Oven-Roasted Ratatouille
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a supremely low-effort, high-yield dish. It’s a nutritional tour-de-force, and very pleasing to the tastebuds too. We use flageolet beans in this recipe; they are small immature kidney beans. If they’re not available, using kidney beans or really any other legume is fine.
You will need
- 2 large zucchini, sliced
- 2 red peppers, sliced
- 1 large eggplant, sliced and cut into semicircles
- 1 red onion, thinly sliced
- 2 cans chopped tomatoes
- 2 cans flageolet beans, drained and rinsed (or 2 cups same, cooked, drained, and rinsed)
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp balsamic vinegar
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tbsp red chili pepper flakes (omit or adjust per your heat preferences)
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Mixed herbs, per your preference. It’s hard to go wrong with this one, but we suggest leaning towards either basil and oregano or rosemary and thyme. We also suggest having some finely chopped to go into the dish, and some held back to go on the dish as a garnish.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 350℉ / 180℃.
2) Mix all the ingredients (except the tomatoes and herbs) in a big mixing bowl, ensuring even distribution.
2) Add the tomatoes. The reason we didn’t add these before is because it would interfere with the oil being distributed evenly across the vegetables.
3) Transfer to a deep-walled oven tray or an ovenproof dish, and roast for 30 minutes.
4) Stir, add the chopped herbs, stir again, and return to the oven for another 30 minutes.
5) Serve (hot or cold), adding any herb garnish you wish to use.
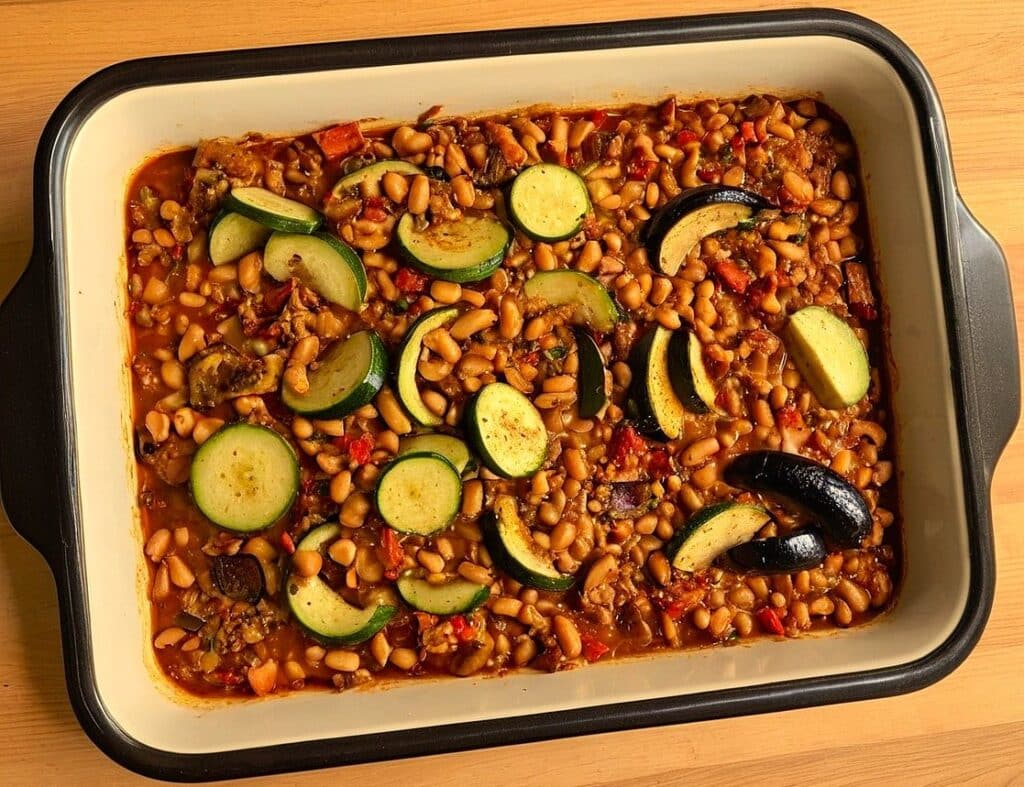

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Recover Quickly From A Stomach Bug
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Recover Quickly From A Stomach Bug
Is it norovirus, or did you just eat something questionable? We’re not doctors, let alone your doctors, and certainly will not try to diagnose from afar. And as ever, if unsure and/or symptoms don’t go away or do get worse, seek professional medical advice.
That out of the way, we can give some very good general-purpose tips for this one…
Help your immune system to help you
So far as you can, you want a happy healthy immune system. For the most part, we’d recommend the following things:
Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
…but you probably don’t want to be exercising with a stomach bug, so perhaps sit that one out. Exercise is the preventative; what you need right now is rest.
Hydrate—but watch out
Hydration is critical for recovery especially if you have diarrhea, but drinking too much water too quickly will just make things worse. Great options for getting good hydration more slowly are:
- Peppermint tea
- (peppermint also has digestion-settling properties)
- Ginger tea
- See also: Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
- Broths
- These will also help replenish your sodium and other nutrients, gently. Chicken soup for your stomach, and all that. A great plant-based option is sweetcorn soup.
- By broths, we mean clear(ish) water-based soups. This is definitely not the time for creamier soups.
❝Milk and dairy products should be avoided for 24 to 48 hours as they can make diarrhea worse.
Initial dietary choices when refeeding should begin with soups and broth.❞
Source: American College of Gastroenterology
Other things to avoid
Caffeine stimulates the digestion in a way that can make things worse.
Fat is more difficult to digest, and should also be avoided until feeling better.
To medicate or not to medicate?
Loperamide (also known by the brand name Imodium) is generally safe when used as directed.
Click here to see its uses, dosage, side effects, and contraindications
Antibiotics may be necessary for certain microbial infections, but should not be anyone’s first-choice treatment unless advised otherwise by your doctor/pharmacist.
Note that if your stomach bug is not something that requires antibiotics, then taking antibiotics can actually make it worse as the antibiotics wipe out your gut bacteria that were busy helping fight whatever’s going wrong in there:
- Facing a new challenge: the adverse effects of antibiotics on gut microbiota and host immunity
- Antibiotics as major disruptors of gut microbiota
- Microbiotoxicity: antibiotic usage and its unintended harm to the microbiome
A gentler helper
If you want to give your “good bacteria” a hand while giving pathogens a harder time of it, then a much safer home remedy is a little (seriously, do not over do it; we are talking 1–2 tablespoons, or around 20ml) apple cider vinegar, taken diluted in a glass of water.
❝Several studies indicate apple cider vinegar (ACV)’s usefulness in lowering postprandial glycemic response, specifically by slowing of gastric motility❞
(Slowing gastric motility is usually exactly what you want in the case of a stomach bug, and apple cider vinegar)
See also:
- Antimicrobial activity of apple cider vinegar against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans
- Antibacterial apple cider vinegar eradicates methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus and resistant Escherichia coli
Take care!
Share This Post
- Peppermint tea
-
Peach vs Papaya – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing peach to papaya, we picked the peach.
Why?
It was close!
In terms of macros, there’s not much between them; they are close to identical on protein, carbs, and fiber. Technically peach has slightly more protein (+0.4g/100g) and papaya has slightly more carbs and fiber (+1.28g/100g carbs, +0.2g/100g fiber), but since the differences are so tiny, we’re calling this section a tie—bearing in mind, these numbers are based on averages, which means that when they’re very close, they’re meaningless—one could easily, for example, pick up a peach that has more fiber than a papaya, because that 0.2g/100g is well within the margin of variation. So, as we say: a tie.
When it comes to vitamins, things are also close; peaches have more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, and E, while papaya has more of vitamins A, B6, B9, and C. This is a 4:4 tie, but since the most notable margin of difference is vitamin C (of which papayas have 9x more) while the others are much closer, we’ll call this a tie-breaker win for papaya.
The category of minerals sets things apart more: peaches have more copper, iron, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while papaya has more calcium, magnesium, and selenium. That’s already a 6:3 win for peaches, before we take into account that the numbers for papaya’s calcium and selenium are tiny, so adding this to the already 6:3 win for peaches makes for a clear and easy win for peaches in this category.
Adding up the sections is 1W/1D/1L for both fruits, but looking at the win/loss for each, it’s clear which won/lost on a tiebreaker, and which won/lost by a large margin, so peaches get the victory here.
Of course, enjoy either or both, though! And see below for a bonus feature of peaches:
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← peaches are high on this list! They kill cancer cells while sparing healthy ones 🙂
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Mediterranean Diet Book Suggestions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝What is Mediterranean diet which book to read?❞
We did a special edition about the Mediterranean Diet! So that’s a great starting point.
As to books, there are so many, and we review books about it from time to time, so keep an eye out for our daily “One-Minute Book Review” section. We do highly recommend “How Not To Die”, which is a science-heavy approach to diet-based longevity, and essentially describes the Mediterranean Diet, with some tweaks.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Cashew Nuts vs Macadamia Nuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cashews to macadamias, we picked the cashews.
Why?
In terms of macros, cashews have more than 2x the protein, while macadamias have nearly 2x the fat. The fats are mostly monounsaturated, so it’s still healthy in moderation, but still, we’re going to prize the protein over it and call this category a nominal win for cashews.
When it comes to vitamins, things are fairly even; cashews have more of vitamins B5, B6, B9, and E, while macadamias have more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, and C.
In the category of minerals, cashews take the clear lead; cashews have more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while macadamias have more calcium and manganese.
In short, enjoy both (as macadamias have their benefits too), but cashews win in total nutrient density.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Even small diet tweaks can lead to sustainable weight loss
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s a well-known fact that to lose weight, you either need to eat less or move more. But how many calories do you really need to cut out of your diet each day to lose weight? It may be less than you think.
To determine how much energy (calories) your body requires, you need to calculate your total daily energy expenditure (TDEE). This is comprised of your basal metabolic rate (BMR) – the energy needed to sustain your body’s metabolic processes at rest – and your physical activity level. Many online calculators can help determine your daily calorie needs.
If you reduce your energy intake (or increase the amount you burn through exercise) by 500-1,000 calories per day, you’ll see a weekly weight loss of around one pound (0.45kg).
But studies show that even small calorie deficits (of 100-200 calories daily) can lead to long-term, sustainable weight-loss success. And although you might not lose as much weight in the short-term by only decreasing calories slightly each day, these gradual reductions are more effective than drastic cuts as they tend to be easier to stick with.
Small diet changes can still lead to weight loss in the long run. Monkey Business Images/ Shutterstock Hormonal changes
When you decrease your calorie intake, the body’s BMR often decreases. This phenomenon is known as adaptive thermogenesis. This adaptation slows down weight loss so the body can conserve energy in response to what it perceives as starvation. This can lead to a weight-loss plateau – even when calorie intake remains reduced.
Caloric restriction can also lead to hormonal changes that influence metabolism and appetite. For instance, thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism, can decrease – leading to a slower metabolic rate. Additionally, leptin levels drop, reducing satiety, increasing hunger and decreasing metabolic rate.
Ghrelin, known as the “hunger hormone”, also increases when caloric intake is reduced, signalling the brain to stimulate appetite and increase food intake. Higher ghrelin levels make it challenging to maintain a reduced calorie diet, as the body constantly feels hungrier.
Insulin, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and fat storage, can improve in sensitivity when we reduce calorie intake. But sometimes, insulin levels decrease instead, affecting metabolism and leading to a reduction in daily energy expenditure. Cortisol, the stress hormone, can also spike – especially when we’re in a significant caloric deficit. This may break down muscles and lead to fat retention, particularly in the stomach.
Lastly, hormones such as peptide YY and cholecystokinin, which make us feel full when we’ve eaten, can decrease when we lower calorie intake. This may make us feel hungrier.
Fortunately, there are many things we can do to address these metabolic adaptations so we can continue losing weight.
Weight loss strategies
Maintaining muscle mass (either through resistance training or eating plenty of protein) is essential to counteract the physiological adaptations that slow weight loss down. This is because muscle burns more calories at rest compared to fat tissue – which may help mitigate decreased metabolic rate.
Portion control is one way of decreasing your daily calorie intake. Fevziie/ Shutterstock Gradual caloric restriction (reducing daily calories by only around 200-300 a day), focusing on nutrient-dense foods (particularly those high in protein and fibre), and eating regular meals can all also help to mitigate these hormonal challenges.
But if you aren’t someone who wants to track calories each day, here are some easy strategies that can help you decrease daily calorie intake without thinking too much about it:
1. Portion control: reducing portion sizes is a straightforward way of reducing calorie intake. Use smaller plates or measure serving sizes to help reduce daily calorie intake.
2. Healthy swaps: substituting high-calorie foods with lower-calorie alternatives can help reduce overall caloric intake without feeling deprived. For example, replacing sugary snacks with fruits or swapping soda with water can make a substantial difference to your calorie intake. Fibre-rich foods can also reduce the calorie density of your meal.
3. Mindful eating: practising mindful eating involves paying attention to hunger and fullness cues, eating slowly, and avoiding distractions during meals. This approach helps prevent overeating and promotes better control over food intake.
4. Have some water: having a drink with your meal can increase satiety and reduce total food intake at a given meal. In addition, replacing sugary beverages with water has been shown to reduce calorie intake from sugars.
4. Intermittent fasting: restricting eating to specific windows can reduce your caloric intake and have positive effects on your metabolism. There are different types of intermittent fasting you can do, but one of the easiest types is restricting your mealtimes to a specific window of time (such as only eating between 12 noon and 8pm). This reduces night-time snacking, so is particularly helpful if you tend to get the snacks out late in the evening.
Long-term behavioural changes are crucial for maintaining weight loss. Successful strategies include regular physical activity, continued mindful eating, and periodically being diligent about your weight and food intake. Having a support system to help you stay on track can also play a big role in helping you maintain weight loss.
Modest weight loss of 5-10% body weight in people who are overweight or obese offers significant health benefits, including improved metabolic health and reduced risk of chronic diseases. But it can be hard to lose weight – especially given all the adaptations our body has to prevent it from happening.
Thankfully, small, sustainable changes that lead to gradual weight loss appear to be more effective in the long run, compared with more drastic lifestyle changes.
Alexandra Cremona, Lecturer, Human Nutrition and Dietetics, University of Limerick
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
7 Kinds Of Rest When Sleep Is Not Enough
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Taking Rest Seriously (More Than Just Sleep)
This is Dr. Matthew Edlund. He has 44 years experience as a psychiatrist, and is also a sleep specialist. He has a holistic view of health, which is reflected in his practice; he advocates for “a more complete health: physical, mental, social, and spiritual well-being”.
What does he want us to know?
Sleep, yes
Sleep cannot do all things for us in terms of rest, but it can do a lot, and it is critical. It is, in short, a necessary-but-not-sufficient condition for being well-rested.
See also: Why You Probably Need More Sleep
Rest actively
Rest is generally thought of as a passive activity, if you’ll pardon the oxymoron. Popular thinking is that it’s not something defined by what we do, so much what we stop doing.
In contrast, Dr. Edlund argues that to take rest seriously, we need do restful things.
Rest is as important as eating, and we wouldn’t want for that to “just happen”, would we?
Dr. Edlund advocates for restful activities such as going to the garden (or a nearby park) to relax. He also suggests we not underestimate the power of sex as an actively restful activity—this one is generally safer in the privacy of one’s home, though!
Rest physically
This is about actively relaxing our body—yoga is a great option here, practised in a way that is not physically taxing, but is physically rejuvenating; gentle stretches are key. Without such things, our body will keep tension, and that is not restful.
For the absolute most restful yogic practice? Check out:
Non-Sleep Deep Rest: A Neurobiologist’s Take
this is about yoga nidra!
Rest mentally
The flipside of the above is that we do need to rest our mind also. When we try to rest from a mental activity by taking on a different mental activity that uses the same faculties of the brain, it is not restful.
Writer’s example: as a writer, I could not rest from my writing by writing recreationally, or even by reading. An accountant, however, could absolutely rest from accounting by picking up a good book, should they feel so inclined.
Rest socially
While we all have our preferences when it comes to how much or how little social interaction we like in our lives, humans are fundamentally social creatures, and it is hardwired into us by evolution to function at our best in a community.
This doesn’t mean you have to go out partying every night, but it does mean you should take care to spend at least a little time with friends, even if just once or twice per week, and yes, even if it’s just a videocall (in person is best, but not everyone lives close by!)
If your social life is feeling a little thin on the ground these days, that’s a very common thing—not only as we get older, but also as many social institutions took a dive in functionality on account of the pandemic, and many are still floundering. Nevertheless, there are more options than you probably realize; yes, even for the naturally reclusive:
How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Rest spiritually
Be we religious or not, there are scientifically well-evidenced benefits to religious practices—some are because of the social aspect, and follow on from what we talked about just above. Other benefits come from activities such as prayer or meditation (which means that having some kind of faith, while beneficial, is not actually a requirement for spiritual rest—comparable practices without faith are fine too).
We discussed the overlapping practices of prayer and meditation, here:
The Science Of Mantra Meditation
Rest at home
Obviously, most people sleep at home. But…
Busy family homes can sometimes need a bit of conscious effort to create a restful environment, even if just for a while. A family dinner together is one great way to achieve this, and also ties in with the social element we mentioned before!
A different challenge faced by a lot of older people without live-in families, on the other hand, is the feeling of too much opportunity for rest—and then a feeling of shame for taking it. The view is commonly held that, for example, taking an afternoon nap is a sign of weakness.
On the contrary: taking an afternoon nap can be a good source of strength! Check out:
How To Nap Like A Pro (No More “Sleep Hangovers”!)
Rest at work
Our readership has a lot of retirees, but we know that’s not the case for everyone. How then, to rest while at work? Ideally we have breaks, of course, but most workplaces do not exactly have an amusement arcade in the break room. Nevertheless, there are some quick resets that can be done easily, anywhere, and (almost) any time:
Meditation Games: Meditation That You’ll Actually Enjoy
Want to know more?
You might also like:
How To Rest More Efficiently (Yes, Really)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: