Long-Covid Patients Are Frustrated That Federal Research Hasn’t Found New Treatments
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Erica Hayes, 40, has not felt healthy since November 2020 when she first fell ill with covid.
Hayes is too sick to work, so she has spent much of the last four years sitting on her beige couch, often curled up under an electric blanket.
“My blood flow now sucks, so my hands and my feet are freezing. Even if I’m sweating, my toes are cold,” said Hayes, who lives in Western Pennsylvania. She misses feeling well enough to play with her 9-year-old son or attend her 17-year-old son’s baseball games.
Along with claiming the lives of 1.2 million Americans, the covid-19 pandemic has been described as a mass disabling event. Hayes is one of millions of Americans who suffer from long covid. Depending on the patient, the condition can rob someone of energy, scramble the autonomic nervous system, or fog their memory, among many other http://symptoms.in/ addition to the brain fog and chronic fatigue, Hayes’ constellation of symptoms includes frequent hives and migraines. Also, her tongue is constantly swollen and dry.
“I’ve had multiple doctors look at it and tell me they don’t know what’s going on,” Hayes said about her tongue.
Estimates of prevalence range considerably, depending on how researchers define long covid in a given study, but the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention puts it at 17 million adults.
Despite long covid’s vast reach, the federal government’s investment in researching the disease — to the tune of $1.15 billion as of December — has so far failed to bring any new treatments to market.
This disappoints and angers the patient community, who say the National Institutes of Health should focus on ways to stop their suffering instead of simply trying to understand why they’re suffering.
“It’s unconscionable that more than four years since this began, we still don’t have one FDA-approved drug,” said Meighan Stone, executive director of the Long COVID Campaign, a patient-led advocacy organization. Stone was among several people with long covid who spoke at a workshop hosted by the NIH in September where patients, clinicians, and researchers discussed their priorities and frustrations around the agency’s approach to long-covid research.
Some doctors and researchers are also critical of the agency’s research initiative, called RECOVER, or Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery. Without clinical trials, physicians specializing in treating long covid must rely on hunches to guide their clinical decisions, said Ziyad Al-Aly, chief of research and development with the VA St Louis Healthcare System.
“What [RECOVER] lacks, really, is clarity of vision and clarity of purpose,” said Al-Aly, saying he agrees that the NIH has had enough time and money to produce more meaningful progress.
Now the NIH is starting to determine how to allocate an additional $662 million of funding for long-covid research, $300 million of which is earmarked for clinical trials. These funds will be allocated over the next four http://years.at/ the end of October, RECOVER issued a request for clinical trial ideas that look at potential therapies, including medications, saying its goal is “to work rapidly, collaboratively, and transparently to advance treatments for Long COVID.”
This turn suggests the NIH has begun to respond to patients. This has stirred cautious optimism among those who say that the agency’s approach to long covid has lacked urgency in the search for effective treatments.Stone calls this $300 million a down payment. She warns it’s going to take a lot more money to help people like Hayes regain some degree of health.“There really is a burden to make up this lost time now,” Stone said.
The NIH told KFF Health News and NPR via email that it recognizes the urgency in finding treatments. But to do that, there needs to be an understanding of the biological mechanisms that are making people sick, which is difficult to do with post-infectious conditions.
That’s why it has funded research into how long covid affects lung function, or trying to understand why only some people are afflicted with the condition.
Good Science Takes Time
In December 2020, Congress appropriated $1.15 billion for the NIH to launch RECOVER, raising hopes in the long-covid patient community.
Then-NIH Director Francis Collins explained that RECOVER’s goal was to better understand long covid as a disease and that clinical trials of potential treatments would come later.
According to RECOVER’s website, it has funded eight clinical trials to test the safety and effectiveness of an experimental treatment or intervention. Just one of those trials has published results.
On the other hand, RECOVER has supported more than 200 observational studies, such as research on how long covid affects pulmonary function and on which symptoms are most common. And the initiative has funded more than 40 pathobiology studies, which focus on the basic cellular and molecular mechanisms of long covid.
RECOVER’s website says this research has led to crucial insights on the risk factors for developing long covid and on understanding how the disease interacts with preexisting conditions.
It notes that observational studies are important in helping scientists to design and launch evidence-based clinical trials.
Good science takes time, said Leora Horwitz, the co-principal investigator for the RECOVER-Adult Observational Cohort at New York University. And long covid is an “exceedingly complicated” illness that appears to affect nearly every organ system, she said.
This makes it more difficult to study than many other diseases. Because long covid harms the body in so many ways, with widely variable symptoms, it’s harder to identify precise targets for treatment.
“I also will remind you that we’re only three, four years into this pandemic for most people,” Horwitz said. “We’ve been spending much more money than this, yearly, for 30, 40 years on other conditions.”
NYU received nearly $470 million of RECOVER funds in 2021, which the institution is using to spearhead the collection of data and biospecimens from up to 40,000 patients. Horwitz said nearly 30,000 are enrolled so far.
This vast repository, Horwitz said, supports ongoing observational research, allowing scientists to understand what is happening biologically to people who don’t recover after an initial infection — and that will help determine which clinical trials for treatments are worth undertaking.
“Simply trying treatments because they are available without any evidence about whether or why they may be effective reduces the likelihood of successful trials and may put patients at risk of harm,” she said.
Delayed Hopes or Incremental Progress?
The NIH told KFF Health News and NPR that patients and caregivers have been central to RECOVER from the beginning, “playing critical roles in designing studies and clinical trials, responding to surveys, serving on governance and publication groups, and guiding the initiative.”But the consensus from patient advocacy groups is that RECOVER should have done more to prioritize clinical trials from the outset. Patients also say RECOVER leadership ignored their priorities and experiences when determining which studies to fund.
RECOVER has scored some gains, said JD Davids, co-director of Long COVID Justice. This includes findings on differences in long covid between adults and kids.But Davids said the NIH shouldn’t have named the initiative “RECOVER,” since it wasn’t designed as a streamlined effort to develop treatments.
“The name’s a little cruel and misleading,” he said.
RECOVER’s initial allocation of $1.15 billion probably wasn’t enough to develop a new medication to treat long covid, said Ezekiel J. Emanuel, co-director of the University of Pennsylvania’s Healthcare Transformation Institute.
But, he said, the results of preliminary clinical trials could have spurred pharmaceutical companies to fund more studies on drug development and test how existing drugs influence a patient’s immune response.
Emanuel is one of the authors of a March 2022 covid roadmap report. He notes that RECOVER’s lack of focus on new treatments was a problem. “Only 15% of the budget is for clinical studies. That is a failure in itself — a failure of having the right priorities,” he told KFF Health News and NPR via email.
And though the NYU biobank has been impactful, Emanuel said there needs to be more focus on how existing drugs influence immune response.
He said some clinical trials that RECOVER has funded are “ridiculous,” because they’ve focused on symptom amelioration, for example to study the benefits of over-the-counter medication to improve sleep. Other studies looked at non-pharmacological interventions, such as exercise and “brain training” to help with cognitive fog.
People with long covid say this type of clinical research contributes to what many describe as the “gaslighting” they experience from doctors, who sometimes blame a patient’s symptoms on anxiety or depression, rather than acknowledging long covid as a real illness with a physiological basis.
“I’m just disgusted,” said long-covid patient Hayes. “You wouldn’t tell somebody with diabetes to breathe through it.”
Chimére L. Sweeney, director and founder of the Black Long Covid Experience, said she’s even taken breaks from seeking treatment after getting fed up with being told that her symptoms were due to her diet or mental health.
“You’re at the whim of somebody who may not even understand the spectrum of long covid,” Sweeney said.
Insurance Battles Over Experimental Treatments
Since there are still no long-covid treatments approved by the Food and Drug Administration, anything a physician prescribes is classified as either experimental — for unproven treatments — or an off-label use of a drug approved for other conditions. This means patients can struggle to get insurance to cover prescriptions.
Michael Brode, medical director for UT Health Austin’s Post-COVID-19 Program — said he writes many appeal letters. And some people pay for their own treatment.
For example, intravenous immunoglobulin therapy, low-dose naltrexone, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy are all promising treatments, he said.
For hyperbaric oxygen, two small, randomized controlled studies show improvements for the chronic fatigue and brain fog that often plague long-covid patients. The theory is that higher oxygen concentration and increased air pressure can help heal tissues that were damaged during a covid infection.
However, the out-of-pocket cost for a series of sessions in a hyperbaric chamber can run as much as $8,000, Brode said.
“Am I going to look a patient in the eye and say, ‘You need to spend that money for an unproven treatment’?” he said. “I don’t want to hype up a treatment that is still experimental. But I also don’t want to hide it.”
There’s a host of pharmaceuticals that have promising off-label uses for long covid, said microbiologist Amy Proal, president and chief scientific officer at the Massachusetts-based PolyBio Research Foundation. For instance, she’s collaborating on a clinical study that repurposes two HIV drugs to treat long covid.
Proal said research on treatments can move forward based on what’s already understood about the disease. For instance, she said that scientists have evidence — partly due to RECOVER research — that some patients continue to harbor small amounts of viral material after a covid infection. She has not received RECOVER funds but is researching antivirals.
But to vet a range of possible treatments for the millions suffering now — and to develop new drugs specifically targeting long covid — clinical trials are needed. And that requires money.
Hayes said she would definitely volunteer for an experimental drug trial. For now, though, “in order to not be absolutely miserable,” she said she focuses on what she can do, like having dinner with her http://family.at/ the same time, Hayes doesn’t want to spend the rest of her life on a beige couch.
RECOVER’s deadline to submit research proposals for potential long-covid treatments is Feb. 1.
This article is from a partnership that includes NPR and KFF Health News.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can apps and digital resources support your child with autism or ADHD?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Neurodevelopmental conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and autism affect about one in ten children. These conditions impact development, behaviour and wellbeing.
But children with these conditions and their caregivers often can’t get the support they need. Families report difficulties accessing health-care providers and experience long wait lists to receive care.
Digital tools, such as apps and websites, are often viewed as a solution to these gaps. With a single click or a download, families might be able to access information to support their child.
There are lots of digital tools available, but it’s hard to know what is and isn’t useful. Our new study evaluated freely available digital resources for child neurodevelopment and mental health to understand their quality and evidence base.
We found many resources were functional and engaging. However, resources often lacked evidence for the information provided and the claimed positive impact on children and families.
This is a common problem in the digital resource field, where the high expectations and claims of impact from digital tools to change health care have not yet been realised.
Fabio Principe/Shutterstock What type of resources?
Our study identified 3,435 separate resources, of which 112 (43 apps and 69 websites) met our criteria for review. These resources all claimed to provide information or supports for child neurodevelopment, mental health or wellbeing.
Resources had to be freely available, in English and have actionable information for children and families.
The most common focus was on autism, representing 17% of all resources. Resources suggested they provided strategies to promote speech, language and social development, and to support challenging behaviours.
Other common areas included language and communication (14%), and ADHD (10%).
Resources had various purposes, including journalling and providing advice, scheduling support, and delivering activities and strategies for parents. Resources delivered information interactively, with some apps organising content into structured modules.
Resources also provided options for alternative and assistive communication for people with language or communication challenges.
Most apps were functional and accessible
Our first question was about how engaging and accessible the information was. Resources that are hard to use aren’t used frequently, regardless of the information quality.
We evaluated aesthetics, including whether digital tools were easy to use and navigate, stylistically consistent, with clean and appealing graphics for users.
Most resources were rated as highly engaging, with strong accessibility and functionality.
Most apps and websites we evaluated were engaging. jamesteohart/Shutterstock But many lacked quality information
We ranked resources on various features from 1 (inadequate) to 5 (excellent), with a ranking of 3 considered acceptable. These ratings looked at how credible the resource was and whether there was evidence supporting it.
Despite their functionality, 37% of reviewed apps did not meet the minimum acceptable standards for information quality. This means many apps could not be recommended. Most websites fared better than apps.
There also wasn’t a lot of scientific evidence to suggest using either apps or digital resources actually helped families. Studies show long-term engagement with digital tools is rare, and downloads don’t correspond to frequent usage or benefits.
Digital tools are often viewed as a panacea to health-care gaps, but the evidence is yet to show they fill such gaps. Digital health is a fast-moving field and resources are often made available before they have been properly evaluated.
What should you look for in digital resources?
We found the highest quality resources were developed in collaboration with institutions, such as health, university or government groups.
One highly rated resource was the Raising Children’s Network and the associated app, Raising Healthy Minds. These are co-developed with a university and hospital, and by people with appropriate qualifications.
This resource provides information to support children’s overall health, development and wellbeing, with dedicated sections addressing neurodevelopmental needs and concerns.
The Raising Children Network provides resources for child health, including neurodevelopmental needs. Raising Children Network screenshot Our research shows parents can assess whether digital resources are high quality by checking they are:
- factually correct. Look for where the app or resource is getting its information. Does the author have the qualifications and training to provide the information? Are they a registered health expert who is accountable to a regulatory body (such as AHPRA, the Australian Health Practitioners Regulation Agency) for providing information that does not cause harm?
- consistent across multiple credible sources, such as health institutions.
- linked to supporting information. Look for reliable links to reputable institutions. Links to peer-reviewed scientific journals are often helpful as those articles will also usually describe the limitations of the research presented.
- up-to-date. Apps should be frequently updated. For websites, dates of update are usually found on the homepage or at the bottom of individual pages.
Check when information was last updated. fizkes/Shutterstock Beware of red flags
Some things to watch out for are:
- testimonials and anecdotes without evidence and scientific links to back the anecdotes up. If it sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
- no information provided about conflicts of interest. Organisations gain when you click on their links or take their advice (financial, reputation and brand development). Think about what they gain when you use their information to help keep a balanced perspective.
Remember, the app’s star rating doesn’t mean it will contain factual information from a reliable source or be helpful for you and your child.
The role of digital tools
Digital tools won’t usually replace a health professional, but they can support care in many different ways. They may be used to help to educate and prepare for meetings, and to collaborate with health providers.
They may also be used to collect information about daily needs. Studies show reporting on sleep in children can be notoriously difficult, for example. But tracking sleep behaviour with actigraphy, where movement and activity patterns are measured using a wearable device, can provide information to support clinical care. With the promise of artificial intelligence, there will also be new opportunities to support daily living.
Our findings reflect a broader problem for digital health, however. Much investment is often made in developing products to drive use, with spurious claims of health benefits.
What’s needed is a system that prioritises the funding, implementation and evaluation of tools to demonstrate benefits for families. Only then may we realise the potential of digital tools to benefit those who use them.
Kelsie Boulton, Senior Research Fellow in Child Neurodevelopment, Brain and Mind Centre, University of Sydney and Adam Guastella, Professor and Clinical Psychologist, Michael Crouch Chair in Child and Youth Mental Health, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Trout vs Haddock – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing trout to haddock, we picked the trout.
Why?
It wasn’t close.
In terms of macros, trout has more protein and more fat, although the fat is mostly healthy (some saturated though, and trout does have more cholesterol). This category could be a win for either, depending on your priorities. But…
When it comes to vitamins, trout has a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B12, C, D, and E, while haddock is not higher in any vitamins.
In the category of minerals, trout has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, potassium, and zinc, while haddock has slightly more selenium. Given that a 10oz portion of trout already contains 153% of the RDA of selenium, however, the same size portion of haddock having 173% of the RDA isn’t really a plus for haddock (especially as selenium can cause problems if we get too much). Oh, and haddock is also higher in sodium, but in industrialized countries, most people most of the time need less of that, not more.
On balance, the overwhelming nutritional density of trout wins the day.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Farmed Fish vs Wild Caught: It Makes Quite A Difference!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
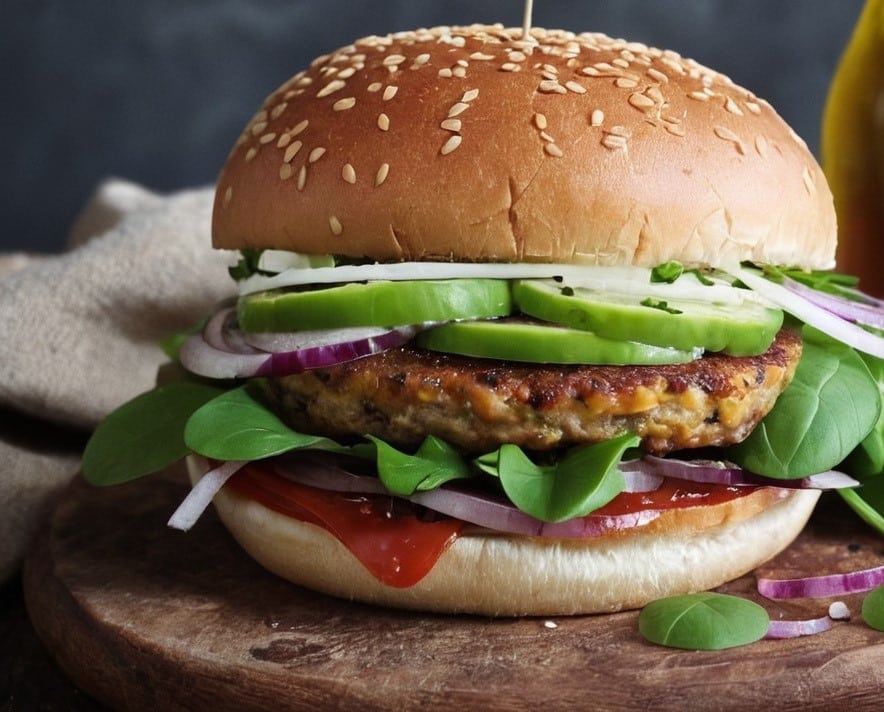
Sunflower Corn Burger
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Burgers are rarely a health food, but in this case, everything in the patty is healthy, and it’s packed with protein, fiber, and healthy fats.
You will need
- 1 can chickpeas
- ¾ cup frozen corn
- ½ cup chopped fresh parsley
- ⅓ cup sunflower seeds
- ⅓ cup cornichon pickles
- ⅓ cup wholegrain bread crumbs (gluten-free, if desired/required)
- ¼ bulb garlic (or more if you want a stronger flavor)
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil, plus more for frying
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast (or 1 tsp yeast extract)
- 2 tsp ground cumin
- 2 tsp red pepper flakes
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp Dijon mustard
- To serve: 4 burger buns; these are not usually healthy, so making your own is best, but if you don’t have the means/time, then getting similarly shaped wholegrain bread buns works just fine.
- Optional: your preferred burger toppings, e.g. greenery, red onion, tomato slices, avocado, jalapeños, whatever does it for you
Note: there is no need to add salt; there is enough already in the pickles.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine all the ingredients except the buns (and any optional toppings) in a food processor, pulsing a few times for a coarse texture (not a purée).
2) Shape the mixture into 4 burger patties, and let them chill in the fridge for at least 30 minutes.
3) Heat a skillet over a medium-high heat with some olive oil, and fry the burgers on both sides until they develop a nice golden crust; this will probably take about 4 minutes per side.
4) Assemble in the buns with any toppings you want, and serve:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Sunflower Seeds vs Pumpkin Seeds – Which is Healthier? ← pumpkin seeds have more micronutrients; sunflower seeds have more healthy fats; feel free to use either or both in this recipe
- What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Brain Benefits in 3 Months…through walking?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Keeping it Simple
Today’s video (below) is another Big Think production (can you tell that we love their work?). Wendy Suzuki does a wonderful job of breaking down the brain benefits of exercise into three categories, within three minutes.
The first question to ask yourself is: what is your current level of fitness?
Low Fitness
Exercising, even if it’s just going on a walk, 2-3 times a week improves baseline mood state, as well as enhances prefrontal and hippocampal function. These areas of the brain are crucial for complex behaviors like planning and personality development, as well as memory and learning.
Mid Fitness
The suggested regimen is, without surprise, to slightly increase your regular workouts over three months. Whilst you’re already getting the benefits from the low-fitness routine, there is a likelihood that you’ll increase your baseline dopamine and serotonin levels–which, of course, we love! Read more on dopamine here, here, or here.
High Fitness
If you consider yourself in the high fitness bracket then well done, you’re doing an amazing job! Wendy Suzuki doesn’t make many suggestions for you; all she mentions is that there is the possibility of “too much” exercise actually having negative effects on the brain. However, if you’re not competing at an Olympic level, you should be fine.
Fitness and Exercise in General
Of course, fitness and exercise are both very broad terms. We would suggest that you find an exercise routine that you genuinely enjoy–something that is easy to continue over the long term. Try browsing different areas of exercise to see what resonates with you. For instance, Total Fitness After 40 is a great book on all things fitness in the second half of your life. Alternatively, search through our archive for fitness-related material.
Anyway, without further ado, here is today’s video:
How was the video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Ice Baths: To Dip Or Not To Dip?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
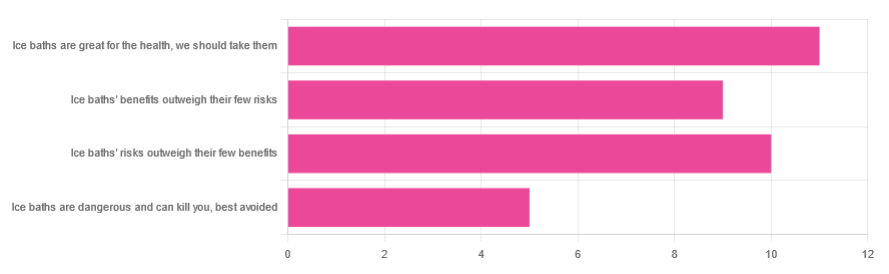
We asked you for your (health-related) view of ice baths, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 31% said “ice baths are great for the health; we should take them”
- About 29% said “ice baths’ risks outweigh their few benefits”
- About 26% said “ice baths’ benefits outweigh their few risks”
- About 14% said “ice baths are dangerous and can kill you; best avoided”
So what does the science say?
Freezing water is very dangerous: True or False?
True! Water close to freezing point is indeed very dangerous, and can most certainly kill you.
Fun fact, though: many such people are still saveable with timely medical intervention, in part because the same hypothermia that is killing them also slows down the process* of death
Source (and science) for both parts of that:
Cold water immersion: sudden death and prolonged survival
*and biologically speaking, death is a process, not an event, by the way. But we don’t have room for that today!
(unless you die in some sudden violent way, such as a powerful explosion that destroys your brain instantly; then it’s an event)
Ice baths are thus also very dangerous: True or False?
False! Assuming that they are undertaken responsibly and you have no chronic diseases that make it more dangerous for you.
What does “undertaken responsibly” mean?
Firstly, the temperature should not be near freezing. It should be 10–15℃, which for Americans is 50–59℉.
You can get a bath thermometer to check this, by the way. Here’s an example product on Amazon.
Secondly, your ice bath should last no more than 10–15 minutes. This is not a place to go to sleep.
What chronic diseases would make it dangerous?
Do check with your doctor if you have any doubts, as no list we make can be exhaustive and we don’t know your personal medical history, but the main culprits are:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Hypertension
- Diabetes (any type)
The first two are for heart attack risk; the latter is because diabetes can affect core temperature regulation.
Ice baths are good for the heart: True or False?
True or False depending on how they’re done, and your health before starting.
For most people, undertaking ice baths responsibly, repeated ice bath use causes the cardiovascular system to adapt to better maintain homeostasis when subjected to thermal shock (i.e. sudden rapid changes in temperature).
For example: Respiratory and cardiovascular responses to cold stress following repeated cold water immersion
And because that was a small study, here’s a big research review with a lot of data; just scroll to where it has the heading“Specific thermoregulative adaptations to regular exposure to cold air and/or cold water exposure“ for many examples and much discussion:
Health effects of voluntary exposure to cold water: a continuing subject of debate
Ice baths are good against inflammation: True or False?
True! Here’s one example:
Uric acid and glutathione levels (important markers of chronic inflammation) are also significantly affected:
Uric acid and glutathione levels during short-term whole body cold exposure
Want to know more?
That’s all we have room for today, but check out our previous “Expert Insights” main feature looking at Wim Hof’s work in cryotherapy:
A Cold Shower A Day Keeps The Doctor Away?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When Bitter Is Better
A good general rule of thumb for “does this food contain a lot of healthy polyphenols?” is:
“is this (edible) plant bitter/astringent/pungent”?
If it is, it’s probably rich in polyphenols:
Deciphering the role of bitter and astringent polyphenols in promoting well-being
…which is why it’s no surprise that black coffee and bitter chocolate score highly, as do hot peppers and even garlic.
See also: Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Even fruits, generally considered something sweet to eat, often contain more polyphenols when they are bitter—many berries are great examples of this!
Read more: Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
You can read more about the science of this here:
Sensory Nutrition and Bitterness and Astringency of Polyphenols
Important for multiple reasons (including heart and brain health)
Polyphenols have many benefits, and they’re most well known for their heart-healthy properties, but their antioxidant effect (and other mechanisms) also means these foods are generally neuroprotectants too:
The science of this is not all as obvious as you might think!
It is reasonable to expect “ok, this has antioxidant effect, so it will reduce oxidative damage to brain cells too”, and while that is true (and yes, polyphenols do cross the blood-brain barrier), they also help in other ways, including through the gut:
What if I don’t like bitter/astringent/pungent foods?
If you do not have a medical condition that proscribes them (do check with your doctor if unsure), the best advice is to simply eat them anyway, and your tastes will adapt.
It will also help if you avoid sweet foods (though this too is also a good general rule of thumb!), as this will move the balance of where your brain’s “set range” is for “good taste”.
Bonus tip: dark chocolate (80%+ cocoa if possible, 95% if you can get it) and chilli peppers go great with each other. Here’s an example of a chilli chocolate product on Amazon; it’s 70% cocoa (which is not bad, but could be better). You might be able to get a higher percentage locally, especially if you ask your local chocolatière, or make it yourself!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: