The Sun Exposure Dilemma
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Sun Exposure Dilemma
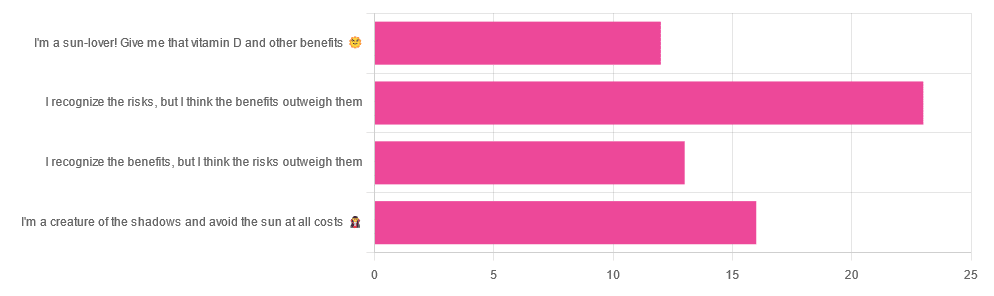
Yesterday, we asked you about your policy on sun exposure, and got the above-pictured, below-described, set of answers:
- A little over a third of respondents chose “I recognize the risks, but I think the benefits outweigh them”
- A quarter of respondents chose “I am a creature of the shadows and I avoid the sun at all costs”
- A little over a fifth of respondents chose “I recognize the benefits, but I think the risks outweigh them”
- A little under a fifth of respondents chose “I’m a sun-lover! Give me that vitamin D and other benefits!”
All in all, this is perhaps the most even spread of answers we’ve had for Friday mythbuster polls—though the sample size was smaller than it often is.
Of those who added comments, common themes were to mention your local climate, and the importance of sunscreen and/or taking vitamin D supplements.
One subscriber mentioned having lupus and living in Florida, which is a particularly unfortunate combination:
Lupus Foundation | Lupus & UV exposure: What you need to know
Another subscriber wrote:
❝Use a very good sunscreen with a high SPF all the time. Reapply after swimming or as needed! I also wear polarized sunglasses anytime I’m outside.❞
…which are important things to note too, and a lot of people forget!
See also: Who Screens The Sunscreens? (on fearing chemical dangers, vs the protection given)
But, onto today’s science for the topic at hand…
We need to get plenty of sun to get plenty of vitamin D: True or False?
True or False, depending on so many factors—to the point that many people get it wildly wrong in either direction.
Whether we are getting enough vitamin D depends on many circumstances, including:
- The climate (and depending on latitude, time of year) where we live
- Our genes, and especially (but not only) our skintone
- The clothes we wear (or don’t)
- Our diet (and not just “how much vitamin D do we consume”)
- Chronic diseases that affect vitamin D metabolism and/or requirements and/or sensitivity to the sun
For a rundown on these factors and more, check out:
Should I be getting my vitamin D levels checked?
Notably, on the topic of whether you should stay in the sun for longer to get more vitamin D…
❝The body can only produce a certain amount of vitamin D at the time, so staying in the sun any longer than needed (which could be just a few minutes, in a sunny climate) is not going to help increase your vitamin D levels, while it will increase your risk of skin cancer.❞
In contrast, she does also note:
❝During winter, catching enough sun can be difficult, especially if you spend your days confined indoors. Typically, the required exposure increases to two to three hours per week in winter. This is because sunlight exposure can only help produce vitamin D if the UVB rays reach us at the correct angle. So in winter we should regularly spend time outside in the middle of the day to get our dose of vitamin D.❞
See also: Vitamin D & Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
We can skip the sun and get our vitamin D from diet/supplements: True or False?
True! However, vitamin D is not the only health benefit of sun exposure.
Not only is sunlight-induced serotonin production important for many things ranging from mood to circadian rhythm (which in turn affects many other aspects of health), but also…
While too much sun can cause skin cancer, too little sun could cause other kinds of cancer:
Benefits of Sunlight: A Bright Spot for Human Health
Additionally, according to new research, the circadian rhythm benefits we mentioned above may also have an impact on type 2 diabetes:
Can catching some rays help you fight off type 2 diabetes?
Which way to jump?
A lot of it depends on who you are, ranging from the factors we mentioned earlier, to even such things as “having many moles” or “having blonde hair”.
This latter item, blonde hair, is a dual thing: it’s a matter of genetic factors that align with being prone to being more sensitive to the sun, as well as being a lesser physical barrier to the sun’s rays than dark hair (that can block some UV rays).
So for example, if two people have comparably gray hair now, but one of them used to have dark hair and the other blonde, there will still be a difference in how they suffer damage, or don’t—and yes, even if their skin is visually of the same approximate skintone.
You probably already know for yourself whether you are more likely to burn or tan in the sun, and the former group are less resistant to the sun’s damage… But the latter group are more likely to spend longer in the sun, and accumulate more damage that way.
If you’d like a very comprehensive downloadable, here are the guidelines issued by the UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence:
NICE Guidelines | Sunlight exposure: risks and benefits
…and skip to “At risk groups”, if you don’t want to read the whole thing; “Skin type” is also an important subsection, which also uses your hair and eye color as indicators.
Writer’s note: genetics are complicated and not everyone will fall neatly into categories, which is why it’s important to know the individual factors.
For example, I am quite light-skinned with slightly graying dark hair and gray-blue eyes, and/but also have an obscure Sámi gene that means my skin makes vitamin D easily, while simultaneously being unusually resistant to burning (I just tan). Basically: built for the midnight sun of the Arctic circle.
And yet! My hobbies include not getting skin cancer, so I tend to still be quite mindful of UV levels in different weathers and times of day, and make choices (schedule, clothing, sunscreen or not) accordingly.
Bottom line:
That big self-perpetuating nuclear explosion in the sky is responsible for many things, good and bad for our health, so be aware of your own risk factors, especially for vitamin D deficiency, and skin cancer.
- If you have a predisposition to both, that’s unfortunate, but diet and supplementation at least can help with the vitamin D while getting modest amounts of sun at most.
- Remember that you can only make so much vitamin D at once, so sunbathing for health benefits need only take a few minutes
- Remember that sunlight is important for our circadian rhythm, which is important for many things.
- That’s governed by specific photoreceptor cells, though, so we don’t need our skin to be exposed for that; we just need to be able to see sunlight.
- If you’re going to be out in the sun, and not covered up, sunscreen is your friend, and yes, that goes for clear cold days under the winter sun too.
- Most phone weather apps these days have a UV index score as part of the data they give. Get used to checking it as often as you’d check for rain.
Stay safe, both ways around!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Polyvagal Theory – by Dr. Stephen Porges
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Do you ever find that your feelings (or occasionally: lack thereof) sometimes can seem mismatched with the observed facts of your situation? This book unravels that mystery—or rather, that stack of mysteries.
Dr. Porges’ work on this topic is, by the way, the culmination of 40 years of research. While he’s not exactly a household name to the layperson, he’s very respected in his field, and this book is his magnum opus.
Here he explains the disparate roles of the two branches of the vagus nerve (hence: polyvagal theory). At least, the two branches that we mammals have; non-mammalian vertebrates have only one. This makes a big difference, because of the cascade of inhibitions that this allows.
The answer to the very general question “What stops you from…?” is usually found somewhere down this line of cascade of inhibitions.
These range from “what stops you from quitting your job/relationship/etc” to “what stops you from freaking out” to “what stops you from relaxing” to “what stops you from reacting quickly” to “what stop you from giving up” to “what stops you from gnawing your arm off” and many many more.
And because sometimes we wish we could do something that we can’t, or wish we wouldn’t do something that we do, understanding this process can be something of a cheat code to life.
A quick note on style: the book is quite dense and can be quite technical, but should be comprehensible to any layperson who is content to take their time, because everything is explained as we go along.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand the mysteries of how you feel vs how you actually are, and what that means for what you can or cannot wilfully do, this is a top-tier book
Click here to check out Polyvagal Theory, and take control of your responses!
Share This Post
-
Sesame Oil vs Almond Oil – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sesame oil to almond oil, we picked the almond.
Why?
We were curious about this one! Were you, or were you confident? You see, almonds tend to blow away all the other nuts with their nutritional density, but they’re far from the oiliest of nuts, and their greatest strengths include their big dose of protein and fiber (which don’t make it into the oil), vitamins (most of which don’t make it into the oil) and minerals (which don’t make it into the oil). So, a lot will come down to the fat profile!
On which note, looking at the macros first, it’s 100% fat in both cases, but sesame oil has more saturated fat and polyunsaturated fat, while almond oil has more monounsaturated fat. Since the mono- and poly-unsaturated fats are both healthy and each oil has more of one or the other, the deciding factor here is which has the least saturated fat—and that’s the almond oil, which has close to half the saturated fat of sesame oil. As an aside, neither of them are a source of omega-3 fatty acids.
In terms of vitamins, there’s not a lot to say here, but “not a lot” is not nothing: sesame oil has nearly 2x the vitamin K, while almond oil has 28x the vitamin E*, and 2x the choline. So, another win for almond oil.
*which is worth noting, not least of all because seeds are more widely associated with vitamin E in popular culture, but it’s the almond oil that provide much more here. Not to get too distracted into looking at the values of the actual seeds and nuts, almonds themselves do have over 102x the vitamin E compared to sesame seeds.
Now, back to the oils:
In the category of minerals, there actually is nothing to say here, except you can’t get more than the barest trace of any mineral from either of these two oils. So it’s a tie on this one.
Adding up the categories makes for a clear win for almond oil!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Online Reaction Tests & Women’s Cognitive Health (Test Yours!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A team of researchers have looked into the use of online reaction tests (in which, for example, one clicks whenever a certain prompt is shown, or for more of a cognitive challenge, one presses a numerical key when the corresponding digit is shown) to cognitive health in women at different ages.
Why women? To quote the man who had the honor of being the first-listed author on the study (something that happens mysteriously often in science),
❝Women have long been under-represented in healthy aging research, despite making up more than half the population. We developed an easy way to measure cognitive function in the home, without the need for individuals to travel to clinics or receive home visits. Our research shows that testing of cognitive function in the home largely acceptable, easy and convenient❞
About that convenience: they used data from the UK Women’s Cohort Study, which involved over 35,000 British women, and then specifically focused on a follow-up study of 768 participants aged 48–85.
Of the two kinds of online reaction tests we described up top, they used the numerical kind. The participants also filled in a questionnaire about their personal traits (demographic data, mostly, though things like self-reported level of health literacy, and how they would rate their overall health).
What they found
The findings included:
- Younger women were more likely to participate, with participation rates dropping from 89% at age 45 to 44% at age 65.
- Each higher level of education increased the likelihood of volunteering by 7%.
- Women who rated themselves as having “high” intelligence were 19% more likely to participate than those who considered themselves of “average” intelligence.
- Women with lower self-reported health literacy made fewer errors, possibly due to taking longer to decide on answers—consistent with findings from older adults.
You can read the full paper itself here: Health literacy in relation to web-based measurement of cognitive function in the home: UK Women’s Cohort Study
Why this matters
We wrote, a little while ago, about the use of online games (of a specific kind) to improve cognitive function:
Synergistic Brain-Training: Let The Games Begin (But It Matters What Kind) ← the good news is, these are very accessible too
When it comes to rapid and/but correct reactions, this becomes really critical:
How (And Why) To Train Your Pre-Frontal Cortex ← Dr. Sandra Chapman advocates strongly for this, and it’s closely related to working memory and the ability to focus
Want to test yours?
Here are two ways to do it (now, for free, without needing to sign up for anything; the tests are right there on the page):
- HumanBenchmark.com’s Reaction Time Test ← this one’s just a “click when the red panel turns green” test, but the merit here is that it compares your scores to a very large dataset of other people
- Keypress Reaction Time Test ← this one’s the kind that was used in the study, and requires pressing the correct numerical key when the corresponding digit is shown on the screen. You can make it easier or harder by restricting or increasing the range of numbers it uses (default setting is to use the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6)
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Sometimes, Perfect Isn’t Practical!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝10 AM breakfast is not realistic for most. What’s wrong with 8 AM and Evening me at 6. Don’t quite understand the differentiation.❞
(for reference, this is about our “Breakfasting For Health?” main feature)
It’s not terrible to do it the way you suggest It’s just not optimal, either, that’s all!
Breakfasting at 08:00 and then dining at 18:00 is ten hours apart, so no fasting benefits between those. Let’s say you take half an hour to eat dinner, then eat nothing again until breakfast, that’s 18:30 to 08:00, so that’s 13½ hours fasting. You’ll recall that fasting benefits start at 12 hours into the fast, so that means you’d only get 1½ hours of fasting benefits.
As for breakfasting at 08:00 regardless of intermittent fasting considerations, the reason for the conclusion of around 10:00 being optimal, is based on when our body is geared up to eat breakfast and get the most out of that, which the body can’t do immediately upon waking. So if you wake and get sunlight at 08:30, get a little moderate exercise, then by 10:00 your digestive system will be perfectly primed to get the most out of breakfast.
However! This is entirely based on you waking and getting sunlight at 08:30.
So, iff you wake and get sunlight at 06:30, then in that case, breakfasting at 08:00 would give the same benefits as described above. What’s important is the 1½ hour priming-time.
Writer’s note: our hope here is always to be informational, not prescriptive. Take what works for you; ignore what doesn’t fit your lifestyle.
I personally practice intermittent fasting for about 21hrs/day. I breakfast (often on nuts and perhaps a little salad) around 16:00, and dine at around 18:00ish, giving myself a little wiggleroom. I’m not religious about it and will slide it if necessary.
As you can see: that makes what is nominally my breakfast practically a pre-dinner snack, and I clearly ignore the “best to eat in the morning” rule because that’s not consistent with my desire to have a family dinner together in the evening while still practicing the level of fasting that I prefer.
Science is science, and that’s what we report here. How we apply it, however, is up to us all as individuals!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Seniors: Improve Blood Flow & Circulation In Your Legs
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Doug Weiss, a physiotherapist (and thus: a doctor of physical therapy), has advice on how and why to increase blood flow and circulation in your legs, keeping yourself healthier for longer and avoiding a lot of potential unpleasantries.
The exercises
The exercises here are not complex; they are as follows, and he suggests 3 sets of 10 reps of each, daily:
- Sitting ankle pumps: sitting on a chair or the edge of a bed, lift the toes up, then heels up, squeezing the muscles.
- Sitting knee extensions: sitting as before, kick one leg up until knee is straight, then switch legs.
- Heel raises: standing this time, with a sturdy support such as a countertop, raise on toes as high as possible, then lower heels back to the ground
- Pillow squats: placing pillows on a chair, cross hands on chest, and simply stand up and sit down—similar to the “getting up off the floor without using your hands” exercise, but an easier version.
For visuals on these, and more details including the specific benefits of each, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
4 Tips To Stand Without Using Hands ← this time it’s the full movement, from the floor, and this is a really important movement to be able to do, as it’s a big indicator of healthy longevity
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Body Is Not an Apology – by Sonya Renee Taylor
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, a couple of things that this book is not about:
- Self-confidence (it’s about more than merely thinking highly of oneself)
- Self-acceptance (it’s about more than merely settling for “good enough”)
In contrast, it’s about loving and celebrating what is, while striving for better, for oneself and for others.
You may be wondering: whence this “radical” in the title?
The author argues that often, the problem with our bodies is not actually our bodies. If we have cancer, or diabetes, then sure, that’s a problem with the body. But most of the time, the “problem with our bodies” is simply society’s rejection of our “imperfect” bodies as somehow “less than”, and something we must invest time and money to correct. Hence, the need for a radical uprooting of ideas, to fix the real problem.
Bottom line: if, like most of us, you have a body that would not entirely pass for that of a Marvel Comics superhero, this is a book for you. And if you do have a MCU body? This is also a book for you, because we have bad news for you about what happens with age.
Click here to check out The Body Is Not An Apology, and appreciate more about yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: