Staying Healthy and Active After 60
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Questions and Answers at 10almonds
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
This newsletter has been growing a lot lately, and so have the questions/requests, and we love that! In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
Q: How to be your best self after 60: Self motivation / Avoiding or limiting salt, sugar & alcohol: Alternatives / Ways to sneak in more movements/exercise
…and, from a different subscriber…
Q: Inflammation & over 60 weight loss. Thanks!
Here are some of our greatest hits on those topics:
- Where Nutrition Meets Habits ← focusing on food that’s all three of: healthy + easy + cheap
- How To Keep On Keeping On ← exercise tips for when the motivation wanes
- Keep Inflammation At Bay ← science-based tips and advice
Also, while we’ve recommended a couple of books on stopping (or reducing) drinking, we’ve not done a main feature on that, so we definitely will one of these days!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Aspirin, CVD Risk, & Potential Counter-Risks
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Aspirin Pros & Cons
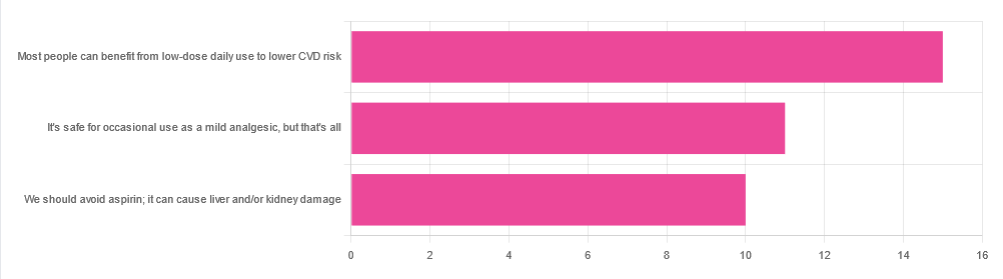
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked your health-related opinion of aspirin, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- About 42% said “Most people can benefit from low-dose daily use to lower CVD risk”
- About 31% said “It’s safe for occasional use as a mild analgesic, but that’s all”
- About 28% said “We should avoid aspirin; it can cause liver and/or kidney damage”
So, what does the science say?
Most people can benefit from low-dose daily aspirin use to lower the risk of cardiovascular disease: True or False?
True or False depending on what we mean by “benefit from”. You see, it works by inhibiting platelet function, which means it simultaneously:
- decreases the risk of atherothrombosis
- increases the risk of bleeding, especially in the gastrointestinal tract
When it comes to balancing these things and deciding whether the benefit merits the risk, you might be asking yourself: “which am I most likely to die from?” and the answer is: neither
While aspirin is associated with a significant improvement in cardiovascular disease outcomes in total, it is not significantly associated with reductions in cardiovascular disease mortality or all-cause mortality.
In other words: speaking in statistical generalizations of course, it may improve your recovery from minor cardiac events but is unlikely to help against fatal ones
The current prevailing professional (amongst cardiologists) consensus is that it may be recommended for secondary prevention of ASCVD (i.e. if you have a history of CVD), but not for primary prevention (i.e. if you have no history of CVD). Note: this means personal history, not family history.
In the words of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology:
❝Low-dose aspirin (75-100 mg orally daily) might be considered for the primary prevention of ASCVD among select adults 40 to 70 years of age who are at higher ASCVD risk but not at increased bleeding risk (S4.6-1–S4.6-8).
Low-dose aspirin (75-100 mg orally daily) should not be administered on a routine basis for the primary prevention of ASCVD among adults >70 years of age (S4.6-9).
Low-dose aspirin (75-100 mg orally daily) should not be administered for the primary prevention of ASCVD among adults of any age who are at increased risk of bleeding (S4.6-10).❞
~ Dr. Donna Arnett et al. (those section references are where you can find this information in the document)
Read in full: Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology
Or if you’d prefer a more pop-science presentation:
Many older adults still use aspirin for CVD prevention, contrary to clinical guidance
Aspirin can cause liver and/or kidney damage: True or False?
True, but that doesn’t mean we must necessarily abstain, so much as exercise caution.
Aspirin is (at recommended doses) not usually hepatotoxic (toxic to the liver), but there is a strong association between aspirin use in children and the development of Reye’s syndrome, a disease involving encephalopathy and a fatty liver. For this reason, most places have an official recommendation that aspirin not be used by children (cut-off age varies from place to place, for example 12 in the US and 16 in the UK, but the key idea is: it’s potentially dangerous for those who are not fully grown).
Aspirin is well-established as nephrotoxic (toxic to the kidneys), however, the toxicity is sufficiently low that this is not expected to be a problem to otherwise healthy adults taking it at no more than the recommended dose.
For numbers, symptoms, and treatment, see this very clear and helpful resource:
An evidence based flowchart to guide the management of acute salicylate (aspirin) overdose
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Mocktails – by Moira Clark
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed books about quitting alcohol before (such as this one), but today’s is not about quitting, so much as about enjoying non-alcoholic drinks; it’s simply a recipe book of zero-alcohol cocktails, or “mocktails”.
What sets this book apart from many of its kind is that every recipe uses only natural and fresh ingredients, rather than finding in the ingredients list some pre-made store-bought component. Instead, because of its “everything from scratch” approach, this means:
- Everything is reliably as healthy as the ingredients you use
- Every recipe’s ingredients can be found easily unless you live in a food desert
Each well-photographed and well-written recipe also comes with a QR code to see a step-by-step video tutorial (or if you get the ebook version, then a direct link as well).
Bottom line: this is the perfect mocktail book to have in (and practice with!) before the summer heat sets in.
Click here to check out Mocktails: A Delicious Collection of Non-Alcoholic Drinks, and get mixing!
Share This Post
-
Avoiding Razor Burn, Ingrown Hairs & Other Shaving Irritation
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How Does The Video Help?
Dr. Simi Adedeji’s incredibly friendly persona makes this video (below) on avoiding skin irritation, ingrown hairs, and razor burn after shaving a pleasure to watch.
To keep things simple, she breaks down her guide into 10 simple tips.
What Are The 10 Simple Tips?
Tip 1: Prioritize Hydration. Shaving dry hair can lead to increased skin irritation, so Dr. Simi recommends moistening the hair by showering or using a warm, wet towel for 2-4 minutes before getting the razor out.
Tip 2: Avoid Dry Shaving. Dry shaving not only removes hair but can also remove the protective upper layer of skin, which contributes to razor burn. To prevent this, simply use some shaving gel or cream.
Tip 3: Keep Blades New and Sharp. This one’s simple: dull blades can cause skin irritation, whilst a sharp blade ensures a smoother and more comfortable shaving experience.
Tip 4: Avoid Shaving the Same Area Repeatedly. Multiple passes over the same area can remove skin layers, leading to cuts and irritation. Aim to shave each area only once for safer results.
Tip 5: Consider Hair Growth Direction. Shaving in the direction of hair growth results in less irritation, although it may not provide the closest shave.
Tip 6: Apply Gentle Pressure While Shaving. Excessive pressure can lead to cuts and nicks. Use a gentle touch to reduce these risks.
Tip 7: Incorporate Exfoliation into Your Routine. Exfoliating helps release trapped hairs and reduces the risk of ingrown hairs. For those with sensitive skin, it’s recommended to exfoliate either two days before or after shaving.
Tip 8: Avoid Excessive Skin Stretching. Over-stretching the skin during shaving can cause hairs to become ingrown.
Tip 9: Moisturize After Shaving. Shaving can compromise the skin barrier, leading to dryness. Using a moisturizer can be a simple fix.
Tip 10: Regularly Rinse Your Blade. Make sure that, during the shaving process, you are rinsing your blade frequently to remove hair and skin debris. This keeps it sharp during your shave.
If this summary doesn’t do it for you, then you can watch the full video here:
How did you find that video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
A Guide to Rational Living – by Drs. Albert Ellis and Robert Harper
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve talked before about the evidence-based benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), and this book is indeed about CBT. In fact, it’s in many ways the book that popularized Third Wave CBT—in other words, CBT in its modern form.
Dr. Ellis’s specific branch of CBT is Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy, (REBT). What this means is using rationality to rewire emotions so that we’re not constantly sabotaging ourselves and our lives.
This is very much a “for the masses” book and doesn’t assume any prior knowledge of psychology, therapy, or psychotherapy. Or, for that matter, philosophy, since Stoic philosopher Epictetus had a lot to say that influenced Dr. Ellis’s work, too!
This book has also been described as “a self-help book for people who don’t like self-help books”… and certainly that Stoicism we mentioned does give the work a very different feel than a lot of books on the market.
The authors kick off with an initial chapter “How far can you go with self-therapy?”, and the answer is: quite far, even if it’s not a panacea. Everything has its limitations, and this book is no exception. On the other hand…
What the book does offer is a whole stack of tools, resources, and “How to…” chapters. In fact, there are so many “How to…” items in this book that, while it can be read cover-to-cover, it can also be used simply as a dip-in reference guide to refer to in times of need.
Bottom line: this book is highly recommendable to anyone and everyone, and if you don’t have it on your bookshelf, you should.
Click here to check out “A Guide To Rational Living” on Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Metformin Slows Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Metformin And How It Slows Down Aging
That’s a bold claim for a title, but the scientific consensus is clear, and this Research Review Monday we’re going to take a look at exactly that!
Metformin is a common diabetes-management drug, used to lower blood sugar levels in people who either don’t have enough insulin or the insulin isn’t being recognized well enough by the body.
However, it also slows aging, which is a quality it’s also been studied for for more than a decade. We’ll look at some of the more recent research, though. Let’s kick off with an initial broad statement, from the paper “The Use of Metformin to Increase the Human Healthspan”, as part of the “Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology” series:
In recent years, more attention has been paid to the possibility of using metformin as an anti-aging drug. It was shown to significantly increase the lifespan in some model organisms and delay the onset of age-associated declines. Growing amounts of evidence from clinical trials suggest that metformin can effectively reduce the risk of many age-related diseases and conditions, including cardiometabolic disorders, neurodegeneration, chronic inflammation and frailty.
How does it work?
That’s still being studied, but the scientific consensus is that it works by inducing hormesis—the process by which minor stress signals cells to start repairing themselves. How does it induce that hormesis? Again, still being studied, but it appears to do it by activating a specific enzyme; namely, the AMP-activated protein kinase:
Read: Metformin-enhances resilience via hormesis
It also has been found to slow aging by means of an anti-inflammatory effect, as a bonus!
Any bad news?
Well, firstly, in most places it’s only prescribed for diabetes management, not for healthy life extension. A lot of anti-aging enthusiasts have turned to the grey market online to get it, and we can’t recommend that.
Secondly, it does have some limitations:
- Its bioavailability isn’t great in tablet form (the form in which it is most commonly given)
- It has quite a short elimination half-life (around 6 hours), which makes it great to fix transient hyperglycemia in diabetics—job done and it’s out—but presents a logistical challenge when it comes to something so pernicious as aging.
- Some people are non-responders (a non-responder, in medicine, is someone for whom a drug simply doesn’t work, for no obvious reason)
Want to know more? Check out:
Metformin in aging and aging-related diseases: clinical applications and relevant mechanism
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Debunking the myth that vaccines cause autism
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The myth that autism is linked to childhood vaccines first appeared in a 1998 study by British physician Dr. Andrew Wakefield. The study was later retracted, and Wakefield was discredited. But nearly three decades after the study’s publication, the myth persists, championed by activists, political leaders, and even potential health officials.
There is overwhelming evidence that there is no link between vaccines and autism. “No one has any real or solid evidence that vaccines cause autism,” says Catherine Lord, a psychologist and autism researcher at the University of California, Los Angeles.
Here are just some of the many reasons that we know vaccines don’t cause autism.
The Wakefield study has been thoroughly discredited
In 1998, the Lancet published a study describing a small group of children who reportedly had bowel inflammation and developed autism within a month of getting the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine. The study proposed that the vaccination triggered bowel inflammation and developmental delays, including autism. Lead author Andrew Wakefield coined the term “autistic enterocolitis” to describe the condition he and his colleagues claimed to have discovered.
The study received significant media attention and immediate criticism from scientists, who pointed out the study’s small size, lack of controls, and insufficient evidence to support its conclusions.
Subsequent research published over the next few years refuted Wakefield’s findings. A 1999 Lancet study found no link between autism and the MMR vaccine, and a 2001 study found no evidence of a link or the existence of so-called autistic enterocolitis.
In 2010, the Lancet finally retracted Wakefield’s fraudulent study, noting that “several elements” of the study were “incorrect” and that the experiments carried out on children had not been approved by an ethics board. The journal’s editor called the paper’s conclusions “utterly false.”
A few months later, Wakefield was stripped of his medical license by the United Kingdom’s General Medical Council. The council deemed Wakefield “dishonest and irresponsible” and concluded that he conducted unethical experiments on children.
The committee’s investigation also revealed that, less than a year before he published his study claiming that the MMR vaccine was linked to bowel inflammation that triggered autism, Wakefield filed a patent for a standalone measles vaccine and inflammatory bowel disease treatment.
Thimerosal was removed from childhood vaccines in 2001—with no effect on autism rates
A 2003 study published by a conservative group known for promoting anti-science myths—including that HIV doesn’t cause AIDS—first proposed that the preservative thimerosal in childhood vaccines is linked to autism. This supposed link was subsequently disproven.
Thimerosal is added in small amounts to some vaccines to prevent dangerous bacterial and fungal contamination. The substance contains ethylmercury, a form of mercury that the body quickly and safely processes in small doses.
Ethylmercury is different from methylmercury, a far more dangerous form of mercury that is toxic at low doses. By contrast, the small amount of thimerosal in some vaccines is harmless to humans and is equal to the amount of mercury in a can of tuna.
The preservative was removed from childhood vaccines as a precautionary measure in 2001. With the exception of some flu shots, no childhood vaccine contains the preservative and hasn’t for more than two decades. Autism rates have not decreased as a result of thimerosal being removed from childhood immunization vaccines. While some types of the annual flu vaccine contain thimerosal, you can get one without it.
Extensive research also shows that neither thimerosal nor methylmercury at any dose is linked to autism. A 2008 study of statewide California data found that autism rates “increased consistently for children born from 1989 through 2003, inclusive of the period when exposure to [thimerosal-containing vaccines] has declined.”
Autism rates are the same in vaccinated and unvaccinated children
Vaccine opponents often falsely claim that vaccinated children are more likely than unvaccinated children to develop autism. Decades of research disprove this false claim.
A 2002 analysis of every child born in Denmark over eight years found that children who received MMR vaccines were no more likely to be diagnosed with autism than unvaccinated children.
A 2015 study of over 95,000 U.S. siblings found that MMR vaccination is not associated with increased autism diagnosis. This was true even among the siblings of children with autism, who are seven times more likely to develop autism than children without an autistic sibling.
And a 2018 study found some evidence that children with autism—and their siblings—were more likely to be unvaccinated or under-vaccinated than children without autism.
Vaccination also has no impact on autism rates at the population level, regardless of the age at which children get vaccinated.
“In comparing countries that have different timing and levels of vaccination … there’s no difference in autism,” says Lord. “You can look at different countries with different rates of autism, and there’s no relationship between the rates of autism and vaccinations.”
Countries such as Taiwan, Tunisia, Turkey, and Morocco, which have some of the world’s lowest autism rates, have childhood immunization rates that are nearly identical to countries with the highest autism rates, including Sweden, Japan, Brunei, and Singapore.
Improved awareness and diagnosis play a role in rising autism rates
Autism was first described in 1911 when it was considered to be a form of severe schizophrenia. Over a century later, our understanding of autism has changed drastically, as have diagnostic standards.
A 2013 scientific article describing how medical and social perceptions of autism have evolved explains that “the diagnoses of schizophrenia, psychosis and autism in children were largely interchangeable during the 1940s and 1950s.” Beginning in the 1960s, methods of diagnosing autism improved, “increasing the number of children who were considered to display autistic traits.”
The autism diagnosis was changed to autism spectrum disorder in 2013. “This category is now very broad, which was an intentional choice to help provide services to the greatest number of people who might need them,” writes Gideon Meyerowitz-Katz, an epidemiologist and creator of the popular Health Nerd blog.
“Rather than the severe intellectual disability of the 1940s and 50s, [autism spectrum disorder] is a group of behaviours that can be any severity as long as they are persistent and impact people’s daily functioning in a significant way.”
For more information about autism, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: