Sugar Blues – by William Dufty
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a “read it cover to cover” book. It charts the rise of sugar’s place in world diets in general and the American diet in particular, and draws many conclusions about the effect this has had on us.
This book will challenge you. Sometimes, it will change your mind. Sometimes, you’ll go “no, I’m sure that’s not right”, and you’ll go Googling. Either way, you’ll learn something.
And that, for us, is the most important measure of any informational book: did we gain something from it? In Sugar Blues, perhaps the single biggest “gain” for the reader is that it’s an eye-opener and a call-to-arms—the extent to which you heed that is up to you, but it sure is good to at least be familiar with the battlefield.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
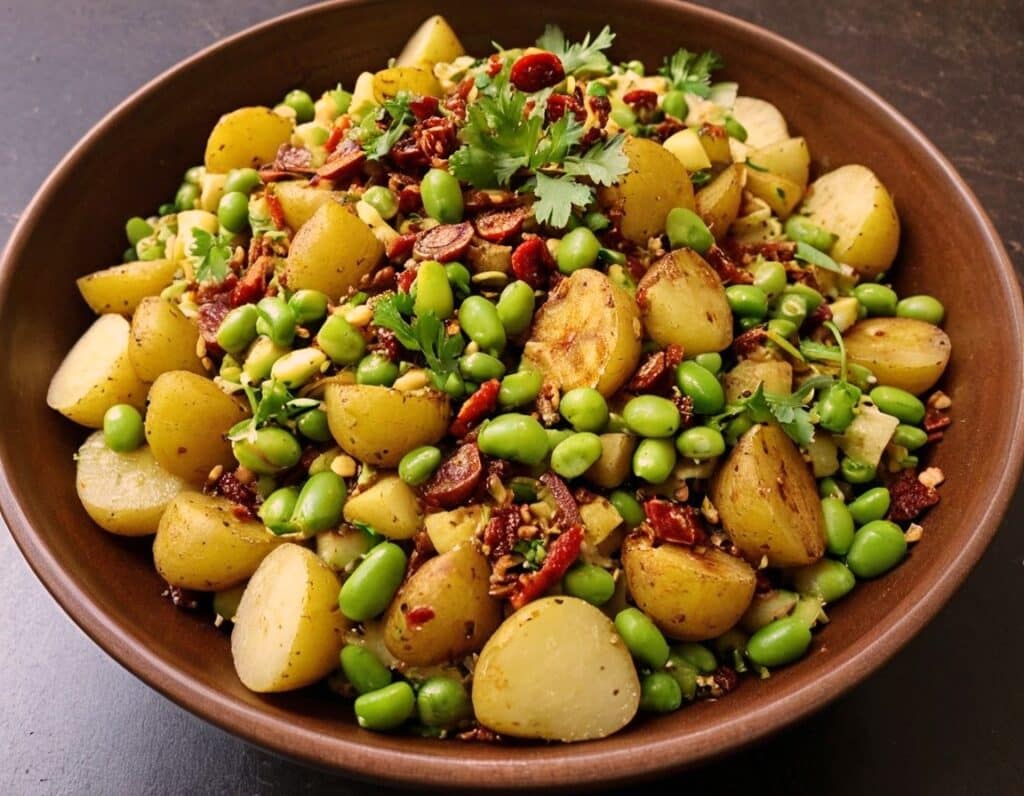
Chaat Masala Spiced Potato Salad With Beans
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is an especially gut-healthy dish; the cooked-and-cooled potatoes are not rich with resistant starches (that’s good), the beans bring protein (as well as more fiber and micronutrients), and many of the spices bring their own benefits. A flavorful addition to your table!
You will need
- 1 lb new potatoes, boiled or steamed, with skin on, quartered, cooled ← this is a bit of a “mini recipe”, but we expect you can handle it
- 5 oz blanched broad beans
- 2 oz sun-dried tomatoes, chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic, crushed
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 2 tsp amchoor
- 2 tsp ground cumin
- 2 tsp ground coriander
- 1 tsp ground ginger
- 1 tsp ground asafoetida
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp red chili powder
- 1 tsp ground turmeric
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Juice of ½ lemon
And then…
- To garnish: finely chopped cilantro, or if you have the “cilantro tastes like soap” gene, then substitute with parsley
- To serve: a nice chutney; you can use our Spiced Fruit & Nut Chutney recipe
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Mix all the ingredients from the main section, ensuring an even distribution on the spices.
2) Add the garnish, and serve with the chutney. That’s it. There was more work in the prep (and potentially, finding all the ingredients) today.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we scored all five today!
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More ← don’t underestimate those sun-dried tomatoes, either!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
7 Steps to Get Off Sugar and Carbohydrates – by Susan Neal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We will not keep the steps a mystery; abbreviated, they are:
- decide to really do this thing
- get knowledge and support
- clean out that pantry/fridge/etc and put those things behind you
- buy in healthy foods while starving your candida
- plan for an official start date, so that everything is ready
- change the way you eat (prep methods, timings, etc)
- keep on finding small ways to improve, without turning back
Particularly important amongst those are starving the candida (the fungus in your gut that is responsible for a lot of carb cravings, especially sugar and alcohol—which latter can be broken down easily into sugar), and changing the “how” of eating as well as the “what”; those are both things that are often overlooked in a lot of guides, but this one delivers well.
Walking the reader by the hand through things like that is probably the book’s greatest strength.
In the category of subjective criticism, the author does go off-piste a little at the end, to take a moment while she has our attention to talk about other things.
For example, you may not need “Appendix 7: How to Become A Christian and Disciple of Jesus Christ”.
Of course if that calls to you, then by all means, follow your heart, but it certainly isn’t a necessary step of quitting sugar. Nevertheless, the diversion doesn’t detract from the good dietary change advice that she has just spent a book delivering.
Bottom line: there’s no deep science here, but there’s a lot of very good, very practical advice, that’s consistent with good science.
Click here to check out 7 Steps to Get Off Sugar, and watch your health improve!
Share This Post
-
Here’s how to help protect your family from norovirus
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- Norovirus is a very contagious infection that causes vomiting and diarrhea.
- The best way to help protect against norovirus is to wash your hands often with soap and warm water, since hand sanitizer may not be effective at killing the virus.
- If someone in your household has symptoms of norovirus, isolate them away from others, watch for signs of dehydration, and take steps to help prevent it from spreading.
If you feel like everyone is sick right now, you’re not alone. Levels of respiratory illnesses like COVID-19, flu, and RSV remain remain high in many states, and the U.S. is also battling a wave of norovirus, one of several viruses that cause a very contagious infection of the stomach and intestines.
Although norovirus infections are more common during the colder months—it’s also called the “winter vomiting disease”—the virus can spread at any time. Right now, however, cases have more than doubled since last year’s peak.
Read on to learn about the symptoms of norovirus, how it spreads, and what to do if someone in your household gets sick.
What are the symptoms of norovirus?
Norovirus is a very contagious infection that causes vomiting and diarrhea, which typically begins 12 to 48 hours after exposure to the virus. Additional symptoms may include stomach pain, body aches, headaches, and a fever. Norovirus typically resolves within three days, but people who are infected may still be contagious for up to two days after symptoms resolve.
Norovirus may cause dehydration, or a dangerous loss of fluids, especially in young children and older adults. See a health care provider if you or someone in your household shows signs of dehydration, which may include decreased urination, dizziness, a dry mouth and throat, sleepiness, and crying without tears.
How can you help protect against norovirus?
You can get norovirus if you have close contact with someone who is infected, touch a contaminated surface and then touch your mouth or nose, or consume contaminated food or beverages.
The best way to help protect yourself and others against norovirus is to wash your hands often with soap and warm water, since hand sanitizer may not be effective at killing the virus. Other ways to help protect yourself may include cooking food thoroughly and washing fruits and vegetables before eating them.
You can get sick with norovirus even if you’ve had it before, since there are many different strains.
How can families help protect against the spread of norovirus at home?
If someone in your household has symptoms of norovirus, isolate them away from others and watch for signs of dehydration. If you are sick with norovirus, do not prepare food for others in your household and use a separate bathroom, if possible.
When cleaning up after someone who has norovirus, wear rubber, latex, or nitrile gloves. Then wash your hands thoroughly.
Clean surfaces using a solution containing five to 25 tablespoons of bleach (that’s 12.5 fluid ounces, or just over ¾ cup), per gallon of water. Leave the bleach-water mix on surfaces for at least five minutes before wiping it off.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What’s the difference between miscarriage and stillbirth?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s the difference? is a new editorial product that explains the similarities and differences between commonly confused health and medical terms, and why they matter.
Former US First Lady Michelle Obama revealed in her memoir she had a miscarriage. UK singer-songwriter and actor Lily Allen has gone on the record about her stillbirth.
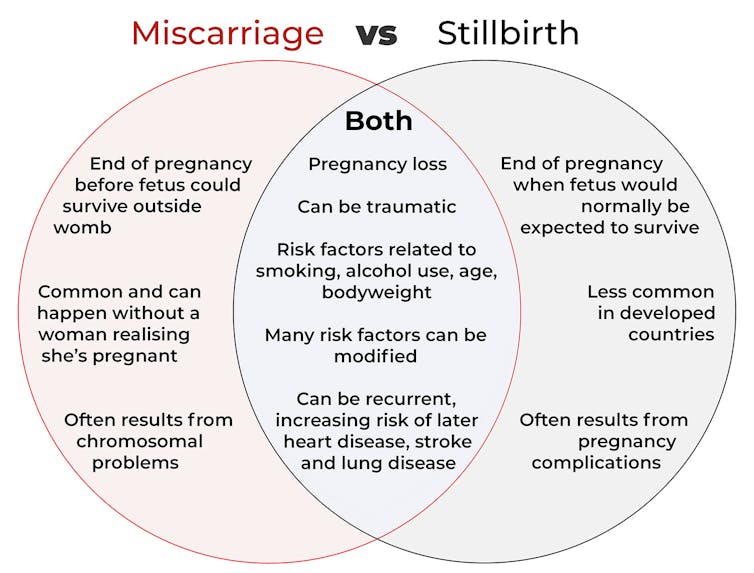
Both miscarriage and stillbirth are sadly familiar terms for pregnancy loss. They can be traumatic life events for the prospective parents and family, and their impacts can be long-lasting. But the terms can be confused.
Here are some similarities and differences between miscarriage and stillbirth, and why they matter.
christinarosepix/Shutterstock Let’s start with some definitions
In broad terms, a miscarriage is when a pregnancy ends while the fetus is not yet viable (before it could survive outside the womb).
This is the loss of an “intra-uterine” pregnancy, when an embryo is implanted in the womb to then develop into a fetus. The term miscarriage excludes ectopic pregnancies, where the embryo is implanted outside the womb.
However, stillbirth refers to the end of a pregnancy when the fetus is normally viable. There may have been sufficient time into the pregnancy. Alternatively, the fetus may have grown large enough to be normally expected to survive, but it dies in the womb or during delivery.
The Australian Institute of Health and Welfare defines stillbirth as a fetal death of at least 20 completed weeks of gestation or with a birthweight of at least 400 grams.
Internationally, definitions of stillbirth vary depending on the jurisdiction.
How common are they?
It is difficult to know how common miscarriages are as they can happen when a woman doesn’t know she is pregnant. There may be no obvious symptoms or something that looks like a heavier-than-normal period. So miscarriages are likely to be more common than reported.
Studies from Europe and North America suggest a miscarriage occurs in about one in seven pregnancies (15%). More than one in eight women (13%) will have a miscarriage at some time in her life.
Around 1–2% of women have recurrent miscarriages. In Australia this is when someone has three or more miscarriages with no pregnancy in between.
Australia has one of the lowest rates of stillbirth in the world. The rate has been relatively steady over the past 20 years at 0.7% or around seven per 1,000 pregnancies.
Who’s at risk?
Someone who has already had a miscarriage or stillbirth has an increased risk of that outcome again in a subsequent pregnancy.
Compared with women who have had a live birth, those who have had a stillbirth have double the risk of another. For those who have had recurrent miscarriages, the risk of another miscarriage is four-fold higher.
Some factors have a u-shaped relationship, with the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth lowest in the middle.
For instance, maternal age is a risk factor for both miscarriage and stillbirth, especially if under 20 years old or older than 35. Increasing age of the male is only a risk factor for stillbirth, especially for fathers over 40.
An older dad can be a risk factor for stillbirth, but not miscarriage. Elizaveta Galitckaia/Shutterstock Similarly for maternal bodyweight, women with a body mass index or BMI in the normal range have the lowest risk of miscarriage and stillbirth compared with those in the obese or underweight categories.
Lifestyle factors such as smoking and heavy alcohol drinking while pregnant are also risk factors for both miscarriage and stillbirth.
So it’s important to not only avoid smoking and alcohol while pregnant, but before getting pregnant. This is because early in the pregnancy, women may not know they have conceived and could unwittingly expose the developing fetus.
Why do they happen?
Miscarriage often results from chromosomal problems in the developing fetus. However, genetic conditions or birth defects account for only 7-14% of stillbirths.
Instead, stillbirths often relate directly to pregnancy complications, such as a prolonged pregnancy or problems with the umbilical cord.
Maternal health at the time of pregnancy is another contributing factor in the risk of both miscarriage and stillbirths.
Chronic diseases, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), polycystic ovary syndrome, problems with the immune system (such as an autoimmune disorder), and some bacterial and viral infections are among factors that can increase the risk of miscarriage.
Similarly mothers with diabetes, high blood pressure, and untreated infections, such as malaria or syphilis, face an increased risk of stillbirth.
In many cases, however, the specific cause of pregnancy loss is not known.
How about the long-term health risks?
Miscarriage and stillbirth can be early indicators of health issues later in life.
For instance, women who have had recurrent miscarriages or recurrent stillbirths are at higher risk of cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease or stroke).
Our research has also looked at the increased risk of stroke. Compared with women who had never miscarried, we found women with a history of three or more miscarriages had a 35% higher risk of non-fatal stroke and 82% higher risk of fatal stroke.
Women who had a stillbirth had a 31% higher risk of a non-fatal stroke, and those who had had two or more stillbirths were at a 26% higher risk of a fatal stroke.
We saw similar patterns in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or COPD, a progressive lung disease with respiratory symptoms such as breathlessness and coughing.
Our data showed women with a history of recurrent miscarriages or stillbirths were at a 36% or 67% higher risk of COPD, respectively, even after accounting for a history of asthma.
Long-term health risks of recurrent miscarriages or stillbirths include developing lung disease later in life. PRPicturesProduction/Shutterstock Why is all this important?
Being well-informed about the similarities and differences between these two traumatic life events may help explain what has happened to you or a loved one.
Where risk factors can be modified, such as smoking and obesity, this information can be empowering for individuals who wish to reduce their risk of miscarriage and stillbirth and make lifestyle changes before they become pregnant.
More information and support about miscarriage and stillbirth is available from SANDS and Pink Elephants.
Gita Mishra, Professor of Life Course Epidemiology, Faculty of Medicine, The University of Queensland; Chen Liang, PhD student, reproductive history and non-communicable diseases in women, The University of Queensland, and Jenny Doust, Clinical Professorial Research Fellow, School of Public Health, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Altered Traits – by Dr. Daniel Goleman & Dr. Richard Davidson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We know that meditation helps people to relax, but what more than that?This book explores the available science.
We say “explore the available science”, but it’d be remiss of us not to note that the authors have also expanded the available science, conducting research in their own lab.
From stress tests and EEGs to attention tests and fMRIs, this book looks at the hard science of what different kinds of meditation do to the brain. Not just in terms of brain state, either, but gradual cumulative anatomical changes, too. Powerful stuff!
The style is very pop-science in presentation, easily comprehensible to all. Be aware though that this is an “if this, then that” book of science, not a how-to manual. If you want to learn to meditate, this isn’t the book for that.
Bottom line: if you’d like to understand more about how different kinds of meditation affect the brain differently, this is the book for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Compass of Pleasure – by Dr. David Linden
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are a lot of books about addiction, so what sets this one apart?
Mostly, it’s that this one maintains that addiction is neither good nor bad per se—just, some behaviors and circumstances are. Behaviors and circumstances caused, directly or indirectly, by addiction.
But, Dr. Linden argues, not every addiction has to be so. Especially behavioral addictions; the rush of dopamine one gets from a good session at the gym or learning a new language, that’s not a bad thing, even if they can fundamentally be addictions too.
Similarly, we wouldn’t be here as a species without some things that rely on some of the same biochemistry as addictions; orgasms and eating food, for example. Yet, those very same urges can also inconvenience us, and in the case of foods and other substances, can harm our health.
In this book, the case is made for shifting our addictive tendencies to healthier addictions, and enough information is given to help us do so.
Bottom line: if you’d like to understand what is going on when you get waylaid by some temptation, and how to be tempted to better things, this book can give the understanding to do just that.
Click here to check out The Compass of Pleasure, and make yours work in your favor!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: