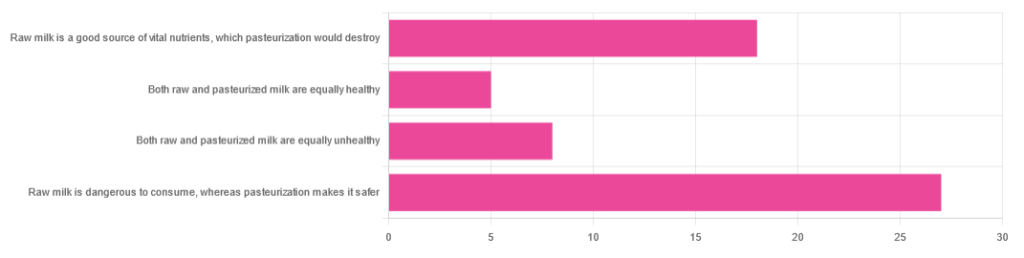
In Wednesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your health-related opinions of raw (cow’s) milk, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 47% said “raw milk is dangerous to consume, whereas pasteurization makes it safer”
- About 31% said “raw milk is a good source of vital nutrients which pasteurization would destroy”
- About 14% said “both raw milk and pasteurized milk are equally unhealthy”
- About 9% said “both raw milk and pasteurized milk are equally healthy”
Quite polarizing! So, what does the science say?
“Raw milk is dangerous to consume, whereas pasteurization makes it safer: True or False?”
True! Coincidentally, the 47% who voted for this are mirrored by the 47% of the general US population in a similar poll, deciding between the options of whether raw milk is less safe to drink (47%), just as safe to drink (15%), safer to drink (9%), or not sure (30%):
Public Fails to Appreciate Risk of Consuming Raw Milk, Survey Finds
As for what those risks are, by the way, unpasteurized dairy products are estimated to cause 840x more illness and 45x more hospitalizations than pasteurized products.
This is because unpasteurized milk can (and often does) contain E. coli, Listeria, Salmonella, Cryptosporidium, and other such unpleasantries, which pasteurization kills.
Source for both of the above claims:
(we know the title sounds vague, but all this information is easily visible in the abstract, specifically, the first two paragraphs)
Raw milk is a good source of vital nutrients which pasteurization would destroy: True or False?
False! Whether it’s a “good” source can be debated depending on other factors (e.g., if we considered milk’s inflammatory qualities against its positive nutritional content), but it’s undeniably a rich source. However, pasteurization doesn’t destroy or damage those nutrients.
Incidentally, in the same survey we linked up top, 16% of the general US public believed that pasteurization destroys nutrients, while 41% were not sure (and 43% knew that it doesn’t).
Note: for our confidence here, we are skipping over studies published by, for example, dairy farming lobbies and so forth. Those do agree, by the way, but nevertheless we like sources to be as unbiased as possible. The FDA, which is not completely unbiased, has produced a good list of references for this, about half of which we would consider biased, and half unbiased; the clue is generally in the journal names. For example, Food Chemistry and the Journal of Food Science and Journal of Nutrition are probably less biased than the International Dairy Association and the Journal of Dairy Science:
FDA | Raw Milk Misconceptions and the Danger of Raw Milk Consumption
this page covers a lot of other myths too, more than we have room to “bust” here, but it’s very interesting reading and we recommend to check it out!
Notably, we also weren’t able to find any refutation by counterexample on PubMed, with the very slight exception that some studies sometimes found that in the case of milks that were of low quality, pasteurization can reduce the vitamin E content while increasing the vitamin A content. For most milks however, no significant change was found, and in all cases we looked at, B-vitamins were comparable and vitamin D, popularly touted as a benefit of cow’s milk, is actually added later in any case. And, importantly, because this is a common argument, no change in lipid profiles appears to be findable either.
In science, when something has been well-studied and there aren’t clear refutations by counterexample, and the weight of evidence is clearly very much tipped into one camp, that usually means that camp has it right.
Milk generally is good/bad for the health: True or False?
True or False, depending on what we want to look at. It’s definitely not good for inflammation, but the whole it seems to be cancer-neutral and only increases heart disease risk very slightly:
- Keep Inflammation At Bay ← short version is milk is bad, fermented milk products are fine in moderation
- Is Dairy Scary? ← short version is that milk is neither good nor terrible; fermented dairy products however are health-positive in numerous ways when consumed in moderation
You may be wondering…
…how this goes for the safety of dairy products when it comes to the bird flu currently affecting dairy cows, so:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Ketogenic Diet: Burning Fat Or Burning Out?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
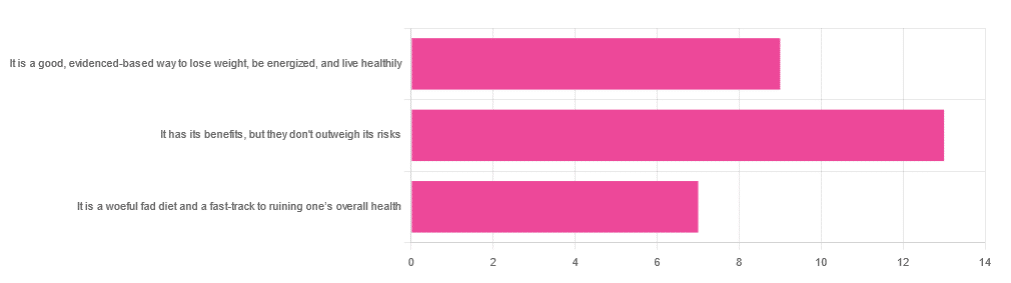
In Wednesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion of the keto diet, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- About 45% said “It has its benefits, but they don’t outweigh the risks”
- About 31% said “It is a good, evidence-based way to lose weight, be energized, and live healthily”
- About 24% said “It is a woeful fad diet and a fast-track to ruining one’s overall health”
So what does the science say?
First, what is the ketogenic diet?
There are two different stories here:
- Per science, it’s a medical diet designed to help treat refractory epilepsy in children.
- Per popular lore, it’s an energizing weight loss diet for Instagrammers and YouTubers.
Can it be both? The answer is: yes, but with some serious caveats, which we’ll cover over the course of today’s feature.
The ketogenic diet works by forcing the body to burn fat for energy: True or False?
True! This is why it helps for children with refractory epilepsy. By starving the body (including the brain) of glucose, the liver must convert fat into fatty acids and ketones, which latter the brain (and indeed the rest of the body) can now use for energy instead of glucose, thus avoiding one of the the main triggers of refractory epilepsy in children.
See: The Ketogenic Diet: One Decade Later | Pediatrics
Even the pediatric epilepsy studies, however, conclude it does have unwanted side effects, such as kidney stones, constipation, high cholesterol, and acidosis:
Source: Dietary Therapies for Epilepsy
The ketogenic diet is good for weight loss: True or False?
True! Insofar as it does cause weight loss, often rapidly. Of course, so do diarrhea and vomiting, but these are not usually held to be healthy methods of weight loss. As for keto, a team of researchers recently concluded:
❝As obesity rates in the populace keep rising, dietary fads such as the ketogenic diet are gaining traction.
Although they could help with weight loss, this study had a notable observation of severe hypercholesterolemia and increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease among the ketogenic diet participants.❞
~ Dr. Shadan Khdher et al.
On which note…
The ketogenic diet is bad for the heart: True or False?
True! As Dr. Joanna Popiolek-Kalisz concluded recently:
❝In terms of cardiovascular mortality, the low-carb pattern is more beneficial than very low-carbohydrate (including the ketogenic diet). There is still scarce evidence comparing ketogenic to the Mediterranean diet.
Other safety concerns in cardiovascular patients such as adverse events related to ketosis, fat-free mass loss, or potential pharmacological interactions should be also taken into consideration in future research.❞
~ Dr. Joanna Popiolek-Kalisz
Read in full: Ketogenic diet and cardiovascular risk: state of the art review
The ketogenic diet is good for short-term weight loss, but not long-term maintenance: True or False?
True! Again, insofar as it works in the short term. It’s not the healthiest way to lose weight and we don’t recommend it, but it did does indeed precipitate short-term weight loss. Those benefits are not typically observed for longer than a short time, though, as the above-linked paper mentions:
❝The ketogenic diet does not fulfill the criteria of a healthy diet. It presents the potential for rapid short-term reduction of body mass, triglycerides level, Hb1Ac, and blood pressure.
Its efficacy for weight loss and the above-mentioned metabolic changes is not significant in long-term observations.❞
~ Ibid.
The ketogenic diet is a good, evidence-based way to lose weight, be energized, and live healthily: True or False?
False, simply, as you may have gathered from the above, but we’ve barely scratched the surface in terms of the risks.
That said, as mentioned, it will induce short-term weight loss, and as for being energized, typically there is a slump-spike-slump in energy:
- At first, the body is running out of glucose, and so naturally feels weak and tired.
- Next, the body enters ketosis, and so feels energized and enlivened ← this is the part where the popular enthusiastic reviews come from
- Then, the body starts experiencing all the longer-term problems associated with lacking carbohydrates and having an overabundance of fat, so becomes gradually more sick and tired.
Because of this, the signs of symptoms of being in ketosis (aside from: measurably increased ketones in blood, breath, and urine) are listed as:
- Bad breath
- Weight loss
- Appetite loss
- Increased focus and energy
- Increased fatigue and irritability
- Digestive issues
- Insomnia
The slump-spike-slump we mentioned is the reason for the seemingly contradictory symptoms of increased energy and increased fatigue—you get one and then the other.
Here’s a small but illustrative study, made clearer by its participants being a demographic whose energy levels are most strongly affected by dietary factors:
The ketogenic diet is a woeful fad diet and a fast-track to ruining one’s overall health: True or False?
True, subjectively in the first part, as it’s a little harsher than we usually go for in tone, though it has been called a fad diet in scientific literature. The latter part (ruining one’s overall health) is observably true.
One major problem is incidental-but-serious, which is that a low-carb diet is typically a de facto low-fiber diet, which is naturally bad for the gut and heart.
Other things are more specific to the keto diet, such as the problems with the kidneys:
However, kidney stones aren’t the worst of the problems:
Is Losing Weight Worth Losing Your Kidney: Keto Diet Resulting in Renal Failure
We’re running out of space and the risks associated with the keto diet are many, but for example even in the short term, it already increases osteoporosis risk:
❝Markers of bone modeling/remodeling were impaired after short-term low-carbohydrate high-fat diet, and only one marker of resorption recovered after acute carbohydrate restoration❞
~ Dr. Ida Heikura et al.
A Short-Term Ketogenic Diet Impairs Markers of Bone Health in Response to Exercise
Want a healthier diet?
We recommend the Mediterranean diet.
See also: Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean
(the above is about keeping to the Mediterranean diet, while tweaking one’s choices within it for a specific extra health focus such as an anti-inflammatory upgrade, a heart-healthy upgrade, a gut-healthy upgrade, and a brain-healthy upgrade)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Green Tea Allergies and Capsules
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Hey Sheila – As always, your articles are superb !! So, I have a topic that I’d love you guys to discuss: green tea. I used to try + drink it years ago but I always got an allergic reaction to it. So the question I’d like answered is: Will I still get the same allergic reaction if I take the capsules ? Also, because it’s caffeinated, will taking it interfere with iron pills, other vitamins + meds ? I read that the health benefits of the decaffeinated tea/capsules are not as great as the caffeinated. Any info would be greatly appreciated !! Thanks much !!❞
Hi! I’m not Sheila, but I’ll answer this one in the first person as I’ve had a similar issue:
I found long ago that taking any kind of tea (not herbal infusions, but true teas, e.g. green tea, black tea, red tea, etc) on an empty stomach made me want to throw up. The feeling would subside within about half an hour, but I learned it was far better to circumvent it by just not taking tea on an empty stomach.
However! I take an l-theanine supplement when I wake up, to complement my morning coffee, and have never had a problem with that. Of course, my physiology is not your physiology, and this “shouldn’t” be happening to either of us in the first place, so it’s not something there’s a lot of scientific literature about, and we just have to figure out what works for us.
This last Monday I wrote (inspired in part by your query) about l-theanine supplementation, and how it doesn’t require caffeine to unlock its benefits after all, by the way. So that’s that part in order.
I can’t speak for interactions with your other supplements or medications without knowing what they are, but I’m not aware of any known issue, beyond that l-theanine will tend to give a gentler curve to the expression of some neurotransmitters. So, if for example you’re talking anything that affects that (e.g. antidepressants, antipsychotics, ADHD meds, sleepy/wakefulness meds, etc) then checking with your doctor is best.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: