Redcurrants vs Cranberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing redcurrants to cranberries, we picked the redcurrants.
Why?
First know: here we’re comparing raw redcurrants to raw cranberries, with no additives in either case. If you buy jelly made from either, or if you buy dried fruits but the ingredients list has a lot of added sugar and often some vegetable oil, then that’s going to be very different. But for now… Let’s look at just the fruits:
In terms of macros, redcurrants are higher in carbs, but also higher in fiber, and have the lower glycemic index as cranberries have nearly 2x the GI.
When it comes to vitamins, redcurrants have more of vitamins B1, B2, B6, B9, C, K, and choline, while cranberries have more of vitamins A, B5, and E. In other words, a clear win for redcurrants.
In the category of minerals, redcurrants sweep even more convincingly with a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. On the other hand, cranberries boast a little more manganese; they also have about 2x the sodium.
Both berries have generous amounts of assorted phytochemicals (flavonoids and others), and/but nothing to set one ahead of the other.
As per any berries that aren’t poisonous, both of these are fine choices for most people most of the time, but redcurrants win with room to spare in most categories.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Health Benefits Of Cranberries (But: You’d Better Watch Out)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Replacing Sugar: Top 10 Anti-Inflammatory Sweet Foods
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For those with a sweet tooth, it can be challenging to indulge one’s desires while also avoiding inflammation. Happily, Dr. Jia-Yia Lui has scientific insights to share!
Dr. Liu’s Top 10
We’ll not keep them a mystery; they are:
- Grapes
- Goji berries
- Barberries
- Persimmons
- Longans
- Lychees
- Raisins¹
- Applesauce²
- Plums³
- Dates
¹Yes, these are technically also grapes, but there are enough differences that Dr. Liu tackles them separately.
²It makes a difference how it’s made, though.
³And dried plums, in other words, prunes.For more details on all of these, plus their extra benefits and relevant considerations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- How to Prevent (or Reduce) Inflammation
- The Not-So-Sweet Science Of Sugar Addiction
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
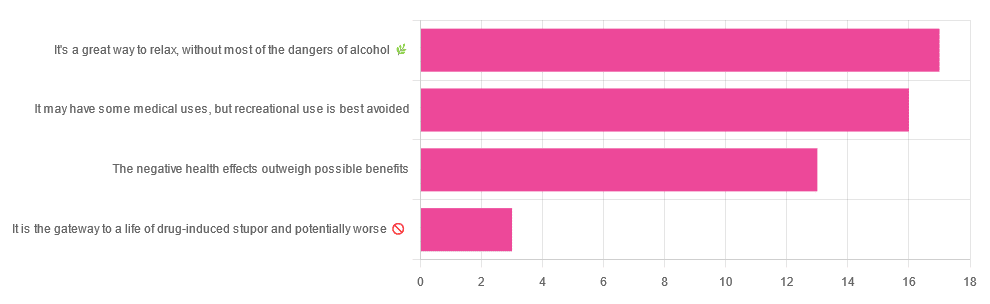
We asked you for your (health-related) opinion on cannabis use—specifically, the kind with psychoactive THC, not just CBD. We got the above-pictured, below-described, spread of responses:
- A little over a third of you voted for “It’s a great way to relax, without most of the dangers of alcohol”.
- A little under a third of you voted for “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”.
- About a quarter of you voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits”
- Three of you voted for “It is the gateway to a life of drug-induced stupor and potentially worse”
So, what does the science say?
A quick legal note first: we’re a health science publication, and are writing from that perspective. We do not know your location, much less your local laws and regulations, and so cannot comment on such. Please check your own local laws and regulations in that regard.
Cannabis use can cause serious health problems: True or False?
True. Whether the risks outweigh the benefits is a personal and subjective matter (for example, a person using it to mitigate the pain of late stage cancer is probably unconcerned with many other potential risks), but what’s objectively true is that it can cause serious health problems.
One subscriber who voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits” wrote:
❝At a bare minimum, you are ingesting SMOKE into your lungs!! Everyone SEEMS TO BE against smoking cigarettes, but cannabis smoking is OK?? Lung cancer comes in many forms.❞
Of course, that is assuming smoking cannabis, and not consuming it as an edible. But, what does the science say on smoking it, and lung cancer?
There’s a lot less research about this when it comes to cannabis, compared to tobacco. But, there is some:
❝Results from our pooled analyses provide little evidence for an increased risk of lung cancer among habitual or long-term cannabis smokers, although the possibility of potential adverse effect for heavy consumption cannot be excluded.❞
Read: Cannabis smoking and lung cancer risk: Pooled analysis in the International Lung Cancer Consortium
Another study agreed there appears to be no association with lung cancer, but that there are other lung diseases to consider, such as bronchitis and COPD:
❝Smoking cannabis is associated with symptoms of chronic bronchitis, and there may be a modest association with the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Current evidence does not suggest an association with lung cancer.❞
Read: Cannabis Use, Lung Cancer, and Related Issues
Cannabis edibles are much safer than smoking cannabis: True or False?
Broadly True, with an important caveat.
One subscriber who selected “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”, wrote:
❝I’ve been taking cannabis gummies for fibromyalgia. I don’t know if they’re helping but they’re not doing any harm. You cannot overdose you don’t become addicted.❞
Firstly, of course consuming edibles (rather than inhaling cannabis) eliminates the smoke-related risk factors we discussed above. However, other risks remain, including the much greater ease of accidentally overdosing.
❝Visits attributable to inhaled cannabis are more frequent than those attributable to edible cannabis, although the latter is associated with more acute psychiatric visits and more ED visits than expected.❞
Note: that “more frequent” for inhaled cannabis, is because more people inhale it than eat it. If we adjust the numbers to control for how much less often people eat it, suddenly we see that the numbers of hospital admissions are disproportionately high for edibles, compared to inhaled cannabis.
Or, as the study author put it:
❝There are more adverse drug events associated on a milligram per milligram basis of THC when it comes in form of edibles versus an inhaled cannabis. If 1,000 people smoked pot and 1,000 people at the same dose in an edible, then more people would have more adverse drug events from edible cannabis.❞
See the numbers: Acute Illness Associated With Cannabis Use, by Route of Exposure
Why does this happen?
- It’s often because edibles take longer to take effect, so someone thinks “this isn’t very strong” and has more.
- It’s also sometimes because someone errantly eats someone else’s edibles, not realising what they are.
- It’s sometimes a combination of the above problems: a person who is now high, may simply forget and/or make a bad decision when it comes to eating more.
On the other hand, that doesn’t mean inhaling it is necessarily safer. As well as the pulmonary issues we discussed previously, inhaling cannabis has a higher risk of cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (and the resultant cyclic vomiting that’s difficult to treat).
You can read about this fascinating condition that’s sometimes informally called “scromiting”, a portmanteau of screaming and vomiting:
Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome
You can’t get addicted to cannabis: True or False?
False. However, it is fair to say that the likelihood of developing a substance abuse disorder is lower than for alcohol, and much lower than for nicotine.
See: Prevalence of Marijuana Use Disorders in the United States Between 2001–2002 and 2012–2013
If you prefer just the stats without the science, here’s the CDC’s rendering of that:
Addiction (Marijuana or Cannabis Use Disorder)
However, there is an interesting complicating factor, which is age. One is 4–7 times more likely to develop a substance abuse disorder, if one starts use as an adolescent, rather than later in life:
Cannabis is the gateway to use of more dangerous drugs: True or False?
False, generally speaking. Of course, for any population there will be some outliers, but there appears to be no meaningful causal relation between cannabis use and other substance use:
Interestingly, the strongest association (where any existed at all) was between cannabis use and opioid use. However, rather than this being a matter of cannabis use being a gateway to opioid use, it seems more likely that this is a matter of people looking to both for the same purpose: pain relief.
As a result, growing accessibility of cannabis may actually reduce opioid problems:
- Cannabis as a Gateway Drug for Opioid Use Disorder
- Association between medical cannabis laws and opioid overdose mortality has reversed over time
Some final words…
Cannabis is a complex drug with complex mechanisms and complex health considerations, and research is mostly quite young, due to its historic illegality seriously cramping science by reducing sample sizes to negligible. Simply put, there’s a lot we still don’t know.
Also, we covered some important topics today, but there were others we didn’t have time to cover, such as the other potential psychological benefits—and risks. Likely we’ll revisit those another day.
Lastly, while we’ve covered a bunch of risks today, those of you who said it has fewer and lesser risks than alcohol are quite right—the only reason we couldn’t focus on that more, is because to talk about all the risks of alcohol would make this feature many times longer!
Meanwhile, whether you partake or not, stay safe and stay well.
Share This Post
-
Teriyaki Chickpea Burgers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Burgers are often not considered the healthiest food, but they can be! Ok, so the teriyaki sauce component itself isn’t the healthiest, but the rest of this recipe is, and with all the fiber this contains, it’s a net positive healthwise, even before considering the protein, vitamins, minerals, and assorted phytonutrients.
You will need
- 2 cans chickpeas, drained and rinsed (or 2 cups of chickpeas, cooked drained and rinsed)
- ¼ cup chickpea flour (also called gram flour or garbanzo bean flour)
- ¼ cup teriyaki sauce
- 2 tbsp almond butter (if allergic, substitute with a seed butter if available, or else just omit; do not substitute with actual butter—it will not work)
- ½ bulb garlic, minced
- 1 large chili, minced (your choice what kind, color, or even whether or multiply it)
- 1 large shallot, minced
- 1″ piece of ginger, grated
- 2 tsp teriyaki sauce (we’re listing this separately from the ¼ cup above as that’ll be used differently)
- 1 tsp yeast extract (even if you don’t like it; trust us, it’ll work—this writer doesn’t like it either but uses it regularly in recipes like these)
- 1 tbsp black pepper
- 1 tsp fennel powder
- ½ tsp sweet cinnamon
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil for frying
For serving:
- Burger buns (you can use our Delicious Quinoa Avocado Bread recipe)
- Whatever else you want in there; we recommend mung bean sprouts, red onion, and a nice coleslaw
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃.
2) Roast the chickpeas spaced out on a baking tray (lined with baking paper) for about 15 minutes. Leave the oven on afterwards; we still need it.
3) While that’s happening, heat a little oil in a skillet to a medium heat and fry the shallot, chili, garlic, and ginger, for about 2–3 minutes. You want to release the flavors, but not destroy them.
4) Let them cool, and when the chickpeas are done, let them cool for a few minutes too, before putting them all into a food processor along with the rest of the ingredients from the main section, except the oil and the ¼ cup teriyaki sauce. Process them into a dough.
5) Form the dough into patties; you should have enough dough for 4–6 patties depending on how big you want them.
6) Brush them with the teriyaki sauce; turn them onto a baking tray (lined with baking paper) and brush the other side too. Be generous.
7) Bake them for about 15 minutes, turn them (taking the opportunity to add more teriyaki sauce if it seems to merit it) and bake for another 5–10 minutes.
8) Assemble; we recommend the order: bun, a little coleslaw, burger, red onion, more coleslaw, mung bean sprouts, bun, but follow your heart!
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Three Daily Servings of Beans/Legumes?
- Hoisin Sauce vs Teriyaki Sauce – Which is Healthier?
- Sprout Your Seeds, Grains, Beans, Etc
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we scored 4/5 today!
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Why ’10almonds’? Newsletter Name Explained
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day!
Each Thursday, we respond to subscriber questions and requests! If it’s something small, we’ll answer it directly; if it’s something bigger, we’ll do a main feature in a follow-up day instead!
So, no question/request to big or small; they’ll just get sorted accordingly
Remember, you can always hit reply to any of our emails, or use the handy feedback widget at the bottom. We always look forward to hearing from you!
Q: Why is your newsletter called 10almonds? Maybe I missed it in the intro email, but my curiosity wants to know the significance. Thanks!”
It’s a reference to a viral Facebook hoax! There was a post going around that claimed:
❝HEADACHE REMEDY. Eat 10–12 almonds, the equivalent of two aspirins, next time you have a headache❞ ← not true!
It made us think about how much health-related disinformation there was online… So, calling ourselves 10almonds was a bit of a tongue-in-cheek reference to that story… but also a reminder to ourselves:
We must always publish information with good scientific evidence behind it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Polyphenol Paprika Pepper Penne
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This one’s easier to promptly prepare than it is to pronounce unprepared! Ok, enough alliteration: this dish is as full of flavor as it is full of antioxidants, and it’s great for digestive health and heart health too.
You will need
- 4 large red bell peppers, diced
- 2 red onions, roughly chopped
- 1 bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 2 cups cherry tomatoes, halved
- 10oz wholemeal penne pasta
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tbsp smoked paprika
- 1 tbsp black pepper
- Extra virgin olive oil for drizzling
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 200℃ / 400℉ / Gas mark 6
2) Put the vegetables in a roasting tin; drizzle with oil, sprinkle with the seasonings (nooch, paprika, black pepper), stir well to mix and distribute the seasonings evenly, and roast for 20–25 minutes, stirring/turning occasionally. When the edges begin to caramelize, turn off the heat, but leave to keep warm.
3) Cook the penne al dente (this should take 7–8 minutes in boiling salted water). Rinse in cold water, then pass a kettle of hot water over them to reheat. This process removed starch and lowered the glycemic index, before reheating the pasta so that it’s hot to serve.
4) Place the roasted vegetables in a food processor and blitz for just a few seconds. You want to produce a very chunky sauce—but not just chunks or just sauce.
5) Combine the sauce and pasta to serve immediately.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Which Bell Peppers To Pick? A Spectrum Of Specialties ← note how red bell peppers are perfect for this, as their lycopene quadruples in bioavailability when cooked
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- What Matters Most For Your Heart? Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Exercise That Protects Your Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Neuroscientist In The Gym
This is Dr. Wendy Suzuki. She’s a neuroscientist, and an expert in the neurobiology of memory, as well as neuroplasticity, and the role of exercise in neuroprotection.
We’ve sneakily semi-featured her before when we shared her Big Think talk:
Brain Benefits In Three Months… Through Walking?
Today we’re going to expand on that a little!
A Quick Recap
To share the absolute key points of that already fairly streamlined rundown:
- Exercise boosts levels of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin (and, which wasn’t mentioned there, noradrenaline)
- These are responsible for motivation, happiness, and focus (amongst other things)
- Persistent exercise boosts certain regions of the brain in particular, most notably the pre-frontal cortex and the hippocampi*
- These are responsible for planning and memory (amongst other things)
Dr. Suzuki advocates for stepping up your exercise routine if you can, with more exercise generally being better than less (unless you have some special medical reason why that’s not the case for you).
*often referred to in the singular as the hippocampus, but you have one on each side of your brain (unless a serious accident/incident destroyed one, but you’ll know if that applies to you, unless you lost both, in which case you will not remember about it).
What kind(s) of workout?
While a varied workout is best for overall health, for these brain benefits specifically, what’s most important is that it raises your heart rate.
This is why in her Big Think talk we shared before, she talks about the benefits of taking a brisk walk daily. See also:
If that’s not your thing, though (and/or is for whatever reason an inaccessible form of exercise for you), there is almost certainly some kind of High Intensity Interval Training that is a possibility for you. That might sound intimidating, but if you have a bit of floor and can exercise for one minute at a time, then HIIT is an option for you:
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Dr. Suzuki herself is an ardent fan of “intenSati” which blends cardio workouts with yoga for holistic mind-and-body fitness. In fact, she loves it so much that she became a certified exercise instructor:
How much is enough?
It’s natural to want to know the minimum we can do to get results, but Dr. Suzuki would like us to bear in mind that when it comes to our time spent exercising, it’s not so much an expense of time as an investment in time:
❝Exercise is something that when you spend time on it, it will buy you time when you start to work❞
Read more: A Neuroscientist Experimented on Her Students and Found a Powerful Way to Improve Brain Function
Ok, but we really want to know how much!
Dr. Suzuki recommends at least three to four 30-minute exercise sessions per week.
Note: this adds up to less than the recommended 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, but high-intensity exercise counts for twice the minutes for these purposes, e.g. 1 minute of high-intensity exercise is worth 2 minutes of moderate exercise.
How soon will we see benefits?
Benefits start immediately, but stack up cumulatively with continued long-term exercise:
❝My lab showed that a single workout can improve your ability to shift and focus attention, and that focus improvement will last for at least two hours. ❞
…which is a great start, but what’s more exciting is…
❝The more you’re working out, the bigger and stronger your hippocampus and prefrontal cortex gets. Why is that important?
Because the prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus are the two areas that are most susceptible to neurodegenerative diseases and normal cognitive decline in aging. ❞
In other words, while improving your heart rate through regular exercise will help prevent neurodegeneration by the usual mechanism of reducing neuroinflammation… It’ll also build the parts of your brain most susceptible to decline, meaning that when/if decline sets in, it’ll take a lot longer to get to a critical level of degradation, because it had more to start with.
Read more:
Inspir Modern Senior Living | Dr. Wendy Suzuki Boosts Brain Health with Exercise
Want more from Dr. Suzuki?
You might enjoy her TED talk:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
Prefer text? TED.com has a transcript for you
Prefer lots of text? You might like her book, which we haven’t reviewed yet but will soon:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Exercise boosts levels of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin (and, which wasn’t mentioned there, noradrenaline)