How To Reduce The Harm Of Festive Drinking (Without Abstaining)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Reduce The Harm Of Festive Drinking
Not drinking alcohol is—of course—the best way to avoid the harmful effects of alcohol. However, not everyone wants to abstain, especially at this time of year, so today we’re going to be focusing on harm reduction without abstinence.
If you do want to quit (or even reduce) drinking, you might like our previous article about that:
For everyone else, let’s press on with harm reduction:
Before You Drink
A common (reasonable, but often unhelpful) advice is “set yourself a limit”. The problem with this is that when we’re sober, “I will drink no more than n drinks” is easy. After the first drink, we start to feel differently about it.
So: delay your first drink of the day for as long as possible
That’s it, that’s the tip. The later you start drinking, not only will you likely drink less, but also, your liver will have had longer to finish processing whatever you drank last night, so it’s coming at the new drink(s) fresh.
On that note…
Watch your meds! Often, especially if we are taking medications that also tax our liver (acetaminophen / paracetamol / Tylenol is a fine example of this), we are at risk of having a bit of a build-up, like an office printer that still chewing on the last job while you’re trying to print the next.
Additionally: do indeed eat before you drink.
While You Drink
Do your best to drink slowly. While this can hit the same kind of problem as the “set yourself a limit” idea, in that once you start drinking you forget to drink slowly, it’s something to try for.
If your main reason for drinking is the social aspect, then merely having a drink in your hand is generally sufficient. You don’t need to be keeping pace with anyone.
It is further good to alternate your drinks with water. As in, between each alcoholic drink, have a glass of water. This helps in several ways:
- Hydrates you, which is good for your body’s recovery abilities
- Halves the amount of time you spend drinking
- Makes you less thirsty; it’s easy to think “I’m thirsty” and reach for an alcoholic drink that won’t actually help. So, it may slow down your drinking for that reason, too.
At the dinner table especially, it’s very reasonable to have two glasses, one filled with water. Nobody will be paying attention to which glass you drink from more often.
After You Drink
Even if you are not drunk, assume that you are.
Anything you wouldn’t let a drunk person in your care do, don’t do. Now is not the time to drive, have a shower, or do anything you wouldn’t let a child do in the kitchen.
Hospital Emergency Rooms, every year around this time, get filled up with people who thought they were fine and then had some accident.
The biggest risks from alcohol are:
- Accidents
- Heart attacks
- Things actually popularly associated with alcohol, e.g. alcohol poisoning etc
So, avoiding accidents is as important as, if not more important than, avoiding damage to your liver.
Drink some water, and eat something.
Fruit is great, as it restocks you on vitamins, minerals, and water, while being very easy to digest.
Go to bed.
There is a limit to how much trouble you can get into there. Sleep it off.
In the morning, do not do “hair of the dog”; drinking alcohol will temporarily alleviate a hangover, but only because it kicks your liver back into an earlier stage of processing the alcohol—it just prolongs the inevitable.
Have a good breakfast, instead. Remember, fruit is your friend (as explained above).
Want to know more?
Here’s a great service with a lot of further links to a lot more resources:
With You | How to safely detox from alcohol at home
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Growing Inequality in Life Expectancy Among Americans
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The life expectancy among Native Americans in the western United States has dropped below 64 years, close to life expectancies in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Haiti. For many Asian Americans, it’s around 84 — on par with life expectancies in Japan and Switzerland.
Americans’ health has long been unequal, but a new study shows that the disparity between the life expectancies of different populations has nearly doubled since 2000. “This is like comparing very different countries,” said Tom Bollyky, director of the global health program at the Council on Foreign Relations and an author of the study.
Called “Ten Americas,” the analysis published late last year in The Lancet found that “one’s life expectancy varies dramatically depending on where one lives, the economic conditions in that location, and one’s racial and ethnic identity.” The worsening health of specific populations is a key reason the country’s overall life expectancy — at 75 years for men and 80 for women — is the shortest among wealthy nations.
To deliver on pledges from the new Trump administration to make America healthy again, policymakers will need to fix problems undermining life expectancy across all populations.
“As long as we have these really severe disparities, we’re going to have this very low life expectancy,” said Kathleen Harris, a sociologist at the University of North Carolina. “It should not be that way for a country as rich as the U.S.”
Since 2000, the average life expectancy of many American Indians and Alaska Natives has been steadily shrinking. The same has been true since 2014 for Black people in low-income counties in the southeastern U.S.
“Some groups in the United States are facing a health crisis,” Bollyky said, “and we need to respond to that because it’s worsening.”
Heart disease, car fatalities, diabetes, covid-19, and other common causes of death are directly to blame. But research shows that the conditions of people’s lives, their behaviors, and their environments heavily influence why some populations are at higher risk than others.
Native Americans in the West — defined in the “Ten Americas” study as more than a dozen states excluding California, Washington, and Oregon — were among the poorest in the analysis, living in counties where a person’s annual income averages below about $20,000. Economists have shown that people with low incomes generally live shorter lives.
Studies have also linked the stress of poverty, trauma, and discrimination to detrimental coping behaviors like smoking and substance use disorders. And reservations often lack grocery stores and clean, piped water, which makes it hard to buy and cook healthy food.
About 1 in 5 Native Americans in the Southwest don’t have health insurance, according to a KFF report. Although the Indian Health Service provides coverage, the report says the program is weak due to chronic underfunding. This means people may delay or skip treatments for chronic illnesses. Postponed medical care contributed to the outsize toll of covid among Native Americans: About 1 of every 188 Navajo people died of the disease at the peak of the pandemic.
“The combination of limited access to health care and higher health risks has been devastating,” Bollyky said.
At the other end of the spectrum, the study’s category of Asian Americans maintained the longest life expectancies since 2000. As of 2021, it was 84 years.
Education may partly underlie the reasons certain groups live longer. “People with more education are more likely to seek out and adhere to health advice,” said Ali Mokdad, an epidemiologist at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington, and an author of the paper. Education also offers more opportunities for full-time jobs with health benefits. “Money allows you to take steps to take care of yourself,” Mokdad said.
The group with the highest incomes in most years of the analysis was predominantly composed of white people, followed by the mainly Asian group. The latter, however, maintained the highest rates of college graduation, by far. About half finished college, compared with fewer than a third of other populations.
The study suggests that education partly accounts for differences among white people living in low-income counties, where the individual income averaged less than $32,363. Since 2000, white people in low-income counties in southeastern states — defined as those in Appalachia and the Lower Mississippi Valley — had far lower life expectancies than those in upper midwestern states including Montana, Nebraska, and Iowa. (The authors provide details on how the groups were defined and delineated in their report.)
Opioid use and HIV rates didn’t account for the disparity between these white, low-income groups, Bollyky said. But since 2010, more than 90% of white people in the northern group were high school graduates, compared with around 80% in the southeastern U.S.
The education effect didn’t hold true for Latino groups compared with others. Latinos saw lower rates of high school graduation than white people but lived longer on average. This long-standing trend recently changed among Latinos in the Southwest because of covid. Hispanic or Latino and Black people were nearly twice as likely to die from the disease.
On average, Black people in the U.S. have long experienced worse health than other races and ethnicities in the United States, except for Native Americans. But this analysis reveals a steady improvement in Black people’s life expectancy from 2000 to about 2012. During this period, the gap between Black and white life expectancies shrank.
This is true for all three groups of Black people in the analysis: Those in low-income counties in southeastern states like Mississippi, Louisiana, and Alabama; those in highly segregated and metropolitan counties, such as Queens, New York, and Wayne, Michigan, where many neighborhoods are almost entirely Black or entirely white; and Black people everywhere else.
Better drugs to treat high blood pressure and HIV help account for the improvements for many Americans between 2000 to 2010. And Black people, in particular, saw steep rises in high school graduation and gains in college education in that period.
However, progress stagnated for Black populations by 2016. Disparities in wealth grew. By 2021, Asian and many white Americans had the highest incomes in the study, living in counties with per capita incomes around $50,000. All three groups of Black people in the analysis remained below $30,000.
A wealth gap between Black and white people has historical roots, stretching back to the days of slavery, Jim Crow laws, and policies that prevented Black people from owning property in neighborhoods that are better served by public schools and other services. For Native Americans, a historical wealth gap can be traced to a near annihilation of the population and mass displacement in the 19th and 20th centuries.
Inequality has continued to rise for several reasons, such as a widening pay gap between predominantly white corporate leaders and low-wage workers, who are disproportionately people of color. And reporting from KFF Health News shows that decisions not to expand Medicaid have jeopardized the health of hundreds of thousands of people living in poverty.
Researchers have studied the potential health benefits of reparation payments to address historical injustices that led to racial wealth gaps. One new study estimates that such payments could reduce premature death among Black Americans by 29%.
Less controversial are interventions tailored to communities. Obesity often begins in childhood, for example, so policymakers could invest in after-school programs that give children a place to socialize, be active, and eat healthy food, Harris said. Such programs would need to be free for children whose parents can’t afford them and provide transportation.
But without policy changes that boost low wages, decrease medical costs, put safe housing and strong public education within reach, and ensure access to reproductive health care including abortion, Harris said, the country’s overall life expectancy may grow worse.
“If the federal government is really interested in America’s health,” she said, “they could grade states on their health metrics and give them incentives to improve.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
5 Ways To Beat Cancer (And Other Diseases)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A Systematic Approach To Healthy Eating
This is Dr. William Li. He’s a physician, cancer researcher, and educator. He also founded the Angiogenesis Foundation back in 1994.
We recently reviewed one of his books, “Eat To Beat Disease”.
He has another book that we haven’t reviewed at time of writing, “Eat To Beat Your Diet“, which you might like to check out.
What does he want us to know?
He wants us to know how to eat to beat cancer and other diseases, by means of five specific angles:
Angiogenesis
This is about replacing blood vessels, which of course happens all the time, but it becomes a problem when it is feeding a cancer in the process.
Here, based on Dr. Li’s work, is what can be done about it:
A List of Anti-Angiogenic Foods for a Cancer-Fighting Diet
Regeneration
Generally speaking, we want to replace healthy cells early, because if we wait until they get damaged, then that damage will be copied forwards. As well as intermittent fasting, there are other things we can do to promote this—even, Dr. Li’s research shows, for stem cells:
Doctor’s Tip: Regeneration (stem cells)—one of your body’s five defense systems
Microbiome health
Healthy gut, healthy rest of the body. We’ve written about this before:
Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
DNA protection
DNA gets unravelled and damaged with age, the telomere caps get shorter, and mistakes get copied forward. So there more we can protect our DNA, the longer we can live healthily. There are many ways to do this, but Dr. Li was one of the first to bring to light the DNA-protecting benefits of kiwi fruit:
Immunity
Paradoxically, what’s good for your immune system (making it stronger) also helps to protect against autoimmune diseases (for most people, for the most part).
In short: it’s good to have an immune system that’s powerful not just in its counterattacks, but also in its discerning nature. There are dietary and other lifestyle approaches to both, and they’re mostly the same things:
Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
and thus see also:
Want to know more?
You might enjoy his blog or podcast, and here’s his TED talk:
Want to watch it, but not right now? Bookmark it for later
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
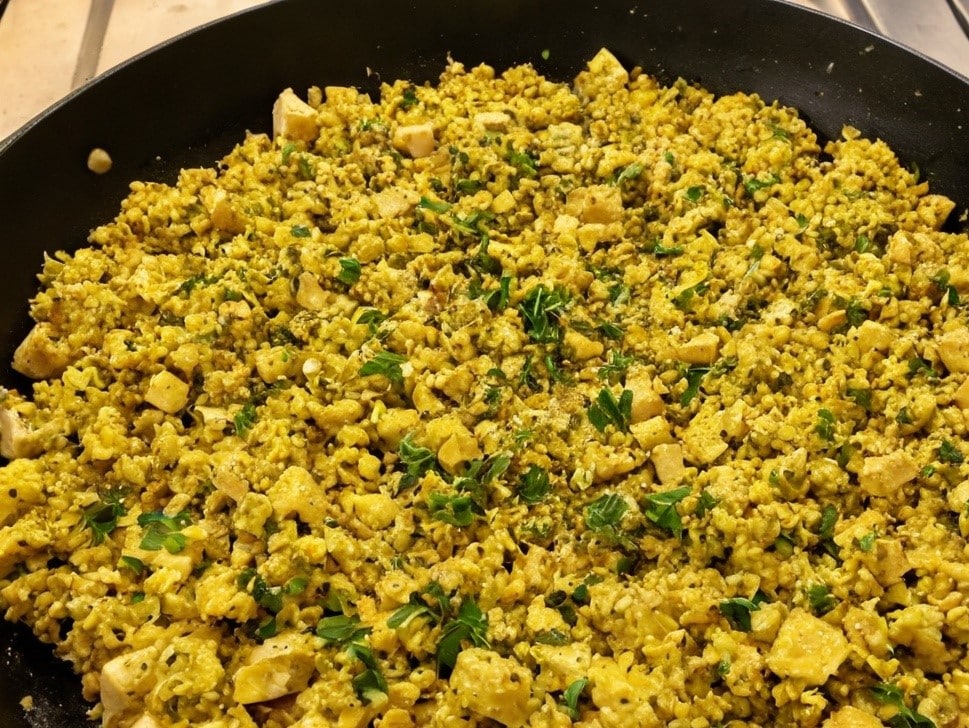
Tasty Tofu Scramble
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’re trying to eat more plant-based, this is a great way to enjoy a culinary experience that hits the same notes as scrambled egg, with many similar nutritional benefits too, and some of its own!
You will need
- 1 cup (10oz) silken tofu
- ¼ bulb garlic, crushed
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp chia seeds
- 2 tsp dried thyme, or 1 tsp fresh thyme, stripped (i.e. pulled off the stalks)
- 2 tsp turmeric
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp red chili flakes
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil, for frying
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat a skillet with olive oil in it; if you want a low-calorie option, you can use quite little oil here; the tofu is a lot more forgiving than egg in this regard and is almost impossible to burn unless you actively try. If you don’t want a low-calorie option, feel free to be generous with the oil if you prefer; it’ll go into the tofu and make it fattier, much like egg.
2) Add the tofu. You can just drop it (carefully) straight in; you don’t need to press it or anything.
3) Scramble it with a spatula, just the same as you would if it were egg.
4) Add the rest of the ingredients, mixing them in as you continue to scramble it, until it reaches the desired consistency.
5) Serve! Serving it on wholegrain toast is a great option—but this dish can also be enjoyed any other way you might use scrambled eggs (including for making
egg-friedtofu-fried rice; just stir it into our Tasty Versatile Rice recipe!)Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
It’s Not You, It’s Your Hormones – by Nicki Williams, DipION, mBANT, CNHC
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So, first a quick note: this book is very similar to the popular bestseller “The Galveston Diet”, not just in content, but all the way down to its formatting. Some Amazon reviewers have even gone so far as to suggest that “It’s Not You, It’s Your Hormones” (2017) brazenly plagiarized “The Galveston Diet” (2023). However, after carefully examining the publication dates, we feel quite confident that this book is not a copy of the one that came out six years after it. As such, we’ve opted for reviewing the original book.
Nicki Williams’ basic principle is that we can manage our hormonal fluctuations, by managing our diet. Specifically, in three main ways:
- Intermittent fasting
- Anti-inflammatory diet
- Eating more protein and healthy fats
Why should these things matter to our hormones? The answer is to remember that our hormones aren’t just the sex hormones. We have hormones for hunger and satedness, hormones for stress and relaxation, hormones for blood sugar regulation, hormones for sleep and wakefulness, and more. These many hormones make up our endocrine system, and affecting one part of it will affect the others.
Will these things magically undo the effects of the menopause? Well, some things yes, other things no. No diet can do the job of HRT. But by tweaking endocrine system inputs, we can tweak endocrine system outputs, and that’s what this book is for.
The style is very accessible and clear, and Williams walks us through the changes we may want to make, to avoid the changes we don’t want.
In the category of criticism, there is some extra support that’s paywalled, in the sense that she wants the reader to buy her personally-branded online plan, and it can feel a bit like she’s holding back in order to upsell to that.
Bottom line: this book is aimed at peri-menopausal and post-menopausal women. It could also definitely help a lot of people with PCOS too, and, when it comes down to it, pretty much anyone with an endocrine system. It’s a well-evidenced, well-established, healthy way of eating regardless of age, sex, or (most) physical conditions.
Click here to check out It’s Not You, It’s Your Hormones, and take control of yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Weight Vests Against Osteoporosis: Do They Really Build Bone?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Doug Lucas is a dual board-certified physician specializing in optimizing healthspan and bone health for women experiencing osteoporosis, perimenopause, and menopause. Here, he talks weight vests:
Worth the weight?
Dr. Lucas cites “Wolf’s Law”—bones respond to stress. A weighted vest adds stress, to help build bone density. That said, they may not be suitable for everyone (for example, in cases of severe osteoporosis or a recent vertebral fracture).
He also cites some studies:
- Erlanger Fitness Study (2004): participants with a weighted vest maintained or improved bone density compared to a control group, but there was no group with exercise alone, making it unclear if the vest itself had the biggest impact.
- Newer studies (2016, 2017): showed improved outcomes for groups wearing a weighted vest, but again lacked an exercise-only group for comparison.
- 2012 study: included three groups (control, weighted vest, exercise only). Results showed no significant bone density difference between vest and exercise-only groups, though the vest group showed better balance and motor control.
Dr. Lucas concludes that weighted vests are a useful tool while nevertheless not being a magic bullet for bone health. In other words, they can complement exercise but you will also be fine without. If you do choose to level-up your exercise by using a weight vest, then starting with 5–10% of body weight in a vest is often recommended, but it depends on individual circumstances. If in doubt, start low and build up. Wearing the vest for daily activities can be effective, but improper use (awkward positions or improper impact training) can increase injury risk, so do be careful with that.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Osteoporosis & Exercises: Which To Do (And Which To Avoid)
- One More Resource Against Osteoporosis!
- The Osteoporosis Breakthrough – by Dr. Doug Lucas ← we reviewed his book a while back!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Saturated Fat: What’s The Truth?
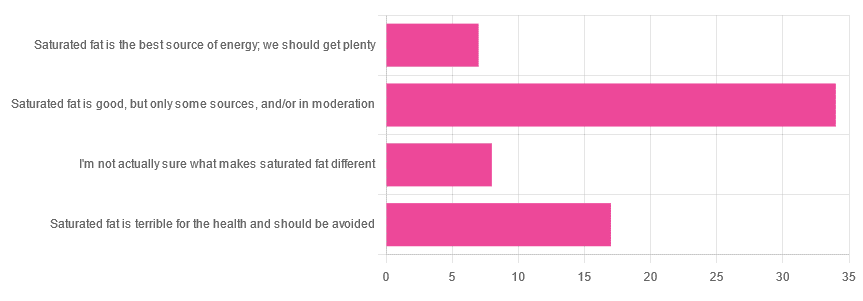
We asked you for your health-related opinion of saturated fat, and got the above-pictured, below-described, set of results.
- Most recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation”
- This is an easy one to vote for, because of the “and/or in moderation” part, which tends to be a “safe bet” for most things.
- Next most popular was “Saturated fat is terrible for the health and should be avoided”
- About half as many recorded votes were for “I’m not actually sure what makes saturated fat different”, which is a very laudable option to click. Admitting when we don’t know things (and none of us know everything) is a very good first step to learning about them!
- Fewest recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is the best source of energy; we should get plenty”.
So, what does the science say?
First, a bit of physics, chemistry, and biology
You may be wondering what, exactly, saturated fats are “saturated” with. That’s a fair question, so…
All fats have a molecular structure made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Saturated fats are saturated with hydrogen, and thus have only single bonds between carbon atoms (unsaturated fats have at least one double-bond between carbon atoms).
The observable effect this has on them, is that fats that are saturated with hydrogen are solid at room temperature, whereas unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature. Their different properties also make for different interactions inside the human body, including how likely or not they are to (for example) clog arteries.
See also: Could fat in your bloodstream cause blood clots?
Saturated fat is the best source of energy; we should get plenty: True or False?
False, in any reasonable interpretation, anyway. That is to say, if your idea of “plenty” is under 13g (e.g: two tablespoons of butter, and no saturated fat from other sources, e.g. meat) per day, then yes, by all means feel free to eat plenty. More than that, though, and you might want to consider trimming it down a bit.
The American Heart Association has this to say:
❝When you hear about the latest “diet of the day” or a new or odd-sounding theory about food, consider the source.
The American Heart Association recommends limiting saturated fats, which are found in butter, cheese, red meat and other animal-based foods, and tropical oils.
Decades of sound science has proven it can raise your “bad” cholesterol and put you at higher risk for heart disease.❞
Source: The American Heart Association Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations on Saturated Fat
The British Heart Foundation has a similar statement:
❝Despite what you read in the media, our advice is clear: replace saturated fats with unsaturated fats and avoid trans fats. Saturated fat is the kind of fat found in butter, lard, ghee, fatty meats and cheese. This is linked to an increased risk of heart and circulatory disease❞
Source: British Heart Foundation: What does fat do and what is saturated fat?
As for the World Health Organization:
❝1. WHO strongly recommends that adults and children reduce saturated fatty acid intake to 10% of total energy intake
2. WHO suggests further reducing saturated fatty acid intake to less than 10% of total energy intake
3. WHO strongly recommends replacing saturated fatty acids in the diet with polyunsaturated fatty acids; monounsaturated fatty acids from plant sources; or carbohydrates from foods containing naturally occurring dietary fibre, such as whole grains, vegetables, fruits and pulses.❞
Source: Saturated fatty acid and trans-fatty acid intake for adults and children: WHO guideline
Please note, organizations such as the AHA, the BHF, and the WHO are not trying to sell us anything, and just would like us to not die of heart disease, the world’s #1 killer.
As for “the best source of energy”…
We evolved to eat (much like our nearest primate cousins) a diet consisting mostly of fruits and other edible plants, with a small supplementary amount of animal-source protein and fats.
That’s not to say that because we evolved that way we have to eat that way—we are versatile omnivores. But for example, we are certainly not complete carnivores, and would quickly sicken and die if we tried to live on only meat and animal fat (we need more fiber, more carbohydrates, and many micronutrients that we usually get from plants)
The closest that humans tend to come to doing such is the ketogenic diet, which focuses on a high fat, low carbohydrate imbalance, to promote ketosis, in which the body burns fat for energy.
The ketogenic diet does work, and/but can cause a lot of health problems if a lot of care is not taken to avoid them.
See for example: 7 Keto Risks To Keep In Mind
Saturated fat is terrible for the health and should be avoided: True or False?
False, if we are talking about “completely”.
Firstly, it’s practically impossible to cut out all saturated fats, given that most dietary sources of fat are a mix of saturated, unsaturated (mono- and poly-), and trans fats (which are by far the worst, but beyond the scope of today’s main feature).
Secondly, a lot of research has been conducted and found insignificant or inconclusive results, in cases where saturated fat intake was already within acceptable levels (per the recommendations we mentioned earlier), and then cut down further.
Rather than fill up the newsletter with individual studies of this kind here’s a high-quality research review, looking at 19 meta-analyses, each of those meta-analyses having looked at many studies:
Dietary saturated fat and heart disease: a narrative review
Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation: True or False?
True! The moderation part is easy to guess, so let’s take a look at the “but only some sources”.
We were not able to find any convincing science to argue for health-based reasons to favor plant- or animal-sourced saturated fat. However…
Not all saturated fats are created equal (there are many kinds), and also many of the foods containing them have additional nutrients, or harmful compounds, that make a big difference to overall health, when compared gram-for-gram in terms of containing the same amount of saturated fat.
For example:
- Palm oil’s saturated fat contains a disproportionate amount of palmitic acid, which raises LDL (“bad” cholesterol) without affecting HDL (“good” cholesterol), thus having an overall heart-harmful effect.
- Most animal fats contain a disproportionate amount of stearic acid, which has statistically insignificant effects on LDL and HDL levels, and thus is broadly considered “heart neutral” (in moderation!)
- Coconut oil’s saturated fat contains a disproportionate amount of lauric acid, which raises total cholesterol, but mostly HDL without affecting LDL, thus having an overall heart-beneficial effect (in moderation!)
Do you know what’s in the food you eat?
Test your knowledge with the BHF’s saturated fat quiz!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Most recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation”