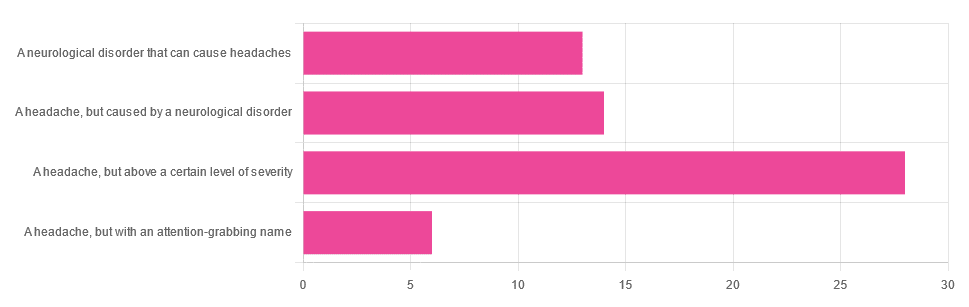Foods That Cause You to Lose Weight – by Dr. Neal Barnard
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We previously reviewed Dr. Barnard’s “The Power Foods Diet”, and this time his work is about weight loss.
This time there are more recipes (which take up most of the book, so this one could be reasonably described as a cookbook), but not until after nearly a hundred pages of concepts, principles, and tips.
The recipes themselves are again very respectable, even if some may be a little redundant (e.g. the double-page recipe for blueberry muffins is followed by a double-page recipe for banana and date muffins, instead of just saying “or substitute this”—things like that) and run the gamut from salad dressings to hearty main meals.
A strength of the book is that it’s about what you eat, not how much of it you eat, so if you love eating (which is a very healthy trait to have in general), then you’ll enjoy that aspect.
Bottom line: if you’d like to eat more and weigh less, then this is a top-tier book for you.
Click here to check out “Foods That Cause You To Lose Weight”, and enjoy eating!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Chorus or Cacophony? Cicada Song Hits Some Ears Harder Than Others
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
ST. LOUIS — Shhhooo. Wee-uuu. Chick, chick, chick. That’s the sound of three different cicada species. For some people, those sounds are the song of the summer. Others wish the insects would turn it down. The cacophony can be especially irritating for people on the autism spectrum who have hearing sensitivity.
Warren Rickly, 14, lives in suburban south St. Louis County, Missouri. Warren, who has autism, was at the bus stop recently waiting for his younger brother when the sound of cicadas became too much to bear.
“He said it sounds like there’s always a train running next to him,” his mother, Jamie Reed, said.
Warren told her the noise hurt.
Starting this spring, trillions of the red-eyed insects crawled their way out of the ground across the Midwest and Southeast. It’s part of a rare simultaneous emergence of two broods — one that appears every 13 years, the other every 17.
The noisy insects can be stressful. People with autism can have a sensitivity to texture, brightness, and sound.
“I think the difference for individuals with autism is the level of intensity or how upsetting some of these sensory differences are,” said Rachel Follmer, a developmental and behavioral pediatrician at Lurie Children’s Hospital in Chicago.
“It can get to the extreme where it can cause physical discomfort,” she said.
When a large group of cicadas starts to sing, the chorus can be as loud as a motorcycle. Researchers at the University of Missouri-St. Louis this year crowdsourced cicada noise levels as high as 86 decibels, about as loud as a food blender.
That can be stressful, not melodic, Follmer said.
To help children cope, she suggests giving them a primer before they encounter a noisy situation. For cicadas, that could mean explaining what they are, that they don’t bite or sting, and that they’ll be here for just a short time.
“When something is uncomfortable, not having power in that situation can be very scary for a lot of individuals, whether you’re on the spectrum or not,” Follmer said.
Jamie Reed’s family has been using this and other strategies to help her son. Warren wears noise-canceling headphones, listens to music, and has been teaching himself about cicadas.
“For him, researching it and looking into it I think grounds him a little bit,” Reed said.
Fatima Husain is a professor and neuroscientist at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and studies how the brain processes sound. She said people with tinnitus may also struggle with cicada song.
Tinnitus, a ringing or other noise in the ears, is a person’s perception of sound without an external source.
“Some people say it sounds like buzzing, like wind blowing through trees, and ironically, quite a few people say it sounds like cicadas,” Husain said.
For most people with tinnitus the cicada’s song is harmless background noise, according to Husain, but for others the ringing can prevent easy conversation or sleep. Those with tinnitus are also more likely to have anxiety or depression. A loud persistent sound, like singing cicadas, can make someone’s tinnitus worse, Husain said.
It’s not always bad, though. The cicada’s song can also be a relief.
For some, tinnitus gets worse in a quiet environment. Husain said she’s seen reports this year of patients saying the cicadas’ song has been like soothing white noise.
“The sound is loud enough that in some ways it’s drowning their internal tinnitus,” Husain said.
As loud as the cicadas can be, they won’t necessarily damage anyone’s hearing, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hearing loss builds up over time from repeated exposure to loud sounds. Cicadas aren’t loud enough for long enough to do lasting damage, Husain said.
Everyday sources of noise come with a higher risk. Husain said constant exposure to loud highways, an airport, industrial sites, or household appliances like blenders and hair dryers can be a concern. And they can take a toll on someone’s emotional well-being.
“If you are being exposed to very loud sounds for a part of your school day or your working day, it may make you more stressed out; it may make you more angry about things,” she said.
Unlike the highway or an airport, cicadas won’t be around long. Most of the current brood will be gone in the next few weeks. Just in time for another noisy summer event: the Fourth of July.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
The Silent Struggle – by L. William Ross-Child, MLC
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The vast majority of literature out there about ADHD is about children. And fair enough, there are enough popular misunderstandings of ADHD in children so it’s good those works exist… but what about adults?
Adults face different challenges than children, and have different responsibilities. People have different expectations. And even if you say you have ADHD… If you’re not behaving like a squirrel, they will often not accept this, much less understand it, because half the actual symptoms are not what most people think they are.
Ross-Child first lays out the neurobiological underpinnings of ADHD. This is a good place to start, because the physiology of it explains a lot of the other parts of it that can otherwise seem quite mystifying.
Thereafter, he looks one-by-one at the various cognitive and behavioral aspects of ADHD in adults, which will surely help the reader to better understand themself (or perhaps a loved one).
The next part of the book is given over to an exploration of ADHD and the differences it can make in the workplace, relationships (incl. ADHD and sex), as well as parenting, and how these things can all be navigated better by all concerned.
The style throughout is light and very readable, peppered with science made comprehensible. If there’s any flaw, it’s that there are only two pages of references in the bibliography—we’d have liked to have seen more.
All in all though, a really useful guide if you or a loved one has ADHD and you’d like strategies for working with (or around) this condition in a world not made to be kind to such.
Order your copy of “The Silent Struggle: Taking Charge of ADHD in Adults” from Amazon today!
Share This Post
-
Sensitive – by Jenn Granneman and Andre Sólo
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is written for what is called the “Highly Sensitive Person”, which makes it sound like a very rare snowflake condition, when in fact the diagnostic criteria (discussed early in the book) yield a population bell curve of 30:40:30, whereupon 30% are in the band of “high sensitivity”, 40% “normal sensitivity” and the remainder “low sensitivity”. You may note that “high” and “low” together outnumber “normal”, but statistics is like that.
So, if you’re one of the approximately one in three people who fall into the higher category, and/or you have a loved one who is in that category, then this book looks at the many advantages to a commonly stigmatized and (by cruel irony) criticized personality trait.
Those advantages range from personal life to work and even public life (yes, really), and can be grown, positively highlighted, used, and enjoyed.
In the category of criticism, the book does not usefully cover the benefit of psychological resilience. Resilience does not mean losing sensitivity, just, being able to also dry one’s tears and weather life’s slings and arrows when the world is harsher than one might like. But for the authors, they have stacked all their chips on “we must make the world a better place”. Which is a noble goal, if not always an immediately attainable one.
Bottom line: if you are more sensitive than average and would like to use that to benefit yourself and those around you, then this is the book for you!
Click here to check out Sensitive, and make the most of your strengths!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Cows’ Milk, Bird Flu, & You
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to dairy products, generally speaking, fermented ones (such as most cheeses and yogurts) are considered healthy in moderation, and unfermented ones have their pros and cons that can be argued and quibbled “until the cows come home”. We gave a broad overview, here:
Furthermore, you may recall that there’s some controversy/dissent about when human babies can have cows’ milk:
When can my baby drink cow’s milk? It’s sooner than you think
So, what about bird flu now?
Earlier this year, the information from the dairy industry was that it was nothing to be worried about for the time being:
Bird Flu Is Bad for Poultry and Dairy Cows. It’s Not a Dire Threat for Most of Us — Yet.
More recently, the latest science has found:
❝We found a first-order decay rate constant of −2.05 day–1 equivalent to a T99 of 2.3 days. Viral RNA remained detectable for at least 57 days with no degradation. Pasteurization (63 °C for 30 min) reduced infectious virus to undetectable levels and reduced viral RNA concentrations, but reduction was less than 1 log10.
The prolonged persistence of viral RNA in both raw and pasteurized milk has implications for food safety assessments and environmental surveillance❞
You can find the study here:
Infectivity and Persistence of Influenza A Virus in Raw Milk
In short: raw milk keeps the infectious virus; pasteurization appears to render it uninfectious, though viral RNA remains present.
This is relevant, because of the bird flu virus being found in milk:
World Health Organization | H5N1 strain of bird flu found in milk
To this end, a moratorium has been placed on the sale of raw milk, first by the California Dept of Public Health (following an outbreak in California):
California halts sales of raw milk due to bird flu virus contamination
And then, functionally, by the USDA, though rather than an outright ban, it’s requiring testing for the virus:
USDA orders testing of milk supply for presence of bird flu virus
So, is pasteurized milk safe?
The official answer to this, per the FDA, is… Honestly, a lot of hand-wringing and shrugging. What we do know is:
- the bird flu virus has been found in pasteurized milk too
- the test for this is very sensitive, and has the extra strength/weakness that viral fragments will flag it as a positive
- it is assumed that the virus was inactivated by the pasteurization process
- it could, however, have been the entire virus, the test simply does not tell us which
In the FDA’s own words:
❝The pasteurization process has served public health well for more than 100 years. Even if the virus is detected in raw milk, pasteurization is generally expected to eliminate pathogens to a level that does not pose a risk to consumer health❞
So, there we have it: the FDA does not have a reassurance exactly, but it does have a general expectation.
Source: US Officials: Bird flu viral fragments found in pasteurized milk
Want to know more?
You might like this mythbusting edition we did a little while back:
Pasteurization: What It Does And Doesn’t Do ← this is about its effect on risks and nutrients
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Migraine Mythbusting
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Migraine: When Headaches Are The Tip Of The Neurological Iceberg
Yesterday, we asked you “What is a migraine?” and got the above-depicted, below-described spread of responses:
- Just under 46% said “a headache, but above a certain level of severity”
- Just under 23% said “a headache, but caused by a neurological disorder”
- Just over 21% said “a neurological disorder that can cause headaches”
- Just under 10% said “a headache, but with an attention-grabbing name”
So… What does the science say?
A migraine is a headache, but above a certain level of severity: True or False?
While that’s usually a very noticeable part of it… That’s only one part of it, and not a required diagnostic criterion. So, in terms of defining what a migraine is, False.
Indeed, migraine may occur without any headache, let alone a severe one, for example: Abdominal Migraine—though this is much less well-researched than the more common with-headache varieties.
Here are the defining characteristics of a migraine, with the handy mnemonic 5-4-3-2-1:
- 5 or more attacks
- 4 hours to 3 days in duration
- 2 or more of the following:
- Unilateral (affects only one side of the head)
- Pulsating
- Moderate or severe pain intensity
- Worsened by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity
- 1 or more of the following:
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Sensitivity to both light and sound
Source: Cephalalgia | ICHD-II Classification: Parts 1–3: Primary, Secondary and Other
As one of our subscribers wrote:
❝I have chronic migraine, and it is NOT fun. It takes away from my enjoyment of family activities, time with friends, and even enjoying alone time. Anyone who says a migraine is just a bad headache has not had to deal with vertigo, nausea, loss of balance, photophobia, light sensitivity, or a host of other symptoms.❞
Migraine is a neurological disorder: True or False?
True! While the underlying causes aren’t known, what is known is that there are genetic and neurological factors at play.
❝Migraine is a recurrent, disabling neurological disorder. The World Health Organization ranks migraine as the most prevalent, disabling, long-term neurological condition when taking into account years lost due to disability.
Considerable progress has been made in elucidating the pathophysiological mechanisms of migraine, associated genetic factors that may influence susceptibility to the disease❞
Source: JHP | Mechanisms of migraine as a chronic evolutive condition
Migraine is just a headache with a more attention-grabbing name: True or False?
Clearly, False.
As we’ve already covered why above, we’ll just close today with a nod to an old joke amongst people with chronic illnesses in general:
“Are you just saying that because you want attention?”
“Yes… Medical attention!”
Want to learn more?
You can find a lot of resources at…
NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders & Stroke | Migraine
and…
The Migraine Trust ← helpfully, this one has a “Calm mode” to tone down the colorscheme of the website!
Particularly useful from the above site are its pages:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Rebuild Your Cartilage
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve covered before the topic of wear-and-tear on joints such as:
Avoiding/Managing Osteoarthritis
But what of cartilage, in particular? A common belief is “once it’s gone, it’s gone”, but that’s not quite right.
Cartilage is living tissue (metabolically active, with living cells). Within this tissue, specialist cells called chondrocytes produce extracellular cartilage matrix and collagen fibers, which provide smooth joint gliding as well as shock absorption.
Is exercise good or bad for cartilage?
Yes, yes it is. Exercise is good or bad for cartilage depending on the details:
- High-impact exercise e.g. running, jumping) places stress on cartilage, which is broadly bad
- However, impact loading strengthens the subchondral bone plate (layer under cartilage)
Strengthening this bone layer can help in long-term adaptation for high-impact sports.
See also: Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
So, how to do that without wiping out your cartilage first?
Building up
A gradual process is what’s called-for here:
- Start with cyclic, non-impact moderate resistance exercises (e.g. cycling, rowing, swimming).
- Gradually add soft-impact loading (e.g. fast walking, soft jogging).
- Incorporate strength training to improve overall joint stability (e.g. leg press, for lower body joints)
- Slowly transition to running and jumping over a long period to allow tissues to adapt.
How exactly you go about that is a matter of personal taste, but here are some illustrative examples:
- Indoor* cycling
- Cross trainer
- Leg press machine
- Tennis
*Why indoor? It’s so that you can control the resistance level at the twist of a knob, and get on and off when you want.
See also: Treadmill vs Road ← for similar considerations when it comes to walking/running. Outdoor definitely has its advantages, but so does indoor!
And the very related: How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Note that HIIT is High Intensity Interval Training, not High Impact Interval Training!
Strength from the inside
One of the most important things for cartilage is collagen. You can supplement that, or if you’re vegetarian/vegan, you can take its constituent parts to improve your own synthesis of it.
See: Collagen For Your Skin, Joints, & Bones: We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
Another supplement that can be helpful is glucosamine & chondroitin, which is best taken alongside a good omega-3 intake:
Want to know more?
This book is technically about (re)building strength and mobility in the case of arthritis specifically, but if your joints have more wear than you’d like, you may find this one an invaluable resource:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: