No, sugar doesn’t make your kids hyperactive
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s a Saturday afternoon at a kids’ birthday party. Hordes of children are swarming between the spread of birthday treats and party games. Half-eaten cupcakes, biscuits and lollies litter the floor, and the kids seem to have gained superhuman speed and bounce-off-the-wall energy. But is sugar to blame?
The belief that eating sugary foods and drinks leads to hyperactivity has steadfastly persisted for decades. And parents have curtailed their children’s intake accordingly.
Balanced nutrition is critical during childhood. As a neuroscientist who has studied the negative effects of high sugar “junk food” diets on brain function, I can confidently say excessive sugar consumption does not have benefits to the young mind. In fact, neuroimaging studies show the brains of children who eat more processed snack foods are smaller in volume, particularly in the frontal cortices, than those of children who eat a more healthful diet.
But today’s scientific evidence does not support the claim sugar makes kids hyperactive.

The hyperactivity myth
Sugar is a rapid source of fuel for the body. The myth of sugar-induced hyperactivity can be traced to a handful of studies conducted in the 1970s and early 1980s. These were focused on the Feingold Diet as a treatment for what we now call Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), a neurodivergent profile where problems with inattention and/or hyperactivity and impulsivity can negatively affect school, work or relationships.
Devised by American paediatric allergist Benjamin Feingold, the diet is extremely restrictive. Artificial colours, sweeteners (including sugar) and flavourings, salicylates including aspirin, and three preservatives (butylated hydroxyanisole, butylated hydroxytoluene, and tert-Butrylhdryquinone) are eliminated.
Salicylates occur naturally in many healthy foods, including apples, berries, tomatoes, broccoli, cucumbers, capsicums, nuts, seeds, spices and some grains. So, as well as eliminating processed foods containing artificial colours, flavours, preservatives and sweeteners, the Feingold diet eliminates many nutritious foods helpful for healthy development.
However, Feingold believed avoiding these ingredients improved focus and behaviour. He conducted some small studies, which he claimed showed a large proportion of hyperactive children responded favourably to his diet.

Flawed by design
The methods used in the studies were flawed, particularly with respect to adequate control groups (who did not restrict foods) and failed to establish a causal link between sugar consumption and hyperactive behaviour.
Subsequent studies suggested less than 2% responded to restrictions rather than Feingold’s claimed 75%. But the idea still took hold in the public consciousness and was perpetuated by anecdotal experiences.
Fast forward to the present day. The scientific landscape looks vastly different. Rigorous research conducted by experts has consistently failed to find a connection between sugar and hyperactivity. Numerous placebo-controlled studies have demonstrated sugar does not significantly impact children’s behaviour or attention span.
One landmark meta-analysis study, published almost 20 years ago, compared the effects of sugar versus a placebo on children’s behaviour across multiple studies. The results were clear: in the vast majority of studies, sugar consumption did not lead to increased hyperactivity or disruptive behaviour.
Subsequent research has reinforced these findings, providing further evidence sugar does not cause hyperactivity in children, even in those diagnosed with ADHD.
While Feingold’s original claims were overstated, a small proportion of children do experience allergies to artificial food flavourings and dyes.
Pre-school aged children may be more sensitive to food additives than older children. This is potentially due to their smaller body size, or their still-developing brain and body.
Hooked on dopamine?
Although the link between sugar and hyperactivity is murky at best, there is a proven link between the neurotransmitter dopamine and increased activity.
The brain releases dopamine when a reward is encountered – such as an unexpected sweet treat. A surge of dopamine also invigorates movement – we see this increased activity after taking psychostimulant drugs like amphetamine. The excited behaviour of children towards sugary foods may be attributed to a burst of dopamine released in expectation of a reward, although the level of dopamine release is much less than that of a psychostimulant drug.
Dopamine function is also critically linked to ADHD, which is thought to be due to diminished dopamine receptor function in the brain. Some ADHD treatments such as methylphenidate (labelled Ritalin or Concerta) and lisdexamfetamine (sold as Vyvanse) are also psychostimulants. But in the ADHD brain the increased dopamine from these drugs recalibrates brain function to aid focus and behavioural control.

Why does the myth persist?
The complex interplay between diet, behaviour and societal beliefs endures. Expecting sugar to change your child’s behaviour can influence how you interpret what you see. In a study where parents were told their child had either received a sugary drink, or a placebo drink (with a non-sugar sweetener), those parents who expected their child to be hyperactive after having sugar perceived this effect, even when they’d only had the sugar-free placebo.
The allure of a simple explanation – blaming sugar for hyperactivity – can also be appealing in a world filled with many choices and conflicting voices.
Healthy foods, healthy brains
Sugar itself may not make your child hyperactive, but it can affect your child’s mental and physical health. Rather than demonising sugar, we should encourage moderation and balanced nutrition, teaching children healthy eating habits and fostering a positive relationship with food.
In both children and adults, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends limiting free sugar consumption to less than 10% of energy intake, and a reduction to 5% for further health benefits. Free sugars include sugars added to foods during manufacturing, and naturally present sugars in honey, syrups, fruit juices and fruit juice concentrates.
Treating sugary foods as rewards can result in them becoming highly valued by children. Non-sugar rewards also have this effect, so it’s a good idea to use stickers, toys or a fun activity as incentives for positive behaviour instead.
While sugar may provide a temporary energy boost, it does not turn children into hyperactive whirlwinds.
Amy Reichelt, Senior Lecturer (Adjunct), Nutritional neuroscientist, University of Adelaide
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How does cancer spread to other parts of the body?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
All cancers begin in a single organ or tissue, such as the lungs or skin. When these cancers are confined in their original organ or tissue, they are generally more treatable.
But a cancer that spreads is much more dangerous, as the organs it spreads to may be vital organs. A skin cancer, for example, might spread to the brain.
This new growth makes the cancer much more challenging to treat, as it can be difficult to find all the new tumours. If a cancer can invade different organs or tissues, it can quickly become lethal.
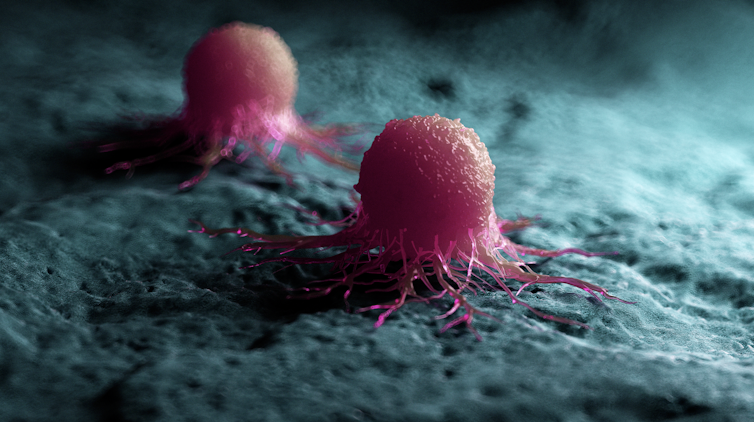
When cancer spreads in this way, it’s called metastasis. Metastasis is responsible for the majority (67%) of cancer deaths.
Cells are supposed to stick to surrounding tissue
Our bodies are made up of trillions of tiny cells. To keep us healthy, our bodies are constantly replacing old or damaged cells.
Each cell has a specific job and a set of instructions (DNA) that tells it what to do. However, sometimes DNA can get damaged.
This damage might change the instructions. A cell might now multiply uncontrollably, or lose a property known as adherence. This refers to how sticky a cell is, and how well it can cling to other surrounding cells and stay where it’s supposed to be.
If a cancer cell loses its adherence, it can break off from the original tumour and travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to almost anywhere. This is how metastasis happens.
Many of these travelling cancer cells will die, but some will settle in a new location and begin to form new cancers.
Some cells settle in a new location.
Scipro/ShutterstockParticular cancers are more likely to metastasise to particular organs that help support their growth. Breast cancers commonly metastasise to the bones, liver, and lungs, while skin cancers like melanomas are more likely to end up in the brain and heart.
Unlike cancers which form in solid organs or tissues, blood cancers like leukaemia already move freely through the bloodstream, but can escape to settle in other organs like the liver or brain.
When do cancers metastasise?
The longer a cancer grows, the more likely it is to metastasise. If not caught early, a patient’s cancer may have metastasised even before it’s initially diagnosed.
Metastasis can also occur after cancer treatment. This happens when cancer cells are dormant during treatment – drugs may not “see” those cells. These invisible cells can remain hidden in the body, only to wake up and begin growing into a new cancer months or even years later.
For patients who already have cancer metastases at diagnosis, identifying the location of the original tumour – called the “primary site” – is important. A cancer that began in the breast but has spread to the liver will probably still behave like a breast cancer, and so will respond best to an anti-breast cancer therapy, and not anti-liver cancer therapy.
As metastases can sometimes grow faster than the original tumour, it’s not always easy to tell which tumour came first. These cancers are called “cancers of unknown primary” and are the 11th most commonly diagnosed cancers in Australia.
One way to improve the treatment of metastatic cancer is to improve our ways of detecting and identifying cancers, to ensure patients receive the most effective drugs for their cancer type.
What increases the chances of metastasis and how can it be prevented?
If left untreated, most cancers will eventually acquire the ability to metastasise.
While there are currently no interventions that specifically prevent metastasis, cancer patients who have their tumours surgically removed may also be given chemotherapy (or other drugs) to try and weed out any hidden cancer cells still floating around.
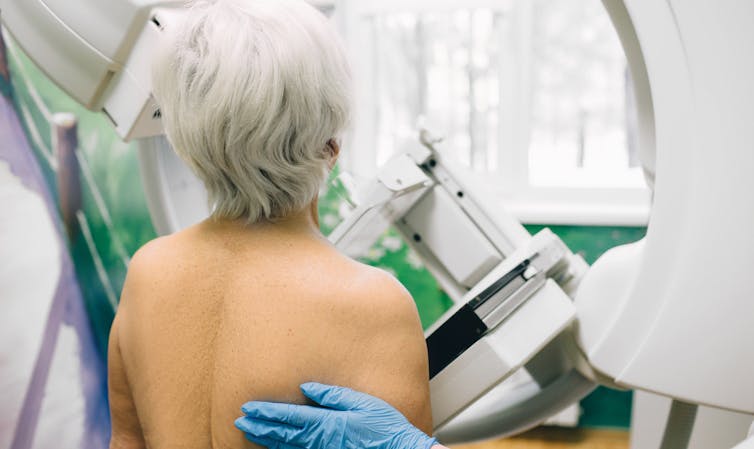
The best way to prevent metastasis is to diagnose and treat cancers early. Cancer screening initiatives such as Australia’s cervical, bowel, and breast cancer screening programs are excellent ways to detect cancers early and reduce the chances of metastasis.
The best way to prevent cancer spreading is to diagnose and treat them early.
Peakstock/ShutterstockNew screening programs to detect cancers early are being researched for many types of cancer. Some of these are simple: CT scans of the body to look for any potential tumours, such as in England’s new lung cancer screening program.
Using artificial intelligence (AI) to help examine patient scans is also possible, which might identify new patterns that suggest a cancer is present, and improve cancer detection from these programs.
More advanced screening methods are also in development. The United States government’s Cancer Moonshot program is currently funding research into blood tests that could detect many types of cancer at early stages.
One day there might even be a RAT-type test for cancer, like there is for COVID.
Will we be able to prevent metastasis in the future?
Understanding how metastasis occurs allows us to figure out new ways to prevent it. One idea is to target dormant cancer cells and prevent them from waking up.
Directly preventing metastasis with drugs is not yet possible. But there is hope that as research efforts continue to improve cancer therapies, they will also be more effective at treating metastatic cancers.
For now, early detection is the best way to ensure a patient can beat their cancer.
Sarah Diepstraten, Senior Research Officer, Blood Cells and Blood Cancer Division, Walter and Eliza Hall Institute and John (Eddie) La Marca, Senior Resarch Officer, Walter and Eliza Hall Institute
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Stop Cancer 20 Years Ago
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Get Abreast And Keep Abreast
This is Dr. Jenn Simmons. Her specialization is integrative oncology, as she—then a breast cancer surgeon—got breast cancer, decided the system wasn’t nearly as good from the patients’ side of things as from the doctors’ side, and took to educate herself, and now others, on how things can be better.
What does she want us to know?
Start now
If you have breast cancer, the best time to start adjusting your lifestyle might be 20 years ago, but the second-best time is now. We realize our readers with breast cancer (or a history thereof) probably have indeed started already—all strength to you.
What this means for those of us without breast cancer (or a history therof) is: start now
Even if you don’t have a genetic risk factor, even if there’s no history of it in your family, there’s just no reason not to start now.
Start what, you ask? Taking away its roots. And how?
Inflammation as the root of cancer
To oversimplify: cancer occurs because an accidentally immortal cell replicates and replicates and replicates and takes any nearby resources to keep on going. While science doesn’t know all the details of how this happens, it is a factor of genetic mutation (itself a normal process, without which evolution would be impossible), something which in turn is accelerated by damage to the DNA. The damage to the DNA? That occurs (often as not) as a result of cellular oxidation. Cellular oxidation is far from the only genotoxic thing out there, and a lot of non-food “this thing causes cancer” warnings are usually about other kinds of genotoxicity. But cellular oxidation is a big one, and it’s one that we can fight vigorously with our lifestyle.
Because cellular oxidation and inflammation go hand-in-hand, reducing one tends to reduce the other. That’s why so often you’ll see in our Research Review Monday features, a line that goes something like:
“and now for those things that usually come together: antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and anti-aging”
So, fight inflammation now, and have a reduced risk of a lot of other woes later.
See: How to Prevent (or Reduce) Inflammation
Don’t settle for “normal”
People are told, correctly but not always helpfully, such things as:
- It’s normal to have less energy at your age
- It’s normal to have a weaker immune system at your age
- It’s normal to be at a higher risk of diabetes, heart disease, etc
…and many more. And these things are true! But that doesn’t mean we have to settle for them.
We can be all the way over on the healthy end of the distribution curve. We can do that!
(so can everyone else, given sufficient opportunity and resources, because health is not a zero-sum game)
If we’re going to get a cancer diagnosis, then our 60s are the decade where we’re most likely to get it. Earlier than that and the risk is extant but lower; later than that and technically the risk increases, but we probably got it already in our 60s.
So, if we be younger than 60, then now’s a good time to prepare to hit the ground running when we get there. And if we missed that chance, then again, the second-best time is now:
See: Focusing On Health In Our Sixties
Fast to live
Of course, anything can happen to anyone at any age (alas), but this is about the benefits of living a fasting lifestyle—that is to say, not just fasting for a 4-week health kick or something, but making it one’s “new normal” and just continuing it for life.
This doesn’t mean “never eat”, of course, but it does mean “practice intermittent fasting, if you can”—something that Dr. Simmons strongly advocates.
See: Intermittent Fasting: We Sort The Science From The Hype
While this calls back to the previous “fight inflammation”, it deserves its own mention here as a very specific way of fighting it.
It’s never too late
All of the advices that go before a cancer diagnosis, continue to stand afterwards too. There is no point of “well, I already have cancer, so what’s the harm in…?”
The harm in it after a diagnosis will be the same as the harm before. When it comes to lifestyle, preventing a cancer and preventing it from spreading are very much the same thing, which is also the same as shrinking it. Basically, if it’s anticancer, it’s anticancer, no matter whether it’s before, during, or after.
Dr. Simmons has seen too many patients get a diagnosis, and place their lives squarely in the hands of doctors, when doctors can only do so much.
Instead, Dr. Simmons recommends taking charge of your health as best you are able, today and onwards, no matter what. And that means two things:
- Knowing stuff
- Doing stuff
So it becomes our responsibility (and our lifeline) to educate ourselves, and take action accordingly.
Want to know more?
We recently reviewed her book, and heartily recommend it:
The Smart Woman’s Guide to Breast Cancer – by Dr. Jenn Simmons
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
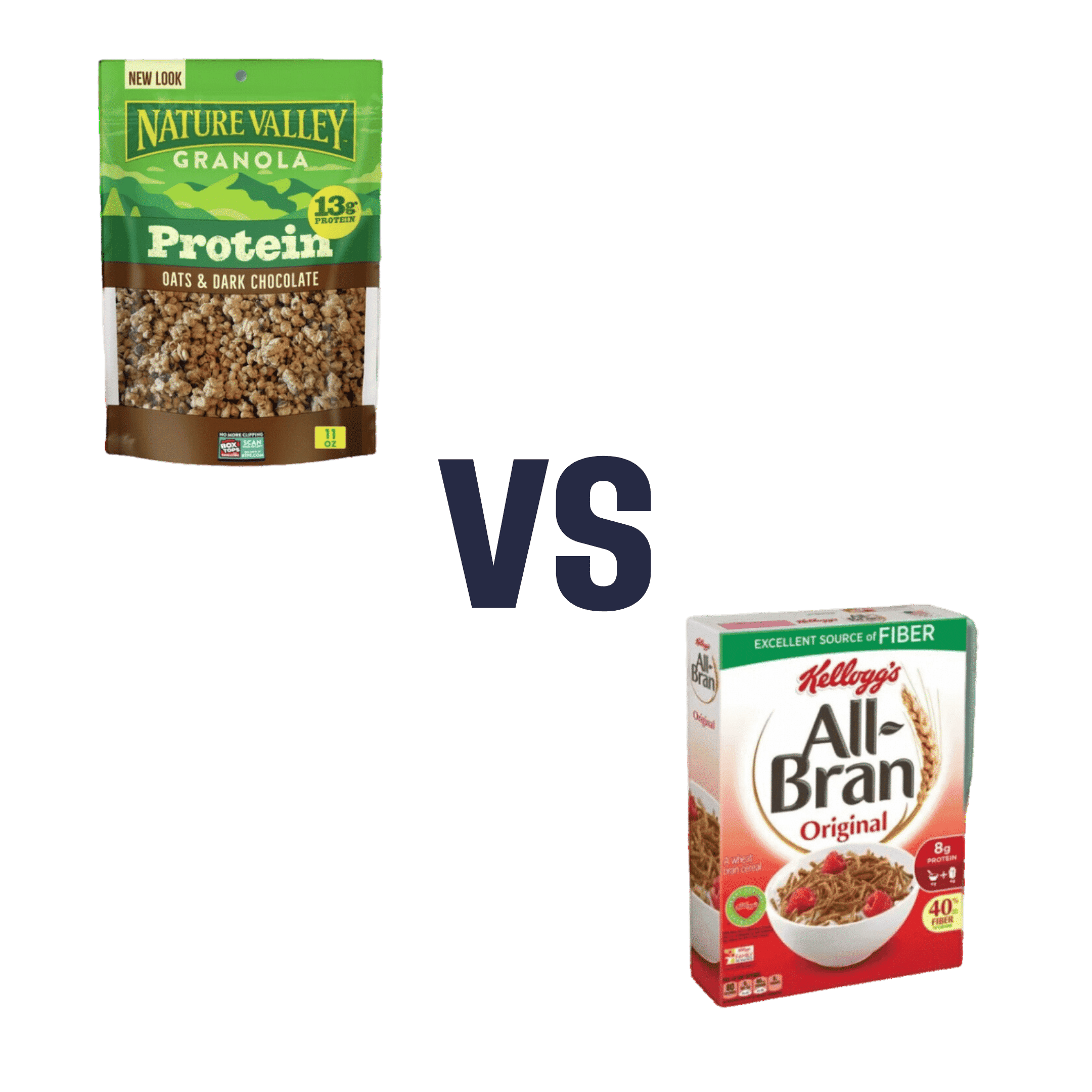
Nature Valley Protein Granola vs Kellog’s All-Bran – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Nature Valley Protein Granola to Kellog’s All-Bran, we picked the All-Bran.
Why?
While the Protein Granola indeed contains more protein (13g/cup, compared to 5g/cup), it also contains three times as much sugar (18g/cup, compared to 9g/cup) and only ⅓ as much fiber (4g/cup, compared to 12g/cup)
Given that fiber is what helps our bodies to absorb sugar more gently (resulting in fewer spikes), this is extremely important, especially since 18g of sugar in one cup of Protein Granola is already most of the recommended daily allowance, all at once!
For reference: the AHA recommends no more than 25g added sugar for women, or 32g for men
Hence, we went for the option with 3x as much fiber and ⅓ of the sugar, the All-Bran.
For more about keeping blood sugars stable, see:
10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Peaches vs Plums – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing peaches to plums, we picked the peaches.
Why?
Both are great! But there is a clear winner out of these two botanically-similar fruits:
In terms of macronutrients they are very similar. Peaches have slightly more protein and plums have slightly more carbs, but the numbers are close enough to make no meaningful difference; they’re both mostly water.
They’re also not too far from each other in the category of vitamins; peaches have more of vitamins B2, B3, B5, E, and choline, while plums have more of vitamins B1, B6, B9, C, and K. They’re equal on vitamin A, by the way, and the vitamins they do differ in, differ by around the same margins, so this category is a clear tie.
When it comes to minerals, however, peaches win easily with more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. The two fruits are equal on calcium, and plum is not higher in any minerals.
While they already won easily because of the mineral situation, it should be noted that peaches also have the lower glycemic index. But honestly, plums are fine too; peaches are just even lower.
So: enjoy both, but if you’re going to pick one, peaches boast the most!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer
- Apricots vs Peaches – Which is Healthier?
- Dried Apricots vs Dried Prunes – Which is Healthier? (prunes are dried plums, usually partially rehydrated)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Staying Sane In A Hyper-Connected World
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Staying Sane In A Hyper-Connected World
There’s a war over there, a genocide in progress somewhere else, and another disease is ravaging the population of somewhere most Americans would struggle to point out on the map. Not only that, but that one politician is at it again, and sweeping wildfires are not doing climate change any favors.
To borrow an expression from Gen-Z…
“Oof”.
A Very Modern Mental Health Menace
For thousands of years, we have had wars and genocides and plagues and corrupt politicians and assorted major disasters. Dire circumstances are not new to us as a species. So what is new?
As some reactionary said during the dot-com boom, “the Internet doesn’t make people stupid; it just makes their stupidity more accessible”.
The same is true now of The Horrors™.
The Internet doesn’t, by and large, make the world worse. But what it does do is make the bad things much, much more accessible.
Understanding and empathy are not bad things, but watch out…
- When soldiers came home from the First World War, those who hadn’t been there had no conception of the horrors that had been endured. That made it harder for the survivors to get support. That was bad.
- Nowadays, while mass media covering horrors certainly doesn’t convey the half of it, even the half it does convey can be overwhelming. This is also bad.
The insidious part is: while people are subjectively reporting good physical/mental health, the reports of the symptoms of poor physical/mental health from the same population do not agree:
Stress in America 2023: A nation grappling with psychological impacts of collective trauma
Should we just not watch the news?
In principle that’s an option, but it’s difficult to avoid, unless you truly live under a rock, and also do not frequent any social media at all. And besides, isn’t it our duty as citizens of this world to stay informed? How else can we make informed choices?
Staying informed, mindfully
There are steps that can be taken to keep ourselves informed, while protecting our mental health:
- Choose your sources wisely. Primary sources (e.g. tweets and videos from people who are there) will usually be most authentic, but also most traumatizing. Dispassionate broadsheets may gloss over or misrepresent things more (something that can be countered a bit by reading an opposing view from a publication you hate on principle), but will offer more of an emotional buffer.
- Boundary your consumption of the news. Set a timer and avoid doomscrolling. Your phone (or other device) may help with this if you set a screentime limit per app where you consume that kind of media.
- Take (again, boundaried) time to reflect. If you don’t, your brain will keep grinding at it “like a fork in the garbage disposal”. Talking about your feelings on the topic with a trusted person is great; journaling is also a top-tier more private option.
- If you feel helpless, help. Taking even small actions to help in the face of suffering somewhere else (e.g. donating to relief funds, engaging in advocacy / hounding your government about it), can help alleviate feelings of anguish and helplessness. And of course, as a bonus, it actually helps in the real world too.
- When you relax, relax fully. Even critical care doctors need downtime, nobody can be “always on” without burning out. So whatever distracts and relaxes you completely, make sure to make time for that too.
Want to know more?
That’s all we have room for today, but you might like to check out:
- Distressing images and videos can take a toll on our mental health. How can we stay informed without being traumatised?
- PTSD expert on how to protect yourself and your kids from overexposure to war images from the Mideast
You also might like our previous main features:
- C-PTSD, And What To Do When Life Genuinely Sucks
- A Surprisingly Powerful Tool: Eye Movement Desensitization & Reprocessing
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Does Kaempferol Do, Anyway?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝In the this or that article, you said kampeferol was a famously good flavonol on a par with quercetin, does it do the same thing or does it do something different, and is it worth supplementing?❞
So, this will be in reference to a This-or-That from last week:
Cantaloupe vs Cucumber – Which is Healthier?
Let’s break down your question into parts:
- Is it comparable to quercetin?
- Does it have special properties of its own?
- Is it worth supplementing?
Is it comparable to quercetin?
They are both flavonols, and potent ones at that. Similarities include that they’re found in many of the same plants, and that (like most if not all polyphenols) they have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits, which in turn usually translate to anti-aging and anticancer benefits too.
You can read more about quercetin here: Fight Inflammation & Protect Your Brain, With Quercetin
You can read more about polyphenols in general here: 21 Most Beneficial Polyphenols & What Foods Have Them ← quercetin and kaempferol are #1 and #2 on this list, respectively
Does it have special properties of its own?
Yes it does!
❝Epidemiological studies have shown an inverse relationship between kaempferol intake and cancer.
Kaempferol may help by augmenting the body’s antioxidant defense against free radicals, which promote the development of cancer.
At the molecular level, kaempferol has been reported to modulate a number of key elements in cellular signal transduction pathways linked to apoptosis, angiogenesis, inflammation, and metastasis.
Significantly, kaempferol inhibits cancer cell growth and angiognesis and induces cancer cell apoptosis, but on the other hand, kaempferol appears to preserve normal cell viability, in some cases exerting a protective effect.❞
Read in full: A review of the dietary flavonoid, kaempferol on human health and cancer chemoprevention
It is also particularly good for the gut:
❝Most recently, an increasing number of studies have demonstrated the significance of kaempferol in the regulation of intestinal function and the mitigation of intestinal inflammation❞
Read in full: A Critical Review of Kaempferol in Intestinal Health and Diseases
This also means it is particularly efficacious against food allergies:
❝we screened food ingredients with the expectation of finding dietary compounds that exert beneficial effects on intestinal immune tolerance and identified kaempferol, a flavonoid, as the compound that most effectively increased Aldh1a2 mRNA levels❞
(that’s good)
That one’s a bit scientifically denser than we usually try to find when citing sources here, so here’s a pop-science article about the same thing, which explains in more words than we have room to here:
Flavonoid kaempferol could offer natural relief for food allergies ← much lighter reading, but still very informative
Kaempferol (like quercetin, granted) is also a potent neuroprotective agent, not least of all because its anti-inflammatory powers extend to reducing neuroinflammation (not everything does, because not everything we ingest can pass the blood-brain barrier to affect what goes on in the brain):
…and more:
❝it may be used to treat numerous acute and chronic inflammation-induced diseases, including intervertebral disc degeneration and colitis, as well as post-menopausal bone loss and acute lung injury. In addition, it has beneficial effects against cancer, liver injury, obesity and diabetes, inhibits vascular endothelial inflammation, protects the cranial nerve and heart function, and may be used for treating fibroproliferative disorders, including hypertrophic scar.❞
Read in full: Recent progress regarding kaempferol for the treatment of various diseases
Is it worth supplementing?
If you eat a lot of leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, and/or citrus fruits, and/or drink tea (true teas from tea plants, not miscellaneous herbal infusions), then you probably get a good dose of kaempferol already.
However, if you want to supplement, hawthorn berry is not a bad one to go with, like this example product on Amazon 😎
We wrote about this before, here: Hawthorn For The Heart (& More)
As for teas, if you’re wondering about the merits of black, white, green or red, check out:
Black, White, Green, Red: Which Kind Of Tea Is Best For The Health, According To Science? ← this covers many factors
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: