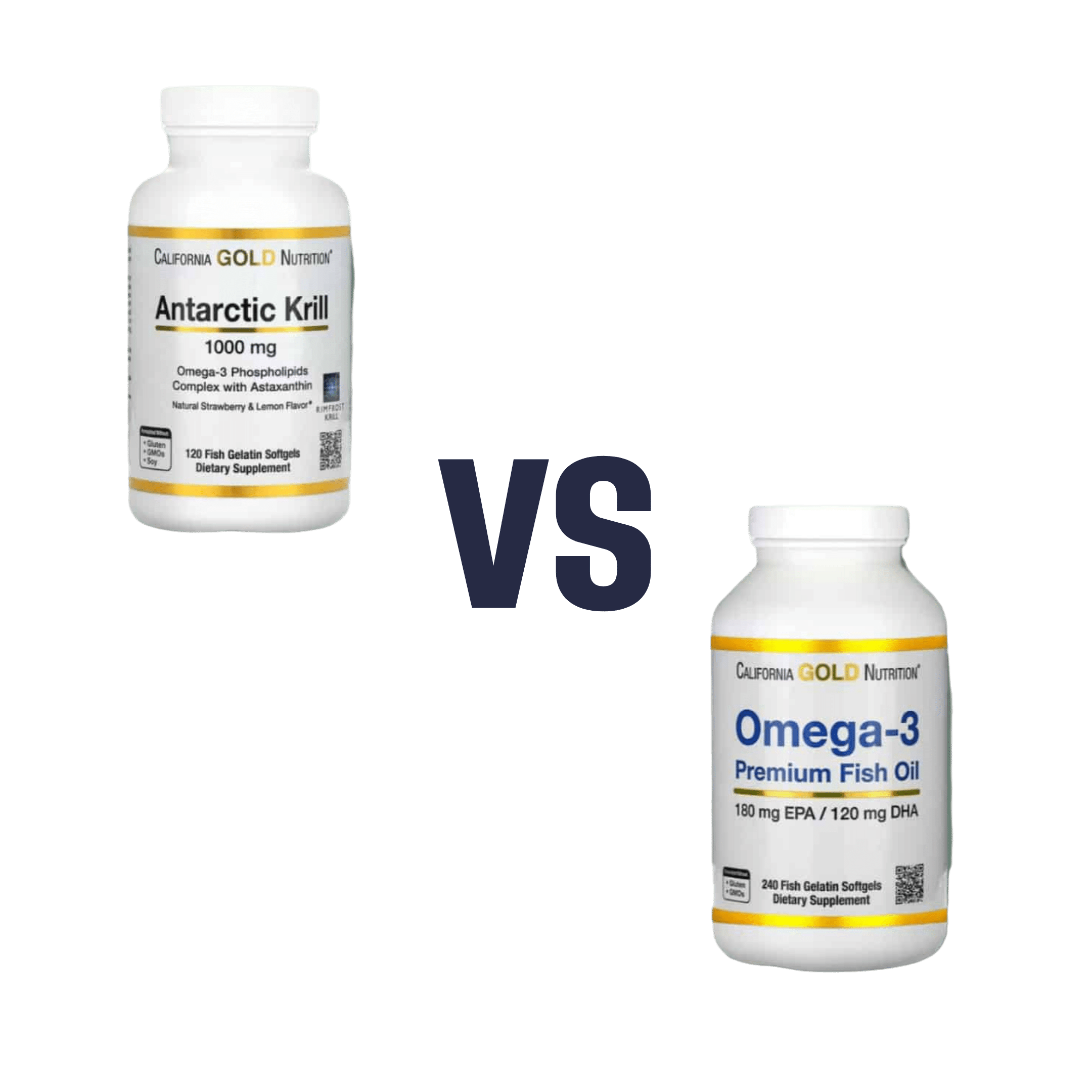
Krill Oil vs Fish Oil – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing krill oil to fish oil, we picked the krill oil.
Why?
Both of these products are good sources of omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, and for the specific brand depicted above, in both cases 2 softgels will give you the recommended daily amount (which is generally held to be 250–500mg combined omega-3s per day).
This brand’s fish oil gives more (640mg combined omega-3s per 2 softgels, to the same brand’s krill oil’s 480mg per 2 softgels), but since the krill oil is already in the high end of RDA territory, the excess beyond the RDA is not helpful, and not a huge factor. More quantity is not always better, when the body can only process so much at a time.
However, the krill oil gives some extra things that the fish oil doesn’t:
- Astaxanthin, a “super-antioxidant”
- and neuroprotectant, heart-healthy phospholipids
Additional considerations
We have declared “the winner” based on health considerations only. That’s a sticking point for us in all our writings; we’ll occasionally look at and mention other factors, but we know that health is what you’re here for, so that’s what we’ll always treat as most critical.
However, in case these factors may interest you and/or influence you to one or the other:
• The fish oil is about 30% cheaper financially
• The krill oil is a lot more sustainable environmentally
Back to the health science…
Read more:
• What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
• Astaxanthin: Super-Antioxidant & Neuroprotectant
Want some? Here for your convenience are some example products on Amazon:
(brands available will vary per region, but now you know what to look out for on the labels!)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
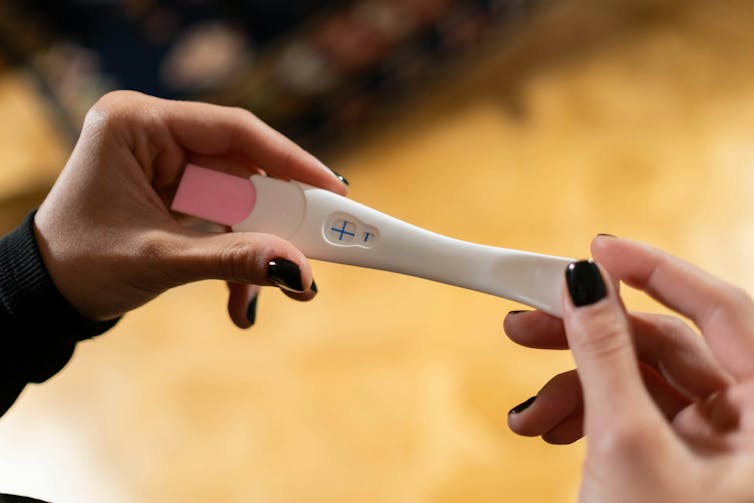
What are ‘Ozempic babies’? Can the drug really increase your chance of pregnancy?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are taking drugs like Ozempic to lose weight. But what do we actually know about them? This month, The Conversation’s experts explore their rise, impact and potential consequences.
We’ve heard a lot about the impacts of Ozempic recently, from rapid weight loss and lowered blood pressure, to persistent vomiting and “Ozempic face”.
Now we’re seeing a rise in stories about “Ozempic babies”, where women who use drugs like Ozempic (semaglutide) report unexpected pregnancies.
But does semaglutide (also sold as Wegovy) improve fertility? And if so, how? Here’s what we know so far.
Remind me, what is Ozempic?
Ozempic and related drugs (glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists or GLP-1-RAs) were developed to help control blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes.
But the reason for Ozempic’s huge popularity worldwide is that it promotes weight loss by slowing stomach emptying and reducing appetite.
Ozempic is prescribed in Australia as a diabetes treatment. It’s not currently approved to treat obesity but some doctors prescribe it “off label” to help people lose weight. Wegovy (a higher dose of semaglutide) is approved for use in Australia to treat obesity but it’s not yet available.
How does obesity affect fertility?
Obesity affects the fine-tuned hormonal balance that regulates the menstrual cycle.
Women with a body mass index (BMI) above 27 are three times more likely than women in the normal weight range to be unable to conceive because they are less likely to ovulate.
The metabolic conditions of type 2 diabetes and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are both linked to obesity and fertility difficulties.
Women with type 2 diabetes are more likely than other women to have obesity and to experience fertility difficulties and miscarriage.
Similarly, women with PCOS are more likely to have obesity and trouble conceiving than other women because of hormonal imbalances that cause irregular menstrual cycles.
In men, obesity, diabetes and metabolic syndrome (a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease and stroke) have negative effects on fertility.
Low testosterone levels caused by obesity or type 2 diabetes can affect the quality of sperm.
So how might Ozempic affect fertility?
Weight loss is recommended for people with obesity to reduce the risk of health problems. As weight loss can improve menstrual irregularities, it may also increase the chance of pregnancy in women with obesity.
This is why weight loss and metabolic improvement are the most likely reasons why women who use Ozempic report unexpected pregnancies.
But unexpected pregnancies have also been reported by women who use Ozempic and the contraceptive pill. This has led some experts to suggest that some GLP-1-RAs might affect the absorption of the pill and make it less effective. However, it’s uncertain whether there is a connection between Ozempic and contraceptive failure.
Some women have reported getting pregnant while taking the contraceptive pill and Ozempic. Cottonbro Studio/Pexels In men with type 2 diabetes, obesity and low testosterone, drugs like Ozempic have shown promising results for weight loss and increasing testosterone levels.
Avoid Ozempic if you’re trying to conceive
It’s unclear if semaglutide can be harmful in pregnancy. But data from animal studies suggest it should not be used in pregnancy due to potential risks of fetal abnormalities.
That’s why the Therapeutic Goods Administration recommends women of childbearing potential use contraception when taking semaglutide.
Similarly, PCOS guidelines state health professionals should ensure women with PCOS who use Ozempic have effective contraception.
Guidelines recommended stopping semaglutide at least two months before planning pregnancy.
For women who use Ozempic to manage diabetes, it’s important to seek advice on other options to control blood glucose levels when trying for pregnancy.
What if you get pregnant while taking Ozempic?
For those who conceive while using Ozempic, deciding what to do can be difficult. This decision may be even more complicated considering the unknown potential effects of the drug on the fetus.
While there is little scientific data available, the findings of an observational study of pregnant women with type 2 diabetes who were on diabetes medication, including GLP-1-RAs, are reassuring. This study did not indicate a large increased risk of major congenital malformations in the babies born.
Women considering or currently using semaglutide before, during, or after pregnancy should consult with a health provider about how to best manage their condition.
When pregnancies are planned, women can take steps to improve their baby’s health, such as taking folic acid before conception to reduce the risk of neural tube defects, and stopping smoking and consuming alcohol.
While unexpected pregnancies and “Ozempic babies” may be welcomed, their mothers have not had the opportunity to take these steps and give them the best start in life.
Read the other articles in The Conversation’s Ozempic series here.
Karin Hammarberg, Senior Research Fellow, Global and Women’s Health, School of Public Health & Preventive Medicine, Monash University and Robert Norman, Emeritus Professor of Reproductive and Periconceptual Medicine, The Robinson Research Institute, University of Adelaide
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Good to Go – by Christie Aschwanden
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many of us may more often need to recover from a day of moving furniture than running a marathon, but the science of recovery can still teach us a lot. The author, herself an endurance athlete and much-decorated science journalist, sets out to do just that.
She explores a lot of recovery methods, and examines whether the science actually backs them up, and if so, to what degree. She also, in true science journalism style, talks to a lot of professionals ranging from fellow athletes to fellow scientists, to get their input too—she is nothing if not thorough, and this is certainly not a book of one person’s opinion with something to sell.
Indeed, on the contrary, her findings show that some of the best recovery methods are the cheapest, or even free. She also looks at the psychological aspect though, and why many people are likely to continue with things that objectively do not work better than placebo.
The style is very easy-reading jargon-free pop-science, while nevertheless being backed up with hundreds of studies cited in the bibliography—a perfect balance of readability and reliability.
Bottom line: for those who wish to be better informed about how to recover quickly and easily, this book is a treasure trove of information well-presented.
Click here to check out Good To Go, and always be good to go!
Share This Post
-
Marrakesh Sorghum Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As the name suggests, it’s a Maghreb dish today! Using sorghum, a naturally gluten-free whole grain with a stack of vitamins and minerals. This salad also comes with fruit and nuts (apricots and almonds; a heavenly combination for both taste and nutrients) as well as greens, herbs, and spices.
Note: to keep things simple today, we’ve listed ras el-hanout as one ingredient. If you’re unfamiliar, it’s a spice blend; you can probably buy a version locally, but you might as well know how to make it yourself—so here’s our recipe for that!
You will need
- 1½ cups sorghum, soaked overnight in water (if you can’t find it locally, you can order it online (here’s an example product on Amazon), or substitute quinoa) and if you have time, soaked overnight and then kept in a jar with just a little moisture for a few days until they begin to sprout—this will be best of all. But if you don’t have time, don’t worry about it; overnight soaking is sufficient already.
- 1 carrot, grated
- ½ cup chopped parsley
- 1 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- ½ tbsp chopped chives
- 2 tbsp ras el-hanout
- 3 cloves garlic, crushed
- 2 tbsp almond butter
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- 1 tsp white miso paste
- ½ cup sliced almonds
- 4 fresh apricots, pitted and cut into wedges
- 1 cup mint leaves, chopped
- To serve: your choice of salad greens; we suggest chopped romaine lettuce and rocket
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the sorghum, which means boiling it for about 45 minutes, or 30 in a pressure cooker. If unsure, err on the side of cooking longer—even up to an hour will be totally fine. You have a lot of wiggle room, and will soon get used to how long it takes with your device/setup. Drain the cooked sorghum, and set it aside to cool. If you’re entertaining, we recommend doing this part the day before and keeping it in the fridge.
2) When it’s cool, add the carrot, the parsley, the chives, the vinegar, and 1 tbsp of the ras el-hanout. Toss gently but thoroughly to combine.
3) Make the dressing, which means putting ¼ cup water into a blender with the other 1 tbsp of the ras el-hanout, the garlic, the almond butter, the lemon juice, and the miso paste. Blend until smooth.
4) Assemble the salad, which means adding the dressing to sorghum-and-ingredients bowl, along with the almonds, apricots, and mint leaves. Toss gently, but sufficiently that everything is coated.
5) Serve on a bed of salad greens.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet ← including an anti-inflammatory version, which is functionally what we’re doing today. As an aside when people hear “Mediterranean” they often think “Italy and Greece”. Which, sure, but N. Africa (and thus Maghreb cuisine) is also very much Mediterranean, and it shows!
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Mediterranean Air Fryer Cookbook – by Naomi Lane
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are Mediterranean Diet cookbooks, and there are air fryer cookbooks. And then there are (a surprisingly large intersection of!) Mediterranean Diet air fryer cookbooks. We wanted to feature one of them in today’s newsletter… And as part of the selection process, looked through quite a stack of them, and honestly, were quite disappointed with many. This one, however, was one of the ones that stood out for its quality of both content and clarity, and after a more thorough reading, we now present it to you:
Naomi Lane is a professional dietician, chef, recipe developer, and food writer… And it shows, on all counts.
She covers what the Mediterranean diet is, and she covers far more than this reviewer knew it was even possible to know about the use of an air fryer. That alone would make the book a worthy purchase already.
The bulk of the book is the promised 200 recipes. They cover assorted dietary requirements (gluten-free, dairy-free, etc) while keeping to the Mediterranean Diet.
The recipes are super clear, just what you need to know, no reading through a nostalgic storytime first to find things. Also no pictures, which will be a plus for some readers and a minus for others. The recipes also come complete with nutritional information for each meal (including sodium), so you don’t have to do your own calculations!
Bottom line: this is the Mediterranean Diet air fryer cook book. Get it, thank us later!
Get your copy of “Mediterranean Air Fryer Cookbook” on Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why are people on TikTok talking about going for a ‘fart walk’? A gastroenterologist weighs in
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Fart walks” have become a cultural phenomenon, after a woman named Mairlyn Smith posted online a now-viral video about how she and her husband go on walks about 60 minutes after dinner and release their gas.
Smith, known on TikTok as @mairlynthequeenoffibre and @mairlynsmith on Instagram, has since appeared on myriad TV and press interviews extolling the benefits of a fart walk. Countless TikTok and Instagram users and have now shared their own experiences of feeling better after taking up the #fartwalk habit.
So what’s the evidence behind the fart walk? And what’s the best way to do it?
CandyBox Images/Shutterstock Exercise can help get the gas out
We know exercise can help relieve bloating by getting gas moving and out of our bodies.
Researchers from Barcelona, Spain in 2006 asked eight patients complaining of bloating, seven of whom had irritable bowel syndrome, to avoid “gassy” foods such as beans for two days and to fast for eight hours before their study.
Each patient was asked to sit in an armchair, in order to avoid any effects of body position on the movement of gas. Gas was pumped directly into their small bowel via a thin plastic tube that went down their mouth, and the gas expelled from the body was collected into a bag via a tube placed in the rectum. This way, the researchers could determine how much gas was retained in the gut.
The patients were then asked to pedal on a modified exercise bike while remaining seated in their armchairs.
The researchers found that much less gas was retained in the patients’ gut when they exercised. They determined exercise probably helped the movement and release of intestinal gas.
Walking may have another bonus; it may trigger a nerve reflex that helps propel foods and gas contents through the gut.
Walking can also increase internal abdominal pressure as you use your abdominal muscles to stay upright and balance as you walk. This pressure on the colon helps to push intestinal gas out.
Proper fart walk technique
One study from Iran studied the effects of walking in 94 individuals with bloating.
They asked participants to carry out ten to 15 minutes of slow walking (about 1,000 steps) after eating lunch and dinner. They filled out gut symptom questionnaires before starting the program and again at the end of the four week program.
The researchers found walking after meals resulted in improvements to gut symptoms such as belching, farting, bloating and abdominal discomfort.
Now for the crucial part: in the Iranian study, there was a particular way in which participants were advised to walk. They were asked to clasp hands together behind their back and to flex their neck forward.
The clasped hands posture leads to more internal abdominal pressure and therefore more gentle squeezing out of gas from the colon. The flexed neck posture decreases the swallowing of air during walking.
This therefore is the proper fart walk technique, based on science.
Could walking with your hands behind your back yield better or more farts? candy candy/Shutterstock What about constipation?
A fart walk can help with constipation.
One study involved middle aged inactive patients with chronic constipation, who did a 12 week program of brisk walking at least 30 minutes a day – combined with 11 minutes of strength and flexibility exercises.
This program, the researchers found, improved constipation symptoms through reduced straining, less hard stools and more complete evacuation.
It also appears that the more you walk the better the benefits for gut symptoms.
In patients with irritable bowel syndrome, one study increasing the daily step count to 9,500 steps from 4,000 steps led to a 50% reduction in the severity of their symptoms.
And just 30 minutes of a fart walk has been shown to improve blood sugar levels after eating.
Walking after eating can help keep your blood sugar levels under control. IndianFaces/Shutterstock What if I can’t get outside the house?
If getting outside the house after dinner is impossible, could you try walking slowly on a treadmill or around the house for 1,000 steps?
If not, perhaps you could borrow an idea from the Barcelona research: sit back in an armchair and pedal using a modified exercise bike. Any type of exercise is better than none.
Whatever you do, don’t be a couch potato! Research has found more leisure screen time is linked to a greater risk of developing gut diseases.
We also know physical inactivity during leisure time and eating irregular meals are linked to a higher risk of abdominal pain, bloating and altered bowel motions.
Try the fart walk today
It may not be for everyone but this simple physical activity does have good evidence behind it. A fart walk can improve common symptoms such as bloating, abdominal discomfort and constipation.
It can even help lower blood sugar levels after eating.
Will you be trying a fart walk today?
Vincent Ho, Associate Professor and clinical academic gastroenterologist, Western Sydney University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
You’ve probably heard of people drinking apple cider vinegar for its health benefits. It’s not very intuitive, so today we’re going to see what the science has to say…
Apple cider vinegar for managing blood sugars
Whether diabetic, prediabetic, or not at all, blood sugar spikes aren’t good for us, so anything that evens that out is worth checking out. As for apple cider vinegar…
Diabetes Control: Is Vinegar a Promising Candidate to Help Achieve Targets?
…the answer found by this study was “yes”, but their study was small, and they concluded that more research would be worthwhile. So…
…was also a small study, with the same (positive) results.
But! We then found a much larger systematic review was conducted, examining 744 previously-published papers, adding in another 14 they found via those. After removing 47 duplicates, and removing another 15 for not having a clinical trial or not having an adequate control, they concluded:
❝In this systematic review and meta-analyses, the effect of vinegar consumption on postprandial glucose and insulin responses were evaluated through pooled analysis of glucose and insulin AUC in clinical trials. Vinegar consumption was associated with a statistically significant reduction in postprandial glucose and insulin responses in both healthy participants and participants with glucose disorder.❞
~ Sishehbor, Mansoori, & Shirani
Check it out:
Apple cider vinegar for weight loss?
Yep! It appears to be an appetite suppressant, probably moderating ghrelin and leptin levels.
But…
As a bonus, it also lowers triglycerides and total cholesterol, while raising HDL (good cholesterol), and that’s in addition to doubling the weight loss compared to control:
How much to take?
Most of these studies were done with 1–2 tbsp of apple cider vinegar in a glass of water, at mealtime.
Obviously, if you want to enjoy the appetite-suppressant effects, take it before the meal! If you forget and/or choose to take it after though, it’ll still help keep your blood sugars even and still give you the cholesterol-moderating benefits.
Where to get it?
Your local supermarket will surely have it. Or if you buy it online, you can even get it in capsule form!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: