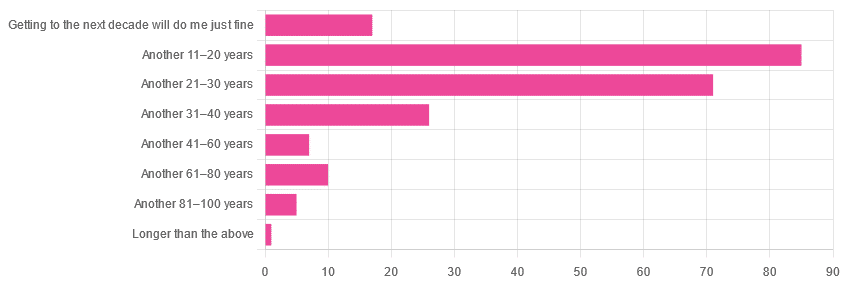When Bad Joints Stop You From Exercising (5 Things To Change)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The first trick to exercising with bad joints is to have better joints.
Now, this doesn’t necessarily mean you can take a supplement and magically your joint problems will be cured, but there are adjustable lifestyle factors that can and will make things relatively better or worse.
We say “and will”, because you don’t get a choice in that part. Everything we do, every little choice in our day, makes our health a little better or a little worse in some aspect(s). But we do get a choice between “relatively better” and “relatively worse”.
With that in mind, do check out:
- Avoiding/Managing Osteoarthritis
- Avoiding/Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
- How To Really Look After Your Joints
Ok, you have bad joints though; what next?
Let’s assume you’re doing your best with the above, and/or have simply decided not to, which is your call. You know your circumstances best. Either way, your joints are still not in sufficiently good condition to be able to exercise the way you’d like.
First, the obvious: enjoy low-impact exercises
For example:
- Swimming
- Yoga (much more appropriate here than the commonly-paired “and tai chi”)*
- Isometric exercises (i.e. exercise without movement, e.g. squeezing things, or stationary stability exercises)
*This is not to say that tai chi is bad. But if your problem is specifically your knees, there are many movements in most forms of tai chi that require putting the majority of one’s weight on one bent leg, which means the knee of that leg is going to suffer. If your knees are fine, then this won’t be an issue and it will simply continue strengthening your knees without discomfort. But they have to be fine first.
See also: Exercising With Osteoporosis
Second: support your joints through a full range of motion
If you have bad joints, you probably know that there’s an unfortunate paradox whereby you get to choose between:
- Exercise, and inflame your joints
- Rest, and your joints seize up
This is the way to get around that damaging dilemma.
Moving your joints through a full range of motion regularly is critical for their maintenance, so do that in a way that isn’t straining them:
If it’s your shoulders, for example, you can do (slow, gentle!) backstroke or front-crawl or butterfly motions while standing in the comfort of your living room.
If it’s your knees, then supported squats can do you a world of good. That means, squat in front of a table or other stable object, with your fingertips (or as much of your hands as you need) on it, to take a portion of your weight (it can be a large portion; that’s fine too!) while you go through the full range of motion of the squat. Repeat.
And so forth for other joints.
See also: The Most Underrated Hip Mobility Exercise (Not Stretching)
Third: work up slowly, and stop early
You can do exercises that involve impact, and if you live a fairly normal life, you’ll probably have to (walking is an impact exercise). You can also enjoy cycling (low-impact, but not so low-impact as we discussed in the last section) and work up to running if you want to.
However…
While building up your joints’ mobility and strength, it is generally a good idea to stop before you think you need to.
This means that it’s important to do those exercises in a way that you can stop early. For example, an exercise bike or a treadmill can be a lot of use here, so that you don’t find you need to stop for the day while miles from your house.
If you get such a device, it doesn’t even have to be fancy and/or expensive. This writer got herself an inexpensive exercise bike like this one, and it’s perfectly adequate.
Fourth: prioritize recovery, even if it doesn’t feel like you need it
Everyone should do this anyway, but if your joints are bad, it goes double:
Overdone It? How To Speed Up Recovery After Exercise (According To Actual Science)
Fifth: get professional help
Physiotherapists are great for this. Find one, and take their advice for your specific body and your specific circumstances and goals.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Harm Can One Sleepless Night Do?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ll not bury the lede: a study found that just one night of 24-hour sleep deprivation can alter immune cell profiles in young, lean, healthy people to resemble those of people with obesity and chronic inflammation.
Chronic inflammation, in turn, causes very many other chronic diseases, and worsens most of the ones it doesn’t outright cause.
The reason this happens is because in principle, inflammation is supposed to be good for us—it’s our body’s defenses coming to the rescue. However, if we imagine our immune cells as firefighters, then compare:
- A team of firefighters who are in great shape and ready to deploy at a moment’s notice, are mostly allowed to rest, sometimes get training, and get called out to a fire from time time, just enough to keep them on their toes. Today, something in your house caught fire, and they showed up in 5 minutes and put it out safely.
- A team of firefighters who have been pulling 24-hour shifts every day for the past 20 years, getting called out constantly for lost cats, burned toast, wrong numbers, the neighbor’s music, a broken fridge, and even the occasional fire. Today, your printer got jammed so they broke down your door and also your windows just for good measure, and blasted your general desk area with a fire hose, which did not resolve the problem but now your computer itself is broken.
Which team would you rather have?
The former team is a healthy immune system; the latter is the immune system of someone with chronic inflammation.
But if it’s one night, it’s not chronic, right?
Contingently true. However, the problem is that because the immune profile was made to be like the bad team we described (imagine that chaos in your house, now remember that for this metaphor, it’s your body that that’s happening to), the immediate strong negative health impact will already have knock-on effects, which in turn make it more likely that you’ll struggle to get your sleep back on track quickly.
For example, the next night you may oversleep “to compensate”, but then the following day your sleep schedule is now slid back considerably; one thing leads to another, and a month later you’re thinking “I really must sort my sleep out”.
See also: How Regularity Of Sleep Can Be Even More Important Than Duration ← A recent, large (n=72,269) 8-year prospective* observational study of adults aged 40-79 found a strong association between irregular sleep and major cardiovascular events, to such an extent that it was worse than undersleeping.
*this means they started the study at a given point, and measured what happened for the next eight years—as opposed to a retrospective study, which would look at what had happened during the previous 8 years.
What about sleep fragmentation?
In other words: getting sleep, but heavily disrupted sleep.
The answer is: basically the same deal as with missed sleep.
Specifically, elevated proinflammatory cytokines (in this context, that’s bad) and an increase in nonclassical monocytes—as are typically seen in people with obesity and chronic inflammation.
Remember: these were young, lean, healthy participants going into the study, who signed up for a controlled sleep deprivation experiment.
This is important, because the unhealthy inflammatory profile means that people with such are a lot more likely to develop diabetes, heart disease, Alzheimer’s, and many more things besides. And, famously, most people in the industrialized world are not sleeping that well.
Even amongst 10almonds readers, a health-conscious demographic by nature, 62% of 10almonds readers do not regularly get the prescribed 7–9 hours sleep (i.e. they get under 7 hours).
You can see the data on this one, here: Why You Probably Need More Sleep ← yes, including if you are in the older age range; we bust that myth in the article too!*
*Unless you have a (rare!) mutated ADRB1 gene, which reduces that. But we also cover that in the article, and how to know whether you have it.
With regard to “most people in the industrialized world are not sleeping that well”, this means that most people in the industrialized world are subject to an unseen epidemic of sleep-deprivation-induced inflammation that is creating vulnerability to many other diseases. In short, the lifestyle of the industrialized world (especially: having to work certain hours) is making most of the working population sick.
Dr. Fatema Al-Rashed, lead researcher, concluded:
❝In the long term, we aim for this research to drive policies and strategies that recognize the critical role of sleep in public health.
We envision workplace reforms and educational campaigns promoting better sleep practices, particularly for populations at risk of sleep disruption due to technological and occupational demands.
Ultimately, this could help mitigate the burden of inflammatory diseases like obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.❞
You can read the paper in full here: Impact of sleep deprivation on monocyte subclasses and function
What can we do about it?
With regard to sleep, we’ve written so much about this, but here are three key articles that contain a lot of valuable information:
- Get Better Sleep: Beyond The Basics
- Calculate (And Enjoy) The Perfect Night’s Sleep
- Safe Effective Sleep Aids For Seniors
…and with regard to inflammation, a good concise overview of how to dial it down is:
How To Prevent Or Reduce Inflammation
Take care!
Share This Post
-
It’s Not Hysteria – by Dr. Karen Tan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Firstly, who this book is aimed at: in case it wasn’t clear, this book assumes you have, or at least have had, a uterus. If that’s not you, then well, it’ll still be an interesting read but it won’t be about your reproductive health.
Secondly, about that “reproductive health”: it’s mostly not actually about reproductive health literally, but rather, the health of one’s reproductive organs and the things that they affect—which is a lot more than the ability to reproduce!
Dr. Tang takes us on a (respectably in-depth) tour of the relevant anatomy, before moving on to physiology, before continuing to pathology (i.e. things that can go wrong, and often do), and finally various treatment options, including elective procedures, and the pros and cons thereof.
She also talks the reader through talking about things with gynecologists and other healthcare providers, and making sure concerns are not dismissed out-of-hand (something that happens a lot, of course).
The style throughout is quite detailed prose, but without being difficult at all to read, and (assuming one is interested in the topic) it’s very engaging.
Bottom line: if you would like to know more about uteri and everything that is (or commonly/unfortunately) can be attached to them, the effects they have on the rest of the body and health, and what can be done about things not being quite right, then this is a good book for that.
Click here to check out It’s Not Hysteria, and understand more of what’s going on down there!
Share This Post
-
What will aged care look like for the next generation? More of the same but higher out-of-pocket costs
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Aged care financing is a vexed problem for the Australian government. It is already underfunded for the quality the community expects, and costs will increase dramatically. There are also significant concerns about the complexity of the system.
In 2021–22 the federal government spent A$25 billion on aged services for around 1.2 million people aged 65 and over. Around 60% went to residential care (190,000 people) and one-third to home care (one million people).
The final report from the government’s Aged Care Taskforce, which has been reviewing funding options, estimates the number of people who will need services is likely to grow to more than two million over the next 20 years. Costs are therefore likely to more than double.
The taskforce has considered what aged care services are reasonable and necessary and made recommendations to the government about how they can be paid for. This includes getting aged care users to pay for more of their care.
But rather than recommending an alternative financing arrangement that will safeguard Australians’ aged care services into the future, the taskforce largely recommends tidying up existing arrangements and keeping the status quo.
No Medicare-style levy
The taskforce rejected the aged care royal commission’s recommendation to introduce a levy to meet aged care cost increases. A 1% levy, similar to the Medicare levy, could have raised around $8 billion a year.
The taskforce failed to consider the mix of taxation, personal contributions and social insurance which are commonly used to fund aged care systems internationally. The Japanese system, for example, is financed by long-term insurance paid by those aged 40 and over, plus general taxation and a small copayment.
Instead, the taskforce puts forward a simple, pragmatic argument that older people are becoming wealthier through superannuation, there is a cost of living crisis for younger people and therefore older people should be required to pay more of their aged care costs.
Separating care from other services
In deciding what older people should pay more for, the taskforce divided services into care, everyday living and accommodation.
The taskforce thought the most important services were clinical services (including nursing and allied health) and these should be the main responsibility of government funding. Personal care, including showering and dressing were seen as a middle tier that is likely to attract some co-payment, despite these services often being necessary to maintain independence.
The task force recommended the costs for everyday living (such as food and utilities) and accommodation expenses (such as rent) should increasingly be a personal responsibility.
Aged care users will pay more of their share for cooking and cleaning.
Lizelle Lotter/ShutterstockMaking the system fairer
The taskforce thought it was unfair people in residential care were making substantial contributions for their everyday living expenses (about 25%) and those receiving home care weren’t (about 5%). This is, in part, because home care has always had a muddled set of rules about user co-payments.
But the taskforce provided no analysis of accommodation costs (such as utilities and maintenance) people meet at home compared with residential care.
To address the inefficiencies of upfront daily fees for packages, the taskforce recommends means testing co-payments for home care packages and basing them on the actual level of service users receive for everyday support (for food, cleaning, and so on) and to a lesser extent for support to maintain independence.
It is unclear whether clinical and personal care costs and user contributions will be treated the same for residential and home care.
Making residential aged care sustainable
The taskforce was concerned residential care operators were losing $4 per resident day on “hotel” (accommodation services) and everyday living costs.
The taskforce recommends means tested user contributions for room services and everyday living costs be increased.
It also recommends that wealthier older people be given more choice by allowing them to pay more (per resident day) for better amenities. This would allow providers to fully meet the cost of these services.
Effectively, this means daily living charges for residents are too low and inflexible and that fees would go up, although the taskforce was clear that low-income residents should be protected.
Moving from buying to renting rooms
Currently older people who need residential care have a choice of making a refundable up-front payment for their room or to pay rent to offset the loans providers take out to build facilities. Providers raise capital to build aged care facilities through equity or loan financing.
However, the taskforce did not consider the overall efficiency of the private capital market for financing aged care or alternative solutions.
Instead, it recommended capital contributions be streamlined and simplified by phasing out up-front payments and focusing on rental contributions. This echoes the royal commission, which found rent to be a more efficient and less risky method of financing capital for aged care in private capital markets.
It’s likely that in a decade or so, once the new home care arrangements are in place, there will be proportionally fewer older people in residential aged care. Those who do go are likely to be more disabled and have greater care needs. And those with more money will pay more for their accommodation and everyday living arrangements. But they may have more choice too.
Although the federal government has ruled out an aged care levy and changes to assets test on the family home, it has yet to respond to the majority of the recommendations. But given the aged care minister chaired the taskforce, it’s likely to provide a good indication of current thinking.
Hal Swerissen, Emeritus Professor, La Trobe University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
I’m Moving Forward and Facing the Uncertainty of Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It takes a lot of courage to grow old.
I’ve come to appreciate this after conversations with hundreds of older adults over the past eight years for nearly 200 “Navigating Aging” columns.
Time and again, people have described what it’s like to let go of certainties they once lived with and adjust to new circumstances.
These older adults’ lives are filled with change. They don’t know what the future holds except that the end is nearer than it’s ever been.
And yet, they find ways to adapt. To move forward. To find meaning in their lives. And I find myself resolving to follow this path as I ready myself for retirement.
Patricia Estess, 85, of the Brooklyn borough of New York City spoke eloquently about the unpredictability of later life when I reached out to her as I reported a series of columns on older adults who live alone, sometimes known as “solo agers.”
Estess had taken a course on solo aging. “You realize that other people are in the same boat as you are,” she said when I asked what she had learned. “We’re all dealing with uncertainty.”
Consider the questions that older adults — whether living with others or by themselves — deal with year in and out: Will my bones break? Will my thinking skills and memory endure? Will I be able to make it up the stairs of my home, where I’m trying to age in place?
Will beloved friends and family members remain an ongoing source of support? If not, who will be around to provide help when it’s needed?
Will I have enough money to support a long and healthy life, if that’s in the cards? Will community and government resources be available, if needed?
It takes courage to face these uncertainties and advance into the unknown with a measure of equanimity.
“It’s a question of attitude,” Estess told me. “I have honed an attitude of: ‘I am getting older. Things will happen. I will do what I can to plan in advance. I will be more careful. But I will deal with things as they come up.’”
For many people, becoming old alters their sense of identity. They feel like strangers to themselves. Their bodies and minds aren’t working as they used to. They don’t feel the sense of control they once felt.
That requires a different type of courage — the courage to embrace and accept their older selves.
Marna Clarke, a photographer, spent more than a dozen years documenting her changing body and her life with her partner as they grew older. Along the way, she learned to view aging with new eyes.
“Now, I think there’s a beauty that comes out of people when they accept who they are,” she told me in 2022, when she was 70, just before her 93-year-old husband died.
Arthur Kleinman, a Harvard professor who’s now 83, gained a deeper sense of soulfulness after caring for his beloved wife, who had dementia and eventually died, leaving him grief-stricken.
“We endure, we learn how to endure, how to keep going. We’re marked, we’re injured, we’re wounded. We’re changed, in my case for the better,” he told me when I interviewed him in 2019. He was referring to a newfound sense of vulnerability and empathy he gained as a caregiver.
Herbert Brown, 68, who lives in one of Chicago’s poorest neighborhoods, was philosophical when I met him at his apartment building’s annual barbecue in June.
“I was a very wild person in my youth. I’m surprised I’ve lived this long,” he said. “I never planned on being a senior. I thought I’d die before that happened.”
Truthfully, no one is ever prepared to grow old, including me. (I’m turning 70 in February.)
Chalk it up to denial or the limits of imagination. As May Sarton, a writer who thought deeply about aging, put it so well: Old age is “a foreign country with an unknown language.” I, along with all my similarly aged friends, are surprised we’ve arrived at this destination.
For me, 2025 is a turning point. I’m retiring after four decades as a journalist. Most of that time, I’ve written about our nation’s enormously complex health care system. For the past eight years, I’ve focused on the unprecedented growth of the older population — the most significant demographic trend of our time — and its many implications.
In some ways, I’m ready for the challenges that lie ahead. In many ways, I’m not.
The biggest unknown is what will happen to my vision. I have moderate macular degeneration in both eyes. Last year, I lost central vision in my right eye. How long will my left eye pick up the slack? What will happen when that eye deteriorates?
Like many people, I’m hoping scientific advances outpace the progression of my condition. But I’m not counting on it. Realistically, I have to plan for a future in which I might become partially blind.
It’ll take courage to deal with that.
Then, there’s the matter of my four-story Denver house, where I’ve lived for 33 years. Climbing the stairs has helped keep me in shape. But that won’t be possible if my vision becomes worse.
So my husband and I are taking a leap into the unknown. We’re renovating the house, installing an elevator, and inviting our son, daughter-in-law, and grandson to move in with us. Going intergenerational. Giving up privacy. In exchange, we hope our home will be full of mutual assistance and love.
There are no guarantees this will work. But we’re giving it a shot.
Without all the conversations I’ve had over all these years, I might not have been up for it. But I’ve come to see that “no guarantees” isn’t a reason to dig in my heels and resist change.
Thank you to everyone who has taken time to share your experiences and insights about aging. Thank you for your openness, honesty, and courage. These conversations will become even more important in the years ahead, as baby boomers like me make their way through their 70s, 80s, and beyond. May the conversations continue.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Likely Are You To Live To 100?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How much hope can we reasonably have of reaching 100?
Yesterday, we asked you: assuming a good Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL), how much longer do you hope to live?
We got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- A little over 38% of respondents hope to live another 11–20 years
- A little over 31% hope to live another 31–40 years
- A little over 7% will be content to make it to the next decade
- One (1) respondent hopes to live longer than an additional 100 years
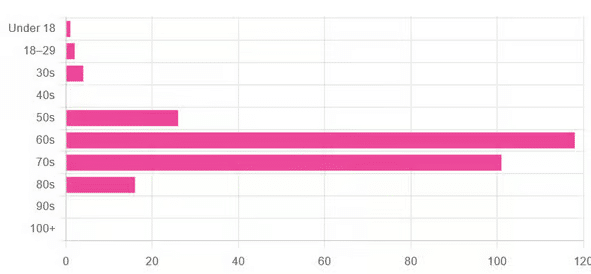
This is interesting when we put it against our graph of how old our subscribers are:
…because it corresponds inversely, right down to the gap/dent in the 40s. And—we may hypothesize—that one person under 18 who hopes to live to 120, perhaps.
This suggests that optimism remains more or less constant, with just a few wobbles that would probably be un-wobbled with a larger sample size.
In other words: most of our education-minded, health-conscious subscriber-base hope to make it to the age of 90-something, while for the most part feeling that 100+ is overly optimistic.
Writer’s anecdote: once upon a time, I was at a longevity conference in Brussels, and a speaker did a similar survey, but by show of hands. He started low by asking “put your hands up if you want to live at least a few more minutes”. I did so, with an urgency that made him laugh, and say “Don’t worry; I don’t have a gun hidden up here!”
Conjecture aside… What does the science say about our optimism?
First of all, a quick recap…
To not give you the same information twice, let’s note we did an “aging mythbusting” piece already covering:
- Aging is inevitable: True or False?
- Aging is, and always will be, unstoppable: True or False?
- We can slow aging: True or False?
- It’s too early to worry about… / It’s too late to do anything about… True or False?
- We can halt aging: True or False?
- We can reverse aging: True or False?
- But those aren’t really being younger, we’ll still die when our time is up: True or False?
You can read the answers to all of those here:
Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
Now, onwards…
It is unreasonable to expect to live past 100: True or False?
True or False, depending on your own circumstances.
First, external circumstances: the modal average person in Hong Kong is currently in their 50s and can expect to live into their late 80s, while the modal average person in Gaza is 14 and may not expect to make it to 15 right now.
To avoid extremes, let’s look at the US, where the modal average person is currently in their 30s and can expect to live into their 70s:
United States Mortality Database
Now, before that unduly worries our many readers already in their 70s…
Next, personal circumstances: not just your health, but your socioeconomic standing. And in the US, one of the biggest factors is the kind of health insurance one has:
SOA Research Institute | Life Expectancy Calculator 2021
You may note that the above source puts all groups into a life expectancy in the 80s—whereas the previous source gave 70s.
Why is this? It’s because the SOA, whose primary job is calculating life insurance risks, is working from a sample of people who have, or are applying for, life insurance. So it misses out many people who die younger without such.
New advances in medical technology are helping people to live longer: True or False?
True, assuming access to those. Our subscribers are mostly in North America, and have an economic position that affords good access to healthcare. But beware…
On the one hand:
The number of people who live past the age of 100 has been on the rise for decades
On the other hand:
The average life expectancy in the U.S. has been on the decline for three consecutive years
COVID is, of course, largely to blame for that, though:
❝The decline of 1.8 years in life expectancy was primarily due to increases in mortality from COVID-19 (61.2% of the negative contribution).
The decline in life expectancy would have been even greater if not for the offsetting effects of decreases in mortality due to cancer (43.1%)❞
Source: National Vital Statistics Reports
The US stats are applicable to Canada, the UK, and Australia: True or False?
False: it’s not quite so universal. Differences in healthcare systems will account for a lot, but there are other factors too:
- Life expectancy in Canada fell for the 3rd year in a row. What’s happening?
- UK life expectancy lagging behind rest of G7 except the US
- Australians are living longer but what does it take to reach 100 years old?
Here’s an interesting (UK-based) tool that calculates not just your life expectancy, but also gives the odds of living to various ages (e.g. this writer was given odds of living to 87, 96, 100).
Check yours here:
Office of National Statistics | Life Expectancy Calculator
To finish on a cheery note…
Data from Italian centenarians suggests a “mortality plateau”:
❝The risk of dying leveled off in people 105 and older, the team reports online today in Science.
That means a 106-year-old has the same probability of living to 107 as a 111-year-old does of living to 112.
Furthermore, when the researchers broke down the data by the subjects’ year of birth, they noticed that over time, more people appear to be reaching age 105.❞
Pop-sci source: Once you hit this age, aging appears to stop
Actual paper: The plateau of human mortality: demography of longevity pioneers
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Behavioral Activation Against Depression & Anxiety
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Behavioral Activation Against Depression & Anxiety
Psychologists do love making fancy new names for things.
You thought you were merely “eating your breakfast”, but now it’s “Happiness-Oriented Basic Behavioral Intervention Therapy (HOBBIT)” or something.
This one’s quite simple, so we’ll keep it short for today, but it is one more tool for your toolbox:
What is Behavioral Activation?
Behavioral Activation is about improving our mood (something we can’t directly choose) by changing our behavior (something we usually can directly choose).
An oversimplified (and insufficient, as we will explain, but we’ll use this one to get us started) example would be “whistle a happy tune and you will be happy”.
Behavioral Activation is not a silver bullet
Or if it is, then it’s the kind you have to keep shooting, because one shot is not enough. However, this becomes easier than you might think, because Behavioral Activation works by…
Creating a Positive Feedback Loop
A lot of internal problems in depression and anxiety are created by the fact that necessary and otherwise desirable activities are being written off by the brain as:
- Pointless (depression)
- Dangerous (anxiety)
The inaction that results from these aversions creates a negative feedback loop as one’s life gradually declines (as does one’s energy, and interest in life), or as the outside world seems more and more unwelcoming/scary.
Instead, Behavioral Activation plans activities (usually with the help of a therapist, as depressed/anxious people are not the most inclined to plan activities) that will be:
- attainable
- rewarding
The first part is important, because the maximum of what is “attainable” to a depressed/anxious person can often be quite a small thing. So, small goals are ideal at first.
The second part is important, because there needs to be some way of jump-starting a healthier dopamine cycle. It also has to feel rewarding during/after doing it, not next year, so short term plans are ideal at first.
So, what behavior should we do?
That depends on you. Behavioral Activation calls for keeping track of our activities (bullet-journaling is fine, and there are apps* that can help you, too) and corresponding moods.
*This writer uses the pragmatic Daylio for its nice statistical analyses of bullet-journaling data-points, and the very cute Finch for more keyword-oriented insights and suggestions. Whatever works for you, works for you, though! It could even be paper and pen.
Sometimes the very thought of an activity fills us with dread, but the actual execution of it brings us relief. Bullet-journaling can track that sort of thing, and inform decisions about “what we should do” going forwards.
Want a ready-made brainstorm to jump-start your creativity?
Here’s list of activities suggested by TherapistAid (a resource hub for therapists)
Want to know more?
You might like:
- How To Use Behavioral Activation (guide for end users)
- Treatment Guide: Behavioral Activation (guide for clinicians)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: