Mindfulness: An Eight-Week Plan – by Dr. Mark Williams & Dr. Danny Penman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The authors, with their PhDs in psychology and biochemistry, respectively, bring the science that you might expect (and some that you might not!) to this book about mindfulness meditation and mindfulness in everyday life.
The book’s realism comes not just from studies, though, but also from a realistic perspective on modern life, in which many of us have sufficient responsibilities to afford us only limited downtime, and we certainly cannot all take time off for a mountaintop retreat.
What we can do, however, is enjoy this eight-week program for finding peace in a frantic world, while still going about our necessary business in that frantic world on a daily basis.
The eight weeks go as follows:
- Waking up to the autopilot
- Keeping the body in mind
- The mouse in the maze
- Moving beyond the rumor mill
- Turning toward difficulties
- Trapped in the past or living in the present?
- When did you stop dancing?
- Your wild and precious life
…with meditations, as well as reframes and other tools, for each.
The style is very easy-reading, with neither scientific jargon nor spiritual arcana, just clear explanations, instructions, and guidance.
Bottom line: if you’re the sort of person who tries to take each day as it comes, but sometimes several days gang up on you at once, then this book can help get things into order.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
An Unexpected Extra Threat Of Alcohol
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If You Could Use Some Exotic Booze…
…then for health reasons, we’re going to have to say “nay”.
We’ve written about alcohol before, and needless to say, it’s not good:
(the answer is “no, we cannot”)
In fact, the WHO (which unlike government regulatory bodies setting “safe” limits on drinking, makes no profit from taxes on alcohol sales) has declared that “the only safe amount of alcohol is zero”:
WHO: No level of alcohol consumption is safe for our health
Up there, where the air is rarefied…
If you’re flying somewhere this summer (Sinatra-style flying honeymoon or otherwise), you might want to skip the alcohol even if you normally do imbibe, because:
❝…even in young and healthy individuals, the combination of alcohol intake with sleeping under hypobaric conditions poses a considerable strain on the cardiac system and might lead to exacerbation of symptoms in patients with cardiac or pulmonary diseases.
These effects might be even greater in older people; cardiovascular symptoms have a prevalence of 7% of inflight medical emergencies, with cardiac arrest causing 58% of aircraft diversions.❞
Source: Alcohol plus cabin pressure at higher altitude may threaten sleeping plane passengers’ heart health
The experiment divided subjects into a control group and a study group; the study group were placed in simulated cabin pressure as though at altitude, which found, when giving some of them two small(we’re talking the kind given on flights) alcoholic drinks:
❝The combination of alcohol and simulated cabin pressure at cruising altitude prompted a fall in SpO2 to an average of just over 85% and a compensatory increase in heart rate to an average of nearly 88 beats/minute during sleep.❞
In contrast, that was 77 beats/minute for those who had alcohol but weren’t at altitude pressure, or 64 beats/minute for those who neither drank nor were at altitude pressure.
Lots more metrics were recorded and the study is interesting to read; if you’ve ever slept on a plane and thought “that sleep was not restful at all”, then know: it wasn’t just the seat’s fault, nor the engine, nor the recycled nature of the air—it was the reduced pressure causing hypoxia (defined as having oxygen levels lower than the healthy clinical norm of 90%) and almost halving your sleep’s effectiveness for a less than 10% drop in available oxygen in the blood (the sleepers not at altitude pressure averaged 96% SpO2, compared to the 85% at altitude).
We say “almost halving” because the deep sleep phase of sleep was reduced from 84 minutes (control) to 67.5 minutes at altitude without alcohol, or 46.5 minutes at altitude with alcohol.
Again, this was a pressure cabin in a lab—so this wasn’t about the other conditions of an airplane (seats, engine hundreds of other people, etc).
Which means: in an actual airplane it’s probably even worse.
Oh, and the study participants? All healthy individuals aged 18–40, so again probably worse for those older (or younger) than that range, or with existing health conditions!
Want to know more?
You can read the study in full here:
Want to drop the drink at any altitude? Check out:
Want to get that vacation feel without alcohol? You’re going to love:
Mocktails – by Moira Clark (book)
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Bitter Melon vs Winter Melon – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing bitter melon to winter melon, we picked the bitter.
Why?
Did you remember the “bitter is better” dictum that goes for most plant-based foods? It certainly stands in this case!
A note on nomenclature before we begin: these two fruits are also known as the bitter gourd and the wax gourd, respectively (amongst many other names for each), but we went with what seems to be their most common names.
In terms of macros, the bitter melon has more than 13x the protein (and actually adding up to a meaningful amount, at 5.3g/100g), as well as more fiber for the same carbs, making it the better choice all around.
When it comes to vitamins, the bitter melon has a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, B7, B9, and C, while the winter melon boasts only more vitamin B5. As in, the vitamin that’s in all foods (even its scientific name means “from everywhere”) and in which it’s pretty much impossible to be deficient unless literally starving. All in all, an easy and clear win for bitter melon.
In the category of minerals, we see a similar story: the bitter melon has very much more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while the winter melon has a modest double-dose of zinc—hardly comparable to, say, bitter melon having over 100x the potassium content, and indeed, in all minerals except zinc, bitter melon had 4x–100x more. Another clear and overwhelming win for the bitter melon.
Looking up polyphenols, we see that the bitter melon also wins in that regard, shocking nobody, with an impressive polyphenolic profile, especially rich in luteolins and catechins of various kinds.
In short, enjoy either or both, but there’s a clear winner here, and it’s the bitter melon.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Beetroot vs Eggplant – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing beetroot to eggplant, we picked the beetroot.
Why?
It’s close!
In terms of macros, they’re equal on fiber, while beetroot has slightly more protein and carbs. In both cases, despite being quite firm vegetables when raw, they are nevertheless both mostly water. We’re calling this category a tie.
In the category of vitamins, beetroot has more of vitamins A, B2, B9, and C, while eggplant has more of vitamins B3, B5, B6, E, and K. That’s a marginal victory for eggplant.
When it comes to minerals, however, beetroot has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while eggplant is not higher in any minerals. A clear and easy win for beetroot this time.
In terms of polyphenols, both have good-but-different health-giving polyphenols to share, including the quercetin in beetroot and caffeic acid in eggplant—nothing that would tip one ahead of the other, though.
All in all, the categories added up are balanced, but beetroot won the minerals category much more convincingly than eggplant won the vitamins category, so we’re giving this one to beetroot, even if only on tie-breakers!
Of course, enjoy either or both; diversity is good 😎
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Beetroot For More Than Just Your Blood Pressure ← more beetroot benefits
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
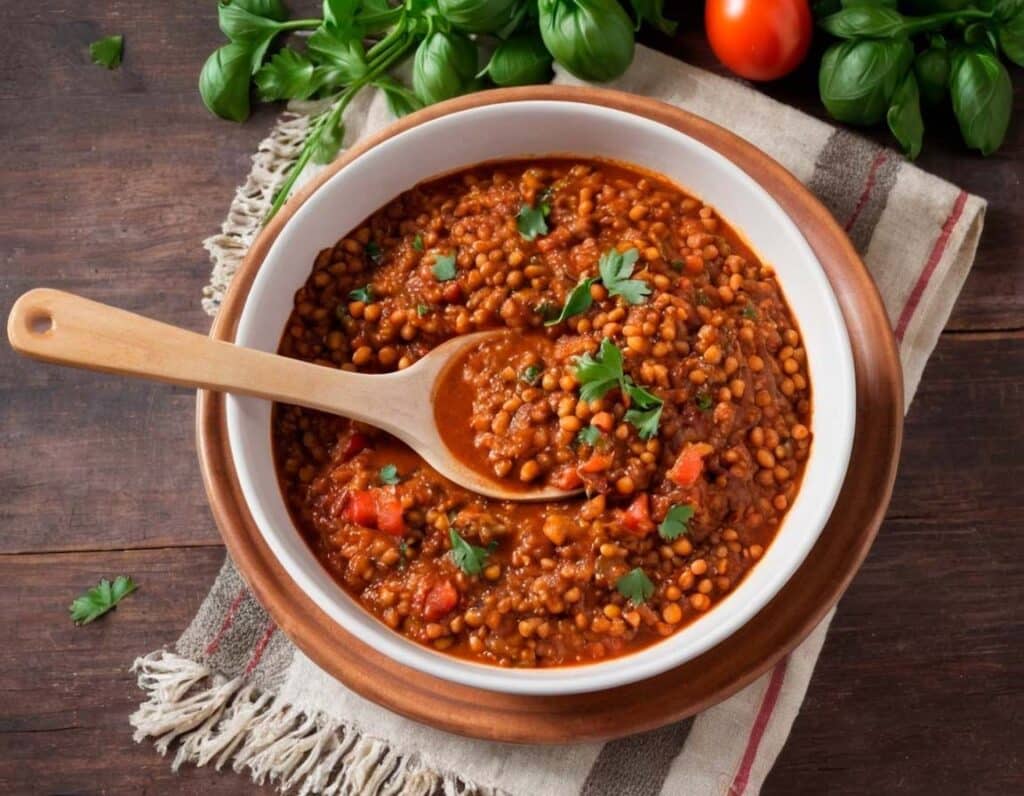
Hearty Healthy Ragù
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ragù is a traditional Italian meaty sauce with tomato, and is the base for a number of other Italian dishes. It can be enjoyed as-is, or with very minor modifications can be turned into a Bolognese sauce or a lasagna filling or various other things. Our variations from tradition are mainly twofold here: we’re using nutrition-packed lentils instead of meat (but with a couple of twists that make them meatier), and we’re not using wine.
Traditionally, red wine is used in a ragù (white wine if you want to make it into a Bolognese sauce, by the way), but with all we’re doing it’s not necessary. If you want to add a splash of wine, we’re not going to call that a healthy ingredient, but we’re also not the boss of you
You will need
- 1 large onion (or equivalent small ones), chopped roughly
- 1 bulb garlic (or to your heart’s content), chopped finely or crushed
- 4 large tomatoes, chopped (or 2 cans chopped tomatoes)
- 1 tube (usually about 7 oz) tomato purée
- 1 cup brown lentils (green lentils will do if you can’t get brown)
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp black pepper, cracked or coarse ground
- 1 bunch fresh basil, finely chopped (or 1 tbsp, freeze-dried)
- 1 bunch fresh oregano, finely chopped (or 1 tbsp, freeze-dried)
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast (failing that, 1 tbsp yeast extract, yes, even if you don’t like it, we promise it won’t taste like it once it’s done; it just makes the dish meatier in taste and also adds vitamin B12)
- 1 tsp cumin, ground (note that this one was tsp, not tbsp like the others)
- 1 tsp MSG, or 2 tsp low-sodium salt
- 4 cups water
- Olive oil for frying (ideally Extra Virgin, but so long as it’s at least marked virgin olive oil and not cut with other oils, that’s fine)
- Parsley, chopped, to garnish
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Put the lentils in a small saucepan, or if you have one, a rice cooker (the rice cooker is better; works better and requires less attention), adding the chia seeds, MSG or low sodium salt, and nutritional yeast (or yeast extract). as well as the cumin. Add 4 cups boiling water and turn on the heat to cook them. This will probably take about 15–20 minutes; you want the lentils to be soft; a tiny bit past al dente, but not so far as mushy.
2) Fry the onion in some olive oil in a big pan (everything is going in here eventually if the pan is big enough; if it isn’t, you’ll need to transfer to a bigger pan in a bit). Once they’re nearly done, throw in the garlic too. If the lentils aren’t done yet, take the onions and garlic off the heat while you wait. After a few times of doing this recipe, you’ll be doing everything like clockwork and it’ll all align perfectly.
3) Drain the lentils (if all the water wasn’t absorbed; again, after doing it a few times, you’ll just use the right amount of water for your apparatus) but don’t rinse them (remember you put seasonings in here!), and add them to the pan with the onions and garlic; add a splash more olive oil if necessary, and stir until all the would-be-excess fat is absorbed into the lentils.
Note: the excess fat to be absorbed by the lentils was a feature not a bug; we wanted a little fat in the lentils! Makes the dish meatier and tastier, as well as more nutrient-dense.
4) add the tomatoes and tomato purée, stirring them in thoroughly; add the basil and oregano too and stir those in as well. Set it on a low heat for at least 10–15 minutes, stirring occasionally to let the flavors blend.
(if you happen to be serving pasta with it, then the time it takes to boil water and cook the pasta is a good time for the flavors to do their thing)
5) take it off the heat, and add the parsley garnish. It’s done!
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- What Is The Mediterranean Diet, Anyway?
- Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure ← one more reason for the brown lentils today
- Chia: The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal
- The Many Health Benefits of Garlic
- Olive Oil: Is “Extra Virgin” Worth It?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to keep your teeth young
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How to keep your teeth young
The association between aging and teeth is so well-established that it’s entered popular idiom, “too long in the tooth”, and when it comes to visual representations, false teeth are well-associated with old age.
And yet, avoiding such outcomes does not get anywhere near so much attention as, say, avoiding wrinkles or hair loss.
At 10almonds, we’ve covered general dental health before, in a three-part series:
- Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
- Flossing, Better (And Easier!)
- Less Common Oral Hygiene Options
Today, we’re going to be looking specifically at keeping our teeth young. What if you have lost your teeth already? Well, gum health remains important, and it’s foundational for everyone, so…
Look after your gums first and last
Hollywood’s most “perfect” whites would be nothing without the gums holding them in place. So, set aside the cosmetic whitening products that often harm gums (anything containing bleach / hydrogen peroxide, is generally a bad idea), andinstead focus on your gums.
As for avoiding gum disease (periodontitis)?
❝In conclusion, periodontitis might enhance the association of biological aging with all-cause mortality in middle-aged and older adults.
Hence, maintaining and enhancing periodontal health is expected to become an intervention to slow aging and extend life span.❞
Source: Does Periodontitis Affect the Association of Biological Aging with Mortality?
Ways to look after gum health include the obvious “floss” and “brush often” and “use fluoride toothpaste”, along with other options we covered in our “Less Common Oral Hygiene Options” article above.
Also important: don’t smoke. It is bad for everything, and this is no exception.
We expect we probably don’t have many subscribers who smoke, but if you do, please consider making quitting a priority.
See also: Smoking, Gum Disease, and Tooth Loss
Consider supplementing with collagen
Everyone’s all about the calcium and vitamin D for bones (and teeth), but a large part of the mass of both is actually collagen. And unlike calcium, which most people not living in a food desert get plenty of, or vitamin D, which is one of the most popular supplements around, collagen is something that gets depleted as we get older. We’ve written about its importance for bones:
We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of—Collagen’s benefits are more than skin deep
And as for its role in combatting gum disease and tooth loss:
Nanoscale Dynamics of Streptococcal Adhesion to AGE-Modified Collagen
By the way, that “AGE” there isn’t about chronological age; it’s about advanced glycation end-products. Those are also something you can and should avoid:
A different kind of “spit and polish”
We imagine you have the “polishing” part in hand; that’s tooth-brushing, of course. But spit?
Saliva is hugely important for our oral health, but it’s not something most of us think about a lot. For example, you might not have known (or might have known but not thought much about) that many common medications affect our saliva, including many blood pressure medications and antidepressants:
Impact of ageing and drug consumption on oral health
Because there are so many possibilities, this is the kind of thing to check with your pharmacist or doctor about. But as a rule, if you take a medication whose side-effects include “dry mouth”, this might be you.
Here’s a really useful (academic) article that covers what drugs cause this, how to diagnose it, and what can be done about it:
Hyposalivation in Elderly Patients
If something’s difficult, find a way to make it easier
Sometimes, as we get older, some things that used to be easy, aren’t. We can lose strength, coordination, manual dexterity, memory, attention, and more. Obviously, we try not to, and do what we can to keep ourselves in good health.
But, if you do have some disability that makes for example brushing and/or flossing difficult to do consistently and/or well, consider talking to your doctor to see if there are assistive devices that can help, or some other kind of support that could allow you to do what you need to.
There’s never any shame in getting help if we need it.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Biological Mind – by Dr. Alan Jasanoff
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How special is our brain? According to Dr. Alan Jasanoff, it’s not nearly as special as we think it is.
In this work, he outlines the case for how we have collectively overstated the brain’s importance. That it’s just another organ like a heart or a kidney, and that who we are is as much a matter of other factors, as what goes on in our brain.
In this reviewer’s opinion, he overcorrects a bit. The heart and kidneys are very simple organs, as organs go. The brain is not. And while everything from our gut microbiota to our environment to our hormones may indeed contribute to what is us, our brain is one thing that can’t just be swapped out.
Nevertheless, this very well-written book can teach us a lot about everything else that makes us us, including many biological factors that many people don’t know about or consider.
Towards the end of the book, he switches into futurist speculation, and his speculation can be summed up as “we cannot achieve anything worthwhile in the future”.
Bottom line: if you’ve an interest in such things as how transplanting glial cells can give a 30% cognitive enhancement, and how a brain transplant wouldn’t result in the same us in a different body, this is the book for you.
Click here to check out The Biological Mind, and learn about yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: