Just Be Well – by Dr. Thomas Sult
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Firstly, what this is not: a “think yourself well” book. It’s not about just deciding to be well.
Rather, it’s about ensuring the foundations of wellness, from which the rest of good health can spring, and notably, an absence of chronic illness. In essence: enjoying chronic good health.
The prescription here is functional medicine, which stands on the shoulders of lifestyle medicine. This latter is thus briefly covered and the basics presented, but most of the book is about identifying the root causes of disease and eliminating them one by one, by taking into account the functions of the body’s processes, both in terms of pathogenesis (and thus, seeking to undermine that) and in terms of correct functioning (i.e., good health).
While the main focus of the book is on health rather than disease, he does cover a number of very common chronic illnesses, and how even in those cases where they cannot yet be outright cured, there’s a lot more that can be done for them than “take two of these and call your insurance company in the morning”, when the goal is less about management of symptoms (though that is also covered) and more about undercutting causes, and ensuring that even if one thing goes wrong, it doesn’t bring the entire rest of the system down with it (something that often happens without functional medicine).
The style is clear, simple, and written for the layperson without unduly dumbing things down.
Bottom line: if you would like glowingly good health regardless of any potential setbacks, this book can help your body do what it needs to for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Saturated Fat: What’s The Truth?
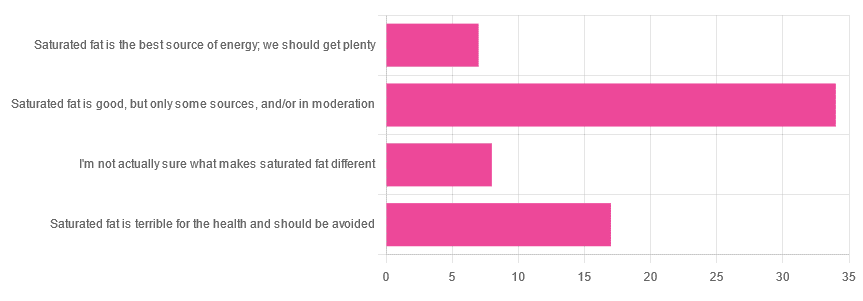
We asked you for your health-related opinion of saturated fat, and got the above-pictured, below-described, set of results.
- Most recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation”
- This is an easy one to vote for, because of the “and/or in moderation” part, which tends to be a “safe bet” for most things.
- Next most popular was “Saturated fat is terrible for the health and should be avoided”
- About half as many recorded votes were for “I’m not actually sure what makes saturated fat different”, which is a very laudable option to click. Admitting when we don’t know things (and none of us know everything) is a very good first step to learning about them!
- Fewest recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is the best source of energy; we should get plenty”.
So, what does the science say?
First, a bit of physics, chemistry, and biology
You may be wondering what, exactly, saturated fats are “saturated” with. That’s a fair question, so…
All fats have a molecular structure made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Saturated fats are saturated with hydrogen, and thus have only single bonds between carbon atoms (unsaturated fats have at least one double-bond between carbon atoms).
The observable effect this has on them, is that fats that are saturated with hydrogen are solid at room temperature, whereas unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature. Their different properties also make for different interactions inside the human body, including how likely or not they are to (for example) clog arteries.
See also: Could fat in your bloodstream cause blood clots?
Saturated fat is the best source of energy; we should get plenty: True or False?
False, in any reasonable interpretation, anyway. That is to say, if your idea of “plenty” is under 13g (e.g: two tablespoons of butter, and no saturated fat from other sources, e.g. meat) per day, then yes, by all means feel free to eat plenty. More than that, though, and you might want to consider trimming it down a bit.
The American Heart Association has this to say:
❝When you hear about the latest “diet of the day” or a new or odd-sounding theory about food, consider the source.
The American Heart Association recommends limiting saturated fats, which are found in butter, cheese, red meat and other animal-based foods, and tropical oils.
Decades of sound science has proven it can raise your “bad” cholesterol and put you at higher risk for heart disease.❞
Source: The American Heart Association Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations on Saturated Fat
The British Heart Foundation has a similar statement:
❝Despite what you read in the media, our advice is clear: replace saturated fats with unsaturated fats and avoid trans fats. Saturated fat is the kind of fat found in butter, lard, ghee, fatty meats and cheese. This is linked to an increased risk of heart and circulatory disease❞
Source: British Heart Foundation: What does fat do and what is saturated fat?
As for the World Health Organization:
❝1. WHO strongly recommends that adults and children reduce saturated fatty acid intake to 10% of total energy intake
2. WHO suggests further reducing saturated fatty acid intake to less than 10% of total energy intake
3. WHO strongly recommends replacing saturated fatty acids in the diet with polyunsaturated fatty acids; monounsaturated fatty acids from plant sources; or carbohydrates from foods containing naturally occurring dietary fibre, such as whole grains, vegetables, fruits and pulses.❞
Source: Saturated fatty acid and trans-fatty acid intake for adults and children: WHO guideline
Please note, organizations such as the AHA, the BHF, and the WHO are not trying to sell us anything, and just would like us to not die of heart disease, the world’s #1 killer.
As for “the best source of energy”…
We evolved to eat (much like our nearest primate cousins) a diet consisting mostly of fruits and other edible plants, with a small supplementary amount of animal-source protein and fats.
That’s not to say that because we evolved that way we have to eat that way—we are versatile omnivores. But for example, we are certainly not complete carnivores, and would quickly sicken and die if we tried to live on only meat and animal fat (we need more fiber, more carbohydrates, and many micronutrients that we usually get from plants)
The closest that humans tend to come to doing such is the ketogenic diet, which focuses on a high fat, low carbohydrate imbalance, to promote ketosis, in which the body burns fat for energy.
The ketogenic diet does work, and/but can cause a lot of health problems if a lot of care is not taken to avoid them.
See for example: 7 Keto Risks To Keep In Mind
Saturated fat is terrible for the health and should be avoided: True or False?
False, if we are talking about “completely”.
Firstly, it’s practically impossible to cut out all saturated fats, given that most dietary sources of fat are a mix of saturated, unsaturated (mono- and poly-), and trans fats (which are by far the worst, but beyond the scope of today’s main feature).
Secondly, a lot of research has been conducted and found insignificant or inconclusive results, in cases where saturated fat intake was already within acceptable levels (per the recommendations we mentioned earlier), and then cut down further.
Rather than fill up the newsletter with individual studies of this kind here’s a high-quality research review, looking at 19 meta-analyses, each of those meta-analyses having looked at many studies:
Dietary saturated fat and heart disease: a narrative review
Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation: True or False?
True! The moderation part is easy to guess, so let’s take a look at the “but only some sources”.
We were not able to find any convincing science to argue for health-based reasons to favor plant- or animal-sourced saturated fat. However…
Not all saturated fats are created equal (there are many kinds), and also many of the foods containing them have additional nutrients, or harmful compounds, that make a big difference to overall health, when compared gram-for-gram in terms of containing the same amount of saturated fat.
For example:
- Palm oil’s saturated fat contains a disproportionate amount of palmitic acid, which raises LDL (“bad” cholesterol) without affecting HDL (“good” cholesterol), thus having an overall heart-harmful effect.
- Most animal fats contain a disproportionate amount of stearic acid, which has statistically insignificant effects on LDL and HDL levels, and thus is broadly considered “heart neutral” (in moderation!)
- Coconut oil’s saturated fat contains a disproportionate amount of lauric acid, which raises total cholesterol, but mostly HDL without affecting LDL, thus having an overall heart-beneficial effect (in moderation!)
Do you know what’s in the food you eat?
Test your knowledge with the BHF’s saturated fat quiz!
Enjoy!
Share This Post
- Most recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation”
-
Krill Oil vs Fish Oil – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
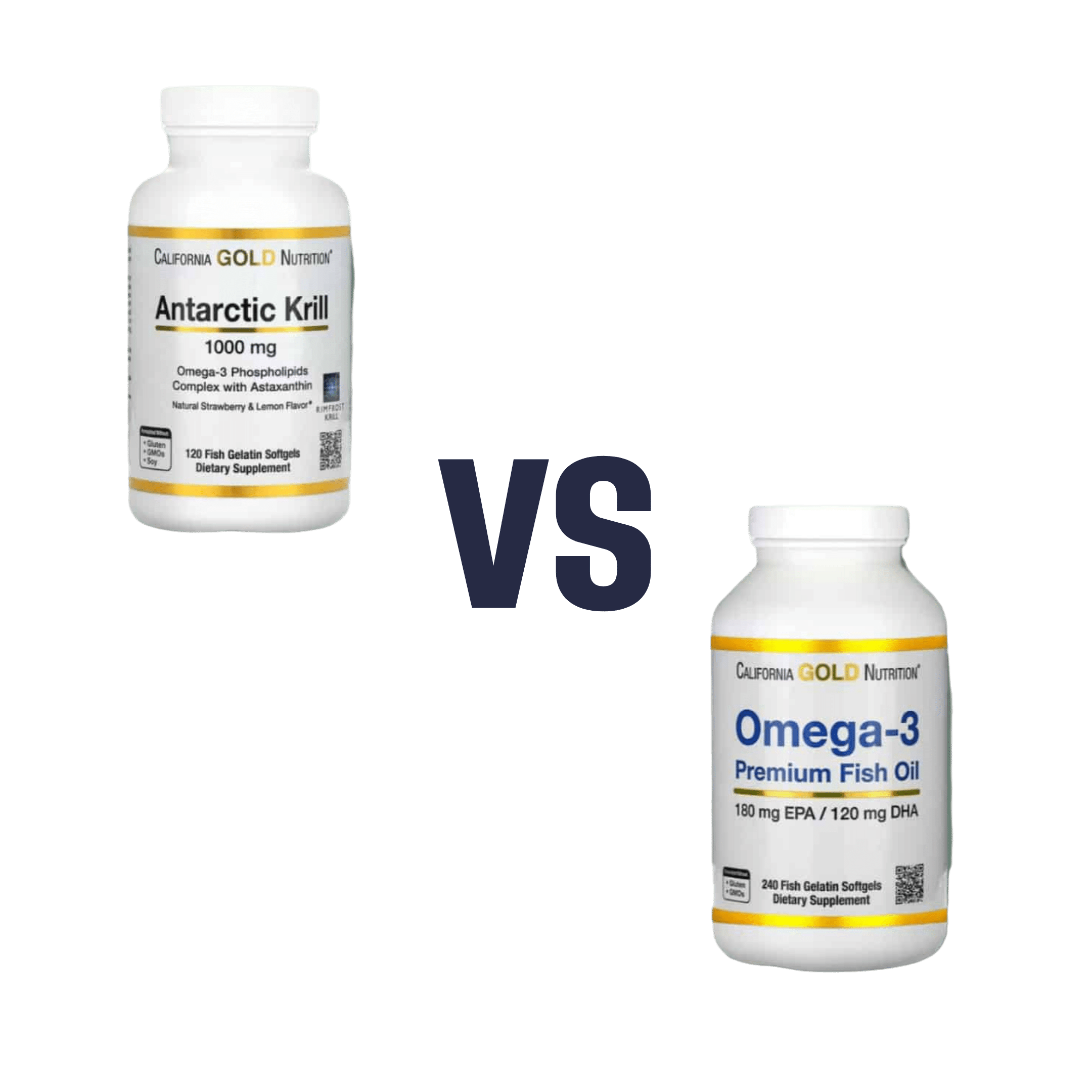
When comparing krill oil to fish oil, we picked the krill oil.
Why?
Both of these products are good sources of omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, and for the specific brand depicted above, in both cases 2 softgels will give you the recommended daily amount (which is generally held to be 250–500mg combined omega-3s per day).
This brand’s fish oil gives more (640mg combined omega-3s per 2 softgels, to the same brand’s krill oil’s 480mg per 2 softgels), but since the krill oil is already in the high end of RDA territory, the excess beyond the RDA is not helpful, and not a huge factor. More quantity is not always better, when the body can only process so much at a time.
However, the krill oil gives some extra things that the fish oil doesn’t:
- Astaxanthin, a “super-antioxidant”
- and neuroprotectant, heart-healthy phospholipids
Additional considerations
We have declared “the winner” based on health considerations only. That’s a sticking point for us in all our writings; we’ll occasionally look at and mention other factors, but we know that health is what you’re here for, so that’s what we’ll always treat as most critical.
However, in case these factors may interest you and/or influence you to one or the other:
• The fish oil is about 30% cheaper financially
• The krill oil is a lot more sustainable environmentallyBack to the health science…
Read more:
• What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
• Astaxanthin: Super-Antioxidant & NeuroprotectantWant some? Here for your convenience are some example products on Amazon:
(brands available will vary per region, but now you know what to look out for on the labels!)
Share This Post
-
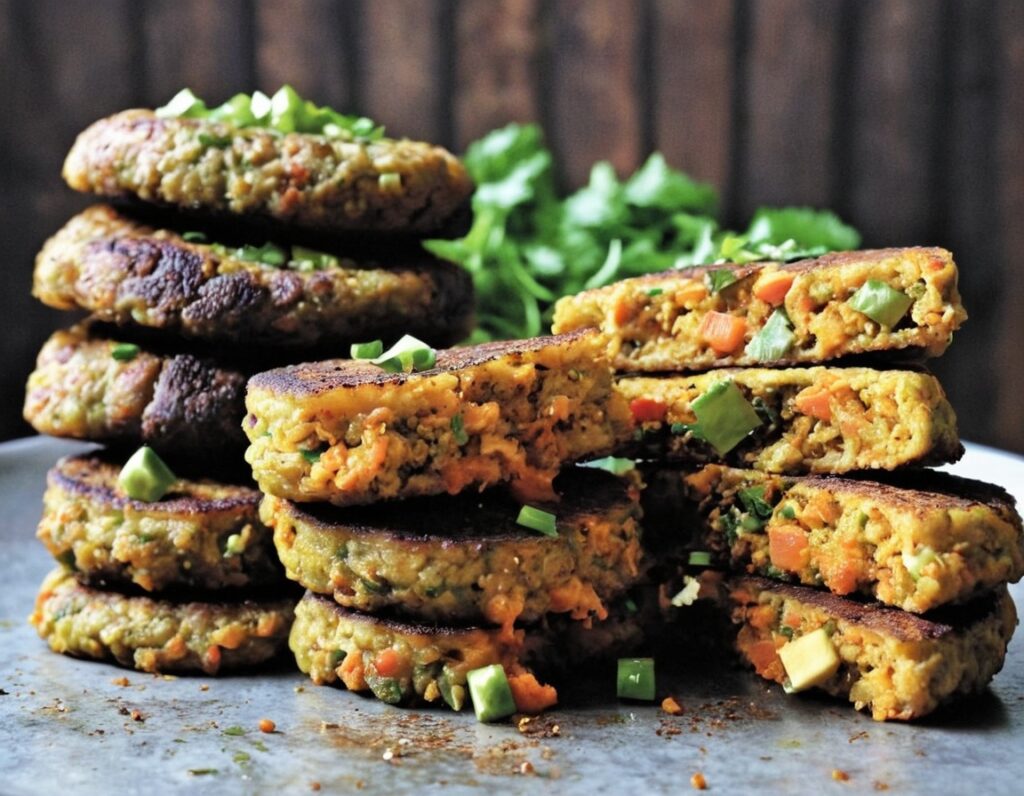
Samosa Spiced Surprise
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You know what’s best about samosas? It’s not actually the fried pastry; that’s just what holds it together. If you were to try eating sheets of pastry alone, it would not be much fun. But, the spiced vegetable filling? Now we’re talking! So, this recipe takes what’s best about samosas, and makes them into healthy snack-sized patties.
You will need
- Extra virgin olive oil, or coconut oil (per your preference) for cooking
- 4 medium potatoes, boiled, peeled, and mashed
- 1 medium onion, diced
- 1 cup peas
- 1 carrot, finely chopped
- ½ cup garbanzo bean flour (chickpea flour, gram flour, whatever your supermarket calls it)
- ¼ cup fresh cilantro, chopped (substitute parsley if you have the soap gene)
- ¼ bulb garlic, minced
- 1 jalapeño pepper, chopped
- 1 tbsp ground cumin
- 2 tsp garam masala
- 1 tsp ground coriander
- 1 tsp ground turmeric
- 1 tsp ground black pepper
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Fry the onion until it is becoming soft and translucent (3–5 minutes).
2) Add the spices (the garlic, both kinds of pepper, cumin, coriander, turmeric, and the garam masala), stirring in well
3) Add the carrot and peas, stirring and cooking until just becoming soft (probably another 3–5 minutes, depending on the heat, how small you chopped the carrot, and whether the peas were frozen or fresh). Take it off the heat.
4) Mix the potato, chickpea flour, and cilantro in a bowl, and carefully add everything from the pan, mixing that in thoroughly too.
5) Shape into patties, and fry them on each side until browned and crispy.
6) Serve as part of a buffet, or perhaps as an appetizer—raita is a fine accompaniment option.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
“Skinny Fat” Explained (& How To Fix It)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Skinny fat” is a term you may have seen floating around social media. It describes people who have a low body weight but a high body fat percentage, often resulting in flabby appearance despite being within a weight range considered healthy. Many try dieting and exercising, only to find that neither work.
This video explains what’s going wrong, and how to fix it:
Diet & exercise won’t work if it’s not right
This problem occurs because common weight-loss approaches, such as restrictive dieting and excessive cardio, fail to improve body composition:
- Restrictive dieting reduces both fat and lean mass, keeping the body fat percentage unchanged
- Cardio burns some calories but the underlying metabolic issue hasn’t meaningfully changed, so any loss will be temporary (and most of any immediate loss will be water weight, anyway)
The key to overcoming skinny fat is resistance training. Lifting weights or doing bodyweight exercises helps build muscle, which not only lowers body fat percentage (by simple mathematics; add more muscle and the percentages of other things must go down even if the total amount is the same) and improves overall definition, which is something most people consider nice. However, the real value here is that it actually addresses the underlying metabolic issue—because muscle costs calories to maintain, one’s basal metabolic rate will now be faster, even when you’re sleeping.
This then becomes… Not quite a self-sustaining system, because you do have to still eat well and continue to do resistance training, but your body will be doing most of the work for you, and you’ll find it’s a lot easier to maintain a healthy body composition than to get one in the first place, for exactly the metabolic reason we described.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It ← this is a different, but adjacent issue (and very important for avoiding metabolic disease risks)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What you need to know about FLiRT, an emerging group of COVID-19 variants
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- COVID-19 wastewater levels are currently low, but a recent group of variants called FLiRT is making headlines.
- KP.2 is one of several FLiRT variants, and early lab tests suggest that it’s more infectious than JN.1.
- Getting infected with any COVID-19 variant can cause severe illness, heart problems, and death.
KP.2, a new COVID-19 variant, is now dominant in the United States. Lab tests suggest that it may be more infectious than JN.1, the variant that was dominant earlier this year.
Fortunately, there’s good news: Current wastewater data shows that COVID-19 infection rates are low. Still, experts are closely watching KP.2 to see if it will lead to an uptick in infections.
Read on to learn more about KP.2 and how to stay informed about COVID-19 cases in your area.
Where can I find data on COVID-19 cases in my area?
Hospitals are no longer required to report COVID-19 hospital admissions or hospital capacity to the Department of Health and Human Services. However, wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) estimates the number of COVID-19 infections in a community based on the amount of COVID-19 viral particles detected in local wastewater.
View this map of wastewater data from the CDC to visualize COVID-19 infection rates throughout the U.S., or look up COVID-19 wastewater trends in your state.
What do we know so far about the new variant?
Early lab tests suggest that KP.2—one of a group of emerging variants called FLiRT—is similar to the previously dominant variant, JN.1, but it may be more infectious. If you had JN.1, you may still get reinfected with KP.2, especially if it’s been several months or longer since your last COVID-19 infection.
A CDC spokesperson said they have no reason to believe that KP.2 causes more severe illness than other variants. Experts are closely watching KP.2 to see if it will lead to an uptick in COVID-19 cases.
How can I protect myself from COVID-19 variants?
Staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines reduces your risk of severe illness, long COVID, heart problems, and death. The CDC recommends that people 65 and older and immunocompromised people receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring.
Wearing a high-quality, well-fitting mask reduces your risk of contracting COVID-19 and spreading it to others. At indoor gatherings, improving ventilation by opening doors and windows, using high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters, and building your own Corsi-Rosenthal box can also reduce the spread of COVID-19.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
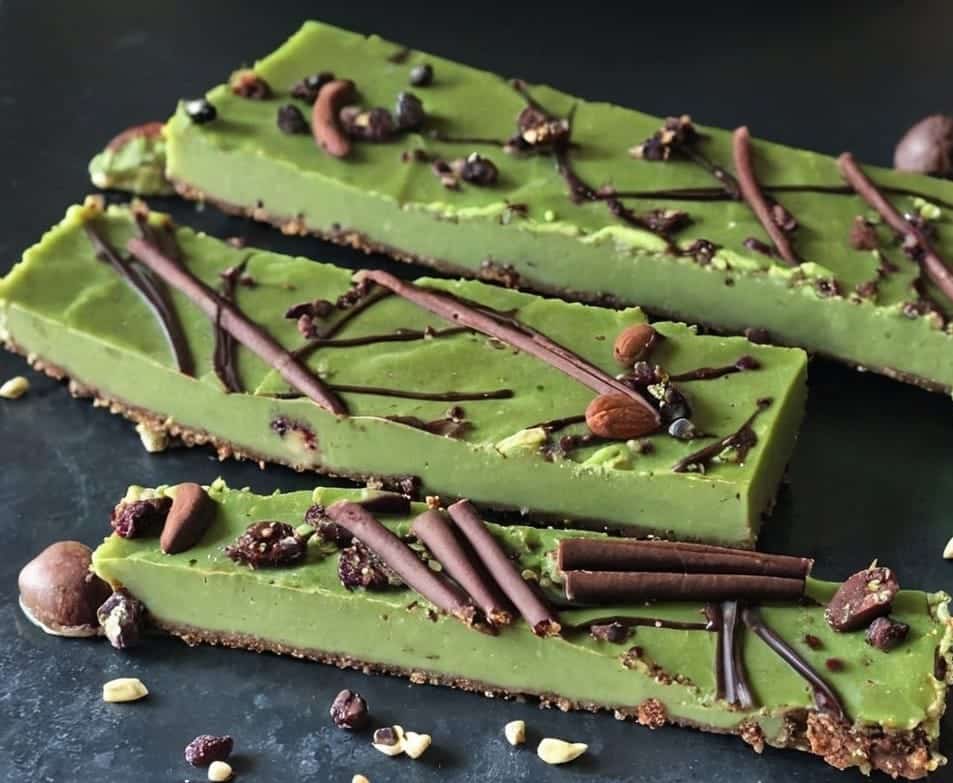
Antioxidant Matcha Snack Bars
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The antioxidants in this come not just from the matcha, but also the cacao nibs and chocolate, as well as lots of nutrients from the hazelnuts and cashews. If you’re allergic to nuts, we’ll give you substitutions that will change the nutritional profile (and flavor), but still work perfectly well and be healthy too.
You will need
For the base:
- ⅔ cup roasted hazelnuts (if allergic, substitute dessicated coconut)
- ⅔ cup chopped dates
For the main part:
- 1 cup raw cashews (if allergic, substitute raw coconut, chopped)
- ½ cup almond milk (or your preferred milk of any kind)
- ½ cup cacao nibs
- 2 tbsp lime juice
- 1 tbsp matcha powder
- 1 tbsp maple syrup (omit if you don’t care for sweetness)
For the topping (optional):
- 2oz dark chocolate, melted (and if you like, tempered—but this isn’t necessary; it’ll just make it glossier if you do)
- Spare cacao nibs, chopped nuts, or anything else you might want on there
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the base ingredients in a food processor until it has a coarse sticky texture, but isn’t yet a paste or dough.
2) Line a cake pan with baking paper and spread the base mix on the base; press it down to compact it a little and ensure it is flat. If there’s room, put this in the freezer while you do the next bit. If not, the fridge will suffice.
3) Blend the main part ingredients apart from the cacao nibs, until smooth. Stir in the cacao nibs with a spoon.
4) Spread the main part evenly over the base, and allow everything you’ve built (in this recipe, not in life in general) to chill in the fridge for at least 4 hours.
5) Cut it into blocks of the size and shape you want to eat them, and (if adding the optional topping) separate the blocks slightly from each other, before drizzling with the chocolate topping. Put it back in the fridge to cool this too; an hour should be sufficient.
6) Serve!
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Which Tea Is Best, By Science?
- Which Plant Milk?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: