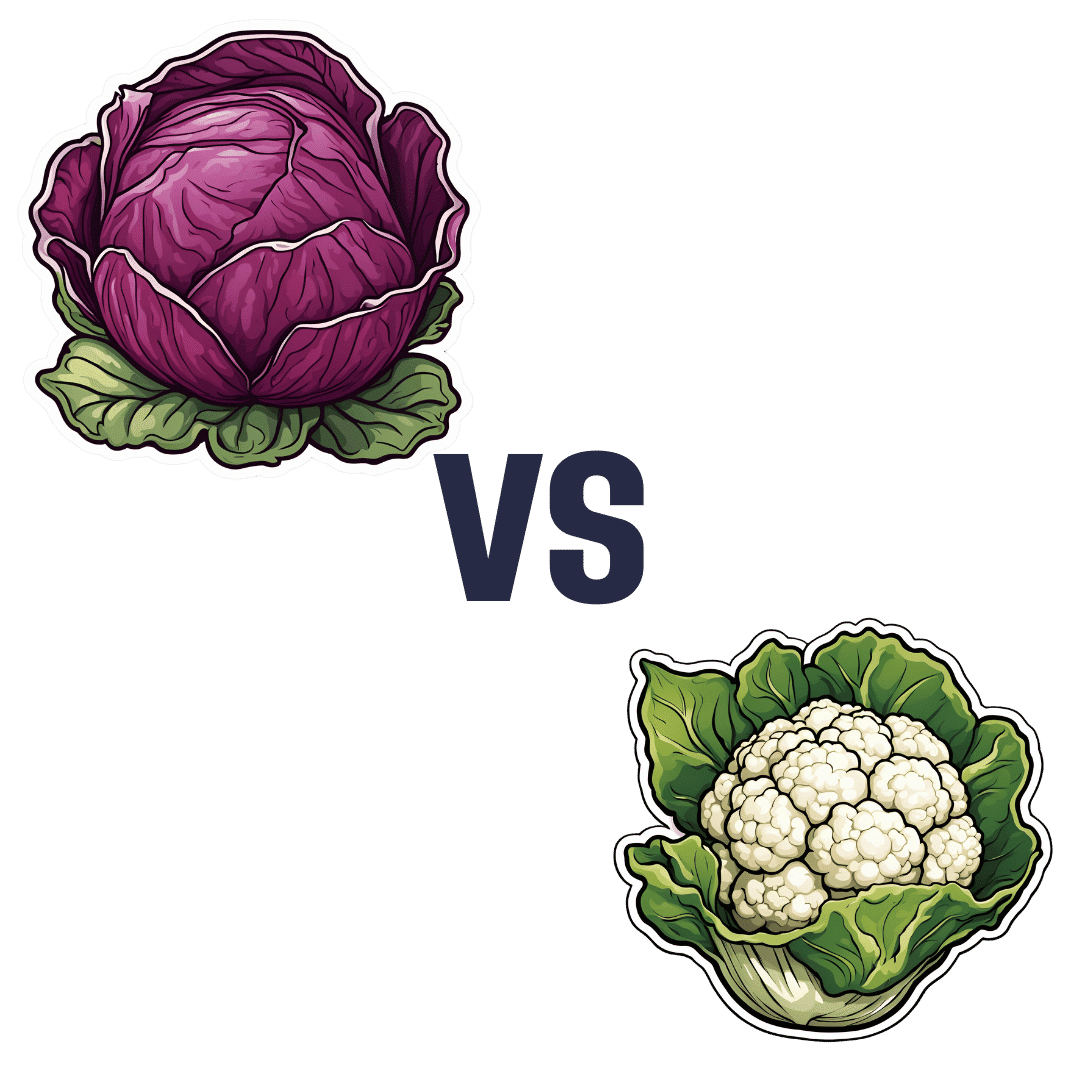
Red Cabbage vs Cauliflower – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing red cabbage to cauliflower, we picked the cabbage.
Why?
In terms of macros, there’s no meaningful difference between them; they’re both mostly water with just enough fiber to hold them together, a small amount of carbs, and an even more trivial amount of protein. So, a tie on macros.
Looking at the vitamins, red cabbage has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, C, E, and K, while cauliflower has more of vitamins B3, B5, B9, and choline. So, a 7:4 win for red cabbage.
In the category of minerals, red cabbage has more calcium, manganese, and iron, while cauliflower has more copper, phosphorus, and potassium. The margins of difference are comparable too, thus, a 3:3 tie on minerals.
It’s always worth taking a look at polyphenols for plants like these, but in this case, once again, there’s not much to set one above the other. However, it’s good to note also that despite them both being Brassica oleracea (same species, different cultivar), there isn’t much overlap in their polyphenol content, meaning they complement each other very well. In particular, red cabbage is a source of luteolin and quercetin, while cauliflower is a source of gallic acid and caffeic acid, for example.
Adding up the three ties and the one win for red cabbage, gives the cabbage the victory today—but do enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
21 Most Beneficial Polyphenols & What Foods Have Them
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hold Me Tight – by Dr. Sue Johnson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of relationship books are quite wishy-washy. This one isn’t.
This one is evidenced-based (and heavily referenced!), and yet at the same time as being deeply rooted in science, it doesn’t lose the human touch.
Dr. Johnson has spent her career as a clinical psychologist and researcher; she’s the primary developer of Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT), which has demonstrated its effectiveness in over 35 years of peer-reviewed clinical research. In other words, it works.
EFT—and thus also this book—finds roots in Attachment Theory. As such, topics this book covers include:
- Recognizing and recovering from attachment injury
- How fights in a relationship come up, and how they can be avoided
- How lot of times relationships end, it’s not because of fights, but a loss of emotional connection
- Building a lifetime of love instead, falling in love again each day
This book lays the groundwork for ensuring a strong, secure, ongoing emotional bond, of the kind that makes/keeps a relationship joyful and fulfilling.
Dr. Johnson has been recognized in her field with a Lifetime Achievement Award, and the Order of Canada.
Share This Post
-
How To Keep Warm (Without Sweat Patches!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I saw an advert on the subway for a pillow spray that guarantees a perfect night’s sleep. What does the science say about smells/sleep?❞
That is certainly a bold claim! Unless it’s contingent, e.g. “…or your money back”. Because otherwise, it absolutely cannot guarantee that.
There is some merit:
❝Odors can modulate the latency to sleep onset, as well as the quality and duration of sleep. Olfactory modulation of sleep may be mediated by direct synaptic interaction between the olfactory system and sleep control nuclei, and/or indirectly through odor modulation of arousal and respiration.
Such modulation appears most heavily influenced by past associations and expectations about the odor, beyond any potential direct physicochemical effect❞
Source: Reciprocal relationships between sleep and smell
Translating that from sciencese:
Sometimes we find pleasant smells relaxing, and placebo effect also helps.
That “any potential direct physiochemical effect”, though, when it does occur, is things like this…
Read: Odor blocking of stress hormone responses
…but that’s a mouse study, and those odors may only work to block three specific mouse stress responses to three specific stressors: physical restraint, predator odor, and male–male confrontation.
In other words: if, perchance, those three things are not what’s stressing you in bed at night (we won’t make assumptions), and/or you are not a mouse, it may not help.
(and this, dear readers, is why we must read articles, and not just headlines!)
But! If you are going to go for a pillow fragrance, something well-associated with being relaxing and soporific, such as lavender, is the way to go:
- Effects of aromatherapy on sleep quality and anxiety of patients
- Effects of Aromatherapy on the Anxiety, Vital Signs, and Sleep Quality of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Patients in Intensive Care Units
- Effect of lavender aromatherapy on vital signs and perceived quality of sleep in the intermediate care unit: a pilot study
tl;dr = patients found lavender fragrances relaxing, experienced less anxiety, got better sleep (significantly or insignificantly, depending on the study) and enjoyed lower blood pressure (significantly or insignificantly, depending on the study).
PS: this writer uses a pillow spray like this one
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Calculate (And Enjoy) The Perfect Night’s Sleep
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Dr. Michael Breus, a clinical psychologist and sleep specialist, and he wants you to get a good night’s sleep, every night.
First, let’s assume you know a lot of good advice about how to do that already in terms of environment and preparation, etc. If you want a recap before proceeding, then we recommend:
Get Better Sleep: Beyond The Basics
Now, what does he want to add?
Wake up refreshed
Of course, how obtainable this is will depend on the previous night’s sleep, but there is something important we can do here regardless, and it’s: beat sleep inertia.
Sleep inertia is what happens when we wake up groggy (for reasons other than being ill, drugged, etc) rather than refreshed. It’s not actually related to how much sleep we have, though!
Rather, it pertains to whether we woke up during a sleep cycle, or between cycles:
- If we wake up between sleep cycles, we’ll avoid sleep inertia.
- If we wake up during a sleep cycle, we’ll be groggy.
Deep sleep generally occurs in 90-minute blocks, albeit secretly that is generally 3× 20 minute blocks in a trenchcoat, with transition periods between, during which the brainwaves change frequency.
REM sleep generally occurs in 20 minute blocks, and will usually arrive in series towards the end of our natural sleep period, to fit neatly into the last 90-minute cycle.
Sometimes these will appear a little out of order, because we are complicated organic beings, but those are the general trends.
In any case, the take-away here is: interrupt them at your peril. You need to wake up between cycles. There are two ways you can do this:
- Carefully calculate everything, and set a very precise alarm clock (this will work so long as you are correct in guessing how long it will take you to fall asleep)
- Use a “sunrise” lamp alarm clock, that in the hour approaching your set alarm time, will gradually increase the light. Because the body will not naturally wake up during a cycle unless a threat is perceived (loud noise, physical rousing, etc), the sunrise lamp method means that you will wake up between sleep cycles at some point during that hour (towards the beginning or end, depending on what your sleep balance/debt is like).
Do not sleep in (even if you have a sleep debt); it will throw everything out.
Caffeine will not help much in the morning
Assuming you got a reasonable night’s sleep, your brain has been cleansed of adenosine (a sleepy chemical), and if you are suffering from sleep inertia, the grogginess is due to melatonin (a different sleepy chemical).
Caffeine is an adenosine receptor blocker, so that will do nothing to mitigate the effects of melatonin in your brain that doesn’t have any meaningful quantity of adenosine in it in the morning.
Adenosine gradually accumulates in the brain over the course of the day (and then gets washed out while we sleep), so if you’re sleepy in the afternoon (for reasons other than: you just had a nap and now have sleep inertia again), then caffeine can block that adenosine in the afternoon.
Of course, caffeine is also a stimulant (it increases adrenaline levels and promotes vasoconstriction), but its effects at healthily small doses are modest for most people, and you’d do better by splashing cold water on your face and/or listening to some upbeat music.
Learn more: The Two Sides Of Caffeine
Time your naps correctly (if you take naps)
Dr. Breus has a lot to say about this, based on a lot of clinical research, but as it’s entirely consistent with what we’ve written before (based on the exact same research), to save space we’ll link to that here:
How To Be An Expert Nap-Artist (With No “Sleep-Hangovers”)
Calculate your bedtime correctly
Remember what we said about sleep cycles? This means that that famous “7–9 hours sleep” is actually “either 7½ or 9 hours sleep”—because those are multiples of 90 minutes, whereas 8 hours (for example) is not.
So, consider the time you want to get up (ideally, this should be relatively early, and the same time every day), and then count backwards either 7½ or 9 hours sleep (you choose), add 20–30 minutes to fall asleep, and that’s your bedtime.
So for example: if you want to have 7½ hours sleep and get up at 6am, then your bedtime is anywhere between 10pm and 10:10pm.
Remember how we said not to sleep in, even if you have a sleep debt? Now is the time to pay it off, if you have one. If you normally sleep 7½ hours, then make tonight a 9-hour sleep (plus 20–30 minutes to fall asleep). This means you’ll still get up at 6am, but your bedtime is now anywhere between 8:30pm and 8:40pm.
Want to know more from Dr. Breus?
You might like this excellent book of his that we reviewed a while back:
The Power of When – by Dr. Michael Breus
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What Different Kinds of Hair Loss/Thinning Say About Your Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Siobhan Deshauer shows us different kinds of hair loss, what causes them, and what can be done about them:
Many different causes
Here’s how to tell them apart:
- Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, causing hair loss that can occur at any age and affects about 1 in 50 people. It often presents as smooth patches of hair loss and can be treated with steroid injections. Severe cases may require high-dose prednisone, which can restore hair growth over time.
- Discoid lupus is an autoimmune disease that affects the skin, leading to inflammation, scarring, and permanent hair loss. Unlike alopecia areata, it causes visible damage to the scalp and hair follicles. This type of lupus typically does not involve internal organs, unlike systemic lupus.
- Telogen effluvium occurs when a major systemic shock, such as an infection, surgery, or significant stress, triggers many hair follicles to enter the resting phase simultaneously, resulting in delayed hair shedding. The condition is diagnosed with a “hair pull test” and is typically temporary, as the resting phase is followed by normal hair growth phases.
- Allergic reactions to products, such as hair dye containing PPD, can cause hair loss due to scalp irritation and inflammation. An allergic response may trigger hair follicles to enter a resting phase, leading to hair loss by the same mechanism as telogen effluvium. Treatment with steroids can calm the reaction, and hair usually regrows after recovery.
- Syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection, can present with varied symptoms, including hair loss in a distinct moth-eaten pattern. Hair loss due to syphilis is reversible and curable with penicillin treatment, with hair regrowth typically occurring a few months after treatment.
- Biotin deficiency is rare due to its production by gut bacteria and presence in foods such as nuts, seeds, and beans such as soybeans. Deficiency can result from excessive consumption of raw egg whites, which block absorption. Severe deficiency causes hair loss and skin issues but can be treated effectively with biotin supplements.
- Iron deficiency anemia can cause hair thinning along with symptoms like fatigue and breathlessness. It often results from inadequate dietary intake, but can also occur after heavy menstrual bleeding. Treatment with iron supplements, or blood transfusions in severe cases, can restore both hair and energy levels, leading to significant improvements.
- Trichotillomania is a psychological condition marked by an uncontrollable urge to pull out one’s hair, often associated with anxiety or depression. Hair patches may show different stages of regrowth. While it can be challenging to manage, the condition can be treated with appropriate psychological and medical support.
- Traction alopecia results from hairstyles that exert prolonged tension on the hair, causing it to thin or fall out. This type of hair loss can be prevented by reducing the strain on the hair. Loosening hairstyles and giving the scalp a break can help hair regrow over time.
- Hypothyroidism causes symptoms like fatigue, dry skin, and hair thinning due to insufficient thyroid hormone production—however, it can be managed with diet, and if necessary, thyroid medications.
- Zinc deficiency may also cause hair loss and a characteristic rash. Treatment with zinc supplements can significantly improve hair growth and other symptoms.
- Medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, Accutane, and anti-seizure medications like valproic acid, are known to cause hair loss as a side effect. This type of hair loss is often reversible once the medication is stopped.
- Male pattern hair loss, or androgenic alopecia, is influenced by testosterone and genetic risk factors—which, contrary to popular belief, can come from either or both sides of the family. Early onset, especially before age 40, is linked to an increased risk of heart disease. However, effective treatments are available, and early intervention is beneficial.
- Female pattern hair loss is basically the same thing as male pattern hair loss (indeed, it is literally still androgenic alopecia), just a) almost always much less severe and b) with a gender-appropriate name. It affects up to 40% of women by age 50 and is characterized by thinning hair at the top of the head. It’s related to hormonal imbalances involving testosterone, such as those seen in PCOS and menopause, amongst other less common causes. Early treatment can be effective, and research is ongoing to develop more targeted therapies.
Dr. Siobhan Deshauer advises, if you’re experiencing hair loss, to monitor other symptoms too if applicable, take photos for tracking, and consult a doctor early for diagnosis and potential treatment.
For more on all of this plus visual illustrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
No, sugar doesn’t make your kids hyperactive
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s a Saturday afternoon at a kids’ birthday party. Hordes of children are swarming between the spread of birthday treats and party games. Half-eaten cupcakes, biscuits and lollies litter the floor, and the kids seem to have gained superhuman speed and bounce-off-the-wall energy. But is sugar to blame?
The belief that eating sugary foods and drinks leads to hyperactivity has steadfastly persisted for decades. And parents have curtailed their children’s intake accordingly.
Balanced nutrition is critical during childhood. As a neuroscientist who has studied the negative effects of high sugar “junk food” diets on brain function, I can confidently say excessive sugar consumption does not have benefits to the young mind. In fact, neuroimaging studies show the brains of children who eat more processed snack foods are smaller in volume, particularly in the frontal cortices, than those of children who eat a more healthful diet.
But today’s scientific evidence does not support the claim sugar makes kids hyperactive.
Sharomka/Shutterstock The hyperactivity myth
Sugar is a rapid source of fuel for the body. The myth of sugar-induced hyperactivity can be traced to a handful of studies conducted in the 1970s and early 1980s. These were focused on the Feingold Diet as a treatment for what we now call Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), a neurodivergent profile where problems with inattention and/or hyperactivity and impulsivity can negatively affect school, work or relationships.
Devised by American paediatric allergist Benjamin Feingold, the diet is extremely restrictive. Artificial colours, sweeteners (including sugar) and flavourings, salicylates including aspirin, and three preservatives (butylated hydroxyanisole, butylated hydroxytoluene, and tert-Butrylhdryquinone) are eliminated.
Salicylates occur naturally in many healthy foods, including apples, berries, tomatoes, broccoli, cucumbers, capsicums, nuts, seeds, spices and some grains. So, as well as eliminating processed foods containing artificial colours, flavours, preservatives and sweeteners, the Feingold diet eliminates many nutritious foods helpful for healthy development.
However, Feingold believed avoiding these ingredients improved focus and behaviour. He conducted some small studies, which he claimed showed a large proportion of hyperactive children responded favourably to his diet.
Even it doesn’t make kids hyperactive, they shouldn’t have too much sugar. DenisMArt/Shutterstock Flawed by design
The methods used in the studies were flawed, particularly with respect to adequate control groups (who did not restrict foods) and failed to establish a causal link between sugar consumption and hyperactive behaviour.
Subsequent studies suggested less than 2% responded to restrictions rather than Feingold’s claimed 75%. But the idea still took hold in the public consciousness and was perpetuated by anecdotal experiences.
Fast forward to the present day. The scientific landscape looks vastly different. Rigorous research conducted by experts has consistently failed to find a connection between sugar and hyperactivity. Numerous placebo-controlled studies have demonstrated sugar does not significantly impact children’s behaviour or attention span.
One landmark meta-analysis study, published almost 20 years ago, compared the effects of sugar versus a placebo on children’s behaviour across multiple studies. The results were clear: in the vast majority of studies, sugar consumption did not lead to increased hyperactivity or disruptive behaviour.
Subsequent research has reinforced these findings, providing further evidence sugar does not cause hyperactivity in children, even in those diagnosed with ADHD.
While Feingold’s original claims were overstated, a small proportion of children do experience allergies to artificial food flavourings and dyes.
Pre-school aged children may be more sensitive to food additives than older children. This is potentially due to their smaller body size, or their still-developing brain and body.
Hooked on dopamine?
Although the link between sugar and hyperactivity is murky at best, there is a proven link between the neurotransmitter dopamine and increased activity.
The brain releases dopamine when a reward is encountered – such as an unexpected sweet treat. A surge of dopamine also invigorates movement – we see this increased activity after taking psychostimulant drugs like amphetamine. The excited behaviour of children towards sugary foods may be attributed to a burst of dopamine released in expectation of a reward, although the level of dopamine release is much less than that of a psychostimulant drug.
Dopamine function is also critically linked to ADHD, which is thought to be due to diminished dopamine receptor function in the brain. Some ADHD treatments such as methylphenidate (labelled Ritalin or Concerta) and lisdexamfetamine (sold as Vyvanse) are also psychostimulants. But in the ADHD brain the increased dopamine from these drugs recalibrates brain function to aid focus and behavioural control.
Maybe it’s less of a sugar rush and more of a dopamine rush? Anastasiya Tsiasemnikava/Shutterstock Why does the myth persist?
The complex interplay between diet, behaviour and societal beliefs endures. Expecting sugar to change your child’s behaviour can influence how you interpret what you see. In a study where parents were told their child had either received a sugary drink, or a placebo drink (with a non-sugar sweetener), those parents who expected their child to be hyperactive after having sugar perceived this effect, even when they’d only had the sugar-free placebo.
The allure of a simple explanation – blaming sugar for hyperactivity – can also be appealing in a world filled with many choices and conflicting voices.
Healthy foods, healthy brains
Sugar itself may not make your child hyperactive, but it can affect your child’s mental and physical health. Rather than demonising sugar, we should encourage moderation and balanced nutrition, teaching children healthy eating habits and fostering a positive relationship with food.
In both children and adults, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends limiting free sugar consumption to less than 10% of energy intake, and a reduction to 5% for further health benefits. Free sugars include sugars added to foods during manufacturing, and naturally present sugars in honey, syrups, fruit juices and fruit juice concentrates.
Treating sugary foods as rewards can result in them becoming highly valued by children. Non-sugar rewards also have this effect, so it’s a good idea to use stickers, toys or a fun activity as incentives for positive behaviour instead.
While sugar may provide a temporary energy boost, it does not turn children into hyperactive whirlwinds.
Amy Reichelt, Senior Lecturer (Adjunct), Nutritional neuroscientist, University of Adelaide
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Yoga of Breath – by Richard Rosen
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You probably know to breathe through your nose, and to breathe with your diaphragm. But did you know you’re usually only breathing through one nostril at a time, and alternate between nostrils every few hours? And did you know how to breathe through both nostrils equally instead, and the benefits that can bring?
The above is one example of many, of things that make this book stand out from the crowd when it comes to breathing exercises. Author Richard Rosen has a deep expertise in this topic, and explains everything clearly and comprehensively, without leaving room for ambiguity.
While most of the book focuses on the mechanics and physical techniques of breathing, he does also cover some more mindstate-related things too—without which, it wouldn’t be yoga.
If the book has a downside, it’s that its comprehensive nature could be off-putting to readers new to breathing work in general. However, since he does explain everything from the ground up, that’s no reason to be put off this book, iff you’re serious about learning.
Bottom line: if you’d like a deeper understanding of breathwork than “breathe slowly through your nose, using your diaphragm”, this book will teach you depths of breathing you probably didn’t know were possible.
Click here to check out The Yoga of Breath, and catch yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: