Studies of Parkinson’s disease have long overlooked Pacific populations – our work shows why that must change
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A form of Parkinson’s disease caused by mutations in a gene known as PINK1 has long been labelled rare. But our research shows it’s anything but – at least for some populations.
Our meta-analysis revealed that people in specific Polynesian communities have a much higher rate of PINK1-linked Parkinson’s than expected. This finding reshapes not only our understanding of who is most at risk, but also how soon symptoms may appear and what that might mean for treatment and testing.
Parkinson’s disease is often thought of as a single condition. In reality, it is better understood as a group of syndromes caused by different factors – genetic, environmental or a combination of both.
These varying causes lead to differences in disease patterns, progression and subsequent diagnosis. Recognising this distinction is crucial as it paves the way for targeted interventions and may even help prevent the disease altogether.

Why we focus on PINK1-linked Parkinson’s
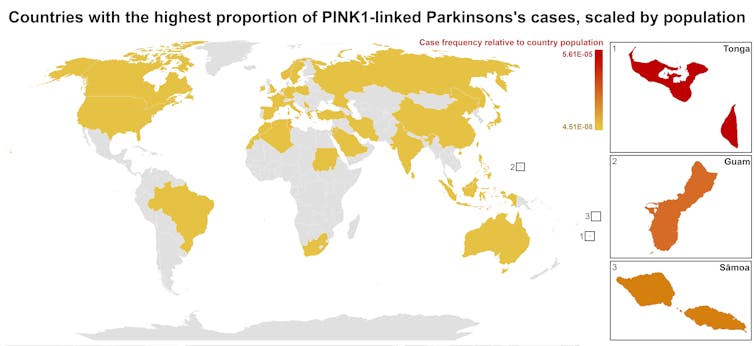
We became interested in this gene after a 2021 study highlighted five people of Samoan and Tongan descent living in New Zealand who shared the same PINK1 mutation.
Previously, this mutation had been spotted only in a few more distant places –Malaysia, Guam and the Philippines. The fact it appeared in people from Samoan and Tongan backgrounds suggested a historical connection dating back to early Polynesian migrations.
One person in 1,300 West Polynesians carries this mutation. This is a frequency well above what scientists usually classify as rare (below one in 2,200). This discovery means we may be overlooking entire communities in Parkinson’s research if we continue to assume PINK1-linked cases are uncommon.
Traditional understanding says PINK1-linked Parkinson’s is both rare and typically strikes younger people, mostly in their 30s or 40s, if they inherit two faulty copies of the gene. In other words, it’s considered a recessive condition, needing two matching puzzle pieces before the disease can unfold.
Our work challenges this view. We show that even one defective PINK1 gene can cause Parkinson’s at an average age of 43, much earlier than the typical onset after 65. That’s a significant departure from the standard belief that only people with two defective gene copies are at risk.
Why this matters for people with the disease
It’s not just genetics that challenge long-held views. Historically, PINK1-linked Parkinson’s was thought to lack some of the classic features of the disease, such as toxic clumps of alpha-synuclein protein.
In typical Parkinson’s, alpha-synuclein builds up in the brain, forming sticky clumps known as Lewy bodies. Our results, contrary to prior beliefs, show that alpha-synuclein pathology is present in 87.5% of PINK1 cases. This finding opens up a promising new avenue for future treatment development.
The biggest concern is early onset. PINK1-linked Parkinson’s can begin as early as 11 years old, although a more common starting point is around the mid-30s. This early onset means living longer with the disease, which can profoundly affect education, work opportunities and family life.
Current treatments (such as levodopa, a precursor of dopamine) help manage symptoms, but they’re not designed to address the root cause. If we know someone has a PINK1 mutation, scientists and clinicians can explore therapies for specific genetic pathways, potentially delivering relief beyond symptom management.
Sex differences add a layer of complexity
In Parkinson’s, generally, men are at higher risk and tend to develop symptoms earlier. However, our findings suggest the opposite pattern for PINK1-linked cases. Particularly, women with two defective copies of the gene experience onset earlier than men.
This highlights the need to consider sex-related factors in Parkinson’s research. Overlooking them risks missing key elements of the disease.
Genetic testing could be a game-changer for PINK1-linked Parkinson’s. Because it often appears earlier, doctors may not recognise it immediately, especially if they are more familiar with the common, later-onset form of Parkinson’s.
Early genetic testing could lead to a faster, more accurate diagnosis, allowing treatment to begin when interventions are most effective. It would help families understand how the disease is inherited, enabling relatives to get tested.
In some cases, where appropriate and culturally acceptable, embryo screening may be considered to prevent the passing of the faulty gene.
Knowing you have a PINK1 mutation could also make finding the right treatment more efficient. Instead of a lengthy trial-and-error process with different medications, doctors could use emerging therapies designed to target the underlying PINK1 mutation rather than relying on general Parkinson’s treatments meant for the broader population.
Addressing research gaps
These findings underscore how crucial it is to include diverse populations in health research.
Many communities, such as those in Samoa, Tonga and other Pacific nations, have had little to no involvement in global Parkinson’s genetics studies. This has created gaps in knowledge and real-world consequences for people who may not receive timely or accurate diagnoses.
Researchers, funding bodies and policymakers must prioritise projects beyond the usual focus on European or industrialised countries to ensure research findings and treatments are relevant to all affected populations.
To better diagnose and treat Parkinson’s, we need a more inclusive approach. Recognising that PINK1-linked Parkinson’s is not as rare as previously thought – and that genetics, sex differences and cultural factors all play a role – allows us to improve care for everyone.
By expanding genetic testing, refining treatments and ensuring research reflects the full spectrum of Parkinson’s, we can move closer to more precise diagnoses, targeted therapies and better support systems for all.
Victor Dieriks, Research Fellow in Health Sciences, University of Auckland, Waipapa Taumata Rau and Eden Paige Yin, PhD candidate in Health Sciences, University of Auckland, Waipapa Taumata Rau
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Lucid Dreaming: How To Do It, & Why
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Lucid Dreaming: Methods & Uses
We’ve written about dreaming more generally before:
Today we’re going to be talking more about a subject we’ve only touched on previously: lucid dreaming
What it is: lucid dreaming is the practice of being mentally awake while dreaming, with awareness that it is a dream, and control over the dream.
Why is it useful? Beyond simply being fun, it can banish nightmares, it can improve one’s relationship with sleep (always something to look forward to, and sleep doesn’t feel like a waste of time at all!), and it can allow for exploring a lot of things that can’t easily be explored otherwise—which can be quite therapeutic.
How to do it
There are various ways to induce lucid dreaming, but the most common and “entry-level” method is called Mnemonic-Induced Lucid Dreaming (MILD).
MILD involves having some means of remembering what one has forgotten, i.e., that one is dreaming. To break it down further, first we’ll need to learn how to perform a reality check. Again, there are many of these, but one of the simplest is to ask yourself:
How did I get here?
- If you can retrace your steps with relative ease and the story of how you got here does not sound too much like a dream sequence, you are probably not dreaming.
- If you are dreaming, however, chances are that nothing actually led to where you are now; you just appeared here.
Other reality checks include checking whether books, clocks, and/or lightswitches work as they should—all are notorious for often being broken in dreams; books have gibberish or missing or repeated text; clocks do not tell the correct time and often do not even tell a time that could be real (e.g: 07:72), and lightswitches may turn a light on/off without actually changing the level of illumination in the room.
Now, a reality check is only useful if you actually perform it, so this is where MILD comes in.
You need to make a habit of doing a reality check frequently. Whenever you remember, it’s a good time to do a reality check, but you should also try tying it to something. Many people use a red light, because then they can also use a timed red light during the night to subconsciously cue them that they are dreaming. But it could be as simple as “whenever I go to the bathroom, I do a reality check”.
With this in mind, a fun method that has extra benefits is to try to use a magical power, such as psychokinesis. If (while fully awake) whenever you go to pick up some object you imagine it just wooshing magically to meet your hand halfway, then at some point you’ll instinctively do that while dreaming, and it’ll stand a good chance of working—and thus cluing you in that you are dreaming.
How to stay lucid
When you awaken within a dream (i.e. become lucid), there’s a good chance of one of two things happening quickly:
- you forget again
- you wake up
So when you realize you are dreaming, do two things at once:
- verbally repeat to yourself “I am dreaming now”. This will help stretch your awareness from one second to the next.
- look at your hands, and touch things, especially the floor and/or walls. This will help to ground you within the dream.
Things to do while lucid
Flying is a good fun entry-level activity; it’s very common to initially find it difficult though, and only be able to lift up very slightly before gently falling down, or things like that. A good tip is: instead of trying to move yourself, you stay still and move the dream around you, as though you are rotating a 3D model (because guess what: you are).
Confronting your nightmares and/or general fears is a good thing for many. Think, while you’re still awake during the day, about what you would do about the source/trigger of your fear if you had magical powers. Whatever you choose, keep it consistent for now, because this is about habit-forming.
Example: let’s say there’s a person from your past who appears in your nightmares. Let’s say your chosen magic would be “I would cause the ground to open up, swallow them, and close again behind them”. Vividly imagine that whenever they come to mind while you are awake, and when you encounter them next in a nightmare, you’ll remember to do exactly that, and it’ll work.
Learning about your own subconscious is a more advanced activity, but once you’re used to lucid dreaming, you can remember that everything in there is an internal projection of your own mind, so you can literally talk to parts of your subconscious, including past versions of yourself, or singular parts of your greater-whole personality, as per IFS:
Take Care Of Your “Unwanted” Parts Too!
Want to know more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Carbonated Water: For Weight Loss, Satiety, Or Just Gas?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are two main mechanisms of action by which sparkling water is considered to help satiety and/or weight loss; they are:
- It “fills us up” such that we feel fuller sooner, and thus eat less, and thus (all other things being equal) perhaps lose weight
- The carbon dioxide is absorbed into the bloodstream, where (as a matter of chemistry) it improves glucose metabolism, thus lowering blood sugars and indirectly leading (potentially) to weight loss, but even if not, lowered blood sugars are good for most people most of the time, right?
However, there are just a few problems:
Full of gas?
Many people self-report enjoying sparkling water as a way to feel fuller while fasting (or even while eating). However, the plural of “anecdote” is not “data”, so, here be data… Ish:
❝In order to determine whether such satiating effects occur through oral carbonic stimulation alone, we conducted modified sham-feeding (SF) tests (carbonated water ingestion (CW), water ingestion (W), carbonated water sham-feeding (CW-SF), and water sham-feeding (W-SF)), employing an equivalent volume and standardized temperature of carbonated and plain water, in a randomized crossover design.
Thirteen young women began fasting at 10 p.m. on the previous night and were loaded with each sample (15ºC, 250 mL) at 9 a.m. on separate days. Electrogastrography (EGG) recordings were obtained from 20 min before to 45 min after the loading to determine the power and frequency of the gastric myoelectrical activity. Appetite was assessed using visual analog scales. After ingestion, significantly increased fullness and decreased hunger ratings were observed in the CW group. After the load, transiently but significantly increased fullness as well as decreased hunger ratings were observed in the CW-SF group. The powers of normogastria (2-4 cpm) and tachygastria (4-9 cpm) showed significant increases in the CW and W groups, but not in the CW-SF and W-SF groups. The peak frequency of normogastria tended to shift toward a higher band in the CW group, whereas it shifted toward a lower band in the CW-SF group, indicating a different EGG rhythm.
Our results suggest that CO2-induced oral stimulation is solely responsible for the feeling of satiety.❞
~ Dr. Maki Suzuki et al.
Now, that’s self-reported, and a sample size of 13, so it’s not the most airtight science ever, but it is at least science. Here’s the paper, by the way:
Oral Carbonation Attenuates Feeling of Hunger and Gastric Myoelectrical Activity in Young Women
Here’s another small study with 8 people, which found that still and sparkling water had the exact same effect:
Effect of carbonated water on gastric emptying and intragastric meal distribution
However, drinking water (still or sparkling) with a meal will not have anywhere near the same effect for satiety as consuming food that has a high water-content.
See also: Some Surprising Truths About Hunger And Satiety ← our main feature in which we examine the science of volumetrics, including a study that shows how water incorporated into a food (but not served with a food) decreases caloric intake.
As an aside, one difference that carbonation can make is to increase ghrelin levels—that’s the hunger hormone (the satiety hormone is leptin, by the way). This one’s a rat study, but it seems reasonable that the same will be true of humans:
…which is worth bearing in mind even if you yourself are not, in fact, a male rat.
The glucose guzzler?
This one has simply been the case of a study being misrepresented, for example here:
Fizzy water might aid weight loss by providing a small boost to glucose uptake and metabolism
The idea is that higher levels of carbon dioxide in the blood mean faster glucose metabolism, which is technically true. Now, often “technically true” is the best kind of true, but not here, because it’s simply not useful.
In short, we produce so much carbon dioxide as part of our normal respiratory processes, that any carbon dioxide we might consume in a carbonated water is barely a blip in the graph.
Oh, and that article we just linked? Even within the article, despite running with that headline, the actual scientists quoted are saying such things as:
❝While there is a hypothetical link between carbonated water and glucose metabolism, this has yet to be tested in well-designed human intervention studies❞
~ Professor Sumantra Ray
Note: the word “hypothetical” means “one level lower than theoretical”. This is very far from being a conclusion.
And the study itself? Wasn’t even about carbonated water, it was about kidney dialysis and how the carbon dioxide content can result in hypoglycemia:
The mechanism of hypoglycemia caused by hemodialysis
…which got referenced in this paper (not a study):
Can carbonated water support weight loss?
…and even that concluded:
❝CO2 in carbonated water may promote weight loss by enhancing glucose uptake and metabolism in red blood cells.
However, the amount is so small that it is difficult to expect weight loss effects solely from the CO2 in carbonated water.
Drinking carbonated water may also affect blood glucose measurements.❞
Note: the word “may”, when used by a scientist and in the absence of any stronger claims, means “we haven’t ruled out the possibility”.
What breaking news that is.
Stop the press! No, really, stop it!
So… What does work?
There are various ways of going about actually hacking hunger (and they stack; i.e. you can use multiple methods and get cumulative results), and we wrote about them here:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Mediterranean Diet… In A Pill?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Does It Come In A Pill?
For any as yet unfamiliar with the Mediterranean diet, you may be wondering what it involves, beyond a general expectation that it’s a diet popularly enjoyed in the Mediterranean. What image comes to mind?
We’re willing to bet that tomatoes feature (great source of lycopene, by the way, and if you’re not getting lycopene, you’re missing out), but what else?
- Salads, perhaps? Vegetables, olives? Olive oil, yea or nay?
- Bread? Pasta? Prosciutto, salami? Cheese?
- Pizza but only if it’s Romana style, not Chicago?
- Pan-seared liver, with some fava beans and a nice Chianti?
In fact, the Mediterranean diet is quite clear on all these questions, so to read about these and more (including a “this yes, that no” list), see:
What Is The Mediterranean Diet, And What Is It Good For?
So, how do we get that in a pill?
A plucky band of researchers, Dr. Chiara de Lucia et al. (quite a lot of “et al.”; nine listed authors on the study), wondered to what extent the benefits of the Mediterranean diet come from the fact that the Mediterranean diet is very rich in polyphenols, and set about testing that, by putting the same polyphenols in capsule form, and running a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover clinical intervention trial.
Now, polyphenols are not the only reason the Mediterranean diet is great; there are also other considerations, such as:
- a great macronutrient balance with lots of fiber, healthy fats, moderate carbs, and protein from select sources
- the absence or at least very low presence of a lot of harmful substances such as refined seed oils, added sugars, refined carbohydrates, and the like (“but pasta” yes pasta; in moderation and wholegrain and served with extra sources of fiber and healthy fats, all of which slow down the absorption of the carbs)
…but polyphenols are admittedly very important too; we wrote about some common aspects of them here:
Tasty Polyphenols: Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
As for what Dr. de Lucia et al. put into the capsule, behold…
The ingredients:
- Apple Extract 10.0%
- Pomegranate Extract 10.0%
- Tomato Powder 2.5%
- Beet, Spray Dried 2.5%
- Olive Extract 7.5%
- Rosemary Extract 7.5%
- Green Coffee Bean Extract (CA) 7.5%
- Kale, Freeze Dried 2.5%
- Onion Extract 10.0%
- Ginger Extract 10.0%
- Grapefruit Extract 2.5%
- Carrot, Air Dried 2.5%
- Grape Skin Extract 17.5%
- Blueberry Extract 2.5%
- Currant, Freeze Dried 2.5%
- Elderberry, Freeze Dried 2.5%
And the relevant phytochemicals they contain:
- Quercetin
- Luteolin
- Catechins
- Punicalagins
- Phloretin
- Ellagic Acid
- Naringin
- Apigenin
- Isorhamnetin
- Chlorogenic Acids
- Rosmarinic Acid
- Anthocyanins
- Kaempferol
- Proanthocyanidins
- Myricetin
- Betanin
And what, you may wonder, did they find? Well, first let’s briefly summarise the setup of the study:
They took volunteers (n=30), average age 67, BMI >25, without serious health complaints, not taking other supplements, not vegetarian or vegan, not consuming >5 cups of coffee per day, and various other stipulations like that, to create a fairly homogenous study group who were expected to respond well to the intervention. In contrast, someone who takes antioxidant supplements, already eats many different color plants per day, and drinks 10 cups of coffee, probably already has a lot of antioxidant activity going on, and someone with a lower BMI will generally have lower resting levels of inflammatory markers, so it’s harder to see a change, proportionally.
About those inflammatory markers: that’s what they were testing, to see whether the intervention “worked”; essentially, did the levels of inflammatory markers go up or down (up is bad; down is good).
For more on inflammation, by the way, see:
How to Prevent (or Reduce) Inflammation
…which also explains what it actually is, and some important nuances about it.
Back to the study…
They gave half the participants the supplement for a week and the other half placebo; had a week’s gap as a “washout”, then repeated it, switching the groups, taking blood samples before and after each stage.
What they found:
The group taking the supplement had lower inflammatory markers after a week of taking it, while the group taking the placebo had relatively higher inflammatory markers after a week of taking it; this trend was preserved across both groups (i.e., when they switched roles for the second half).
The results were very significant (p=0.01 or thereabouts), and yet at the same time, quite modest (i.e. the supplement made a very reliable, very small difference), probably because of the small dose (150mg) and small intervention period (1 week).
What the researchers concluded from this
The researchers concluded that this was a success; the study had been primarily to provide proof of principle, not to rock the world. Now they want the experiment to be repeated with larger sample sizes, greater heterogeneity, larger doses, and longer intervention periods.
This is all very reasonable and good science.
What we conclude from this
That ingredients list makes for a good shopping list!
Well, not the extracts they listed, necessarily, but rather those actual fruits, vegetables, etc.
If nine top scientists (anti-aging specialists, neurobiologists, pharmacologists, and at least one professor of applied statistics) came to the conclusion that to get the absolute most bang-for-buck possible, those are the plants to get the phytochemicals from, then we’re not going to ignore that.
So, take another list above and ask yourself: how many of those 16 foods do you eat regularly, and could you work the others in?
Want to make your Mediterranean diet even better?
While the Mediterranean diet is a top-tier catch-all, it can be tweaked for specific areas of health, for example giving it an extra focus on heart health, or brain health, or being anti-inflammatory, or being especially gut healthy:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Hello Sleep – by Dr. Jade Wu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed other sleep books before, so what makes this one stand out?
Mostly, it’s because this one takes quite a different approach.
While still giving a nod to the sensible advice you’ve already read in many places (including here at 10almonds), Dr. Wu looks to help the reader avoid falling into the trap (or: help the reader get out of the trap, if already there) of focussing so much on getting better sleep that it becomes an all-consuming stressor that takes up much of the day thinking about it, and guess what, much of the night too, because you’re busy working out how sleep-deprived you’re going to be tomorrow.
Instead, Dr. Wu recommends to work with your body rather than against it, worry less, and ultimately sleep better. Of course, the “how” of this is what makes most of the book.
She does also give chapters on things that may be different for you, based on such things as hormones, age, or medical conditions.
The writing style is pop-science but with frequent references to scientific papers as appropriate, making good science very accessible.
Bottom line: if you’ve tried everything else and/but good sleep still eludes you, this book will help you to end the battle and make friends with your sleep (a metaphor the author uses throughout the book, by the way).
Click here to check out Hello Sleep, and indeed get better sleep!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eat To Beat Cancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Controlling What We Can, To Avoid Cancer
Every time a cell in our body is replaced, there’s a chance it will be cancerous. Exactly what that chance is depends on very many factors. Some of them we can’t control; others, we can.
Diet is a critical, modifiable factor
We can’t choose, for example, our genes. We can, for the most part, choose our diet. Why “for the most part”?
- Some people live in a food desert (the Arctic Circle is a good example where food choices are limited by supply)
- Some people have dietary restrictions (whether by health condition e.g. allergy, intolerance, etc or by personal-but-unwavering choice, e.g. vegetarian, vegan, kosher, halal, etc)
But for most of us, most of the time, we have a good control over our diet, and so that’s an area we can and should focus on.
Choose your animal protein wisely
If you are vegan, you can skip this section. If you are not, then the short version is:
- Fish: almost certainly fine
- Poultry: the jury is out; data is leaning towards fine, though
- Red meat: significantly increased cancer risk
- Processed meat: significantly increased cancer risk
For more details (and a run-down on the science behind the above super-summarized version):
- Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy? ← A mythbuster article that outlines many health properties (good and bad) of animal products
- The Whys and Hows of Cutting Meats Out Of Your Diet ← A life-hack article about acting on that information
Skip The Ultra-Processed Foods
Ok, so this one’s probably not a shocker in its simplest form:
❝Studies are showing us is that not only do the ultraprocessed foods increase the risk of cancer, but that after a cancer diagnosis such foods increase the risk of dying❞
Source: Is there a connection between ultraprocessed food and cancer?
There’s an unfortunate implication here! If you took the previous advice to heart and cut out [at least some] meat, and/but then replaced that with ultra-processed synthetic meat, then this was not a great improvement in cancer risk terms.
Ultra-processed meat is worse than unprocessed, regardless of whether it was from an animal or was synthetic.
In other words: if you buy textured soy pieces (a common synthetic meat), it pays to look at the ingredients, because there’s a difference between:
- INGREDIENTS: SOY
- INGREDIENTS: Rehydrated Textured SOY Protein (52%), Water, Rapeseed Oil, SOY Protein Concentrate, Seasoning (SULPHITES) (Dextrose, Flavourings, Salt, Onion Powder, Food Starch Modified, Yeast Extract, Colour: Red Iron Oxide), SOY Leghemoglobin, Fortified WHEAT Flour (WHEAT Flour, Calcium Carbonate, Iron, Niacin, Thiamin), Bamboo Fibre, Methylcellulose, Tomato Purée, Salt, Raising Agent: Ammonium Carbonates
Now, most of those original base ingredients are/were harmless per se (as are/were the grapes in wine—before processing into alcohol), but it has clearly been processed to Hell and back to do all that.
Choose the one that just says “soy”. Or eat soybeans. Or other beans. Or lentils. Really there are a lot of options.
About soy, by the way…
There is (mostly in the US, mostly funded by the animal agriculture industry) a lot of fearmongering about soy. Which is ironic, given the amount of soy that is fed to livestock to be fed to humans, but it does bear addressing:
❝Soy foods are safe for all cancer patients and are an excellent source of plant protein. Studies show soy may improve survival after breast cancer❞
Source: Food risks and cancer: What to avoid
(obviously, if you have a soy allergy then you should not consume soy—for most people, the above advice stands, though)
Advanced Glycation End-Products
These (which are Very Bad™ for very many things, including cancer) occur specifically as a result of processing animal proteins and fats.
Note: not even necessarily ultra-processing, just processing can do it. But ultra-processing is worse. What’s the difference, you wonder?
The difference between “ultra-processed” and just “processed”:
- Your average hotdog has been ultra-processed. It’s not only usually been changed with many artificial additives, it’s also been through a series of processes (physical and chemical) and ends up bearing little relation to the creature it came from.
- Your bacon (that you bought fresh from your local butcher, not a supermarket brand of unknown provenance, and definitely not the kind that might come on the top of frozen supermarket pizza) has been processed. It’s undergone a couple of simple processes on its journey “from farm to table”. Remember also that when you cook it, that too is one more process (and one that results in a lot of AGEs).
Read more: What’s so bad about AGEs?
Note if you really don’t want to cut out certain foods, changing the way you cook them (i.e., the last process your food undergoes before you eat it) can also reduce AGES:
Advanced Glycation End Products in Foods and a Practical Guide to Their Reduction in the Diet
Get More Fiber
❝The American Institute for Cancer Research shows that for every 10-gram increase in fiber in the diet, you improve survival after cancer diagnosis by 13%❞
Source: Plant-based diet is encouraged for patients with cancer
Yes, that’s post-diagnosis, but as a general rule of thumb, what is good/bad for cancer when you have it is good/bad for cancer beforehand, too.
If you’re thinking that increasing your fiber intake means having to add bran to everything, happily there are better ways:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Will there soon be a cure for HIV?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV, is a chronic health condition that can be fatal without treatment. People with HIV can live healthy lives by taking antiretroviral therapy (ART), but this medication must be taken daily in order to work, and treatment can be costly. Fortunately, researchers believe a cure is possible.
In July, a seventh person was reportedly cured of HIV following a 2015 stem cell transplant for acute myeloid leukemia. The patient stopped taking ART in 2018 and has remained in remission from HIV.
Read on to learn more about HIV, the promise of stem cell transplants, and what other potential cures are on the horizon.
What is HIV?
HIV infects and destroys the immune system’s cells, making people more susceptible to infections. If left untreated, HIV will severely impair the immune system and progress to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). People living with untreated AIDS typically die within three years.
People with HIV can take ART to help their immune systems recover and to reduce their viral load to an undetectable level, which slows the progression of the disease and prevents them passing the virus to others.
How can stem cell transplants cure HIV?
Several people have been cured of HIV after receiving stem cell transplants to treat leukemia or lymphoma. Stem cells are produced by the spongy tissue located in the center of some bones, and they can turn into new blood cells.
A mutation on the CCR5 gene prevents HIV from infecting new cells and creates resistance to the virus, which is why some HIV-positive people have received stem cells from donors carrying this mutation. (One person was reportedly cured of HIV after receiving stem cells without the CCR5 mutation, but further research is needed to understand how this occurred.)
Despite this promising news, experts warn that stem cell transplants can be fatal, so it’s unlikely this treatment will be available to treat people with HIV unless a stem cell transplant is needed to treat cancer. People with HIV are at an increased risk for blood cancers, such as Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which stem cell transplants can treat.
Additionally, finding compatible donors with the CCR5 mutation who share genetic heritage with patients of color can be challenging, as donors with the mutation are typically white.
What are other potential cures for HIV?
In some rare cases, people who started ART shortly after infection and later stopped treatment have maintained undetectable levels of HIV in their bodies. There have also been some people whose bodies have been able to maintain low viral loads without any ART at all.
Researchers are studying these cases in their search for a cure.
Other treatment options researchers are exploring include:
- Gene therapy: In addition to stem cell transplants, gene therapy for HIV involves removing genes from HIV particles in patients’ bodies to prevent the virus from infecting other cells.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment is typically used in cancer patients to teach their immune systems how to fight off cancer. Research has shown that giving some HIV patients antibodies that target the virus helps them reach undetectable levels of HIV without ART.
- mRNA technology: mRNA, a type of genetic material that helps produce proteins, has been used in vaccines to teach cells how to fight off viruses. Researchers are seeking a way to send mRNA to immune system cells that contain HIV.
When will there be a cure for HIV?
The United Nations and several countries have pledged to end HIV and AIDS by 2030, and a 2023 UNAIDS report affirmed that reaching this goal is possible. However, strategies to meet this goal include HIV prevention and improving access to existing treatment alongside the search for a cure, so we still don’t know when a cure might be available.
How can I find out if I have HIV?
You can get tested for HIV from your primary care provider or at your local health center. You can also purchase an at-home HIV test from a drugstore or online. If your at-home test result is positive, follow up with your health care provider to confirm the diagnosis and get treatment.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: