Intermittent Fasting, Intermittently?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Have you come across any research on alternate-day intermittent fasting—specifically switching between one day of 16:8 fasting and the next day of regular eating patterns? I’m curious if there are any benefits or drawbacks to this alternating approach, or if the benefits mainly come from consistent intermittent fasting?❞
Short and unhelpful answer: no
Longer and hopefully more helpful answer:
As you probably know, usually people going for approaches based on the above terms either
- practise 16:8 fasting (fast for 16 hours each day, eat during an 8-hour window) or
- practise alternate-day fasting (fast for 24 hours, eat whenever for 24 hours, repeat)
…which latter scored the best results in this large meta-analysis of studies:
There is also the (popular) less extreme version of alternate-day fasting, sometimes called “eat stop eat”, which is not a very helpful description because that describes almost any kind of eating/fasting, but it usually refers to “once per week, take a day off from eating”.
You can read more about each of these (and some other variants), here:
Intermittent Fasting: What’s The Truth?
What you are describing (doing 16:8 fasting on alternate days, eating whenever on the other days) is essentially: intermittent fasting, just with one 16-hour fast per 48 hours instead of per the usual 24 hours.
See also: International consensus on fasting terminology ← the section on the terms “STF & PF” covers why this gets nudged back under the regular IF umbrella
Good news: this means there is a lot of literature into the acute (i.e., occurring the same day, not long-term)* benefits of 16:8 IF, and that means that you will be getting those benefits, every second day.
You remember that meta-analysis we posted above? While it isn’t mentioned in the conclusion (which only praised complete alternate-day fasting producing the best outcomes overall), sifting through the results data discovers that time-restricted eating (which is what you are doing, by these classifications) was the only fasting method to significantly reduce fasting blood glucose levels.
(However, no significant differences were observed between any IF form and the reference (continuous energy restriction, CER, i.e. calorie-controlled) diets in fasting insulin and HbA1c levels)
*This is still good news in the long-term though, because getting those benefits every second day is better than getting those benefits on no days, and this will have a long-term impact on your healthy longevity, just like how it is better to exercise every second day than it is to exercise no days, or better to abstain from alcohol every second day than it is to abstain on no days, etc.
In short, by doing IF every second day, you are still giving your organs a break sometimes, and that’s good.
All the same, if it would be convenient and practical for you, we would encourage you to consider either the complete alternate-day fasting (which, according to a lot of data, gives the best results overall),or time-restricted eating (TRE) every day (which, according to a lot of data, gives the best fasting blood sugar levels).
You could also improve the TRE days by shifting to 20:4 (i.e., 20 hours fasting and 4 hours eating), this giving your organs a longer break on those days.
Want to learn more?
For a much more comprehensive discussion of the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches to intermitted fasting, check out:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
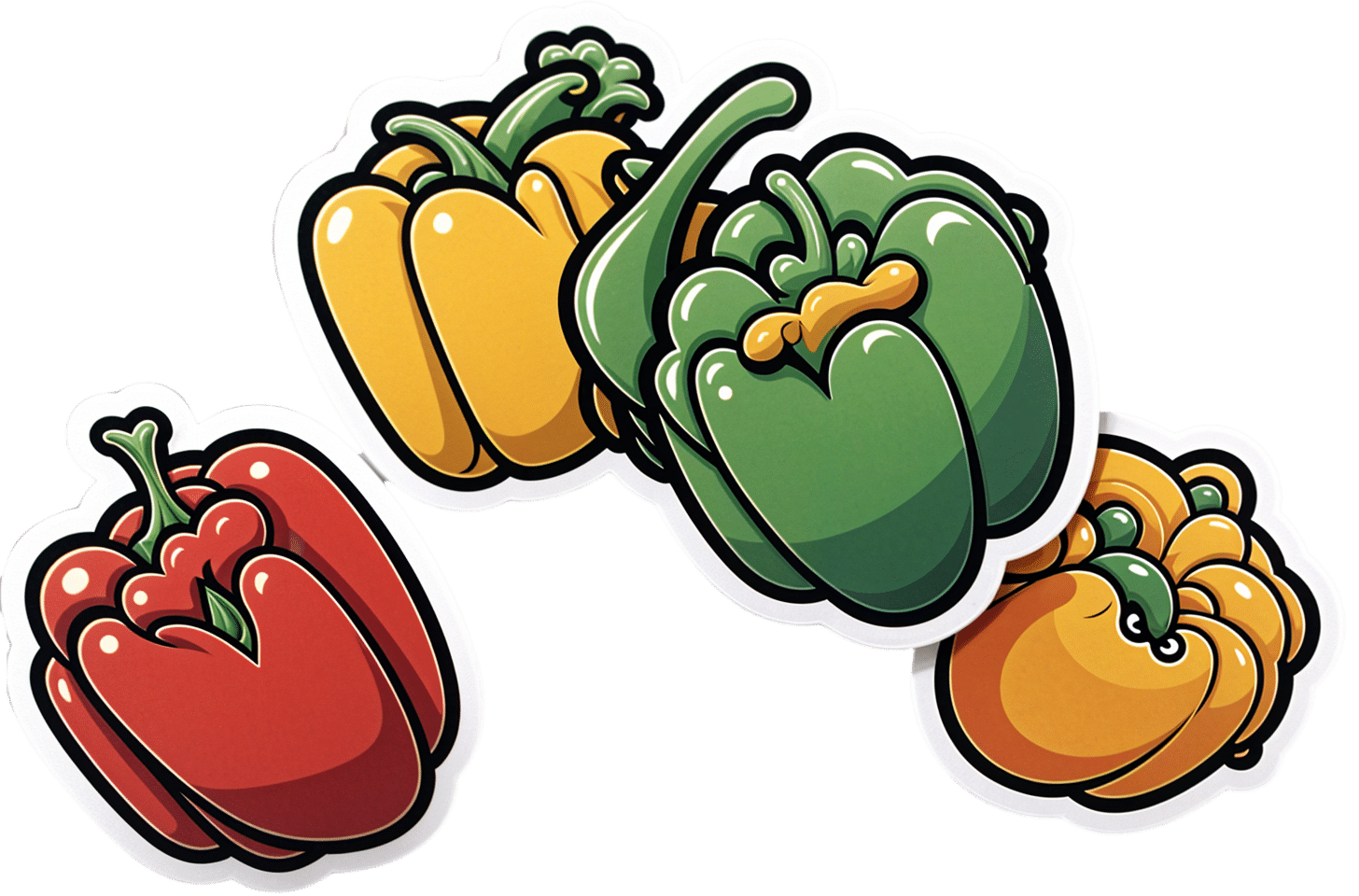
Which Bell Peppers To Pick?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Bell Peppers: A Spectrum Of Specialties
We were going to do this as part of our ongoing “This Or That?” challenge, but as there are four main types all with many different benefits, we thought this bunch of fruits deserved a main feature.
And yes, they’re botanically fruits, even if culinarily used as vegetables—much like tomatoes, famously!
They’re all the same (but also very much not)
A thing to know is that whether bell peppers be green, yellow, orange, or red, they’re all the same plant, Capiscum anuum. All that differs is how early or late they’re harvested.
Notwithstanding the “Capiscum” genus, they don’t contain capsaicin (as is found in hot peppers). Capsaicin’s a wonderful phytochemical:
Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
…but today we’re all about the bell peppers.
So, let’s see how they stack up!
💚 Green for lutein
Lutein is especially important for the eyes and [the rest of the] brain, to the point that there’s now an Alzheimer’s test that measures lutein concentration in the eye:
Green peppers have most of this important carotenoid, though the others all have some too. See also:
💛 Yellow for vitamin C
Yellow peppers are technically highest in vitamin C, but all of them contain far more than the daily dose per fruit already, so if there’s any color of pepper that’s nutritionally the most expendable, it’s yellow, since any other color pepper can take its place.
Watch out, though! Cooking destroys vitamin C, so if you want to get your Cs in, you’re going to want to do it raw.
🧡 Orange for zeaxanthin and cryptoxanthins
Similar in their benefits to lutein, these antioxidant carotenoids are found most generously in orange peppers (20x as much as in yellow, 10x as much as in red, and slightly more than in green).
❤️ Red for vitamins A & B6
Red peppers are richest by far in vitamin A, with one fruit giving the daily dose already. The others have about 10% of that, give or take.
Red peppers also have the most vitamin B6, though the others also have nearly as much.
❤️ Red for lycopene
We must do a main feature for lycopene sometime, as unlike a lot of antioxidant carotenoids, lycopene is found in comparatively very few foods (most famously it’s present in tomatoes).
Red is the only color of pepper to have lycopene.
10almonds tip: to get the most out of your lycopene, cook these ones!
Lycopene becomes 4x more bioavailable when cooked:
Lycopene in tomatoes: chemical and physical properties affected by food processing ← this paper is about tomatoes but lycopene is lycopene and this applies to the lycopene in red peppers, too
And the overall winner is…
You! Because you get to eat all four of them
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Seven Steps to Managing Your Memory – by Dr. Andrew Budson & Dr. Maureen O’Connor
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this is not: a “how to improve your memory” book of the kind marketed to students and/or people who want to do memory-themed party tricks.
What this book actually is: exactly what the title and subtitle claim it to be: seven steps to managing your memory: what’s normal, what’s not, and what to do about it.
Drs. Budson & O’Connor cover:
- which memory errors can (and usually do) happen at any age
- how memory changes with normal aging, and
- what kinds of memory problems are not normal.
One thing that sets this book aside from a lot of its genre is that it also covers which kinds of memory loss are reversible—and, where appropriate, what can be undertaken to effect such a reversal.
The authors talk about what things have (and what things haven’t!) been shown to strengthen memory and reduce cognitive decline, and in the worst case scenario, what medications can help against Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias.
The style is halfway between pop-science and a science textbook. The structure of the book, with its headings, subheadings, bullet points, summaries, etc, helps the reader to process and remember the information.
Bottom line: if you’d like to get on top of managing your memory before you forget, then this book is for you.
Share This Post
-
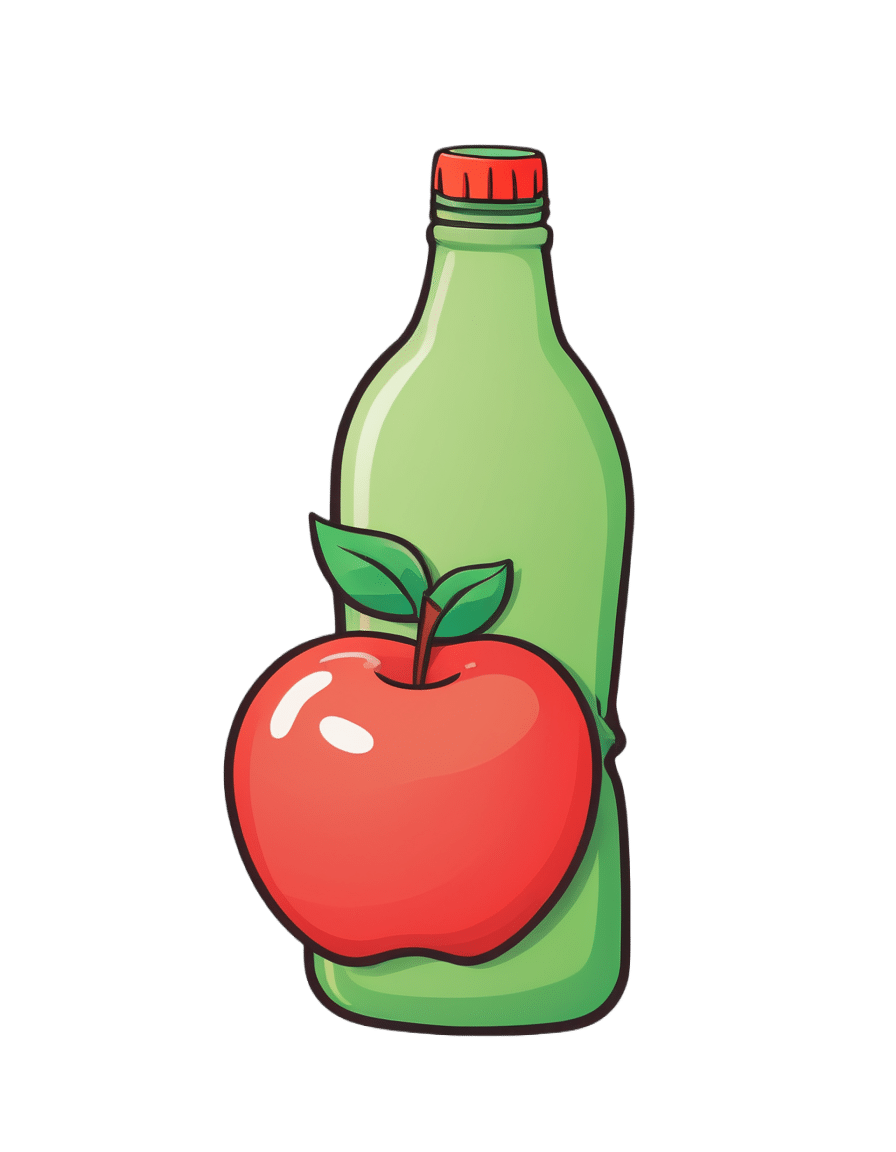
An apple cider vinegar drink a day? New study shows it might help weight loss
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Made from fermented apples and naturally high in acetic acid, apple cider vinegar has been popular in recent years for its purported health benefits – from antibacterial properties to antioxidant effects and potential for helping manage blood sugars.
Its origins as a health tonic stretch much further back. Hippocrates used it to treat wounds, fever and skin sores.
An experimental study, released today, looks into whether apple cider vinegar could be effective for weight loss, reduce blood glucose levels and reduce blood lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides).
The results suggest it could reduce all three – but it might not be as simple as downing an apple cider vinegar drink a day.
What did they do?
A group of scientists in Lebanon did a double-blinded, randomised, clinical trial in a group of overweight and obese young people aged from 12–25 years.
Researchers randomly placed 30 participants in one of four groups. The participants were instructed to consume either 5, 10 or 15ml of apple cider vinegar diluted into 250ml of water each morning before they ate anything for 12 weeks. A control group consumed an inactive drink (a placebo) made (from lactic acid added to water) to look and taste the same.
Typically this sort of study provides high quality evidence as it can show cause and effect – that is the intervention (apple cider vinegar in this case) leads to a certain outcome. The study was also double-blinded, which means neither the participants or the scientists involved with collecting the data knew who was in which group.
So, what did they find?
After a period of three months apple cider vinegar consumption was linked with significant falls in body weight and body mass index (BMI). On average, those who drank apple cider vinegar during that period lost 6–8kg in weight and reduced their BMI by 2.7–3 points, depending on the dose. They also showed significant decreases in the waist and hip circumference.
The authors also report significant decreases in levels of blood glucose, triglycerides, and cholesterol in the apple cider groups. This finding echoes previous studies. The placebo group, who were given water with lactic acid, had much smaller decreases in weight and BMI. There were also no significant decreases in blood glucose and blood lipids.
From animal studies, it is thought the acetic acid in apple cider vinegar may affect the expression of genes involved in burning fats for energy. The new study did not explore whether this mechanism was involved in any weight loss.
Is this good news?
While the study appears promising, there are also reasons for caution.
Firstly, study participants were aged from 12 to 25, so we can’t say whether the results could apply to everyone.
The statistical methods used in the study don’t allow us to confidently say the same amount of weight loss would occur again if the study was done again.
And while the researchers kept records of the participants’ diet and exercise during the study, these were not published in the paper. This makes it difficult to determine if diet or exercise may have had an impact. We don’t know whether participants changed the amount they ate or the types of food they ate, or whether they changed their exercise levels.
The study used a placebo which they tried to make identical in appearance and taste to the active treatment. But people may still be able to determine differences. Researchers may ask participants at the end of a study to guess which group they were in to test the integrity of the placebo. Unfortunately this was not done in this study, so we can’t be certain if the participants knew or not.
Finally, the authors do not report whether anyone dropped out of the study. This could be important and influence results if people who did not lose weight quit due to lack of motivation.
Is that you mother? The enzymes in apple cider vinegar might be health-giving.
ShutterstockAny other concerns?
Apple cider vinegar is acidic and there are concerns it may erode tooth enamel. This can be a problem with any acidic beverages, including fizzy drinks, lemon water and orange juice.
To minimise the risk of acid erosion some dentists recommend the following after drinking acidic drinks:
- rinsing out your mouth with tap water afterwards
- chewing sugar-free gum afterwards to stimulate saliva production
- avoiding brushing your teeth immediately after drinking because it might damage the teeth’s softened top layer
- drink with a straw to minimise contact with the teeth.
Rinsing with water could prevent acid damaging your teeth.
ShutterstockDown the hatch?
This study provides us with some evidence of a link between apple cider vinegar and weight loss. But before health professionals can recommend this as a weight loss strategy we need bigger and better conducted studies across a wider age range.
Such research would need to be done alongside a controlled background diet and exercise across all the participants. This would provide more robust evidence that apple cider vinegar could be a useful aid for weight loss.
Still, if you don’t mind the taste of apple cider vinegar then you could try drinking some for weight loss, alongside a healthy balanced and varied dietary intake. This study does not suggest people can eat whatever they like and drink apple cider vinegar as a way to control weight.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Turns out the viral ‘Sleepy Girl Mocktail’ is backed by science. Should you try it?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many of us wish we could get a better night’s sleep. Wouldn’t it be great if it was as easy as a mocktail before bed?
That’s what the latest viral trend might have us believe. The “Sleepy Girl Mocktail” is a mix of tart cherry juice, powdered magnesium supplement and soda water. TikTok videos featuring the concoction have garnered hundreds of thousands of views. But, what does the science say? Do these ingredients actually help us sleep?
Tart cherry juice
There is research to show including tart cherry juice in your diet improves overall sleep. Clinical trials show tart cherry juice increases sleep quality and quantity, as well as a lessening insomnia symptoms (compared to a placebo). This could be due to the presence of melatonin, a sleep-promoting hormone, in cherries.
Tart cherry varieties such as Jerte Valley or Montmorency have the highest concentration of melatonin (approximately 0.135 micrograms of melatonin per 100g of cherry juice). Over the counter melatonin supplements can range from 0.5 milligram to over 100 milligrams, with research suggesting those beginning to take melatonin start with a dose of 0.5–2 milligrams to see an improvement in sleep.
Melatonin naturally occurs in our bodies. Our body clock promotes the release of melatonin in the evening to help us sleep, specifically in the two hours before our natural bedtime.
If we want to increase our melatonin intake with external sources, such as cherries, then we should be timing our intake with our natural increase in melatonin. Supplementing melatonin too close to bed will mean we may not get the sleep-promoting benefits in time to get off to sleep easily. Taking melatonin too late may even harm our long-term sleep health by sending the message to our body clock to delay the release of melatonin until later in the evening.
Magnesium – but how much?
Magnesium also works to promote melatonin, and magnesium supplements have been shown to improve sleep outcomes.
However, results vary depending on the amount of magnesium people take. And we don’t yet have the answers on the best dose of magnesium for sleep benefits.
We do know magnesium plays a vital role in energy production and bone development, making it an important daily nutrient for our diets. Foods rich in magnesium include wheat cereal or bread, almonds, cashews, pumpkin seeds, spinach, artichokes, green beans, soy milk and dark chocolate.
Bubbly water
Soda water serves as the base of the drink, rather than a pathway to better sleep. And bubbly water may make the mix more palatable. It is important to keep in mind that drinking fluids close to bedtime can be disruptive to our sleep as it might lead to waking during the night to urinate.
Healthy sleep recommendations include avoiding water intake in the two hours before bed. Having carbonated beverages too close to bed can also trigger digestive symptoms such as bloating, gassiness and reflux during the night.
Bottoms up?
Overall, there is evidence to support trying out the Sleepy Girl Mocktail to see if it improves sleep, however there are some key things to remember:
timing: to get the benefits of this drink, avoid having it too close to bed. Aim to have it two hours before your usual bedtime and avoid fluids after this time
consistency: no drink is going to be an immediate cure for poor sleep. However, this recipe could help promote sleep if used strategically (at the right time) and consistently as part of a balanced diet. It may also introduce a calming evening routine that helps your brain relax and signals it’s time for bed
- maximum magnesium: be mindful of the amount of magnesium you are consuming. While there are many health benefits to magnesium, the recommended daily maximum amounts are 420mg for adult males and 320mg for adult females. Exceeding the maximum can lead to low blood pressure, respiratory distress, stomach problems, muscle weakness and mood problems
sugar: in some of the TikTok recipes sugar (as flavoured sodas, syrups or lollies) is added to the drink. While this may help hide the taste of the tart cherry juice, the consumption of sugar too close to bed may make it more difficult to get to sleep. And sugar in the evening raises blood sugar levels at a time when our body is not primed to be processing sugar. Long term, this can increase our risk of diabetes
sleep environment: follow good sleep hygiene practices including keeping a consistent bedtime and wake time, a wind-down routine before bed, avoiding electronic device use like phones or laptops in bed, and avoiding bright light in the evening. Bright light works to suppress our melatonin levels in the evening and make us more alert.
What about other drinks?
Other common evening beverages include herbal tisanes or teas, hot chocolate, or warm milk.
Milk can be especially beneficial for sleep, as it contains the amino acid tryptophan, which can promote melatonin production. Again, it is important to also consider the timing of these drinks and to avoid any caffeine in tea and too much chocolate too close to bedtime, as this can make us more alert rather than sleepy.
Getting enough sleep is crucial to our health and wellbeing. If you have tried multiple strategies to improve your sleep and things are not getting better, it may be time to seek professional advice, such as from a GP.
Charlotte Gupta, Postdoctoral research fellow, CQUniversity Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Green Coffee Bean Extract: Coffee Benefits Without The Coffee?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Coffee is, on balance, very good for the health in moderation. We wrote about it here:
The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
Some quick facts before moving on:
- Coffee is the world’s biggest source of antioxidants
- 65% reduced risk of Alzheimer’s for coffee-drinkers
- 67% reduced risk of type 2 diabetes for coffee-drinkers
- 43% reduced risk of liver cancer for coffee-drinkers
- 53% reduced suicide risk for coffee-drinkers
Those are some compelling statistics!
But what about the caffeine content?
Assuming one doesn’t have a caffeine sensitivity, caffeine is also healthy in moderation—but it is easy to accidentally become dependent on it, so it can be good to take a “tolerance break” once in a while, and then reintroduce it with more modest moderation:
Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
We also, for that matter, have discussed its impact on the gut:
Coffee & Your Gut ← surprise, it’s a positive impact
What if I don’t like coffee?
We suspect that, having seen the title of this article, you know what the answer’s going to be here:
Green coffee bean extract is the extract from green (i.e. unroasted) coffee beans. It has one or two advantages over drinking coffee:
- For those who do not like drinking coffee, this supplement sidesteps that neatly
- Roasting coffee beans destroys a lot (sometimes almost all; it depends on the temperature and duration) of their chlorogenic acid, a highly beneficial polyphenol; using unroasted (i.e. green) coffee beans avoids that
See: Role of roasting conditions in the level of chlorogenic acid content in coffee beans
All about GCE and CGA
That’s “green coffee extract” and “chlorogenic acid”, respectively, bearing in mind that the latter is found generously in the former.
As to what it does:
❝CGA is an important and biologically active dietary polyphenol, playing several important and therapeutic roles such as antioxidant activity, antibacterial, hepatoprotective, cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, neuroprotective, anti-obesity, antiviral, anti-microbial, anti-hypertension, free radicals scavenger and a central nervous system (CNS) stimulator. Furthermore, CGA causes hepatoprotective effects.❞
👆 Those are the things we know for sure that it does. And it may do even more things:
❝In addition, it has been found that CGA could modulate lipid metabolism and glucose in both genetically and healthy metabolic related disorders. It is speculated that CGA can perform crucial roles in lipid and glucose metabolism regulation and thus help to treat many disorders such as hepatic steatosis, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity as well.❞
Read in full: Chlorogenic acid (CGA): A pharmacological review and call for further research
About lipid metabolism…
- Green coffee extract supplementation significantly reduces serum total cholesterol levels.
- Green coffee extract supplementation significantly reduces serum LDL (“bad” cholesterol) levels.
- Increases in HDL (“good” cholesterol) after green coffee bean extract consumption are significant in green coffee bean extract dosages ≥400mg/day.
About blood glucose and insulin…
- Green coffee extract supplementation significantly improved fasting blood sugar levels
- Green coffee extract supplementation at ≥400 mg/day significantly lowered postprandial insulin levels (that’s good)
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
10 Unexpected Benefits Of Slow Jogging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sometimes, less is more:
Slow and steady wins the race?
Here’s the rundown… Slowly:
- You burn more body fat: running at 50-60% of max heart rate primarily burns fat without having the usual compensatory metabolic slump afterwards, unless you go for a very long time.
- You can build more muscle: lower-intensity workouts improve muscle recovery, which is essential too.
- You can reduce muscle soreness: light jogging helps clear lactic acid faster (10almonds note: muscle soreness after exercise isn’t about lactic acid)
- You avoid injuries: less impact on joints reduces injury risk.
- You learn the proper form: running slowly allows better focus on technique.
- You can enjoy it more: slower pace lets you take in surroundings and boosts mood.
- You still improve your cardiorespiratory fitness: strengthens heart and lungs over time.
- You’ll burn more calories than you think: can burn 200–400 calories per 30 minutes.
- You’ll improve your mobility: gentle movement supports joint health and collagen production.
- You can improve your performance: builds endurance and strength for faster running
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: