Chai-Spiced Rice Pudding
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sweet enough for dessert, and healthy enough for breakfast! Yes, “chai tea” is “tea tea”, just as “naan bread” is “bread bread”. But today, we’re going to be using the “tea tea” spices to make this already delicious and healthy dish more delicious and more healthy:
You will need
- 1 cup wholegrain rice (a medium-length grain is best for the optimal amount of starch to make this creamy but not sticky)
- 1½ cups milk (we recommend almond milk, but any milk will work)
- 1 cup full fat coconut milk
- 1 cup water
- 4 Medjool dates, soaked in hot water for 5 minutes, drained, and chopped
- 2 tbsp almond butter
- 1 tbsp maple syrup (omit if you prefer less sweetness)
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 2 tsp ground sweet cinnamon
- 1 tsp ground ginger
- 1 tsp vanilla extract
- ½ tsp ground cardamom
- ½ tsp ground nutmeg
- ½ ground cloves
- Optional garnish: berries (your preference what kind)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Add all of the ingredients except the berries into the cooking vessel* you’re going to use, and stir thoroughly.
*There are several options here and they will take different durations:
- Pressure cooker: 10 minutes at high pressure (we recommend, if available)
- Rice cooker: 25 minutes or thereabouts (we recommend only if the above or below aren’t viable options for you)
- Slow cooker: 3 hours or thereabouts, but you can leave it for 4 if you’re busy (we recommend if you want to “set it and forget it” and have the time; it’s very hard to mess this one up unless you go to extremes)
Options that we don’t recommend:
- Saucepan: highly variable and you’re going to have to watch and stir it (we don’t recommend this unless the other options aren’t available)
- Oven: highly variable and you’re going to have to check it frequently (we don’t recommend this unless the other options aren’t available)
2) Cook, using the method you selected from the list.
3) Get ready to serve. Depending on the method, they may be some extra liquid at the top; this can just be stirred into the rest and it will take on the same consistency.
4) Serve in bowls, with a berry garnish if desired:
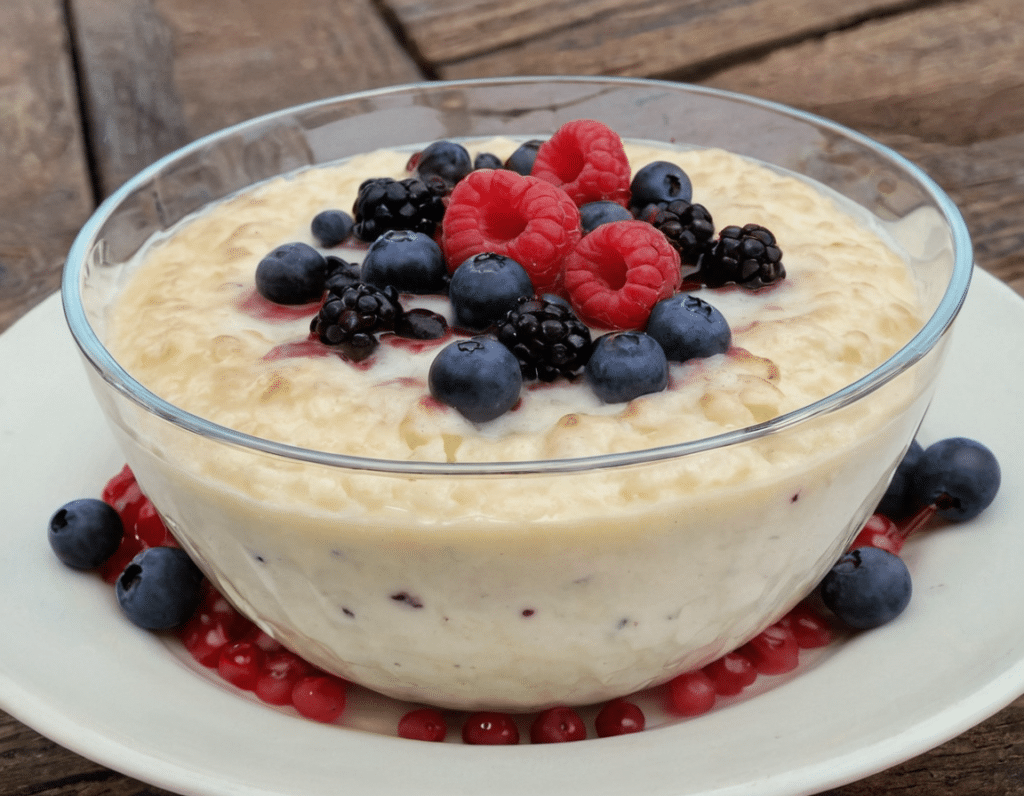

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Grains: Bread Of Life, Or Cereal Killer?
- Which Plant Milk?
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Sweet Cinnamon vs Regular Cinnamon – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to Think More Effectively – by Alain de Botton
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our brain is our most powerful organ, and our mind is an astonishing thing. So why do we sometimes go off-piste?
The School of Life‘s Alain de Botton lays out for us a framework of cumulative thinking, directions for effort, and unlikely tools for cognitive improvement.
The book especially highlights the importance of such things as…
- making time for cumulative thinking
- not, however, trying to force it
- working with, rather than in spite of, distractions
- noting and making use of our irrationalities
- taking what we think/do both seriously and lightly, at once
- practising constructive self-doubt
The style is as clear and easy as you may have come to expect from Alain de Botton / The School of Life, and yet, its ideas are still likely to challenge every reader in some (good!) way.
Bottom line: if you would like what you think, say, do to be more meaningful, this book will help you to make the most of your abilities!
Click here to check out How To Think More Effectively, and upgrade your thought processes!
Share This Post
-
Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Doesn’t Lycopene Do?
Lycopene is an antioxidant carotenoid famously found in tomatoes; it actually appears in even higher levels in watermelon, though. If you are going to get it from tomato, know that cooking improves the lycopene content rather than removing it (watermelon, on the other hand, can be enjoyed as-is and already has the higher lycopene content).
Antioxidant properties
Let’s reiterate the obvious first, for the sake of being methodical and adding a source. Lycopene is a potent antioxidant with multiple health benefits:
Lycopene: A Potent Antioxidant with Multiple Health Benefits
…and as such, it does all the things you might reasonably expect and antioxidant to do. For example…
Anti-inflammatory properties
In particular, it regulates macrophage activity, reducing inflammation while improving immune response:
Lycopene Regulates Macrophage Immune Response through the Autophagy Pathway Mediated by RIPK1
As can be expected of most antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents, it also has…
Anticancer properties
Scientific papers tend to be “per cancer type”, so we’re just going to give one example, but there’s pretty much evidence for its utility against most if not all types of cancer. We’re picking prostate cancer though, as it’s one that’s been studied the most in the context of lycopene intake—in this study, for example, it was found that men who enjoyed at least two servings of lycopene-rich tomato sauce per week were 30% less likely to develop prostate cancer than those who didn’t:
Dietary lycopene intake and risk of prostate cancer defined by ERG protein expression
If you’d like to see something more general, however, then check out:
Potential Use of Tomato Peel, a Rich Source of Lycopene, for Cancer Treatment
It also fights Candida albicans
Ok, this is not (usually) so life-and-death as cancer, but reducing our C. albicans content (specifically: in our gut) has a lot of knock-on effects for other aspects of our health, so this isn’t one to overlook:
The title does not make this clear, but yes: this does mean it has an antifungal effect. We mention this because often cellular apoptosis is good for an overall organism, but in this case, it simply kills the Candida.
It’s good for the heart
A lot of studies focus just on triglyceride markers (which lycopene improves), but more tellingly, here’s a 10-year observational study in which diets rich in lycopene were associated to a 17–26% lower risk of heart disease:
Relationship of lycopene intake and consumption of tomato products to incident CVD
…and a 39% overall reduced mortality in, well, we’ll let the study title tell it:
…which means also:
It’s good for the brain
As a general rule of thumb, what’s good for the heart is good for the brain (because the brain needs healthy blood flow to stay healthy, and is especially vulnerable when it doesn’t get that), and in this case that rule of thumb is also borne out by the post hoc evidence, specifically yielding a 31% decreased incidence of stroke:
Dietary and circulating lycopene and stroke risk: a meta-analysis of prospective studies
Is it safe?
As a common food product, it is considered very safe.
If you drink nothing but tomato juice all day for a long time, your skin will take on a reddish hue, which will go away if you stop getting all your daily water intake in tomato juice.
In all likelihood, even if you went to extremes, you would get sick from the excess of vitamin A (generally present in the same foods) sooner than you’d get sick from the excess of lycopene.
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, and also we recommend simply enjoying tomatoes, watermelons, etc, but if you do want a supplement, here’s an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
More Mediterranean – by American’s Test Kitchen
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Regular 10almonds readers will know that we talk about the Mediterranean diet often, and with good reason; it’s been for quite a while now the “Gold Standard” when it comes to scientific consensus on what constitutes a good diet for healthy longevity.
However, it’s easy to get stuck in a rut of cooking the same three meals and thinking “I must do something different, but not today, because I have these ingredients and don’t know what to cook” and then when one is grocery-shopping, it’s “I should have researched a new thing to cook, but since I haven’t, I’ll just get the ingredients for what I usually cook, since we need to eat”, and so the cycle continues.
This book will help break you out of that cycle! With (as the subtitle promises) hundreds of recipes, there’s no shortage of good ideas. The recipes are “plant-forward” rather than plant-based per se (i.e. there are some animal products in them), though for the vegetarians and vegans, it’s nothing that’s any challenge to substitute.
Bottom line: if you’re looking for “delicious and nutritious”, this book is sure to put a rainbow on your plate and a smile on your face.
Click here to check out More Mediterranean, and inspire your kitchen!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Insider’s Guide To Making Hospital As Comfortable As Possible
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Nobody Likes Surgery, But Here’s How To Make It Much Less Bad
This is Dr. Chris Bonney. He’s an anesthesiologist. If you have a surgery, he wants you to go in feeling calm, and make a quick recovery afterwards, with minimal suffering in between.
Being a patient in a hospital is a bit like being a passenger in an airplane:
- Almost nobody enjoys the thing itself, but we very much want to get to the other side of the experience.
- We have limited freedoms and comforts, and small things can make a big difference between misery and tolerability.
- There are professionals present to look after us, but they are busy and have a lot of other people to tend to too.
So why is it that there are so many resources available full of “tips for travelers” and so few “tips for hospital patients”?
Especially given the relative risks of each, and likelihood, or even near-certainty of coming to at least some harm… One would think “tips for patients” would be more in demand!
Tips for surgery patients, from an insider expert
First, he advises us: empower yourself.
Empowering yourself in this context means:
- Relax—doctors really want you to feel better, quickly. They’re on your side.
- Research—knowledge is power, so research the procedure (and its risks!). Dr. Bonney, himself an anesthesiologist, particularly recommends you learn what specific anesthetic will be used (there are many, and they’re all a bit different!), and what effects (and/or after-effects) that may have.
- Reframe—you’re not just a patient; you’re a customer/client. Many people suffer from MDeity syndrome, and view doctors as authority figures, rather than what they are: service providers.
- Request—if something would make you feel better, ask for it. If it’s information, they will be not only obliged, but also enthusiastic, to give it. If it’s something else, they’ll oblige if they can, and the worst case scenario is something won’t be possible, but you won’t know if you don’t ask.
Next up, help them to help you
There are various ways you can be a useful member of your own care team:
- Go into surgery as healthy as you can. If there’s ever a time to get a little fitter, eat a little healthier, prioritize good quality sleep more, the time approaching your surgery is the time to do this.
- This will help to minimize complications and maximize recovery.
- Take with you any meds you’re taking, or at least have an up-to-date list of what you’re taking. Dr. Bonney has very many times had patients tell him such things as “Well, let me see. I have two little pink ones and a little white one…” and when asked what they’re for they tell him “I have no idea, you’d need to ask my doctor”.
- Help them to help you; have your meds with you, or at least a comprehensive list (including: medication name, dosage, frequency, any special instructions)
- Don’t stop taking your meds unless told to do so. Many people have heard that one should stop taking meds before a surgery, and sometimes that’s true, but often it isn’t. Keep taking them, unless told otherwise.
- If unsure, ask your surgical team in advance (not your own doctor, who will not be as familiar with what will or won’t interfere with a surgery).
Do any preparatory organization well in advance
Consider the following:
- What do you need to take with you? Medications, clothes, toiletries, phone charger, entertainment, headphones, paperwork, cash for the vending machine?
- Will the surgeons need to shave anywhere, and if so, might you prefer doing some other form of depilation (e.g. waxing etc) yourself in advance?
- Is your list of medications ready?
- Who will take you to the hospital and who will bring you back?
- Who will stay with you for the first 24 hours after you’re sent home?
- Is someone available to look after your kids/pets/plants etc?
Be aware of how you do (and don’t) need to fast before surgery
The American Society of Anesthesiologists gives the following fasting guidelines:
- Non-food liquids: fast for at least 2 hours before surgery
- Food liquids or light snacks: fast for at least 6 hours before surgery
- Fried foods, fatty foods, meat: fast for at least 8 hours before surgery
(see the above link for more details)
Dr. Bonney notes that many times he’s had patients who’ve had the worst thirst, or caffeine headache, because of abstaining unnecessarily for the day of the surgery.
Unless told otherwise by your surgical team, you can have black coffee/tea up until two hours before your surgery, and you can and should have water up until two hours before surgery.
Hydration is good for you and you will feel the difference!
Want to know more?
Dr. Bonney has his own website and blog, where he offers lots of advice, including for specific conditions and specific surgeries, with advice for before/during/after your hospital stay.
He also has a book with many more tips like those we shared today:
Calm For Surgery: Supertips For A Smooth Recovery
Take good care of yourself!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Aging Is Inevitable… Or is it?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Aging is inevitable… Or is it?
We’ve talked before about how and why aging happens. We’ve also talked about the work to tackle aging as basically an engineering problem, with the premise that our bodies are biological machines, and machines can be repaired. We also recommended a great book about this, by the way. But that’s about interfering with the biological process of aging. What about if the damage is already done?
“When the damage is done, it’s done”
We can do a lot to try to protect ourselves from aging, and we might be able to slow down the clock, but we can’t stop it, and we certainly can’t reverse it… right?
Wrong! Or at least, so we currently understand, in some respects. Supplementation with phosphatidylserine, for example, has shown promise for not just preventing, but treating, neurodegeneration (such as that caused by Alzheimer’s disease). It’s not a magic bullet and so far the science is at “probably” and “this shows great promise for…” and “this appears to…”
Phosphatidylserene does help slow neurodegeneration
…because of its role in allowing your cells to know whether they have permission to die.
This may seem a flippant way of putting it, but it’s basically how cell death works. Cells do need to die (if they don’t, that’s called cancer) and be replaced with new copies, and those copies need to be made before too much damage is accumulated (otherwise the damage is compounded with each new iteration). So an early cell death-and-replacement is generally better for your overall health than a later one.
However, neurons are tricky to replace, so phosphatidylserine effectively says “not you, hold on” to keep the rate of neuronal cell death nearer to the (slow) rate at which they can be replaced.
One more myth to bust…
For the longest time we thought that adults, especially older adults, couldn’t make new brain cells at all, that we grew a certain number, then had to hang onto them until we died… suffering diminished cognitive ability with age, on account of losing brain cells along the way.
It’s partly true: it’s definitely easier to kill brain cells than to grow them… Mind you, that’s technically true of people, too, yet the population continues to boom!
Anyway, new research showing that adults do, in fact, grow new braincells was briefly challenged by a 2018 study that declared: Human hippocampal neurogenesis drops sharply in children to undetectable levels in adults after all, never mind, go back to your business.
So was adult neurogenesis just a myth to be busted after all? Nope.
It turned out, the 2018 study had a methodological flaw!
To put it in lay terms: they had accidentally melted the evidence.
A 2019 study overcame this flaw by using a shorter fixation time for the cell samples they wanted to look at, and found that there were tens of thousands of “baby neurons” (again with the lay terms), newly-made brain cells, in samples from adults ranging from 43 to 87.
Now, there was still a difference: the samples from the youngest adult had 30% more newly-made braincells than the 87-year-old, but given that previous science thought brain cell generation stopped in childhood, the fact that an 87-year-old was generating new brain cells 30% less quickly than a 43-year-old is hardly much of a criticism!
As an aside: samples from patients with Alzheimer’s also had a 30% reduction in new braincell generation, compared to samples from patients of the same age without Alzheimer’s. But again… Even patients with Alzheimer’s were still growing some new brain cells.
Read it for yourself: Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is abundant in neurologically healthy subjects and drops sharply in patients with Alzheimer’s disease
In a nutshell…
- We can’t fully hit pause on aging just yet, but we can definitely genuinely slow it
- We can also, in some very specific ways, reverse it
- We can slow the loss of brain cells
- We can grow new brain cells
- We can reduce our risk of Alzheimer’s, and at least somewhat mitigate it if it appears
- We know that phosphatidylserine supplementation may help with most (if not all) of the above
- We don’t sell that (or anything else) but for your convenience, here it is on Amazon if you’re interested
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Flossing Without Flossing?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Flossing Without Flossing?
You almost certainly brush your teeth. You might use mouthwash. A lot of people floss for three weeks at a time, often in January.
There are a lot of options for oral hygiene; variations of the above, and many alternatives too. This is a big topic, so rather than try to squeeze it all in one, this will be a several-part series.
The first part was: Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
How important is flossing?
Interdental cleaning is indeed pretty important, even though it may not have the heart health benefits that have been widely advertised:
However! The health of our gums is very important in and of itself, especially as we get older:
Flossing Is Associated with Improved Oral Health in Older Adults
But! It helps to avoid periodontal (e.g. gum) disease, not dental caries:
Flossing for the management of periodontal diseases and dental caries in adults
And! Most certainly it can help avoid a stack of other diseases:
Interdental Cleaning Is Associated with Decreased Oral Disease Prevalence
…so in short, if you’d like to have happy healthy teeth and gums, flossing is an important adjunct, and/but not a one-stop panacea.
Is it better to floss before or after brushing?
As you prefer. A team of scientists led by Dr. Claudia Silva studied this, and found that there was “no statistical difference between brush-floss and floss-brush”:
Flossing is tedious. How do we floss without flossing?
This is (mostly) about water-flossing! Which does for old-style floss what sonic toothbrushes to for old-style manual toothbrushes.
If you’re unfamiliar, it means using a device that basically power-washes your teeth, but with a very narrow high-pressure jet of water.
Do they work? Yes:
As for how it stacks up against traditional flossing, Liang et al. found:
❝In our previous single-outcome analysis, we concluded that interdental brushes and water jet devices rank highest for reducing gingival inflammation while toothpick and flossing rank last.
In this multioutcome Bayesian network meta-analysis with equal weight on gingival inflammation and bleeding-on-probing, the surface under the cumulative ranking curve was 0.87 for water jet devices and 0.85 for interdental brushes.
Water jet devices and interdental brushes remained the two best devices across different sets of weightings for the gingival inflammation and bleeding-on-probing. ❞
~ Journal of Evidence-Based Dental Practice
You may be wondering how safe it is if you have had dental work done, and, it appears to be quite safe, for example:
BDJ | Water-jet flossing: effect on composites
Want to try water-flossing?
Here are some examples on Amazon:
- Waterpik Complete Care 9.0 ← example of a top-end water-flossing device
- Philips Sonicare Power Flosser 3000 ← top-tier not-Waterpik-brand device
- INSMART Cordless Water Dental Flosser ← very low price and still average 4.5 star reviews, so in our opinion, a fine first choice
Bonus: if you haven’t tried interdental brushes, here’s an example for that
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: