Fitness Freedom for Seniors – by Jackie Jacobs
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Exercise books often assume that either we are training for the Olympics, and most likely also that we are 20 years old. This one doesn’t.
Instead, we see a well-researched, well-organized, clearly-illustrated fitness plan with age in mind. Author Jackie Jacobs offers tips and advice for all levels, and a progressive week-by-week plan of 15-minute sessions. This way, we’re neither overdoing it nor slacking off; it’s a perfect balance.
The exercises are aimed at “all areas”, that is to say, improving cardiovascular fitness, balance, flexibility, and strength. It also gives some supplementary advice with regard to diet and suchlike, but the workouts are the real meat of the book.
Bottom line: if you’d like a robust, science-based exercise regime that’s tailored to seniors, this is the book for you.
Click here to check out Fitness Freedom for Seniors, and get yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fluoride Toothpaste vs Non-Fluoride Toothpaste – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing fluoride toothpaste to non-fluoride toothpaste, we picked the fluoride.
Why?
Fluoride is indeed toxic; that’s why it’s in toothpaste (to kill things; namely, bacteria whose waste products would harm our teeth). However, we are much bigger than those bacteria.
Given the amount of fluoride in toothpaste (usually under 1mg per strip of toothpaste to cover a toothbrush head), the amount that people swallow unintentionally (about 1/20th of that, so about 0.1mg daily if brushing teeth twice daily), and the toxicity level of fluoride (32–64mg/kg), then even if we take the most dangerous ends of all those numbers (and an average body size), to suffer ill effects from fluoride due to brushing your teeth, would require that you brush your teeth more than 23,000 times per day.
Alternatively, if you were to ravenously eat the toothpaste instead of spitting it out, you’d only need to brush your teeth a little over 1,000 times per day.
All the same, please don’t eat toothpaste; that’s not the message here.
However! In head-to-head tests, fluoride toothpaste has almost always beaten non-fluoride toothpaste.
Almost? Yes, almost: hydroxyapatite performed equally in one study, but that’s not usually an option on as many supermarket shelves.
We found some on Amazon, though, which is the one we used for today’s head-to-head. Here it is:
However, before you rush to buy it, do be aware that the toxicity of hydroxyapatite appears to be about twice that of fluoride:
Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety Opinion On Hydroxyapatite (Nano)
…which is still very safe (you’d need to brush your teeth, and eat all the toothpaste, about 500 times per day, to get to toxic levels, if we run with the same numbers we discussed before. Again, please do not do that, though).
But, since the science so far suggests it’s about twice as toxic as fluoride, then regardless of that still being very safe, the fluoride is obviously (by the same metric) twice as safe, hence picking the fluoride.
Want more options?
Check out our previous main feature:
Less Common Oral Hygiene Options
(the above article also links back to our discussion of different toothpastes and mouthwashes, by the way)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Gut Bacteria That Improve Your General Decision-Making In Life
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As one YouTube commenter said, “Trust your gut, but make sure you have a trustworthy gut first”!
Dr. Tracey Marks, psychiatrist, explains how:
Gut feelings and more
As you probably know, the gut and brain communicate via the vagus nerve, making gut bacteria highly influential.
How influential? Here are some key points from the video:
- Healthier gut bacteria are linked to more cautious risk-taking and future-oriented decisions.
- Gut bacteria influence serotonin (95% produced in the gut), dopamine, and neurotransmitters essential for decision-making.
- People with good gut health prioritize fairness in decision-making.
- The gut influences decision-making via neurotransmitter production, vagus nerve signaling, and inflammation control.
Gut bacteria produce metabolites (beyond the neurotransmitters mentioned above!) that affect nerve circuits for emotion and executive function. These postbiotics (postbiotics = byproducts of gut bacteria fermenting prebiotics) play a crucial role in brain health. Examples of things they make include short-chain fatty acids (butyrate), enzymes, peptides, and vitamins, which between them strengthen gut lining, reduce inflammation, regulate serotonin, and support immune function. Scientists are even exploring postbiotics for treating metabolic and inflammatory diseases.
Timeline of brain-gut axis health improvements
- Days 4–14: gut bacterial composition starts changing (you probably won’t notice anything brainwise, but you may get gas; this is normal and temporary)
- Weeks 2–6: mood and mental clarity improve (you’ll start feeling it here, most likely first in an abstract “life seems more beautiful” sort of way, plus less brain fog)
- Months 2–3: long-term neural adaptations form (this is where the decision-making improvements come in, so you’ll need some patience about this, but the mood boost you’ve now had since weeks 2–6 should make the next bit even easier).
Dr. Marks’ suggestions, to make the most of this:
- Diversify diet: aim for 30* different plant-based foods per week!
- Try fermented foods: start with small amounts of kimchi, kefir, etc.
- Increase fiber intake: add chia seeds or flaxseeds to meals!
- Limit artificial sweeteners: many of them disrupt gut bacteria.
- Maintain regular meal times: supports bacterial circadian rhythms.
- Don’t rely solely on supplements; whole foods are more effective!
*this is not a random number out of a hat; there is science behind the number! Here’s the science.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Beyond Guarding Against Dementia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When Age’s Brain-Changes Come Knocking
This is Dr. Amy Friday. She’s a psychologist, specializing in geropsychology and neuropsychological assessments.
In other words, she helps people optimize their aging experience, particularly in the context of brain changes as we get older.
What does she want us to know?
First: be not afraid
Ominous first words, but the fact is, there’s a lot to find scary about the prospect of memory loss, dementia, and death.
However, as she points out:
- Death will come for us all sooner or later, barring technology as yet unknown
- Dementia can be avoided, or at least stalled, or at least worked around
- Memory loss, as per the above, can be avoided/stalled/managed
We’ve written a little on these topics too:
…or if the death is not yours:
As for avoiding dementia, the below-linked feature is about Alzheimer’s in particular (which accounts for more than half of all cases of dementia), but the advice goes for most of the other kinds too:
How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
And finally, about memory loss specifically:
How To Boost Your Memory Immediately (Without Supplements)
this one is especially about cementing into one’s brain the kinds of memories that people most fear losing with age. People don’t worry about forgetting their PIN codes; they worry about forgetting their cherished memories with loved ones. So, if that’s important to you, do consider checking out this one!
What is that about managing or working around the symptoms?
If we’re missing a limb, we (usually) get a prosthetic, and/or learn how to operate without that limb.
If we’re missing sight or hearing, partially or fully, there are disability aids for those kinds of things too (glasses are a disability aid! Something being very common does not make it not a disability; you literally have less of an ability—in this case, the ability to see), and/or we learn how to operate with our different (or missing) sense.
Dr. Friday makes the case for this being the same with memory loss, dementia, and other age-related symptoms (reduced focus, increased mental fatigue, etc):
❝We are all screwed up. Here’s my flavor … what’s yours? This is a favorite saying of mine, because we ARE all screwed up in one way or another, and when we acknowledge it we can feel closer in our screwed-up-edness.
We are all experiencing “normal aging,” so that tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon that starts in our thirties and slowly gets worse is REAL. But what if you’re having more problems than normal aging? Is it time to throw in the towel and hide? I’m hoping that there is a group of people who say HELL NO to that idea.
Let’s use lessons from research and clinical practice to help all of us work around our weaknesses, and capitalize on our strengths. ❞
Examples of this might include:
- Writing down the things most important to you (a short list of information and/or statements that you feel define you and what matters most to you), so that you can read it later
- Making sure you have support (partner, family, friends, etc) who are on the same page about this topic—and thus will actually support you and advocate for you, instead of arguing about what is in your best interest without consulting you.
- Labelling stuff around the house, so that you get less confused about what is what and where it is
- Having a named go-to advocate that you can call / ask to be called, if you are in trouble somewhere and need help that you can rely on
- Getting a specialized, simpler bank account; hiring an accountant if relevant and practicable.
The thing is, we all want to keep control. Sometimes we can do that! Sometimes we can’t, and if we’re going to lose some aspect of control, it’ll generally go a lot better if we do it on our own terms, so that we ourselves can look out for future-us in our planning.
Want to know more?
You might enjoy her blog, which includes also links to her many videos on the topic, including such items as:
- Neuroplasticity – #1 Way To Increase Brain Health
- Which Diet PREVENTS Alzheimer’s? | Best Brain Health Diet
- Stop Anxiety About Dementia & Do I Have Dementia?
For the rest, see:
This Beautiful Brain | The Science Of Brain Health
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
I’m feeling run down. Why am I more likely to get sick? And how can I boost my immune system?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It has been a long winter, filled with many viruses and cost-of-living pressures, on top of the usual mix of work, study, life admin and caring responsibilities.
Stress is an inevitable part of life. In short bursts, our stress response has evolved as a survival mechanism to help us be more alert in fight or flight situations.
But when stress is chronic, it weakens the immune system and makes us more vulnerable to illnesses such as the common cold, flu and COVID.
Pexels/Ketut Subiyanto Stress makes it harder to fight off viruses
When the immune system starts to break down, a virus that would normally have been under control starts to flourish.
Once you begin to feel sick, the stress response rises, making it harder for the immune system to fight off the disease. You may be sick more often and for longer periods of time, without enough immune cells primed and ready to fight.
In the 1990s, American psychology professor Sheldon Cohen and his colleagues conducted a number of studies where healthy people were exposed to an upper respiratory infection, through drops of virus placed directly into their nose.
These participants were then quarantined in a hotel and monitored closely to determine who became ill.
One of the most important factors predicting who got sick was prolonged psychological stress.
Cortisol suppresses immunity
“Short-term stress” is stress that lasts for a period of minutes to hours, while “chronic stress” persists for several hours per day for weeks or months.
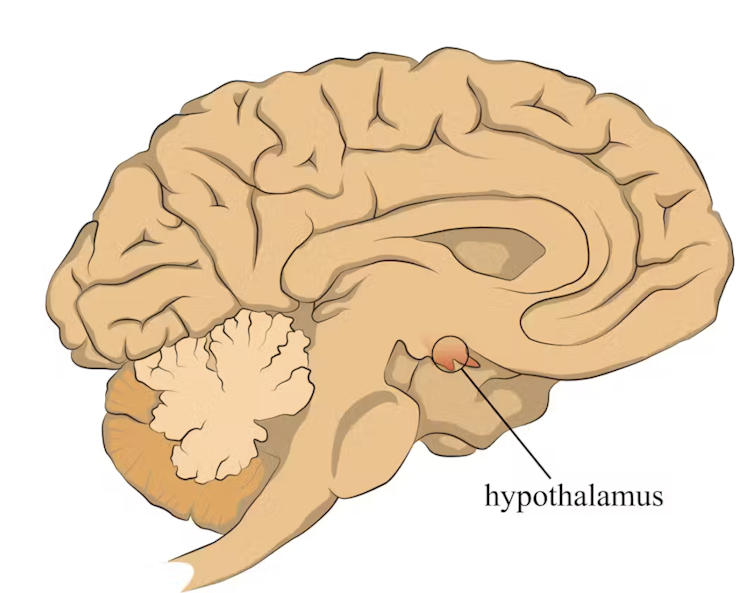
When faced with a perceived threat, psychological or physical, the hypothalamus region of the brain sets off an alarm system. This signals the release of a surge of hormones, including adrenaline and cortisol.
The hypothalamus sets off an alarm system in response to a real or perceived threat. stefan3andrei/Shutterstock In a typical stress response, cortisol levels quickly increase when stress occurs, and then rapidly drop back to normal once the stress has subsided. In the short term, cortisol suppresses inflammation, to ensure the body has enough energy available to respond to an immediate threat.
But in the longer term, chronic stress can be harmful. A Harvard University study from 2022 showed that people suffering from psychological distress in the lead up to their COVID infection had a greater chance of experiencing long COVID. They classified this distress as depression, probable anxiety, perceived stress, worry about COVID and loneliness.
Those suffering distress had close to a 50% greater risk of long COVID compared to other participants. Cortisol has been shown to be high in the most severe cases of COVID.
Stress causes inflammation
Inflammation is a short-term reaction to an injury or infection. It is responsible for trafficking immune cells in your body so the right cells are present in the right locations at the right times and at the right levels.
The immune cells also store a memory of that threat to respond faster and more effectively the next time.
Initially, circulating immune cells detect and flock to the site of infection. Messenger proteins, known as pro-inflammatory cytokines, are released by immune cells, to signal the danger and recruit help, and our immune system responds to neutralise the threat.
During this response to the infection, if the immune system produces too much of these inflammatory chemicals, it can trigger symptoms such as nasal congestion and runny nose.
Our immune response can trigger symptoms such as a runny nose. Alyona Mandrik/Shutterstock What about chronic stress?
Chronic stress causes persistently high cortisol secretion, which remains high even in the absence of an immediate stressor.
The immune system becomes desensitised and unresponsive to this cortisol suppression, increasing low-grade “silent” inflammation and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (the messenger proteins).
Immune cells become exhausted and start to malfunction. The body loses the ability to turn down the inflammatory response.
Over time, the immune system changes the way it responds by reprogramming to a “low surveillance mode”. The immune system misses early opportunities to destroy threats, and the process of recovery can take longer.
So how can you manage your stress?
We can actively strengthen our immunity and natural defences by managing our stress levels. Rather than letting stress build up, try to address it early and frequently by:
1) Getting enough sleep
Getting enough sleep reduces cortisol levels and inflammation. During sleep, the immune system releases cytokines, which help fight infections and inflammation.
2) Taking regular exercise
Exercising helps the lymphatic system (which balances bodily fluids as part of the immune system) circulate and allows immune cells to monitor for threats, while sweating flushes toxins. Physical activity also lowers stress hormone levels through the release of positive brain signals.
3) Eating a healthy diet
Ensuring your diet contains enough nutrients – such as the B vitamins, and the full breadth of minerals like magnesium, iron and zinc – during times of stress has a positive impact on overall stress levels. Staying hydrated helps the body to flush out toxins.
4) Socialising and practising meditation or mindfulness
These activities increase endorphins and serotonin, which improve mood and have anti-inflammatory effects. Breathing exercises and meditation stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, which calms down our stress responses so we can “reset” and reduce cortisol levels.
Sathana Dushyanthen, Academic Specialist & Lecturer in Cancer Sciences & Digital Health| Superstar of STEM| Science Communicator, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Avoid Self-Hatred & Learn To Love Oneself More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Alain de Botton gives a compassionate, but realistic, explanation in this video:
The enemy within
Or rather, the collaborator within. Because there’s usually first an enemy without—those who are critical of us, who consider that we are bad people in some fashion, and may indeed get quite colorful in their expressions of this.
Sometimes, their words will bounce straight off us; sometimes, their words will stick. So what’s the difference, and can we do anything about it?
The difference is: when their words stick, it’s usually because on some level we believe their words may be true. That doesn’t mean they necessarily are true!
They could be (and it would be a special kind of hubris to assume no detractor could ever find a valid criticism of us), but very often the reason we have that belief, or at least that fear/insecurity, is simply because it was taught to us at an early age, often by harsh words/actions of those around us; perhaps our parents, perhaps our schoolteachers, perhaps our classmates, and so forth.
The problem—and solution—is that we learn emotions much the same way that we learn language; only in part by reasoned thought, and rather for the most part, by immersion and repetition.
It can take a lot of conscious self-talk to undo the harm of decades of unconscious self-talk based on what was probably a few years of external criticisms when we were small and very impressionable… But, having missed the opportunity to start fixing this sooner, the next best time to do it is now.
We cannot, of course, simply do what a kind friend might do and expect any better results; if a kind friend tells us something nice that we do not believe is true, then however much they mean it, we’re not going to internalize it. So instead, we must simply chip away at those unhelpful longstanding counterproductive beliefs, and simply build up the habit of viewing ourselves in a kinder light.
For more on all this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Escape From The Clutches Of Shame
- To Err Is Human; To Forgive, Healthy
- How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
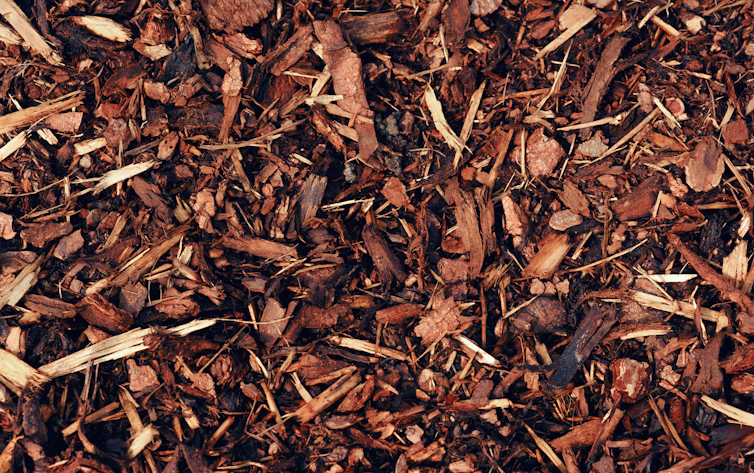
Asbestos in mulch? Here’s the risk if you’ve been exposed
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mulch containing asbestos has now been found at 41 locations in New South Wales, including Sydney parks, schools, hospitals, a supermarket and at least one regional site. Tests are under way at other sites.
As a precautionary measure, some parks have been cordoned off and some schools have closed temporarily. Fair Day – a large public event that traditionally marks the start of Mardi Gras – was cancelled after contaminated mulch was found at the site.
The New South Wales government has announced a new taskforce to help investigate how the asbestos ended up in the mulch.
Here’s what we know about the risk to public health of mulch contaminated with asbestos, including “friable” asbestos, which has been found in one site (Harmony Park in Surry Hills).
What are the health risks of asbestos?
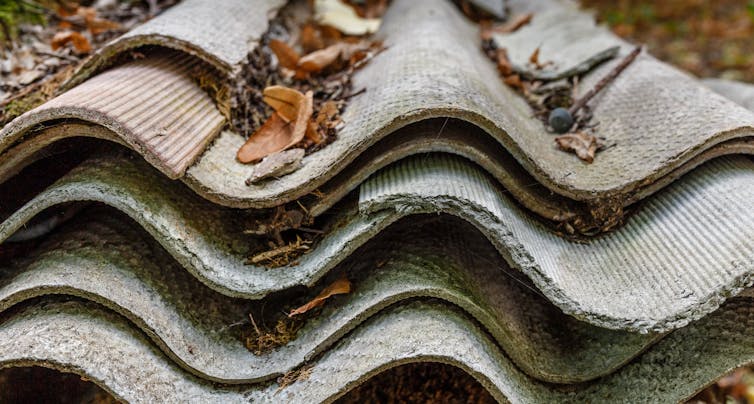
Asbestos is a naturally occurring, heat-resistant fibre that was widely used in building materials from the 1940s to the 1980s. It can be found in either a bonded or friable form.
Bonded asbestos means the fibres are bound in a cement matrix. Asbestos sheeting that was used for walls, fences, roofs and eaves are examples of bonded asbestos. The fibres don’t escape this matrix unless the product is severely damaged or worn.
A lot of asbestos fragments from broken asbestos products are still considered bonded as the fibres are not released as they lay on the ground.
Asbestos sheeting was used for walls and roofs.
Tomas Regina/ShutterstockFriable asbestos, in contrast, can be easily crumbled by touch. It will include raw asbestos fibres and previously bonded products that have worn to the point that they crumble easily.
The risk of disease from asbestos exposure is due to the inhalation of fibres. It doesn’t matter if those fibres are from friable or bonded sources.
However, fibres can more easily become airborne, and therefore inhalable, if the asbestos is friable. This means there is more of a risk of exposure if you are disturbing friable asbestos than if you disturb fragments of bonded asbestos.
Who is most at risk from asbestos exposure?
The most important factor for disease risk is exposure – you actually have to inhale fibres to be at risk of disease.
Just being in the vicinity of asbestos, or material containing asbestos, does not put you at risk of asbestos-related disease.
For those who accessed the contaminated areas, the level of exposure will depend on disturbing the asbestos and how many fibres become airborne due to that disturbance.
However, if you have been exposed to, and inhaled, asbestos fibres it does not mean you will get an asbestos-related disease. Exposure levels from the sites across Sydney will be low and the chance of disease is highly unlikely.
The evidence for disease risk from ingestion remains highly uncertain, although you are not likely to ingest sufficient fibres from the air, or even the hand to mouth activities that may occur with playing in contaminated mulch, for this to be a concern.
The risk of disease from exposure depends on the intensity, frequency and duration of that exposure. That is, the more you are exposed to asbestos, the greater the risk of disease.
Most asbestos-related disease has occurred in people who work with raw asbestos (for example, asbestos miners) or asbestos-containing products (such as building tradespeople). This has been a tragedy and fortunately asbestos is now banned.
There have been cases of asbestos-related disease, most notably mesothelioma – a cancer of the lining of the lung (mostly) or peritoneum – from non-occupational exposures. This has included people who have undertaken DIY home renovations and may have only had short-term exposures. The level of exposure in these cases is not known and it is also impossible to determine if those activities have been the only exposure.
There is no known safe level of exposure – but this does not mean that one fibre will kill. Asbestos needs to be treated with caution.
As far as we are aware, there have been no cases of mesothelioma, or other asbestos-related disease, that have been caused by exposure from contaminated soils or mulch.
Has asbestos been found in mulch before?
Asbestos contamination of mulch is, unfortunately, not new. Environmental and health agencies have dealt with these situations in the past. All jurisdictions have strict regulations about removing asbestos products from the green waste stream but, as is happening in Sydney now, this does not always happen.
Mulch contamination is not new.
gibleho/ShutterstockWhat if I’ve been near contaminated mulch?
Exposure from mulch contamination is generally much lower than from current renovation or construction activities and will be many orders of magnitude lower than past occupational exposures.
Unlike activities such as demolition, construction and mining, the generation of airborne fibres from asbestos fragments in mulch will be very low. The asbestos contamination will be sparsely spread throughout the mulch and it is unlikely there will be sufficient disturbance to generate large quantities of airborne fibres.
Despite the low chance of exposure, if you’re near contaminated mulch, do not disturb it.
If, by chance, you have had an exposure, or think you have had an exposure, it’s highly unlikely you will develop an asbestos-related disease in the future. If you’re worried, the Asbestos Safety and Eradication Agency is a good source of information.
Peter Franklin, Associate Professor and Director, Occupational Respiratory Epidemiology, The University of Western Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: