Homeopathy: Evidence So Tiny That It’s Not there?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Homeopathy: Evidence So Tiny That It’s Not There?
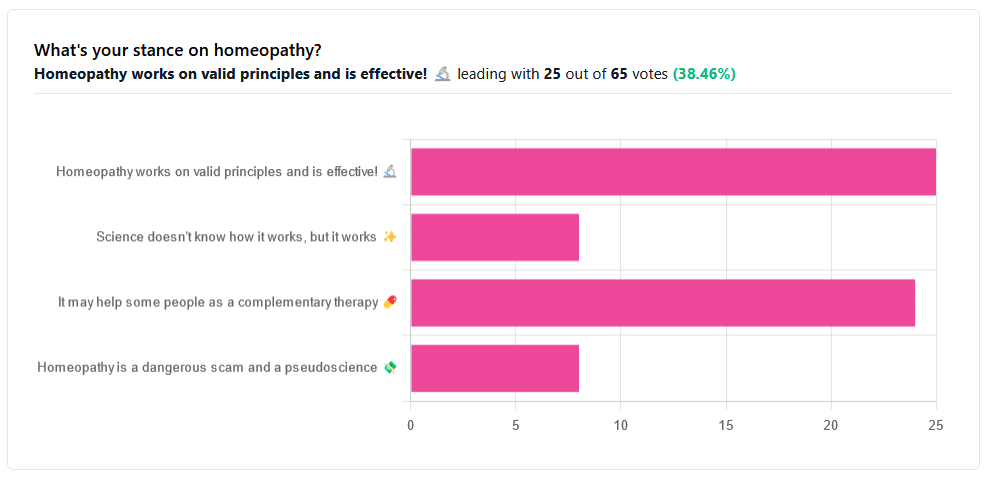
Yesterday, we asked you your opinions on homeopathy. The sample size of responses was a little lower than we usually get, but of those who did reply, there was a clear trend:
- A lot of enthusiasm for “Homeopathy works on valid principles and is effective”
- Near equal support for “It may help some people as a complementary therapy”
- Very few people voted for “Science doesn’t know how it works, but it works”; this is probably because people who considered voting for this, voted for the more flexible “It may help some people as a complementary therapy” instead.
- Very few people considered it a dangerous scam and a pseudoscience.
So, what does the science say?
Well, let us start our investigation by checking out the position of the UK’s National Health Service, an organization with a strong focus on providing the least expensive treatments that are effective.
Since homeopathy is very inexpensive to arrange, they will surely want to put it atop their list of treatments, right?
❝Homeopathy is a “treatment” based on the use of highly diluted substances, which practitioners claim can cause the body to heal itself.
There’s been extensive investigation of the effectiveness of homeopathy. There’s no good-quality evidence that homeopathy is effective as a treatment for any health condition.❞
The NHS actually has a lot more to say about that, and you can read their full statement here.
But that’s just one institution. Here’s what Australia’s National Health and Medical Research Council had to say:
❝There was no reliable evidence from research in humans that homeopathy was effective for treating the range of health conditions considered: no good-quality, well-designed studies with enough participants for a meaningful result reported either that homeopathy caused greater health improvements than placebo, or caused health improvements equal to those of another treatment❞
You can read their full statement here.
The American FDA, meanwhile, have a stronger statement:
❝Homeopathic drug products are made from a wide range of substances, including ingredients derived from plants, healthy or diseased animal or human sources, minerals and chemicals, including known poisons. These products have the potential to cause significant and even permanent harm if they are poorly manufactured, since that could lead to contaminated products or products that have potentially toxic ingredients at higher levels than are labeled and/or safe, or if they are marketed as substitute treatments for serious or life-threatening diseases and conditions, or to vulnerable populations.❞
You can read their full statement here.
Homeopathy is a dangerous scam and a pseudoscience: True or False?
False and True, respectively, mostly.
That may be a confusing answer, so let’s elaborate:
- Is it dangerous? Mostly not; it’s mostly just water. However, two possibilities for harm exist:
- Careless preparation could result in a harmful ingredient still being present in the water—and because of the “like cures like” principle, many of the ingredients used in homeopathy are harmful, ranging from heavy metals to plant-based neurotoxins. However, the process of “ultra-dilution” usually removes these so thoroughly that they are absent or otherwise scientifically undetectable.
- Placebo treatment has its place, but could result in “real” treatment going undelivered. This can cause harm if the “real” treatment was critically needed, especially if it was needed on a short timescale.
- Is it a scam? Probably mostly not; to be a scam requires malintent. Most practitioners probably believe in what they are practising.
- Is it a pseudoscience? With the exception that placebo effect has been highly studied and is a very valid complementary therapy… Yes, aside from that it is a pseudoscience. There is no scientific evidence to support homeopathy’s “like cures like” principle, and there is no scientific evidence to support homeopathy’s “water memory” idea. On the contrary, they go against the commonly understood physics of our world.
It may help some people as a complementary therapy: True or False?
True! Not only is placebo effect very well-studied, but best of all, it can still work as a placebo even if you know that you’re taking a placebo… Provided you also believe that!
Science doesn’t know how it works, but it works: True or False?
False, simply. At best, it performs as a placebo.
Placebo is most effective when it’s a remedy against subjective symptoms, like pain.
However, psychosomatic effect (the effect that our brain has on the rest of our body, to which it is very well-connected) can mean that placebo can also help against objective symptoms, like inflammation.
After all, our body, directed primarily by the brain, can “decide” what immunological defenses to deploy or hold back, for example. This is why placebo can help with conditions as diverse as arthritis (an inflammatory condition) or diabetes (an autoimmune condition, and/or a metabolic condition, depending on type).
Here’s how homeopathy measures up, for those conditions:
(the short answer is “no better than placebo”)
Homeopathy works on valid principles and is effective: True or False?
False, except insofar as placebo is a valid principle and can be effective.
The stated principles of homeopathy—”like cures like” and “water memory”—have no scientific basis.
We’d love to show the science for this, but we cannot prove a negative.
However, the ideas were conceived in 1796, and are tantamount to alchemy. A good scientific attitude means being open-minded to new ideas and testing them. In homeopathy’s case, this has been done, extensively, and more than 200 years of testing later, homeopathy has consistently performed equal to placebo.
In summary…
- If you’re enjoying homeopathic treatment and that’s working for you, great, keep at it.
- If you’re open-minded to enjoying a placebo treatment that may benefit you, be careful, but don’t let us stop you.
- If your condition is serious, please do not delay seeking evidence-based medical treatment.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
100 No-Equipment Workouts – by Neila Rey
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For those of us who for whatever reason prefer to exercise at home rather than at the gym, we must make do with what exercise equipment we can reasonably install in our homes. This book deals with that from the ground upwards—literally!
If you have a few square meters of floorspace (and a ceiling that’s not too low, for exercises that involve any kind of jumping), then all 100 of these zero-equipment exercises are at-home options.
As to what kinds of exercises they are, they each marked as being one or both of “cardio” and “strength”.
They’re also marked as being of “difficulty level” 1, 2, or 3, so that someone who hasn’t exercised in a while (or hasn’t exercised like this at all), can know where best to start, and how best to progress.
The exercises come with clear explanations in the text, and clear line-drawing illustrations of how to do each exercise. Really, they could not be clearer; this is top quality pragmatism, and reads like a military manual.
Bottom line: whatever your strength and fitness goals, this book can see you well on your way to them (if not outright get you there already in many cases). It’s also an excellent “all-rounder” for full-body workouts.
Share This Post
-
What’s Missing from Medicine – by Dr. Saray Stancic
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Another from the ranks of “doctors who got a serious illness and it completely changed how they view the treatment of serious illness”, Dr. Stancic was diagnosed with multiple sclerosis, and wasn’t impressed with the treatments presented.
Taking an evidence-based lifestyle medicine approach, she was able to not only manage her illness sufficiently to resume her normal activities, but even when so far as to run a marathon, and today boasts a symptom-free, active life.
The subtitular six lifestyle changes are not too shocking, and include a plants-centric diet, good exercise, good sleep, stress management, avoidance of substance abuses, and a fostering of social connections, but the value here is in what she has to say about each, especially the ones that aren’t so self-explanatory and/or can even cause harm if done incorrectly (such as exercise, for example).
The style is on the academic end of pop-science, of the kind that has frequent data tables, lots of statistics, and an extensive bibliography, but is still very readable.
Bottom line: if you are faced with a chronic disease, or even just an increased risk of some chronic disease, or simply like to not take chances, then this is a high-value book for you.
Click here to check out What’s Missing From Medicine, and enjoy chronic good health!
Share This Post
-
Is Sugar The New Smoking?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Could you do a this or that of which. Is worse, smoking cigarettes or having a sweet tooth? Also, perhaps have us evaluate one part of newsletter at a time, rather than overall. I especially appreciate your book reviews and often find them through my library system.❞
We’re glad you enjoy the book reviews! We certainly enjoy reading many books to write about them for you.
As for the idea having readers evaluate one part of the newsletter at a time, rather than overall, there is a technical limitation that embedded polls are very large, data-wise, so if we were to do a poll for each section, the email would then get clipped by gmail and other email providers. However, you are always more than welcome to do as you’ve done, and include comments about what section(s) you took the most value from.
Now, onto your main question/request: as it doesn’t quite fit the usual format for our This vs That section, we’ve opted to do it as a main feature here 🙂
So, let’s get into it…
Not a zero-sum game
First, let’s be clear that for most people there is no pressing reason that this should be an either/or decision. There is nothing inherent to quitting either one that makes the other loom larger.
However, that said, if you’re (speaking generally here, and not making any presumptions about the asker) currently smoking regularly and partaking of a lot of added sugar, then you may be wondering which you should prioritize quitting first—as it is indeed generally recommended to only try to quit one thing at a time.
Indeed, we wrote previously, as a guideline for “what to do in one what order”:
Not sure where to start? We suggest this order of priorities, unless you have a major health condition that makes something else a higher priority:
- If you smoke, stop
- If you drink, reduce, or ideally stop
- Improve your diet
About that diet…
Worry less about what to exclude, and instead focus on adding more variety of fruit/veg.
See also: Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
That said, if you’re looking for things to cut, sugar is a top candidate (and red meat is in clear second place albeit some way below)
That’s truncated from a larger list, but those were the top items.
You can read the rest in full, here: The Best Few Interventions For The Best Health: These Top 5 Things Make The Biggest Difference
The flipside of this “you can quit both” reality is that the inverse is also true: much like how having one disease makes it more likely we will get another, unhealthy habits tend to come in clusters too, as each will weaken our resolve with regard to the others. Thus, there is a sort of “comorbidity of habits” that occurs.
The good news is: the same can be said for healthy habits, so they (just like unhealthy habits) can support each other, stack, and compound. This means that while it may seem harder to quit two bad habits than one, in actual fact, the more bad habits you quit, the more it’ll become easy to quit the others. And similarly, the more good habits you adopt, the more it’ll become easy to adopt others.
See also: How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
So, let’s keep that in mind, while we then look at the cases against smoking, and sugar:
The case against smoking
This is perhaps one of the easiest cases to make in the entirety of the health science world, and the only difficult part is knowing where to start, when there’s so much.
The World Health Organization leads with these key facts, on its tobacco fact sheet:
- Tobacco kills up to half of its users who don’t quit.
- Tobacco kills more than 8 million people each year, including an estimated 1.3 million non-smokers who are exposed to second-hand smoke.
- Around 80% of the world’s 1.3 billion tobacco users live in low- and middle-income countries.
- In 2020, 22.3% of the world’s population used tobacco: 36.7% of men and 7.8% of women.
- To address the tobacco epidemic, WHO Member States adopted the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) in 2003. Currently 182 countries are Parties to this treaty.
- The WHO MPOWER measures are in line with the WHO FCTC and have been shown to save lives and reduce costs from averted healthcare expenditure.
Source: World Health Organization | Tobacco
Now, some of those are just interesting sociological considerations (well, they are of practical use to the WHO whose job it is to offer global health policy guidelines, but for us at 10almonds, with the more modest goal of helping individual people lead their best healthy lives, there’s not so much that we can do with the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control, for example), but for the individual smoker, the first two are really very serious, so let’s take a closer look:
❝Tobacco kills up to half of its users who don’t quit.❞
A bold claim, backed up by at least three very large, very compelling studies:
- Mortality in relation to smoking: 50 years’ observations on male British doctors
- Tobacco smoking and all-cause mortality in a large Australian cohort study: findings from a mature epidemic with current low smoking prevalence
- Global burden of disease due to smokeless tobacco consumption in adults: an updated analysis of data from 127 countries
❝Tobacco kills more than 8 million people each year, including an estimated 1.3 million non-smokers who are exposed to second-hand smoke.❞
The WHO’s cited source for this was gatekept in a way we couldn’t access (and so probably most of our readers can’t either), but take a look at what the CDC has to say for the US alone (bearing in mind the US’s population of a little over 300,000,000, which is just 3.75% of the global population of a little over 8,000,000,000):
❝smoking causes more than 480,000 deaths [in the US] annually, with an estimated 41,000 deaths from secondhand smoke exposure, and it can reduce a person’s life expectancy by 10 years. Quitting smoking before the age of 40 reduces the risk of dying from smoking-related disease by about 90%❞
If we now remember that third bullet point, that said “Around 80% of the world’s 1.3 billion tobacco users live in low- and middle-income countries.”, then we can imagine the numbers are worse for many other countries, including large-population countries that have a lower median income than the US, such as India and Brazil.
Source for the CDC comment: Tobacco-Related Mortality
See also: AAMC | Smoking is still the leading cause of preventable death in the U.S.
We only have so much room here, but if that’s not enough…
More than 100 reasons to quit tobacco
The case against sugar
We reviewed an interesting book about this:
The Case Against Sugar – by Gary Taubes
But suffice it to say, added sugar is a big health problem; not in the same league as tobacco, but it’s big, because of how it messes with our metabolism (and when our metabolism goes wrong, everything else goes wrong):
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
The epidemiology of sugar consumption and related mortality is harder to give clear stats about than smoking, because there’s not a clear yes/no indicator, and cause and effect are harder to establish when the waters are so muddied by other factors. But for comparison, we’ll note that compared to the 480,000 deaths caused by tobacco in the US annually, the total death to diabetes (which is not necessarily “caused by sugar consumption”, but there’s at least an obvious link when it comes to type 2 diabetes and refined carbohydrates) was 101,209 deaths due to diabetes in 2022:
National Center for Health Statistics | Diabetes
Now, superficially, that looks like “ok, so smoking is just under 5x more deadly”, but it’s important to remember that almost everyone eats added sugar, whereas a minority of people smoke, and those are mortality per total US population figures, not mortality per user of the substance in question. So in fact, smoking is, proportionally to how many people smoke, many times more deadly than diabetes, which currently ranks 8th in the “top causes of death” list.
Note: we recognize that you did say “having a sweet tooth” rather than “consuming added sugar”, but it’s worth noting that artificial sweeteners are not a get-out-of-illness-free card either:
Let’s get back to sugar though, as while it’s a very different beast than tobacco, it is arguably addictive also, by multiple mechanisms of addiction:
The Not-So-Sweet Science Of Sugar Addiction
That said, those mechanisms of addiction are not necessarily as strong as some others, so in the category of what’s easy or hard to quit, this is on the easier end of things—not that that means it’s easy, just, quitting many drugs is harder. In any case, it can be done:
When It’s More Than “Just” Cravings: Beat Food Addictions!
In summary
Neither are good for the health, but tobacco is orders of magnitude worse, and should be the priority to quit, unless your doctor(s) tell you otherwise because of your personal situation, and even then, try to get multiple opinions to be sure.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The 4 Bad Habits That Cause The Most Falls While Walking
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The risk of falling becomes greater (both in probability and in severity of consequences) as we get older. But, many people who do fall do so for the same reasons, some of which are avoidable. Dr. Doug Weiss has advice based on extensive second-hand experience:
Best foot forward!
If any of these prompt a “surely nobody does that” response, then, good for you to not have that habit, but Dr. Weiss has seen many patients who thusly erred. And if any of these do describe how you walk, then well, you’re not alone—time to fix it, though!
- Walking with Stiff Legs: walking with a hyperextended (straight) knee instead of a slight bend (5-15°) makes it harder to adjust balance, increasing the risk of falls. This can also put extra pressure on the joints, potentially leading to osteoarthritis.
- Crossing Legs While Turning: turning by crossing one leg over the other is a common cause of falls, particularly in the elderly. To avoid this, when turning step first with the foot that is on the side you are going to go. If you have the bad habit, this may feel strange at first, but you will soon adapt.
- Looking Down While Walking: focusing only on the ground directly in front of you can cause you to miss obstacles ahead, leading to falls. Instead, practice “scanning”, alternating between looking down at the ground and looking up to maintain awareness of your surroundings.
- Shuffling Instead of Tandem Walking: shuffling with feet far apart, rather than walking with one foot in front of the other, reduces balance and increases the risk of tripping. Tandem walking, where one foot is placed directly in front of the other, is the safer and more balanced way to walk.
It also helps disguise your numbers.
For more details on all of these, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Fall Special (How To Not Fall, And How To Minimize Injury If You Do) ← this never seems like an urgent thing to learn, but trust us, it’s more fun to read it now, than from your hospital bed later
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Doctors Feel – by Dr. Danielle Ofri
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book discusses how feelings such as shame, fear, anger, empathy, and even love influence patient care. Dr. Ofri notes early on:
❝One might reasonably say, I don’t give a damn how my doctor feels as long as she gets me better. In straightforward medical cases, this line of thinking is probably valid. Doctors who are angry, nervous, jealous, burned out, terrified, or ashamed can usually still treat bronchitis or ankle sprains competently.
The problems arise when clinical situations are convoluted, unyielding, or overlaid with unexpected complications, medical errors, or psychological components. This is where factors other than clinical competency come into play.❞
~ Dr. Danielle Ofri
What then follows is very much a no-holds-barred account of the emotional side of medicine.
Not portraying doctors as heroes or martyrs, just as people. Indeed, she even talks about an early, abject failure of hers as a medical student, literally hiding from a patient who badly needed attention and to whom she had been assigned.
We learn not just about the mistakes of doctors, but also the mistakes of patients that lead to mistakes by doctors. For example, emphasizing the severity of your symptom(s) can sometimes be useful to ensure they get attention, but if your regular doctor has heard you rating every symptom always as a 10 every appointment for the past many years, then the end result is that they don’t have information to work from, and will—at best—become frustrated, which will not work out well for you.
Mostly, though, it’s about what goes on behind that calm collected professional exterior that most doctors show most of the time.
The style is a fascinating blend of well-researched science (there’s an extensive bibliography) and very human tales of suffering, compassion, hope, loss, isolation, connection, and more.
Bottom line: if you want to understand your doctor(s), then you want to read this book.
Click here to check out What Doctors Feel, and learn how emotions affect the practice of medicine!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Vibration Plate, Review After 6 Months: Is It Worth It?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is it push-button exercise, or an expensive fad, or something else entirely? Robin, from “The Science of Self-Care”, has insights:
Science & Experience
According to the science (studies cited in the video and linked-to in the video description, underneath it on YouTube), vibration therapy does have some clear benefits, namely:
- Bone health (helps with bone density, particularly beneficial for postmenopausal women)
- Muscle recovery (reduces lactate levels, aiding faster recovery)
- Joint health (reduces pain and improves function in osteoarthritis patients)
- Muscle stimulation (helps older adults maintain muscle mass)
- Cognitive function (due to increased blood flow to the brain)
And from her personal experience, the benefits included:
- Improved recovery after exercise, reducing muscle soreness and stiffness
- Reduced back pain and improved posture (not surprising, given the need for stabilizing muscles when using one of these)
- Better circulation and (likely resulting from same) skin clarity
She did not, however, notice:
- Any reduction in cellulite
- Any change in body composition (fat loss or muscle gain)
For a deeper look into these things and more, plus a demonstration of how the machine actually operates, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: