Sesame & Peanut Tofu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Yesterday we learned how to elevate tofu from “nutrition” to “nutritious tasty snack” with our Basic Baked Tofu recipe; today we’re expanding on that, to take it from “nutritious tasty snack” to “very respectable meal”.
You will need
For the tofu:
- The Basic Baked Tofu that we made yesterday (consider making this to be “step zero” of today’s recipe if you don’t already have a portion in the fridge)
For the sauce:
- ⅓ cup peanut butter, ideally with no added sugar or salt (if allergic to peanuts specifically, use almond butter; if allergic to nuts generally, use tahini)
- ¼ bulb garlic, grated or crushed
- 1 tbsp tamarind paste
- 1½ tbsp tamari sauce (or low-sodium soy sauce, if a substitution is necessary)
- 1 tbsp sambal oelek (or sriracha sauce, if a substitution is necessary)
- 1 tsp ground coriander
- 1 tsp ground black pepper
- ½ tsp ground sweet cinnamon
- ½ tsp MSG (or else omit; do not substitute with salt in this case unless you have a particular craving)
- zest of 1 lime
For the vegetables:
- 14 oz broccolini / tenderstem broccoli, thick ends trimmed (failing that, any broccoli)
- 6 oz shelled edamame
- 1½ tsp toasted sesame oil
For serving:
- 4 cups cooked rice (we recommend our Tasty Versatile Rice recipe)
- ½ cup raw cashews, soaked in hot water for at least 5 minutes and then drained (if allergic, substitute cooked chickpeas, rinsed and drained)
- 1 tbsp toasted sesame seeds
- 1 handful chopped cilantro, unless you have the “this tastes like soap” gene, in which case substitute chopped parsley
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the sauce ingredients in a bowl and whisk well (or use a blender if you have one that’s comfortable with this relatively small quantity of ingredients). Taste it, and adjust the ingredient ratios if you’d like more saltiness, sweetness, sourness, spiciness, umami.
2) Prepare a bowl with cold water and some ice. Steam the broccolini and edamame for about 3 minutes; as soon as they become tender, dump them into the ice bathe to halt the cooking process. Let them chill for a few minutes, then drain, dry, and toss in the sesame oil.
3) Reheat the tofu if necessary (an air fryer is great for this), and then combine with half of the sauce in a bowl, tossing gently to coat well.
4) Add a little extra water to the remaining sauce, enough to make it pourable, whisking to an even consistency.
5) Assemble; do it per your preference, but we recommend the order: rice, vegetables, tofu, cashews, sauce, sesame seeds, herbs.
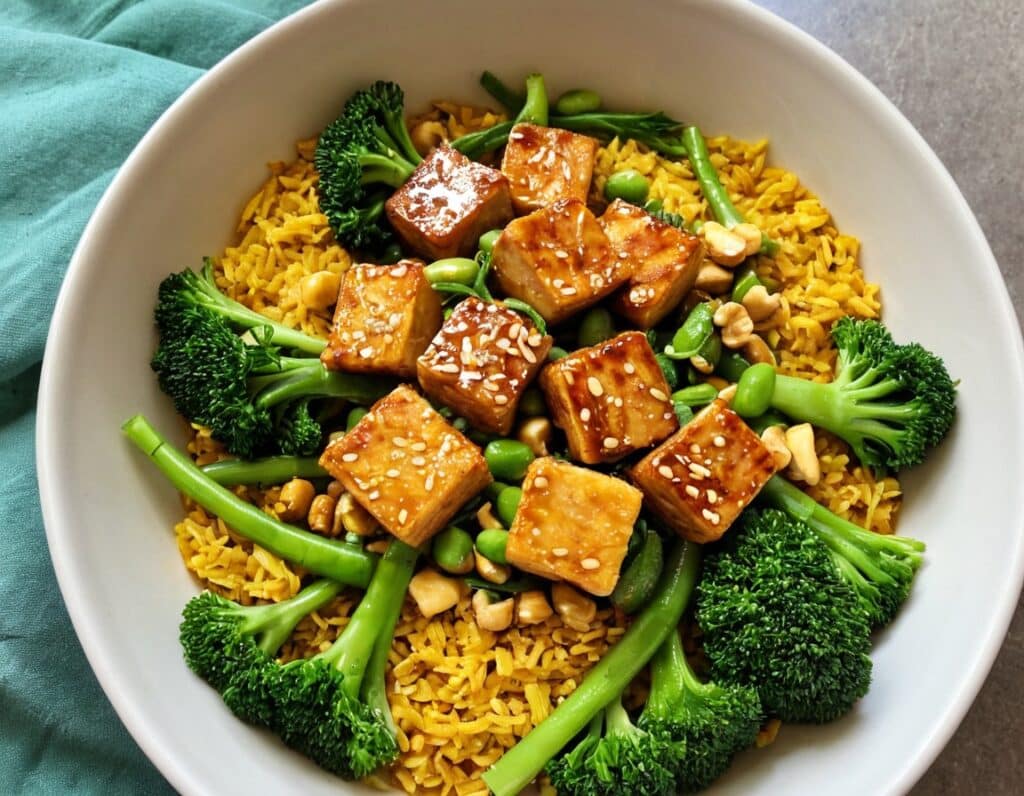

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Tofu vs Seitan – Which is Healthier?
- Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
- Sweet Cinnamon vs Regular Cinnamon – Which is Healthier?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Sugary Food That Lowers Blood Sugars
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Loved the article on goji berries! I read they are good for blood sugars, is that true despite the sugar content?❞
Most berries are! Fruits that are high in polyphenols (even if they’re high in sugar), like berries, have a considerable net positive impact on glycemic health:
- Polyphenols and Glycemic Control
- Polyphenols and their effects on diabetes management: A review
- Dietary polyphenols as antidiabetic agents: Advances and opportunities
And more specifically:
Dietary berries, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: an overview of human feeding trials
Read more: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
As for goji berries specifically, they’re very high indeed in polyphenols, and also have a hypoglycemic effect, i.e., they lower blood sugar levels (and as a bonus, increases HDL (“good” cholesterol) levels too, but that’s not the topic here):
❝The results of our study indicated a remarkable protective effect of LBP in patients with type 2 diabetes. Serum glucose was found to be significantly decreased and insulinogenic index increased during OMTT after 3 months administration of LBP. LBP also increased HDL levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. It showed more obvious hypoglycemic efficacy for those people who did not take any hypoglycemic medicine compared to patients taking hypoglycemic medicines. This study showed LBP to be a good potential treatment aided-agent for type 2 diabetes.❞
- LBP = Lycium barbarum polysaccharide, i.e. polysaccharide in/from goji berries
- OMTT = Oral metabolic tolerance test, a test of how well the blood sugars avoid spiking after a meal
For more about goji berries (and also where to get them), for reference our previous article is at:
Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Shoe Wear Patterns: What They Mean, Why It Matters, & How To Fix It
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you look under your shoes, do you notice how the tread is worn more in some places than others? Specific patterns of shoe wear correspond to how our body applies force, weight, and rotational movement. This reveals how we move, and uneven wear can indicate problematic movement dynamics.
The clues in your shoes
Common shoe wear patterns include:
- Diagonal wear on the outside of the heel: caused by foot angle, leg position, and instability, leading to joint stress.
- Rotational wear at specific points: due to internal or external rotation, often originating from the hip, pelvis, or torso.
- Wear above the big toe: caused by excessive toe lifting, often associated with a “lighter” or kicking leg.
Fixing movement issues to prevent wear involves correcting posture, improving balance, and adjusting how the legs land during walking/running.
Key fixes include:
- Aligning the center of gravity properly to prevent leg overcompensation.
- Ensuring feet land under the hips and not far in front.
- Stabilizing the torso to avoid unnecessary rotation.
- Engaging the glutes effectively to reduce hip flexor dominance and improve leg mechanics.
- Maintaining even weight distribution on both legs to prevent excessive lifting or twisting.
Posture and walking mechanics are vital to reducing uneven wear, but meaningful, lasting change takes time and focused effort, to build new habits.
For more on all this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Steps For Keeping Your Feet A Healthy Foundation
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Tranquility by Tuesday?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
I Know How She Does It: How Successful Women Make The Most of Their Time
This is Laura Vanderkam, author of “Tranquility By Tuesday” (amongst other books). Her “thing” is spending more time on what’s important, and less on what isn’t. Sounds simple, but she’s made a career out of it, so condensed here for you are…
Laura’s 7 Keys To Productivity
Key One: Plan your weeks on Fridays
You don’t want your Monday morning to be a “James Bond intro” (where everything is already in action and you’re just along for the ride, trying to figure out what’s going on). So, take some time last thing each Friday, to plan ahead for the following week!
Key Two: Measure what matters
Whatever that means to you. Laura tracks her use of time in half-hour blocks, and likes keeping track of streaks. For her, that means running daily and keeping a log of it. She also keeps track of the books she reads. For someone else it could be music practice, or a Duolingo streak, or eating fruit each day.
On which note…
“Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen” is simpler than most nutrition trackers (where you must search for everything you eat, or scan barcodes for all ingredients).
Instead, it keeps track of whether you are having certain key health-giving foods often enough to maintain good health.
We might feature his method in a future edition of 10almonds, but for now, check the app out for yourself here:
Get Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen on iOS / Get Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen on Android
Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen @ Nutrition Facts
Key Three: Figure out 2–3 “anchor” events for the weekend
Otherwise, it can become a bit of a haze and on Monday you find yourself thinking “where did the weekend go?”. So, plan some stuff! It doesn’t have to be anything out-of-this-world, just something that you can look forward to in advance and remember afterwards. It could be a meal out with your family, or a session doing some gardening, or a romantic night in with your partner. Whatever makes your life “living” and not passing you by!
Key Four: Tackle the toughest work first
You’ve probably heard about “swallowing frogs”. If not, there are various versions, usually attributed to Mark Twain.
Here’s one:
“If it’s your job to eat a frog, it’s best to do it first thing in the morning. And if it’s your job to eat two frogs, it’s best to eat the biggest one first.”
Top Productivity App “ToDoist” has an option for this, by the way!
Laura’s key advice here is: get the hard stuff done now! Before you get distracted or tired and postpone it to tomorrow (and then lather rinse repeat, so it never gets done)
10almonds Tip:
“But what if something’s really important but not as pressing as some less important, but more urgent tasks?”
Simple!
Set a timer (we love the Pomodoro method, by the way) and do one burst of the important-but-not-urgent task first. Then you can get to the more urgent stuff.
Repeat each day until the important-but-not-urgent task is done!
The 10almonds Team
Key Five: Use bits of time well
If, like many of us, you’ve a neverending “to read” list, use the 5–10 minute breaks that get enforced upon us periodically through the day!
- Use those few minutes before a meeting/phonecall!
- Use the time you spend waiting for public transport or riding on it!
- Use the time you spent waiting for a family member to finish doing a thing!
All those 5–10 minute bits soon add up… You might as well spend that time reading something you know will add value to your life, rather than browsing social media, for example.
Key Six: Make very short daily to-do lists
By “short”, Laura considers this “under 10 items”. Do this as the last part of your working day, ready for tomorrow. Not at bedtime! Bedtime is for winding down, not winding up
Key Seven: Have a bedtime
Laura shoots for 10:30pm, but whatever works for you and your morning responsibilities. Your morning responsibilities aren’t tied to a specific time? Lucky you, but try to keep a bedtime anyway. Otherwise, your daily rhythm can end up sliding around the clock, especially if you work from home!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
52 Small Changes – by Brett Blumenthal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We see a lot of books that exhort us to get a six-pack in a month, change our life in 7 days, learn Japanese in 24 hours. The reality is, things take time!
Brett Blumenthal is more realistic while being just as motivational:
The idea is simple… Make one small change per week for 52 weeks, and at the end of the year, you’ll be healthier and happier.
At 10almonds, we’re big fans of small changes that add up (or rather: compound!) to make big differences, so this one’s absolutely our style!
Best of all, she offers us not just “do this” advice, but also “and here’s the information and resources you’ll need to make this change work the best it can for you”
The advices range in topic from nutrition to exercise to sleep to mental wellness to interpersonal stuff and more. The biggest focus is on personal health, though, with small changes to exercise and nutrition making up the lion’s share of the changes.
Bottom line: this is a book you’ll want to grab once a week. Consider setting a reminder on your phone to check in with it each Sunday, for example!
Take the first step and order “52 Small Changes” from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Well Plated Cookbook – by Erin Clarke
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Clarke’s focus here is on what she calls “stealthy healthy”, with the idea of dishes that feel indulgent while being great for the health.
The recipes, of which there are well over 100, are indeed delicious and easy to make without being oversimplified, and since she encourages the use of in-season ingredients, many recipes come with a “market swaps” substitution guide, to make each recipe seasonal.
The book is largely not vegetarian, let alone vegan, but the required substitutions will be second-nature to any seasoned vegetarian or vegan. Indeed, “skip the meat sometimes” is one of the advices she offers near the beginning of the book, in the category of tips to make things even healthier.
Bottom line: if you want to add dishes to your repertoire that are great for entertaining and still super-healthy, this book will be a fine addition to your collection.
Click here to check out The Well Plated Cookbook, and get cooking!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
‘I keep away from people’ – combined vision and hearing loss is isolating more and more older Australians
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our ageing population brings a growing crisis: people over 65 are at greater risk of dual sensory impairment (also known as “deafblindness” or combined vision and hearing loss).
Some 66% of people over 60 have hearing loss and 33% of older Australians have low vision. Estimates suggest more than a quarter of Australians over 80 are living with dual sensory impairment.
Combined vision and hearing loss describes any degree of sight and hearing loss, so neither sense can compensate for the other. Dual sensory impairment can occur at any point in life but is increasingly common as people get older.
The experience can make older people feel isolated and unable to participate in important conversations, including about their health.
bricolage/Shutterstock Causes and conditions
Conditions related to hearing and vision impairment often increase as we age – but many of these changes are subtle.
Hearing loss can start as early as our 50s and often accompany other age-related visual changes, such as age-related macular degeneration.
Other age-related conditions are frequently prioritised by patients, doctors or carers, such as diabetes or heart disease. Vision and hearing changes can be easy to overlook or accept as a normal aspect of ageing. As an older person we interviewed for our research told us
I don’t see too good or hear too well. It’s just part of old age.
An invisible disability
Dual sensory impairment has a significant and negative impact in all aspects of a person’s life. It reduces access to information, mobility and orientation, impacts social activities and communication, making it difficult for older adults to manage.
It is underdiagnosed, underrecognised and sometimes misattributed (for example, to cognitive impairment or decline). However, there is also growing evidence of links between dementia and dual sensory loss. If left untreated or without appropriate support, dual sensory impairment diminishes the capacity of older people to live independently, feel happy and be safe.
A dearth of specific resources to educate and support older Australians with their dual sensory impairment means when older people do raise the issue, their GP or health professional may not understand its significance or where to refer them. One older person told us:
There’s another thing too about the GP, the sort of mentality ‘well what do you expect? You’re 95.’ Hearing and vision loss in old age is not seen as a disability, it’s seen as something else.
Isolated yet more dependent on others
Global trends show a worrying conundrum. Older people with dual sensory impairment become more socially isolated, which impacts their mental health and wellbeing. At the same time they can become increasingly dependent on other people to help them navigate and manage day-to-day activities with limited sight and hearing.
One aspect of this is how effectively they can comprehend and communicate in a health-care setting. Recent research shows doctors and nurses in hospitals aren’t making themselves understood to most of their patients with dual sensory impairment. Good communication in the health context is about more than just “knowing what is going on”, researchers note. It facilitates:
- shorter hospital stays
- fewer re-admissions
- reduced emergency room visits
- better treatment adherence and medical follow up
- less unnecessary diagnostic testing
- improved health-care outcomes.
‘Too hard’
Globally, there is a better understanding of how important it is to maintain active social lives as people age. But this is difficult for older adults with dual sensory loss. One person told us
I don’t particularly want to mix with people. Too hard, because they can’t understand. I can no longer now walk into that room, see nothing, find my seat and not recognise [or hear] people.
Again, these experiences increase reliance on family. But caring in this context is tough and largely hidden. Family members describe being the “eyes and ears” for their loved one. It’s a 24/7 role which can bring frustration, social isolation and depression for carers too. One spouse told us:
He doesn’t talk anymore much, because he doesn’t know whether [people are] talking to him, unless they use his name, he’s unaware they’re speaking to him, so he might ignore people and so on. And in the end, I noticed people weren’t even bothering him to talk, so now I refuse to go. Because I don’t think it’s fair.
Dual sensory loss can be isolating for older people and carers. Synthex/Shutterstock So, what can we do?
Dual sensory impairment is a growing problem with potentially devastating impacts.
It should be considered a unique and distinct disability in all relevant protections and policies. This includes the right to dedicated diagnosis and support, accessibility provisions and specialised skill development for health and social professionals and carers.
We need to develop resources to help people with dual sensory impairment and their families and carers understand the condition, what it means and how everyone can be supported. This could include communication adaptation, such as social haptics (communicating using touch) and specialised support for older adults to navigate health care.
Increasing awareness and understanding of dual sensory impairment will also help those impacted with everyday engagement with the world around them – rather than the isolation many feel now.
Moira Dunsmore, Senior Lecturer, Sydney Nursing School, Faculty of Medicine and Health, University of Sydney, University of Sydney; Annmaree Watharow, Lived Experience Research Fellow, Centre for Disability Research and Policy, University of Sydney, and Emily Kecman, Postdoctoral research fellow, Department of Linguistics, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: