Should Men Over 50 Get PSA?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Loved the information on prostate cancer. Do recommend your readers get a PSA or equivalent test annually for over 50 yr old men.❞
(This is about: Prostate Health: What You Should Know)
Yep, or best yet, the much more accurate PSE test! But if PSA test is what’s available, it’s a lot better than nothing. And, much as it’s rarely the highlight of anyone’s day, a prostate exam by a suitably qualified professional is also a good idea.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

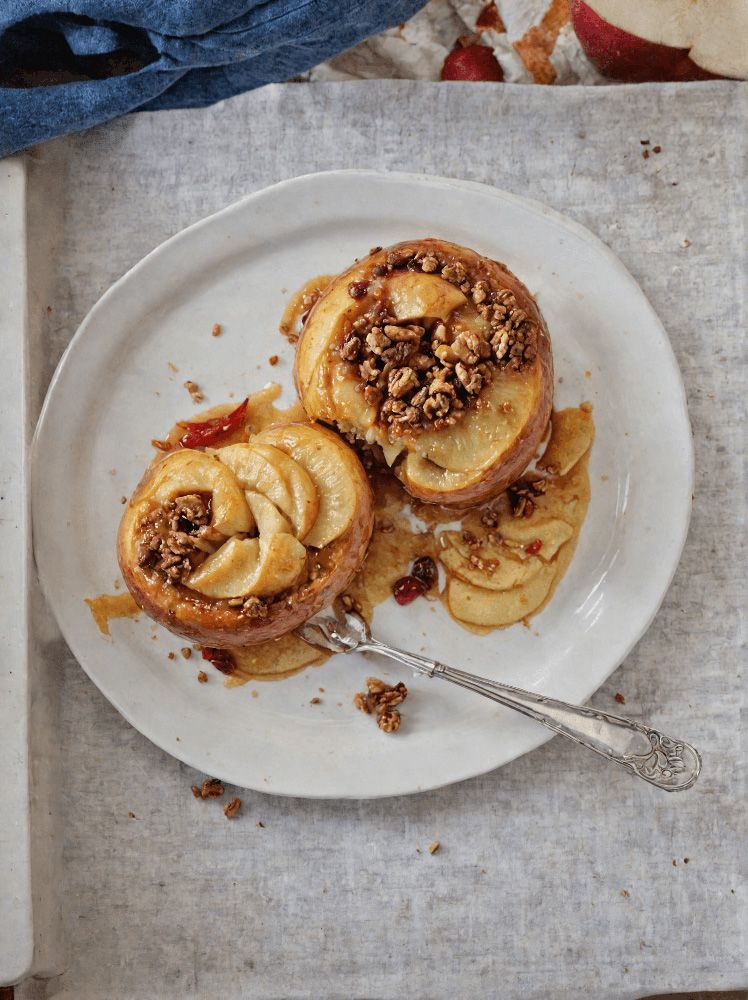
Superfood Baked Apples
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Superfoods, and super-tasty. This is a healthy twist on a classic; your blood sugars will thank you for choosing this tasty sweet delight. It’s also packed with nutrients!
You will need
- 2 large firm baking apples, cored but not peeled
- 1/2 cup chopped walnuts
- 3 tbsp goji berries, rehydrated (soak them in warm water for 10–15minutes and drain)
- 1 tbsp honey, or maple syrup, per your preference (this writer is also a fan of aged balsamic vinegar for its strong flavor and much milder sweetness. If you don’t like things to be too sweet, this is the option for you)
- 2 tsp ground sweet cinnamon
- 1 tsp ground ginger
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 180℃ / 350℉ / gas mark 4
2) Mix the chopped walnuts with the goji berries and the honey (or whatever you used instead of the honey) as well as the sweet cinnamon and the ginger.
3) Place the apples in shallow baking dish, and use the mixture you just made to stuff their holes.
4) Add 1/2 cup water to the dish, around the apples. Cover gently with foil, and bake until soft.
Tip: check them every 20 minutes; they may be done in 40 or it may take 60; in honesty it depends on your oven. If unsure, cook them for longer at a lower temperature.
5) Serve warm.

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose C’s
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- The Sugary Food That Lowers Blood Sugars
- Honey vs Maple Syrup – Which is Healthier?
- A Tale Of Two Cinnamons ← this is important, about why we chose the sweet cinnamon
- Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
Take care!
Share This Post

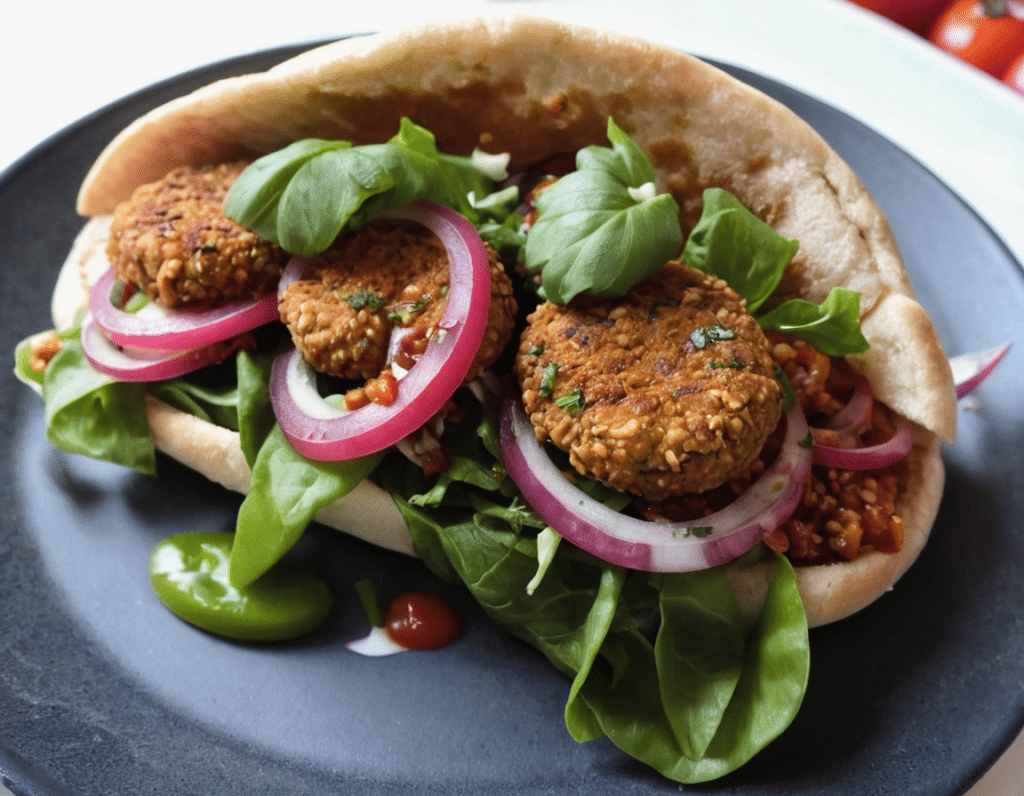
Healthy Harissa Falafel Patties
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You can make these as regular falafel balls if you prefer, but patties are quicker and easier to cook, and are great for popping in a pitta.
You will need
For the falafels:
- 1 can chickpeas, drained, keep the chickpea water (aquafaba)
- 1 red onion, roughly chopped
- 2 tbsp chickpea flour (also called gram flour or garbanzo bean flour)
- 1 bunch parsley
- 1 tbsp harissa paste
- Extra virgin olive oil for frying
For the harissa sauce:
- ½ cup crème fraîche or plant-based equivalent (you can use our Plant-Based Healthy Cream Cheese recipe and add the juice of 1 lemon)*
- 1 tbsp harissa paste (or adjust this quantity per your heat preference)
*if doing this, rather than waste the zest of the lemon, you can add the zest to the falafels if you like, but it’s by no means necessary, just an option
For serving:
- Wholegrain pitta or other flatbread (you can use our Healthy Homemade Flatbreads recipe)
- Salad (your preference; we recommend some salad leaves, sliced tomato, sliced cucumber, maybe some sliced onion, that sort of thing)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the chickpeas, 1 oz of the aquafaba, the onion, the parsley, and the harissa paste, until smooth. Then add in the chickpea flour until you get a thick batter. If you overdo it with the chickpea flour, add a little more of the aquafaba to equalize. Refrigerate the mixture for at least 30 minutes.
2) Heat some oil in a skillet, and spoon the falafel mixture into the pan to make the patties, cooking on both sides (you can use a spatula to gently turn them), and set them aside.
3) Mix the harissa sauce ingredients in a small bowl.
4) Assemble; best served warm, but enjoy it however you like!

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in more of what we have going on today:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- Hero Homemade Hummus ← another great option
Take care!
Share This Post

Are Waist Trainers Just A Waste, And Are Posture Fixers A Quick Fix?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are Waist Trainers Just A Waste, And Are Posture Fixers A Quick Fix?

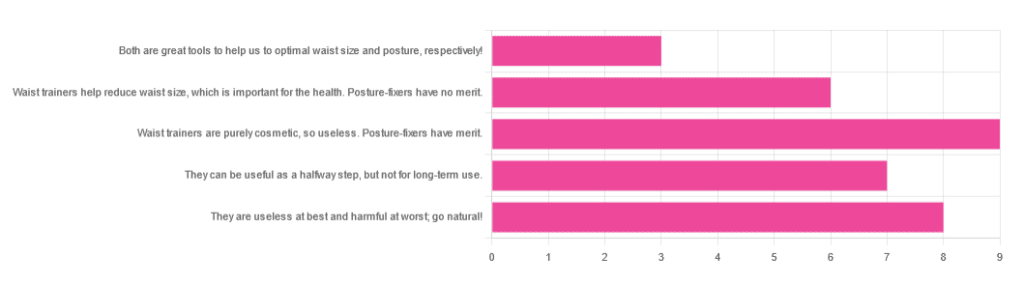
Yesterday, we asked you for your opinions on waist trainers and posture-fixing harnesses, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of results:
- The most popular response was “Waist trainers are purely cosmetic, so useless. Posture-fixers have merit”, with a little over a quarter of the votes.
- The least popular response was “Both are great tools to help us to optimal waist size and posture, respectively!”
- The other three answers each got a little under a quarter of the vote. In terms of discrete data, these were all 7±1, so basically, there was nothing in it.
The sample size was smaller than usual—perhaps the cluster of American holiday dates yesterday and today kept people busy! But, pressing on…
What does the science say?
Waist trainers are purely cosmetic, so, useless. True or False?
True, simply. Honestly, they’re not even that great for cosmetic purposes. They will indeed cinch in your middle, and this shape will be retained for a (very) short while after uncinching, because your organs have been squished inwards and may take a short while to get back to where they are supposed to be.
The American Board of Cosmetic Surgery may not be an unbiased source, but we’re struggling to find scientists who will even touch one of these, so, let’s see what these doctors have to say:
- Waist training can damage vital organs
- You will be slowly suffocating yourself
- Waist training simply doesn’t work
- You cannot drastically change your body shape with a piece of fabric*
Read: ABCS | 4 Reasons to Throw Your Waist Trainer in the Trash
*”But what about foot-binding?”—feet have many bones, whose growth can be physically restricted. Your waist has:
- organs: necessary! (long-term damage possible, but they’re not going away)
- muscles: slightly restrictable! (temporary restriction; no permanent change)
- fat: very squeezable! (temporary muffin; no permanent change)
Posture correctors have merit: True or False?
True—probably, and as a stepping-stone measure only.
The Ergonomics Health Association (a workplace health & safety organization) says:
❝Looking at the clinical evidence of posture correctors, we can say without a doubt that they do work, just not for everyone and not in the same way for all patients.❞
Source: Do Posture Correctors Work? Here’s What Our Experts Think
That’s not very compelling, so we looked for studies, and found… Not much, actually. However, what we did find supported the idea that “they probably do help, but we seriously need better studies with less bias”:
That is also not a compelling title, but here is where it pays to look at the studies and not just the titles. Basically, they found that the results were favorable to the posture-correctors—the science itself was just trash:
❝ The overall findings were that posture-correcting shirts change posture and subjectively have a positive effect on discomfort, energy levels and productivity.
The quality of the included literature was poor to fair with only one study being of good quality. The risk of bias was serious or critical for the included studies. Overall, this resulted in very low confidence in available evidence.❞
Since the benefit of posture correctors like this one is due to reminding the wearer to keep good posture, there is a lot more (good quality!) science for wearable biofeedback tech devices, such as this one:
Spine Cop: Posture Correction Monitor and Assistant
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts

Coconut vs Avocado – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing coconut to avocado, we picked the avocado.
Why?
In terms of macros, avocado is lower in carbs and also in net carbs—coconut’s a little higher in fiber, but not enough to make up for the difference in carbs nor, when it comes to glycemic index and insulin index, the impact of coconut’s much higher fat content on insulin responses too. On which note, while coconut’s fats are broadly considered healthy (its impressive saturated fat content is formed of medium-chain triglycerides which, in moderation, are heart-healthy), avocado’s fats are even healthier, being mostly monounsaturated fat with some polyunsaturated (and about 15x less saturated fat). All in all, a fair win for avocado on the macros front, but coconut isn’t bad in moderation.
When it comes to vitamins, avocados are higher in vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, K, and choline. Most of those differences are by very large margins. Coconuts are not higher in any vitamins. A huge, easy, “perfect score” win for avocados.
In the category of minerals, however, it’s coconut’s turn to sweep with more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, zinc, and selenium—though the margins are mostly not nearly as impressive as avocado’s vitamin margins. Speaking of avocados, they do have more potassium than coconuts do, but the margin isn’t very large. A compelling win for coconut’s mineral content.
Adding up the sections, we get to a very credible win for avocados, but coconuts are also very respectable. So, as ever, enjoy both (although we do recommend exercising moderation in the case of coconuts, mainly because of the saturated fat content), and if you’re choosing between them for some purpose, then avocado will generally be the best option.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy? ← defying Betteridge’s Law here!
- Avocado, Coconut & Lime Crumble Pots ← if you do want to enjoy both, here’s a fabulous way to do so in style
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Fast Exercise – by Dr. Michael Mosley & Peta Bee
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about the benefits of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT), but there’s more to say than we can fit in a short article!
Dr. Michael Mosley, who hates exercise but knows his stuff when it comes to the benefits, teamed up with Peta Bee, who loves exercise and is a science journalist with degrees in sports science and nutrition, to bring us this book.
In it, we learn a lot about:
- the science of HIIT
- what makes it so different from most kinds of exercise
- exactly what benefits one can expect
…in a very detailed clinical fashion (while still remaining very readable).
By “very detailed clinical fashion”, here we mean “one minute of this kind of exercise this many times per week over this period of time will give this many extra healthy life-years”, for example, along with lots of research to back numbers, and explanations of the mechanisms of action (e.g. reducing inflammatory biomarkers of aging, increasing cellular apoptosis, improving cardiometabolic stats for reduced CVD risk, and many things)
There’s also time/space given over to exactly what to do and how to do it, giving enough options to suit personal tastes/circumstances.
Bottom line: if you’d like to make your exercise work a lot harder for you while you spend a lot less time working out, then this book will help you do just that!
Click here to check out Fast Exercise, and enjoy the benefits!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
First things first… How much fiber should we be eating?
- The World Health Organization recommends we each get at least 25g of fiber per day:
- A more recent meta-review of studies, involving thousands of people and decades of time, suggests 25–29g is ideal:
- The British Nutritional Foundation gives 30g as the figure:
- The US National Academy of Sciences’ Institute of Medicine recommends 21g–38g per day, depending on age and sex:
- A large study last year gave 30–40g as the figure:
*This one is also a great read to understand more about the “why” of fiber
Meanwhile, the average American gets 16g of fiber per day.
So, how to get more fiber, without piling on too many carbs?
Foods that contain fiber generally contain carbs (there’s a limit to how much celery most people want to eat), so there are two key ideas here:
- Getting a good carb:fiber ratio
- Making substitutions that boost fiber without overdoing (or in some case, even changing) carbs
Meat → Lentils
Well-seasoned lentils can be used to replaced ground beef or similar. A cup of boiled lentils contains 18g of fiber, so you’re already outdoing the average American’s daily total.
Meat → Beans
Black beans are a top-tier option here (15g per cup, cooked weight), but many kinds of beans are great.
Chicken/Fish → Chickpeas
Yes, chicken/fish is already meat, but we’re making a case for chickpeas here. Cooked and seasoned appropriately, they do the job, and pack in 12g of fiber per cup. Also… Hummus!
Bonus: Hummus, eaten with celery sticks.
White pasta/bread → Wholewheat pasta/bread
This is one where “moderation is key”, but if you’re going to eat pasta/bread, then wholewheat is the way to go. Fiber amounts vary, so read labels, but it will always have far more than white.
Processed salty snacks → Almonds and other nuts
Nuts in general are great, but almonds are top-tier for fiber, amongst other things. A 40g handful of almonds contains about 10g of fiber.
Starchy vegetables → Non-starchy vegetables
Potatoes, parsnips, and their friends have their place. But they cannot compete with broccoli, peas, cabbage, and other non-starchy vegetables for fiber content.
Bonus: if you’re going to have starchy vegetables though, leave the skins on!
Fruit juice → Fruit
Fruit juice has had most, if not all, of its fiber removed. Eat an actual juicy fruit, instead. Apples and bananas are great options; berries such as blackberries and raspberries are even better (at around 8g per cup, compared to the 5g or so depending on the size of an apple/banana)
Processed cereals → Oats
5g fiber per cup. Enough said.
Summary
Far from being a Herculean task, getting >30g of fiber per day can be easily accomplished by a lentil ragù with wholewheat pasta.
If your breakfast is overnight oats with fruit and some chopped almonds, you can make it to >20g already by the time you’ve finished your first meal of the day.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: