I’m iron deficient. Which supplements will work best for me and how should I take them?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Iron deficiency is common and can be debilitating. It mainly affects women. One in three premenopausal women are low in iron compared to just 5% of Australian men. Iron deficiency particularly affects teenage girls, women who do a lot of exercise and those who are pregnant.
The body needs iron to make new red blood cells, and to support energy production, the immune system and cognitive function. If you’re low, you may experience a range of symptoms including fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, headache, irregular heartbeat and reduced concentration.
If a blood test shows you’re iron deficient, your doctor may recommend you start taking an oral iron supplement. But should you take a tablet or a liquid? With food or not? And when is the best time of day?
Here are some tips to help you work out how, when and what iron supplement to take.

How do I pick the right iron supplement?
The iron in your body is called “elemental iron”. Choosing the right oral supplement and dose will depend on how much elemental iron it has – your doctor will advise exactly how much you need.
The sweet spot is between 60-120 mg of elemental iron. Any less and the supplement won’t be effective in topping up your iron levels. Any higher and you risk gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhoea, cramping and stomach pain.

In Australia, iron salts are the most common oral supplements because they are cheap, effective and come in different delivery methods (tablets, capsules, liquid formulas). The iron salts you are most likely to find in your local chemist are ferrous sulfate (~20% elemental iron), ferrous gluconate (~12%) and ferrous fumarate (~33%).
These formulations all work similarly, so your choice should come down to dose and cost.
Many multivitamins may look like an iron supplement, but it’s important to note they usually have too little iron – usually less than 20 mg – to correct an iron deficiency.
Should I take tablets or liquid formulas?
Iron contained within a tablet is just as well absorbed as iron found in a liquid supplement. Choosing the right one usually comes down to personal preference.
The main difference is that liquid formulas tend to contain less iron than tablets. That means you might need to take more of the product to get the right dose, so using a liquid supplement could work out to be more expensive in the long term.
What should I eat with my iron supplement?
Research has shown you will absorb more of the iron in your supplement if you take it on an empty stomach. But this can cause more gastrointestinal issues, so might not be practical for everyone.
If you do take your supplement with meals, it’s important to think about what types of food will boost – rather than limit – iron absorption. For example, taking the supplement alongside vitamin C improves your body’s ability to absorb it.
Some supplements already contain vitamin C. Otherwise you could take the supplement along with a glass of orange juice, or other vitamin C-rich foods.

On the other hand, tea, coffee and calcium all decrease the body’s ability to absorb iron. So you should try to limit these close to the time you take your supplement.
Should I take my supplement in the morning or evening?
The best time of day to take your supplement is in the morning. The body can absorb significantly more iron earlier in the day, when concentrations of hepcidin (the main hormone that regulates iron) are at their lowest.
Exercise also affects the hormone that regulates iron. That means taking your iron supplement after exercising can limit your ability to absorb it. Taking your supplement in the hours following exercise will mean significantly poorer absorption, especially if you take it between two and five hours after you stop.
Our research has shown if you exercise every day, the best time to take your supplement is in the morning before training, or immediately after (within 30 minutes).
My supplements are upsetting my stomach. What should I do?
If you experience gastrointestinal side effects such as diarrhoea or cramps when you take iron supplements, you may want to consider taking your supplement every second day, rather than daily.
Taking a supplement every day is still the fastest way to restore your iron levels. But a recent study has shown taking the same total dose can be just as effective when it’s taken on alternate days. For example, taking a supplement every day for three months works as well as every second day for six months. This results in fewer side effects.
Oral iron supplements can be a cheap and easy way to correct an iron deficiency. But ensuring you are taking the right product, under the right conditions, is crucial for their success.
It’s also important to check your iron levels prior to commencing iron supplementation and do so only under medical advice. In large amounts, iron can be toxic, so you don’t want to be consuming additional iron if your body doesn’t need it.
If you think you may be low on iron, talk to your GP to find out your best options.
Alannah McKay, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Sports Nutrition, Australian Catholic University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Bitter Melon vs Winter Melon – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing bitter melon to winter melon, we picked the bitter.
Why?
Did you remember the “bitter is better” dictum that goes for most plant-based foods? It certainly stands in this case!
A note on nomenclature before we begin: these two fruits are also known as the bitter gourd and the wax gourd, respectively (amongst many other names for each), but we went with what seems to be their most common names.
In terms of macros, the bitter melon has more than 13x the protein (and actually adding up to a meaningful amount, at 5.3g/100g), as well as more fiber for the same carbs, making it the better choice all around.
When it comes to vitamins, the bitter melon has a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, B7, B9, and C, while the winter melon boasts only more vitamin B5. As in, the vitamin that’s in all foods (even its scientific name means “from everywhere”) and in which it’s pretty much impossible to be deficient unless literally starving. All in all, an easy and clear win for bitter melon.
In the category of minerals, we see a similar story: the bitter melon has very much more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while the winter melon has a modest double-dose of zinc—hardly comparable to, say, bitter melon having over 100x the potassium content, and indeed, in all minerals except zinc, bitter melon had 4x–100x more. Another clear and overwhelming win for the bitter melon.
Looking up polyphenols, we see that the bitter melon also wins in that regard, shocking nobody, with an impressive polyphenolic profile, especially rich in luteolins and catechins of various kinds.
In short, enjoy either or both, but there’s a clear winner here, and it’s the bitter melon.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Cool As A Cucumber
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cucumber Extract Beats Glucosamine & Chondroitin… At 1/135th Of The Dose?!
Do you take glucosamine & chondroitin supplements for your bone-and-joint health?
Or perhaps, like many, you take them intermittently because they mean taking several large tablets a day. Or maybe you don’t take them at all because they generally contain ingredients derived from shellfish?
Cucumber extract has your back! (and your knees, and your hips, and…)
It’s plant-derived (being from botanical cucumbers, not sea cucumbers, the aquatic animal!) and requires only 1/135th of the dosage to produce twice the benefits!
Distilling the study to its absolute bare bones for your convenience:
- Cucumber extract (10mg) was pitted against glucosamine & chondroitin (1350mg)
- Cucumber extract performed around 50% better than G&C after 30 days
- Cucumber extract performed more than 200% better than G&C after 180 days
In conclusion, this study indicates that, in very lay terms:
Cucumber extract blows glucosamine & chondroitin out of the water as a treatment and preventative for joint pain
Share This Post
-
Marrakesh Sorghum Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As the name suggests, it’s a Maghreb dish today! Using sorghum, a naturally gluten-free whole grain with a stack of vitamins and minerals. This salad also comes with fruit and nuts (apricots and almonds; a heavenly combination for both taste and nutrients) as well as greens, herbs, and spices.
Note: to keep things simple today, we’ve listed ras el-hanout as one ingredient. If you’re unfamiliar, it’s a spice blend; you can probably buy a version locally, but you might as well know how to make it yourself—so here’s our recipe for that!
You will need
- 1½ cups sorghum, soaked overnight in water (if you can’t find it locally, you can order it online (here’s an example product on Amazon), or substitute quinoa) and if you have time, soaked overnight and then kept in a jar with just a little moisture for a few days until they begin to sprout—this will be best of all. But if you don’t have time, don’t worry about it; overnight soaking is sufficient already.
- 1 carrot, grated
- ½ cup chopped parsley
- 1 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- ½ tbsp chopped chives
- 2 tbsp ras el-hanout
- 3 cloves garlic, crushed
- 2 tbsp almond butter
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- 1 tsp white miso paste
- ½ cup sliced almonds
- 4 fresh apricots, pitted and cut into wedges
- 1 cup mint leaves, chopped
- To serve: your choice of salad greens; we suggest chopped romaine lettuce and rocket
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the sorghum, which means boiling it for about 45 minutes, or 30 in a pressure cooker. If unsure, err on the side of cooking longer—even up to an hour will be totally fine. You have a lot of wiggle room, and will soon get used to how long it takes with your device/setup. Drain the cooked sorghum, and set it aside to cool. If you’re entertaining, we recommend doing this part the day before and keeping it in the fridge.
2) When it’s cool, add the carrot, the parsley, the chives, the vinegar, and 1 tbsp of the ras el-hanout. Toss gently but thoroughly to combine.
3) Make the dressing, which means putting ¼ cup water into a blender with the other 1 tbsp of the ras el-hanout, the garlic, the almond butter, the lemon juice, and the miso paste. Blend until smooth.
4) Assemble the salad, which means adding the dressing to sorghum-and-ingredients bowl, along with the almonds, apricots, and mint leaves. Toss gently, but sufficiently that everything is coated.
5) Serve on a bed of salad greens.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet ← including an anti-inflammatory version, which is functionally what we’re doing today. As an aside when people hear “Mediterranean” they often think “Italy and Greece”. Which, sure, but N. Africa (and thus Maghreb cuisine) is also very much Mediterranean, and it shows!
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How does cancer spread to other parts of the body?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
All cancers begin in a single organ or tissue, such as the lungs or skin. When these cancers are confined in their original organ or tissue, they are generally more treatable.
But a cancer that spreads is much more dangerous, as the organs it spreads to may be vital organs. A skin cancer, for example, might spread to the brain.
This new growth makes the cancer much more challenging to treat, as it can be difficult to find all the new tumours. If a cancer can invade different organs or tissues, it can quickly become lethal.
When cancer spreads in this way, it’s called metastasis. Metastasis is responsible for the majority (67%) of cancer deaths.
Cells are supposed to stick to surrounding tissue
Our bodies are made up of trillions of tiny cells. To keep us healthy, our bodies are constantly replacing old or damaged cells.
Each cell has a specific job and a set of instructions (DNA) that tells it what to do. However, sometimes DNA can get damaged.
This damage might change the instructions. A cell might now multiply uncontrollably, or lose a property known as adherence. This refers to how sticky a cell is, and how well it can cling to other surrounding cells and stay where it’s supposed to be.
If a cancer cell loses its adherence, it can break off from the original tumour and travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to almost anywhere. This is how metastasis happens.
Many of these travelling cancer cells will die, but some will settle in a new location and begin to form new cancers.
Some cells settle in a new location.
Scipro/ShutterstockParticular cancers are more likely to metastasise to particular organs that help support their growth. Breast cancers commonly metastasise to the bones, liver, and lungs, while skin cancers like melanomas are more likely to end up in the brain and heart.
Unlike cancers which form in solid organs or tissues, blood cancers like leukaemia already move freely through the bloodstream, but can escape to settle in other organs like the liver or brain.
When do cancers metastasise?
The longer a cancer grows, the more likely it is to metastasise. If not caught early, a patient’s cancer may have metastasised even before it’s initially diagnosed.
Metastasis can also occur after cancer treatment. This happens when cancer cells are dormant during treatment – drugs may not “see” those cells. These invisible cells can remain hidden in the body, only to wake up and begin growing into a new cancer months or even years later.
For patients who already have cancer metastases at diagnosis, identifying the location of the original tumour – called the “primary site” – is important. A cancer that began in the breast but has spread to the liver will probably still behave like a breast cancer, and so will respond best to an anti-breast cancer therapy, and not anti-liver cancer therapy.
As metastases can sometimes grow faster than the original tumour, it’s not always easy to tell which tumour came first. These cancers are called “cancers of unknown primary” and are the 11th most commonly diagnosed cancers in Australia.
One way to improve the treatment of metastatic cancer is to improve our ways of detecting and identifying cancers, to ensure patients receive the most effective drugs for their cancer type.
What increases the chances of metastasis and how can it be prevented?
If left untreated, most cancers will eventually acquire the ability to metastasise.
While there are currently no interventions that specifically prevent metastasis, cancer patients who have their tumours surgically removed may also be given chemotherapy (or other drugs) to try and weed out any hidden cancer cells still floating around.
The best way to prevent metastasis is to diagnose and treat cancers early. Cancer screening initiatives such as Australia’s cervical, bowel, and breast cancer screening programs are excellent ways to detect cancers early and reduce the chances of metastasis.
The best way to prevent cancer spreading is to diagnose and treat them early.
Peakstock/ShutterstockNew screening programs to detect cancers early are being researched for many types of cancer. Some of these are simple: CT scans of the body to look for any potential tumours, such as in England’s new lung cancer screening program.
Using artificial intelligence (AI) to help examine patient scans is also possible, which might identify new patterns that suggest a cancer is present, and improve cancer detection from these programs.
More advanced screening methods are also in development. The United States government’s Cancer Moonshot program is currently funding research into blood tests that could detect many types of cancer at early stages.
One day there might even be a RAT-type test for cancer, like there is for COVID.
Will we be able to prevent metastasis in the future?
Understanding how metastasis occurs allows us to figure out new ways to prevent it. One idea is to target dormant cancer cells and prevent them from waking up.
Directly preventing metastasis with drugs is not yet possible. But there is hope that as research efforts continue to improve cancer therapies, they will also be more effective at treating metastatic cancers.
For now, early detection is the best way to ensure a patient can beat their cancer.
Sarah Diepstraten, Senior Research Officer, Blood Cells and Blood Cancer Division, Walter and Eliza Hall Institute and John (Eddie) La Marca, Senior Resarch Officer, Walter and Eliza Hall Institute
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Strawberries vs Raspberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing strawberries to raspberries, we picked the raspberries.
Why?
They’re both very respectable fruits, of course! But it’s not even close, and there is a clear winner here…
In terms of macros, the biggest difference is that raspberries have moderately more carbs, and more than 3x the fiber. Technically they also have 2x the protein, but that’s a case of “two times almost nothing is still almost nothing”. All in all, and especially for the “more than 3x the fiber” (6.5g/100g to strawberries’ 2g/100g), this one’s an easy win for raspberries.
When it comes to vitamins, strawberries have more vitamin C, while raspberries have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, E, K, and choline. Another clear and easy win for raspberries.
In the category of minerals, guess what, raspberries win this hands-down, too: strawberries are higher in selenium, while raspberries have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc.
Adding up all the individual wins (all for raspberries), it’s not hard to say that raspberries win the day. Still, of course, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
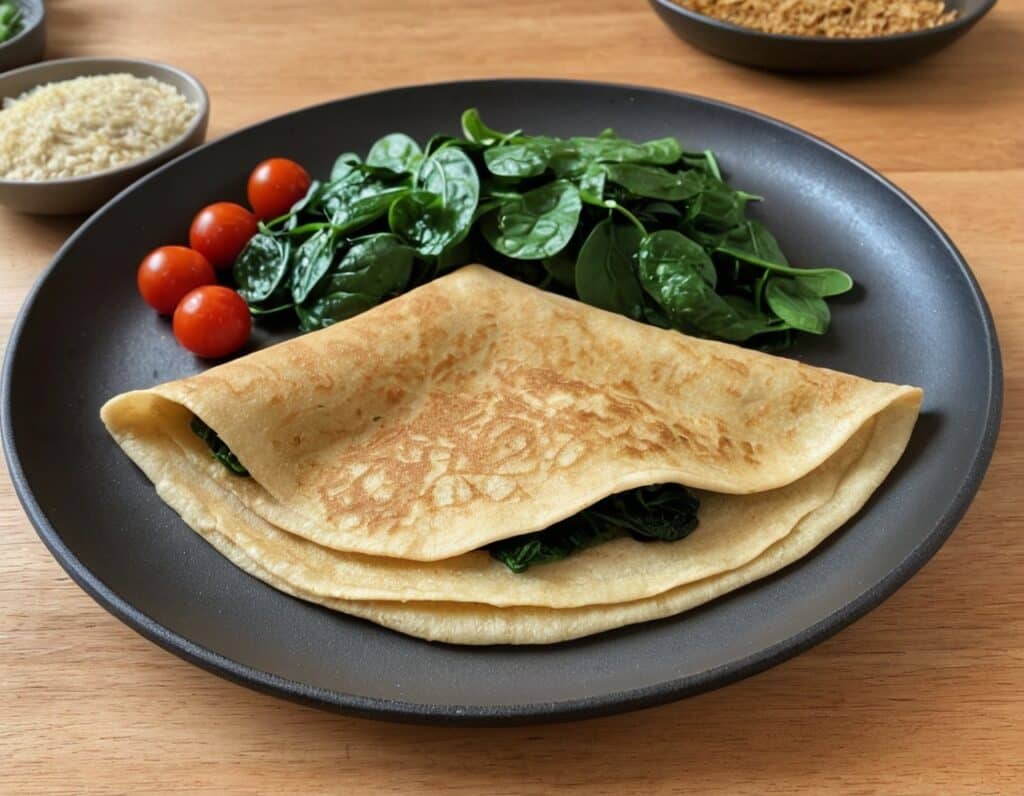
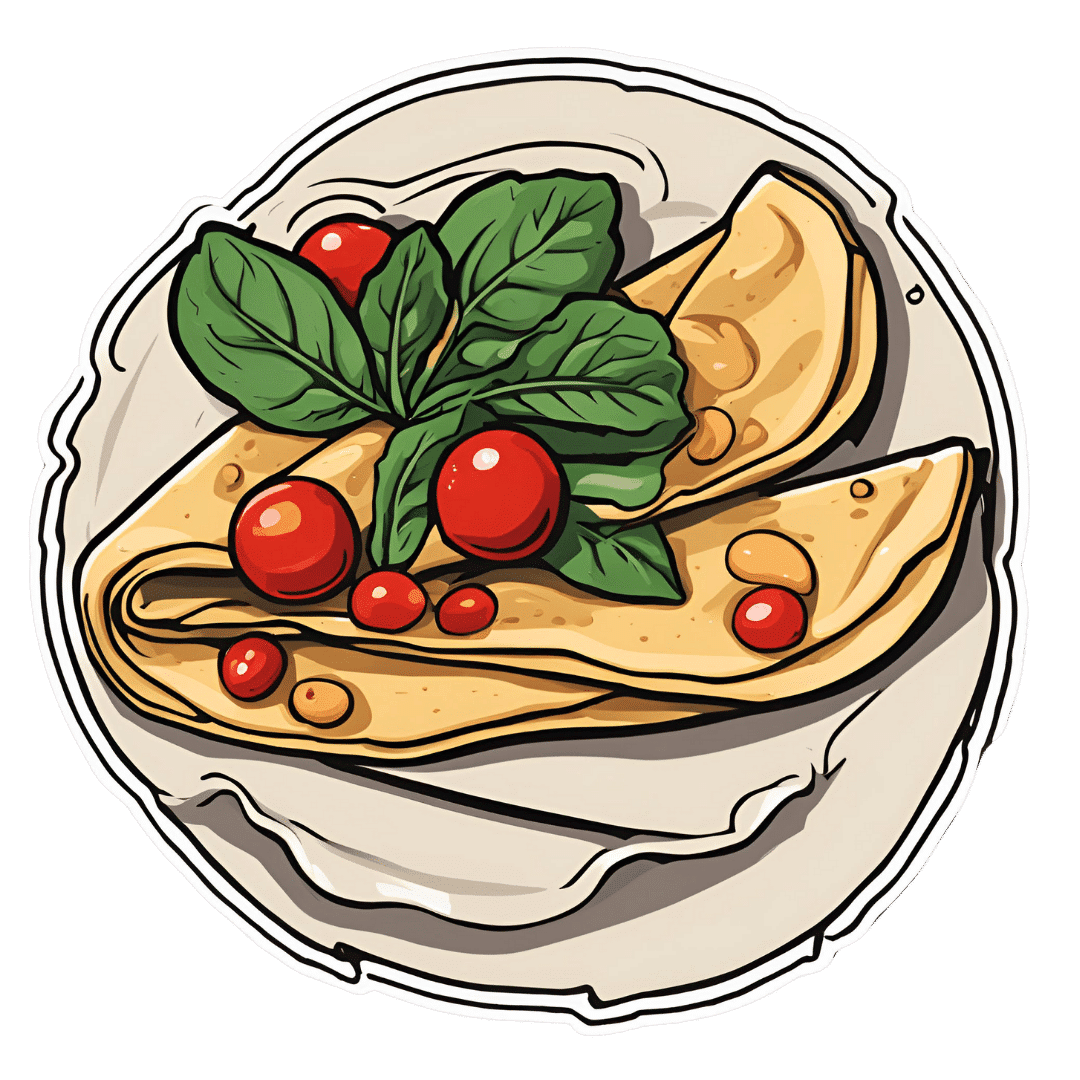
Savory Protein Crêpe
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pancakes have a bad reputation healthwise, but they don’t have to be so. Here’s a very healthy crêpe recipe, with around 20g of protein per serving (which is about how much protein most people’s body’s can use at one sitting) and a healthy dose of fiber too:
You will need
Per crêpe:
- ½ cup milk (your preference what kind; we recommend oat milk for this)
- 2 oz chickpea flour (also called garbanzo bean flour, or gram flour)
- 1 tsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp ras el-hanout (optional but tasty and contains an array of beneficial phytochemicals)
- 1 tsp dried mixed herbs
- ⅛ tsp MSG or ¼ tsp low-sodium salt
For the filling (also per crêpe):
- 6 cherry tomatoes, halved
- Small handful baby spinach
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Mix the dry crêpe ingredients in a bowl, and then stir in the milk, whisking to mix thoroughly. Leave to stand for at least 5 minutes.
2) Meanwhile, heat a little olive oil in a skillet, add the tomatoes and fry for 1 minute, before adding the spinach, stirring, and turning off the heat. As soon as the spinach begins to wilt, set it aside.
3) Heat a little olive oil either in the same skillet (having been carefully wiped clean) or a crêpe pan if you have one, and pour in a little of the batter you made, tipping the pan so that it coats the pan evenly and thinly. Once the top is set, jiggle the pan to see that it’s not stuck, and then flip your crêpe to finish on the other side.
If you’re not confident of your pancake-tossing skills, or your pan isn’t good enough quality to permit this, you can slide it out onto a heatproof chopping board, and use that to carefully turn it back into the pan to finish the other side.
4) Add the filling to one half of the crêpe, and fold it over, pushing down at the edges with a spatula to make a seal, cooking for another 30 seconds or so. Alternatively, you can just serve a stack of crêpes and add the filling at the table, folding or rolling per personal preference:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Three Daily Servings of Beans?
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: