Her Mental Health Treatment Was Helping. That’s Why Insurance Cut Off Her Coverage.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Reporting Highlights
- Progress Denials: Insurers use a patient’s improvement to justify denying mental health coverage.
- Providers Disagree: Therapists argue with insurers and the doctors they employ to continue covering treatment for their patients.
- Patient Harm: Some patients backslid when insurers cut off coverage for treatment at key moments.
These highlights were written by the reporters and editors who worked on this story.
Geneva Moore’s therapist pulled out her spiral notebook. At the top of the page, she jotted down the date, Jan. 30, 2024, Moore’s initials and the name of the doctor from the insurance company to whom she’d be making her case.
She had only one chance to persuade him, and by extension Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Texas, to continue covering intensive outpatient care for Moore, a patient she had come to know well over the past few months.
The therapist, who spoke on the condition of anonymity out of fear of retaliation from insurers, spent the next three hours cramming, as if she were studying for a big exam. She combed through Moore’s weekly suicide and depression assessments, group therapy notes and write-ups from their past few sessions together.
She filled two pages with her notes: Moore had suicidal thoughts almost every day and a plan for how she would take her own life. Even though she expressed a desire to stop cutting her wrists, she still did as often as three times a week to feel the release of pain. She only had a small group of family and friends to offer support. And she was just beginning to deal with her grief and trauma over sexual and emotional abuse, but she had no healthy coping skills.
Less than two weeks earlier, the therapist’s supervisor had struck out with another BCBS doctor. During that call, the insurance company psychiatrist concluded Moore had shown enough improvement that she no longer needed intensive treatment. “You have made progress,” the denial letter from BCBS Texas read.
When the therapist finally got on the phone with a second insurance company doctor, she spoke as fast as she could to get across as many of her points as possible.
“The biggest concern was the abnormal thoughts — the suicidal ideation, self-harm urges — and extensive trauma history,” the therapist recalled in an interview with ProPublica. “I was really trying to emphasize that those urges were present, and they were consistent.”
She told the company doctor that if Moore could continue on her treatment plan, she would likely be able to leave the program in 10 weeks. If not, her recovery could be derailed.
The doctor wasn’t convinced. He told the therapist that he would be upholding the initial denial. Internal notes from the BCBS Texas doctors say that Moore exhibited “an absence of suicidal thoughts,” her symptoms had “stabilized” and she could “participate in a lower level of care.”
The call lasted just seven minutes.
Moore was sitting in her car during her lunch break when her therapist called to give her the news. She was shocked and had to pull herself together to resume her shift as a technician at a veterinary clinic.
“The fact that it was effective immediately,” Moore said later, “I think that was the hardest blow of it all.”
Many Americans must rely on insurers when they or family members are in need of higher-touch mental health treatment, such as intensive outpatient programs or round-the-clock care in a residential facility. The costs are high, and the stakes for patients often are, too. In 2019 alone, the U.S. spent more than $106.5 billion treating adults with mental illness, of which private insurance paid about a third. One 2024 study found that the average quoted cost for a month at a residential addiction treatment facility for adolescents was more than $26,000.
Health insurers frequently review patients’ progress to see if they can be moved down to a lower — and almost always cheaper — level of care. That can cut both ways. They sometimes cite a lack of progress as a reason to deny coverage, labeling patients’ conditions as chronic and asserting that they have reached their baseline level of functioning. And if they make progress, which would normally be celebrated, insurers have used that against patients to argue they no longer need the care being provided.
Their doctors are left to walk a tightrope trying to convince insurers that patients are making enough progress to stay in treatment as long as they actually need it, but not so much that the companies prematurely cut them off from care. And when insurers demand that providers spend their time justifying care, it takes them away from their patients.
“The issues that we grapple with are in the real world,” said Dr. Robert Trestman, the chair of psychiatry and behavioral medicine at the Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine and chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Healthcare Systems and Financing. “People are sicker with more complex conditions.”
Mental health care can be particularly prone to these progress-based denials. While certain tests reveal when cancer cells are no longer present and X-rays show when bones have healed, psychiatrists say they have to determine whether someone has returned to a certain level of functioning before they can end or change their treatment. That can be particularly tricky when dealing with mental illness, which can be fluid, with a patient improving slightly one day only to worsen the next.
Though there is no way to know how often coverage gets cut off mid-treatment, ProPublica has found scores of lawsuits over the past decade in which judges have sharply criticized insurance companies for citing a patient’s improvement to deny mental health coverage. In a number of those cases, federal courts ruled that the insurance companies had broken a federal law designed to provide protections for people who get health insurance through their jobs.
Reporters reviewed thousands of pages of court documents and interviewed more than 50 insiders, lawyers, patients and providers. Over and over, people said these denials can lead to real — sometimes devastating — harm. An official at an Illinois facility with intensive mental health programs said that this past year, two patients who left before their clinicians felt they were ready due to insurance denials had attempted suicide.
Dr. Eric Plakun, a Massachusetts psychiatrist with more than 40 years of experience in residential and intensive outpatient programs, and a former board member of the American Psychiatric Association, said the “proprietary standards” insurers use as a basis for denying coverage often simply stabilize patients in crisis and “shortcut real treatment.”
Plakun offered an analogy: If someone’s house is on fire, he said, putting out the fire doesn’t restore the house. “I got a hole in the roof, and the windows have been smashed in, and all the furniture is charred, and nothing’s working electrically,” he said. “How do we achieve recovery? How do we get back to living in that home?”
Unable to pay the $350-a-day out-of-pocket cost for additional intensive outpatient treatment, Moore left her program within a week of BCBS Texas’ denial. The insurer would only cover outpatient talk therapy.
During her final day at the program, records show, Moore’s suicidal thoughts and intent to carry them out had escalated from a 7 to a 10 on a 1-to-10 scale. She was barely eating or sleeping.
A few hours after the session, Moore drove herself to a hospital and was admitted to the emergency room, accelerating a downward spiral that would eventually cost the insurer tens of thousands of dollars, more than the cost of the treatment she initially requested.
How Insurers Justify Denials
Buried in the denial letters that insurance companies send patients are a variety of expressions that convey the same idea: Improvement is a reason to deny coverage.
“You are better.” “Your child has made progress.” “You have improved.”
In one instance, a doctor working for Regence Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Oregon wrote that a patient who had been diagnosed with major depression was “sufficiently stable,” even as her own doctors wrote that she “continued to display a pattern of severe impairment” and needed round-the-clock care. A judge ruled that “a preponderance of the evidence” demonstrated that the teen’s continued residential treatment was medically necessary. The insurer said it can’t comment on the case because it ended with a confidential settlement.
In another, a doctor working for UnitedHealth Group wrote in 2019 that a teenage girl with a history of major depression who had been hospitalized after trying to take her own life by overdosing “was doing better.” The insurer denied ongoing coverage at a residential treatment facility. A judge ruled that the insurer’s determination “lacked any reasoning or citations” from the girl’s medical records and found that the insurer violated federal law. United did not comment on this case but previously argued that the girl no longer had “concerning medical issues” and didn’t need treatment in a 24-hour monitored setting.
To justify denials, the insurers cite guidelines that they use to determine how well a patient is doing and, ultimately, whether to continue paying for care. Companies, including United, have said these guidelines are independent, widely accepted and evidence-based.
Insurers most often turn to two sets: MCG (formerly known as Milliman Care Guidelines), developed by a division of the multibillion-dollar media and information company Hearst, and InterQual, produced by a unit of UnitedHealth’s mental health division, Optum. Insurers have also used guidelines they have developed themselves.
MCG Health did not respond to multiple requests for comment. A spokesperson for the Optum division that works on the InterQual guidelines said that the criteria “is a collection of established scientific evidence and medical practice intended for use as a first level screening tool” and “helps to move patients safely and efficiently through the continuum of care.”
A separate spokesperson for Optum also said the company’s “priority is ensuring the people we serve receive safe and effective care for their individual needs.” A Regence spokesperson said that the company does “not make coverage decisions based on cost or length of stay,” and that its “number one priority is to ensure our members have access to the care they need when they need it.”
In interviews, several current and former insurance employees from multiple companies said that they were required to prioritize the proprietary guidelines their company used, even if their own clinical judgment pointed in the opposite direction.
“It’s very hard when you come up against all these rules that are kind of setting you up to fail the patient,” said Brittainy Lindsey, a licensed mental health counselor who worked at the Anthem subsidiary Beacon and at Humana for a total of six years before leaving the industry in 2022. In her role, Lindsey said, she would suggest approving or denying coverage, which — for the latter — required a staff doctor’s sign-off. She is now a mental health consultant for behavioral health businesses and clinicians.
A spokesperson for Elevance Health, formerly known as Anthem, said Lindsey’s “recollection is inaccurate, both in terms of the processes that were in place when she was a Beacon employee, and how we operate today.” The spokesperson said “clinical judgment by a physician — which Ms. Lindsey was not — always takes precedence over guidelines.”
In an emailed statement, a Humana spokesperson said the company’s clinician reviewers “are essential to evaluating the facts and circumstances of each case.” But, the spokesperson said, “having objective criteria is also important to provide checks and balances and consistently comply with” federal requirements.
The guidelines are a pillar of the health insurance system known as utilization management, which paves the way for coverage denials. The process involves reviewing patients’ cases against relevant criteria every handful of days or so to assess if the company will continue paying for treatment, requiring providers and patients to repeatedly defend the need for ongoing care.
Federal judges have criticized insurance company doctors for using such guidelines in cases where they were not actually relevant to the treatment being requested or for “solely” basing their decisions on them.
Wit v. United Behavioral Health, a class-action lawsuit involving a subsidiary of UnitedHealth, has become one of the most consequential mental health cases of this century. In that case, a federal judge in California concluded that a number of United’s in-house guidelines did not adhere to generally accepted standards of care. The judge found that the guidelines allowed the company to wrongly deny coverage for certain mental health and substance use services the moment patients’ immediate problems improved. He ruled that the insurer would need to change its practices. United appealed the ruling on grounds other than the court’s findings about the defects in its guidelines, and a panel of judges partially upheld the decision. The case has been sent back to the district court for further proceedings.
Largely in response to the Wit case, nine states have passed laws requiring health insurers to use guidelines that align with the leading standards of mental health care, like those developed by nonprofit professional organizations.
Cigna has said that it “has chosen not to adopt private, proprietary medical necessity criteria” like MCG. But, according to a review of lawsuits, denial letters have continued to reference MCG. One federal judge in Utah called out the company, writing that Cigna doctors “reviewed the claims under medical necessity guidelines it had disavowed.” Cigna did not respond to specific questions about this.
Timothy Stock, one of the BCBS doctors who denied Moore’s request to cover ongoing care, had cited MCG guidelines when determining she had improved enough — something judges noted he had done before. In 2016, Stock upheld a decision on appeal to deny continued coverage for a teenage girl who was in residential treatment for major depression, post-traumatic stress disorder and anxiety. Pointing to the guidelines, Stock concluded she had shown enough improvement.
The patient’s family sued the insurer, alleging it had wrongly denied coverage. Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Illinois argued that there was evidence that showed the patient had been improving. But, a federal judge found the insurer misstated its significance. The judge partially ruled in the family’s favor, zeroing in on Stock and another BCBS doctor’s use of improvement to recommend denying additional care.
“The mere incidence of some improvement does not mean treatment was no longer medically necessary,” the Illinois judge wrote.
In another case, BCBS Illinois denied coverage for a girl with a long history of mental illness just a few weeks into her stay at a residential treatment facility, noting that she was “making progressive improvements.” Stock upheld the denial after an appeal.
Less than two weeks after Stock’s decision, court records show, she cut herself on the arm and leg with a broken light bulb. The insurer defended the company’s reasoning by noting that the girl “consistently denied suicidal ideation,” but a judge wrote that medical records show the girl was “not forthcoming” with her doctors about her behaviors. The judge ruled against the insurer, writing that Stock and another BCBS doctor “unreasonably ignored the weight of the medical evidence” showing that the girl required residential treatment.
Stock declined to comment. A spokesperson for BCBS said the company’s doctors who review requests for mental health coverage are board certified psychiatrists with multiple years of practice experience. The spokesperson added that the psychiatrists review all information received “from the provider, program and members to ensure members are receiving benefits for the right care, at the right place and at the right time.”
The BCBS spokesperson did not address specific questions related to Moore or Stock. The spokesperson said that the examples ProPublica asked about “are not indicative of the experience of the vast majority of our members,” and that it is committed to providing “access to quality, cost-effective physical and behavioral health care.”
A Lifelong Struggle
A former contemporary dancer with a bright smile and infectious laugh, Moore’s love of animals is eclipsed only by her affinity for plants. She moved from Indiana to Austin, Texas, about six years ago and started as a receptionist at a clinic before working her way up to technician.
Moore’s depression has been a constant in her life. It began as a child, when, she said, she was sexually and emotionally abused. She was able to manage as she grew up, getting through high school and attending Indiana University. But, she said, she fell back into a deep sadness after she learned in 2022 that the church she found comfort in as a college student turned out to be what she and others deemed a cult. In September of last year, she began an intensive outpatient program, which included multiple group and individual therapy sessions every week.
Moore, 32, had spent much of the past eight months in treatment for severe depression, post-traumatic stress disorder and anxiety when BCBS said it would no longer pay for the program in January.
The denial had come to her without warning.
“I was starting to get to the point where I did have some hope, and I was like, maybe I can see an actual end to this,” Moore said. “And it was just cut off prematurely.”
At the Austin emergency room where she drove herself after her treatment stopped, her heart raced. She was given medication as a sedative for her anxiety. According to hospital records she provided to ProPublica, Moore’s symptoms were brought on after “insurance said they would no longer pay.”
A hospital social worker frantically tried to get her back into the intensive outpatient program.
“That’s the sad thing,” said Kandyce Walker, the program’s director of nursing and chief operating officer, who initially argued Moore’s case with BCBS Texas. “To have her go from doing a little bit better to ‘I’m going to kill myself.’ It is so frustrating, and it’s heartbreaking.”
After the denial and her brief admission to the hospital emergency department in January, Moore began slicing her wrists more frequently, sometimes twice a day. She began to down six to seven glasses of wine a night.
“I really had thought and hoped that with the amount of work I’d put in, that I at least would have had some fumes to run on,” she said.
She felt embarrassed when she realized she had nothing to show for months of treatment. The skills she’d just begun to practice seemed to disappear under the weight of her despair. She considered going into debt to cover the cost of ongoing treatment but began to think that she’d rather end her life.
“In my mind,” she said, “that was the most practical thing to do.”
Whenever the thought crossed her mind — and it usually did multiple times a day — she remembered that she had promised her therapist that she wouldn’t.
Moore’s therapist encouraged her to continue calling BCBS Texas to try to restore coverage for more intensive treatment. In late February, about five weeks after Stock’s denial, records show that the company approved a request that sent her back to the same facility and at the same level of care as before.
But by that time, her condition had deteriorated so severely that it wasn’t enough.
Eight days later, Moore was admitted to a psychiatric hospital about half an hour from Austin. Medical records paint a harrowing picture of her condition. She had a plan to overdose and the medicine to do it. The doctor wrote that she required monitoring and had “substantial ongoing suicidality.” The denial continued to torment her. She told her doctor that her condition worsened after “insurance stopped covering” her treatment.
Her few weeks stay at the psychiatric hospital cost $38,945.06. The remaining 10 weeks of treatment at the intensive outpatient program — the treatment BCBS denied — would have cost about $10,000.
Moore was discharged from the hospital in March and went back into the program Stock had initially said she no longer needed.
It marked the third time she was admitted to the intensive outpatient program.
A few months later, as Moore picked at her lunch, her oversized glasses sliding down the bridge of her nose every so often, she wrestled with another painful realization. Had the BCBS doctors not issued the denial, she probably would have completed her treatment by now.
“I was really looking forward to that,” Moore said softly. As she spoke, she played with the thick stack of bracelets hiding the scars on her wrists.
A few weeks later, that small facility closed in part because of delays and denials from insurance companies, according to staff and billing records. Moore found herself calling around to treatment facilities to see which ones would accept her insurance. She finally found one, but in October, her depression had become so severe that she needed to be stepped up to a higher level of care.
Moore was able to get a leave of absence from work to attend treatment, which she worried would affect the promotion she had been working toward. To tide her over until she could go back to work, she used up the money her mother sent for her 30th birthday.
She smiles less than she did even a few months ago. When her roommates ask her to hang out downstairs, she usually declines. She has taken some steps forward, though. She stopped drinking and cutting her wrists, allowing scar tissue to cover her wounds.
But she’s still grieving what the denial took from her.
“I believed I could get better,” she said recently, her voice shaking. “With just a little more time, I could discharge, and I could live life finally.”
Kirsten Berg contributed research.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
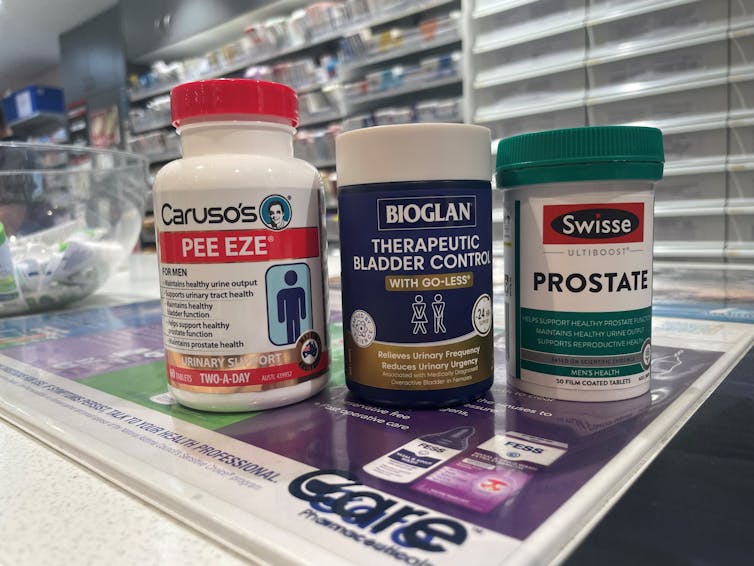
What’s in the supplements that claim to help you cut down on bathroom breaks? And do they work?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
With one in four Australian adults experiencing problems with incontinence, some people look to supplements for relief.
With ingredients such as pumpkin seed oil and soybean extract, a range of products promise relief from frequent bathroom trips.
But do they really work? Let’s sift through the claims and see what the science says about their efficacy.
Christian Moro/Shutterstock What is incontinence?
Incontinence is the involuntary loss of bladder or bowel control, leading to the unintentional leakage of urine or faeces. It can range from occasional minor leaks to a complete inability to control urination and defecation.
This condition can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life, and affects women more often than it affects men.
Some people don’t experience bladder leakage but can sometimes feel an urgent need to go to the bathroom. This is known as overactive bladder syndrome, and occurs when the muscles around the bladder tighten on their own, which greatly reduces its capacity. The result is the person feels the need to go to the bathroom much more frequently.
There are many potential causes of incontinence and overactive bladders, including menopause, pregnancy and child birth, urinary tract infections, pelvic floor disorders, and an enlarged prostate. Conditions such as diabetes, neurological disorders and certain medications (such as diuretics, sleeping pills, antidepressants and blood-pressure drugs) can also contribute.
While pelvic muscle rehabilitation and behavioural techniques for bladder retraining can be helpful, some people are interested in pharmaceutical solutions.
What’s in these products?
A number of supplements are available in Australia that include ingredients used in traditional medicine for urinary incontinence and overactive bladders. The three most common ingredients are:
- Cucurbita pepo (pumpkin seed extract)
- glycine max (soybean extract)
- an extract from the bark of the Crateva magna or nurvala (Varuna) tree.
The supplements have common ingredients. Author How are they supposed to work?
Pumpkin seeds are rich in plant sterols that are thought to reduce the testosterone-related enlargement of the prostate, as well as having broader anti-inflammatory effects. The seed extracts can also contain oleic acid, which may help increase bladder capacity by relaxing the muscles around the organ.
Soybean extracts are rich in isoflavones, especially daidzen and genistein. Like olieic acid, these are thought to act on the muscles around the bladder. Because isoflavones are similar in structure to the female hormone oestrogen, soy extracts may be most beneficial for postmenopausal women who have overactive bladders.
Crateva extract is rich in lupeol- and sterol-based chemicals which have strong anti-inflammatory effects. This has benefits not just for enlarged prostates but possibly also for reducing urinary tract infections.
Do they actually work?
It’s important to note that the government has only approved these types of supplements as “listed medicines”. This means the ingredients have only been assessed for safety. The companies behind the products have not had to provide evidence they actually work.
A 2014 clinical trial examined a combined pumpkin seed and soybean extract called cucurflavone on people with overactive bladders. The 120 participants received either a placebo or a daily 1,000mg dose of the herbal mixture over a period of 12 weeks.
By the end of study, those in the cucurflavone group went to the bathroom around three fewer times per day, compared with people in the control group, who only went to the bathroom on average one fewer time each day.
In a different trial, researchers examined a combination of Crateva bark extract with herbal extracts of horsetail and Japanese evergreen spicebush, called Urox.
For the 150 participants, the Urox formulation helped participants go to the bathroom less frequently when compared with placebo treatment.
After eight weeks of treatment, participants in the placebo group were going to the bathroom to urinate 11 times per day. Those in the Urox group were only going around to 7.5 times per day. And those who took Urox also needed to go to the bathroom one fewer time during the night.
Finally, another study also examined a Creteva, horsetail and Japanese spicebush combination, but this time in children. They were given either a 420mg dose of the supplement or a placebo, and then monitored for how many times they wet the bed.
After two months of taking the supplement, slightly more than 40% of the 24 kids in the supplement group wet the bed less often.
While these results may look promising, there are considerable limitations to the studies which means the data may not be reliable. For example, the trials didn’t include enough participants to have reliable data. To conclusively provide efficacy, final-stage clinical trials require data for between 300 and 3,000 patients.
From the studies, it is also not clear whether some participants were also taking other medicines as well as the supplement. This is important, as medications can interfere with how the supplements work, potentially making them less or more effective.
What if you want to take them?
If you have incontinence or an overactive bladder, you should always discuss this with your doctor, as it may due to a serious or treatable underlying condition.
Otherwise, your GP may give you strategies or exercises to improve your bladder control, prescribe medications or devices, or refer you to a specialist.
If you do decide to take a supplement, discuss this with your doctor and local pharmacist so they can check that any product you choose will not interfere with any other medications you may be taking.
Nial Wheate, Professor of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Macquarie University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Managing Your Mortality
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When Planning Is a Matter of Life and Death
Barring medical marvels as yet unrevealed, we are all going to die. We try to keep ourselves and our loved ones in good health, but it’s important to be prepared for the eventuality of death.
While this is not a cheerful topic, considering these things in advance can help us manage a very difficult thing, when the time comes.
We’ve put this under “Psychology Sunday” as it pertains to processing our own mortality, and managing our own experiences and the subsequent grief that our death may invoke in our loved ones.
We’ll also be looking at some of the medical considerations around end-of-life care, though.
Organizational considerations
It’s generally considered good to make preparations in advance. Write (or update) a Will, tie up any loose ends, decide on funerary preferences, perhaps even make arrangements with pre-funding. Life insurance, something difficult to get at a good rate towards the likely end of one’s life, is better sorted out sooner rather than later, too.
Beyond bureaucracy
What’s important to you, to have done before you die? It could be a bucket list, or it could just be to finish writing that book. It could be to heal a family rift, or to tell someone how you feel.
It could be more general, less concrete: perhaps to spend more time with your family, or to engage more with a spiritual practice that’s important to you.
Perhaps you want to do what you can to offset the grief of those you’ll leave behind; to make sure there are happy memories, or to make any requests of how they might remember you.
Lest this latter seem selfish: after a loved one dies, those who are left behind are often given to wonder: what would they have wanted? If you tell them now, they’ll know, and can be comforted and reassured by that.
This could range from “bright colors at my funeral, please” to “you have my blessing to remarry if you want to” to “I will now tell you the secret recipe for my famous bouillabaisse, for you to pass down in turn”.
End-of-life care
Increasingly few people die at home.
- Sometimes it will be a matter of fighting tooth-and-nail to beat a said-to-be-terminal illness, and thus expiring in hospital after a long battle.
- Sometimes it will be a matter of gradually winding down in a nursing home, receiving medical support to the end.
- Sometimes, on the other hand, people will prefer to return home, and do so.
Whatever your preferences, planning for them in advance is sensible—especially as money may be a factor later.
Not to go too much back to bureaucracy, but you might also want to consider a Living Will, to be enacted in the case that cognitive decline means you cannot advocate for yourself later.
Laws vary from place to place, so you’ll want to discuss this with a lawyer, but to give an idea of the kinds of things to consider:
National Institute on Aging: Preparing A Living Will
Palliative care
Palliative care is a subcategory of end-of-life care, and is what occurs when no further attempts are made to extend life, and instead, the only remaining goal is to reduce suffering.
In the case of some diseases including cancer, this may mean coming off treatments that have unpleasant side-effects, and retaining—or commencing—pain-relief treatments that may, as a side-effect, shorten life.
Euthanasia
Legality of euthanasia varies from place to place, and in some times and places, palliative care itself has been considered a form of “passive euthanasia”, that is to say, not taking an active step to end life, but abstaining from a treatment that prolongs it.
Clearer forms of passive euthanasia include stopping taking a medication without which one categorically will die, or turning off a life support machine.
Active euthanasia, taking a positive action to end life, is legal in some places and the means varies, but an overdose of barbiturates is an example; one goes to sleep and does not wake up.
It’s not the only method, though; options include benzodiazepines, and opioids, amongst others:
Efficacy and safety of drugs used for assisted dying
Unspoken euthanasia
An important thing to be aware of (whatever your views on euthanasia) is the principle of double-effect… And how it comes to play in palliative care more often than most people think.
Say a person is dying of cancer. They opt for palliative care; they desist in any further cancer treatments, and take medication for the pain. Morphine is common. Morphine also shortens life.
It’s common for such a patient to have a degree of control over their own medication, however, after a certain point, they will no longer be in sufficient condition to do so.
After this point, it is very common for caregivers (be they medical professionals or family members) to give more morphine—for the purpose of reducing suffering, of course, not to kill them.
In practical terms, this often means that the patient will die quite promptly afterwards. This is one of the reasons why, after sometimes a long-drawn-out period of “this person is dying”, healthcare workers can be very accurate about “it’s going to be in the next couple of days”.
The take-away from this section is: if you would like for this to not happen to you or your loved one, you need to be aware of this practice in advance, because while it’s not the kind of thing that tends to make its way into written hospital/hospice policies, it is very widespread and normalized in the industry on a human level.
Further reading: Goods, causes and intentions: problems with applying the doctrine of double effect to palliative sedation
One last thing…
Planning around our own mortality is never a task that seems pressing, until it’s too late. We recommend doing it anyway, without putting it off, because we can never know what’s around the corner.
Share This Post
-
9 Reasons To Avoid Mobility Training
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Why might someone not want to do mobility training? Here are some important reasons:
Make an informed choice
Here’s Liv’s hit-list of reasons to skip mobility training:
- Poor Circulation: Avoid mobility training if you don’t want to improve or maintain good blood circulation, which aids muscle recovery and reduces soreness.
- Low Energy Levels: Mobility training increases oxygen flow to the brain and muscles, boosting energy. Skip it if you prefer feeling sluggish!
- Digestive Health: Stretches that rotate the torso aid digestion and relieve bloating. Definitely best to avoid it if you’re uninterested in improving digestive health.
- Joint Health: Mobility work stimulates synovial fluid production, reducing joint friction and promoting longevity. You can skip it if you don’t care about comfortable movement.
- Sleep Quality: Gentle stretching triggers relaxation, aiding restful sleep. Avoid it if you enjoy restless nights!
- Pain Tolerance: Stretching trains the nervous system to handle discomfort better. Skip it if you prefer suffering 🙂
- Headache Reduction: Mobility work relieves tension in the neck and shoulders, reducing the occurrence and severity of headaches. No need to do it if you’re fine with frequent headaches.
- Immune System Support: Mobility training boosts lymphatic circulation, aiding the immune system. Avoid it if you prefer your immune system to get exciting in a bad way.
- Stress Reduction: Mobility exercises release endorphins and lower cortisol levels, reducing stress. So, it is certainly best to skip it if you prefer feeling stressed and enjoy the many harmful symptoms of high cortisol levels!
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Mobility As Though A Sporting Pursuit: Train For The Event Of Your Life!
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Apple vs Pear – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing apple to pear, we picked the pear.
Why?
Both are great! But there’s a category that puts pears ahead of apples…
Looking at their macros first, pears contain more carbs but also more fiber. Both are low glycemic index foods, though.
In the category of vitamins, things are moderately even: apples contain more of vitamins A, B1, B6, and E, while pears contain more of vitamins B3, B9, K, and choline. That’s a 4:4 split, and the two fruits are about equal in the other vitamins they both contain.
When it comes to minerals, pears contain more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. A resounding victory for pears, as apples are not higher in any mineral.
In short, if an apple a day keeps the doctor away, a pear should keep the doctor away for about a day and a half, based on the extra nutrients ← this is slightly facetious as medicine doesn’t work like that, but you get the idea: pears simply have more to offer. Apples are still great though! Enjoy both! Diversity is good.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
From Apples To Bees, And High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why Going Gluten-Free Could Be A Bad Idea
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is A Gluten-Free Diet Right For You?
This is Rachel Begun, MS, RD. She’s a nutritionist who, since her own diagnosis with Celiac disease, has shifted her career into a position of educating the public (and correcting misconceptions) about gluten sensitivity, wheat allergy, and Celiac disease. In short, the whole “gluten-free” field.
First, a quick recap
We’ve written on this topic ourselves before; here’s what we had to say:
On “Everyone should go gluten-free”
Some people who have gone gluten-free are very evangelical about the lifestyle change, and will advise everyone that it will make them lose weight, have clearer skin, more energy, and sing well, too. Ok, maybe not the last one, but you get the idea—a dietary change gets seen as a cure-all.
And for some people, it can indeed make a huge difference!
Begun urges us to have a dose of level-headedness in our approach, though.
Specifically, she advises:
- Don’t ignore symptoms, and/but…
- Don’t self-diagnose
- Don’t just quit gluten
One problem with self-diagnosis is that we can easily be wrong:
But why is that a problem? Surely there’s not a health risk in skipping the gluten just to be on the safe side? As it turns out, there actually is:
If we self-diagnose incorrectly, Begun points out, we can miss the actual cause of the symptoms, and by cheerfully proclaiming “I’m allergic to gluten” or such, a case of endometriosis, or Hashimoto’s, or something else entirely, might go undiagnosed and thus untreated.
“Oh, I feel terrible today, there must have been some cross-contamination in my food” when in fact, it’s an undiagnosed lupus flare-up, that kind of thing.
Similarly, just quitting gluten “to be on the safe side” can mask a different problem, if wheat consumption (for example) contributed to, but did not cause, some ailment.
In other words: it could reduce your undesired symptoms, but in so doing, leave a more serious problem unknown.
Instead…
If you suspect you might have a gluten sensitivity, a wheat allergy, or even Celiac disease, get yourself tested, and take professional advice on proceeding from there.
How? Your physician should be able to order the tests for you.
You can also check out resources available here:
Celiac Disease Foundation | How do I get tested?
Or for at-home gluten intolerance tests, here are some options weighed against each other:
MNT | 5 gluten intolerance tests and considerations
Want to learn more?
Begun has a blog:
Rachel Begun | More than just recipes
(it is, in fact, just recipes—but they are very simple ones!)
You also might enjoy this interview, in which she talks about gluten sensitivity, celiac disease, and bio-individuality:
Want to watch it, but not right now? Bookmark it for later
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sesame Chocolate Fudge
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’d like a sweet treat without skyrocketing your blood sugars with, well, rocket fuel… Today’s recipe can help you enjoy a taste of decadence that’s not bad for your blood sugars, and good for your heart and brain.
You will need
- ½ cup sesame seeds
- ¼ cup cocoa powder
- 3 tbsp maple syrup
- 1 tbsp coconut oil (plus a little extra for the pan)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Lightly toast the sesame seeds in a pan until golden brown. Remove from the heat and allow to cool.
2) Put them in a food processor, and blend on full speed until they start to form a dough-like mixture. This may take a few minutes, so be patient. We recommend doing it in 30-second sessions with a 30-second rest between them, to avoiding overheating the motor.
3) Add the rest of the ingredients and blend to combine thoroughly—this should go easily now and only take 10 seconds or so, but judge it by eye.
4) Grease an 8″ square baking tin with a little coconut oil, and add the mixture, patting it down to fill the tin, making sure it is well-compressed.
5) Allow to chill in the fridge for 6 hours, until firm.
6) Turn the fudge out onto a chopping board, and cut into the size squares you want. Serve, or store in the fridge until ready to serve.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Tasty Polyphenols For Your Heart & Brain
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
- Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: