Can You Reverse Gray Hair? A Dermatologist Explains
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Betteridge’s Law of Headlines states “any headline that ends in a question mark can be answered by the word no“—it’s not really a universal truth, but it’s true surprisingly often, and, as board certified dermatologist “The Beauty MD” Dr. Sam Ellis explains, it’s true in this case.
But, all is not lost.
Physiological Factors
Hair color is initially determined by genes and gene expression, instructing the body to color it with melanin (brown and black) and/or pheomelanin (blonde and red). If and when the body produces less of those pigments, our hair will go gray.
Factors that affect if/when our hair will go gray include:
- Genetics: primary determinant, essentially a programmed change
- Age: related to the above, but critically, the probability of going gray in any given year increases with age
- Ethnicity: the level of melanin in our skin is an indicator of how long we are likely to maintain melanin in our hair. Black people with the darkest skintones will thus generally go gray last, whereas white people with the lightest skintones will generally go gray first, and so on for a spectrum between the two.
- Medical conditions: immune conditions such as vitiligo, thyroid disease, and pernicious anemia promote an earlier loss of pigmentation
- Stress: oxidative stress, mainly, so factors like smoking will cause earlier graying. But yes, also chronic emotional stress does lead to oxidative stress too. Interestingly, this seems to be more about norepinephrine than cortisol, though.
- Nutrient deficiencies: the body can make a lot of things, but it needs the raw ingredients. Not having the right amounts of important vitamins and minerals will result in a loss of pigmentation (amongst other more serious problems). Vitamins B6, B9, and B12 are talked about in the video, as are iron and zinc. Copper is also needed for some hair colors. Selenium is needed for good hair health in general (but not too much, as an excess of selenium paradoxically causes hair loss), and many related things will stop working properly without adequate magnesium. Hair health will also benefit a lot from plenty of vitamin B7.
So, managing the above factors (where possible; obviously some of the above aren’t things we can influence) will result in maintaining one’s hair pigment for longer. As for texture, by the way, the reason gray hair tends to have a rougher texture is not for the lack of pigment itself, but is due to decreased sebum production. Judicious use of exogenous hair oils (e.g. argan oil, coconut oil, or whatever your preference may be) is a fine way to keep your grays conditioned.
However, once your hair has gone gray, there is no definitive treatment with good evidence for reversing that, at present. Dye it if you want to, or don’t. Many people (including this writer, who has just a couple of streaks of gray herself) find gray hair gives a distinguished look, and such harmless signs of age are a privilege not everyone gets to reach, and thus may be reasonably considered a cause for celebration
For more on all of the above, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Knowledge That Harvard Medical School’s Clinical Instructor Dr. Monique Tello Thinks Everyone SHOULD Have About Heart Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Anyone (who has not had a double mastectomy, anyway) can get breast cancer.
Breast cancer, if diagnosed early (before it spreads), has a 98% survival rate.
That survival rate drops to 31% if diagnosed after it has spread through the body.
(The US CDC’s breast cancer “stat bite” page has more stats and interactive graphs, so click here to see those charts and get the more detailed low-down on mortality/survival rates with various different situations)
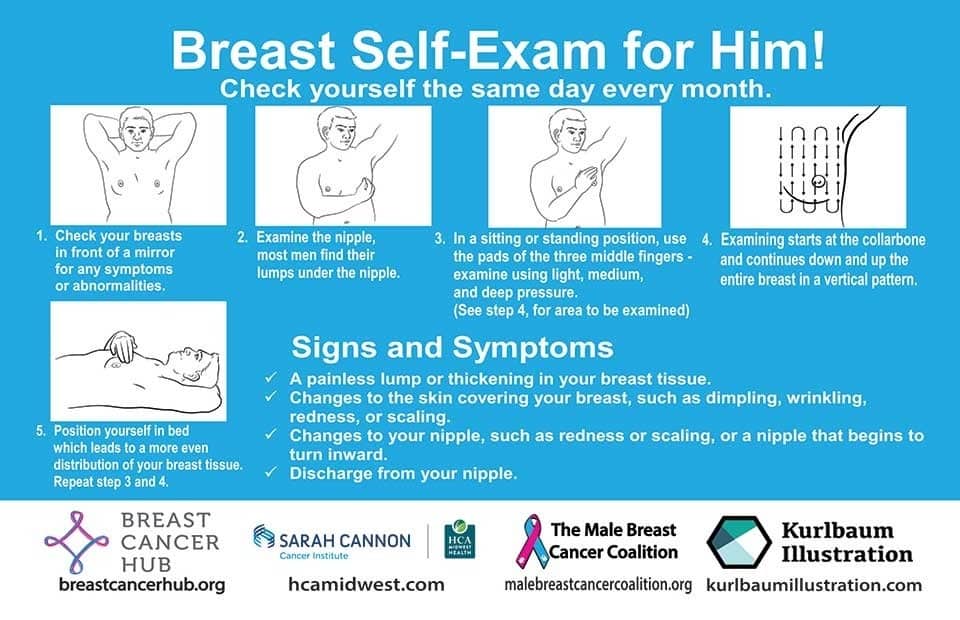
We think that the difference between 98% and 31% survival rates is more than enough reason to give ourselves a monthly self-check at the very least! You’ve probably seen how-to diagrams before, but here are instructions for your convenience:
This graphic created by the Jordan Breast Cancer Program (check them out, as they have lots of resources)
If you don’t have the opportunity to take matters into your own hands right now, rather than just promise yourself “I’ll do that later”, take this free 4-minute Breast Health Assessment from Aurora Healthcare. Again, we think the difference early diagnosis can make to your survival chances make these tests well worth it.
Lest we forget, men can also get breast cancer (the CDC has a page for men too), especially if over 50. But how do you check for breast cancer, when you don’t have breasts in the commonly-understood sense of the word?
So take a moment to do this (yes, really actually do it!), and set a reminder in your calendar to repeat it monthly—there really is no reason not to! Take care of yourself; you’re important.
Pssst! Did you scroll past the diagrams, looking for the online 4-minute test promised by the subtitle? If so, scroll back up; the link is in the middle!
Harvard Medical School’s Clinical Instructor’s Five-Point Plan for Heart Health
Dr. Monique Tello, M.D., M.P.H., is a practicing physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, director of research and academic affairs for the MGH DGM Healthy Lifestyle Program, clinical instructor at Harvard Medical School, and author of the evidence-based lifestyle change guide Healthy Habits for Your Heart.
Here are what she says are the five most important factors to help keep your ticker ticking:
5. Have (at most) a moderate alcohol intake! While there are polyphenols such as resveratrol in red wine that could boost heart health, there’s so little per glass that you may need 100–1000 glasses to get the dosage that provides benefits in mouse studies. If you’re not a mouse, it may not be as beneficial, and Dr. Tello recommends drinking no more than one glass per day of any alcohol. What constitutes a glass? It varies from one kind of drink to another, so here’s a handy guide.
4. Don’t smoke. Best of all to never start. But if you did, quit. Simple as that. There is no healthy amount of smoking. While paradoxically, quitting smoking may of course be stressful to you, the long term gains are considered more than worth it. As with all advice, do consult your own physician for guidance, as individual circumstances may vary, and that may change the best approach for you.
3. Maintain a healthy body weight. While BMI (Body Mass Index) is not a perfect system, it’s a system in popular use, and Dr. Tello recommends keeping a BMI between 18.5 and 24.9.
What’s your BMI? It takes into account your height and weight; here’s a Quick BMI Calculator for your convenience.
2. Keep a healthy level of physical activity—which ideally means at least 30 minutes per day vigorous activity, but obviously if you’re not used to this, take it slowly and build up over time. Even just small lifestyle changes (walking where possible, taking the stairs instead of the elevator where possible, etc) can add up to a big difference.
1. Enjoy a healthy diet. This is the single most important thing, and the best modern scientific consensus holds that the best diet contains plenty of vegetables, fruits and nuts, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids, while it avoids processed meats, sugar-sweetened beverages, trans fats (what are trans fats?), and too much sodium.
Share This Post
-
Fascia Hopping: The Powerful Over-50 Exercise You’re Probably Not Doing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A 62-year-old man reported feeling 10 years younger after just 8 days of fascia hopping. Now, anecdote ≠ data, but it seems worth investigating:
Let’s hop straight to it
Fascia is the web-like layer of connective tissue that divides your muscles and organs from each other. It simultaneously holds some stuff in place, and allows other parts to glide over each other with minimal friction.
At least, that’s what it’s supposed to do.
Like any body part, it can go wrong. And like any body part, it needs maintenance. In fascia’s case, the maintenance is to keep it slippy where it should be slippy and grippy where it should be grippy.
Here’s an exercise series for that, as described/shown in the video:
Prepping the fascia:
- Align posture: head lifted, shoulders down.
- Stretch fascia in all directions (up-down, left-right).
- Maintain a “fascia wetsuit” concept—taut but not unduly tense.
Springboard feet setup:
- Stand on balls of feet, heels slightly raised.
- Bounce gently to engage fascia elasticity.
“Fascia Strength & Power” dance:
- Move hips in a figure-eight motion.
- Keep shoulders relaxed, allowing movement to flow from the center.
Fascia hopping:
- Keep heels fixed, bounce lightly.
- Progress to small hops if possible.
- Maintain a smooth rhythm to activate elasticity.
Do these for 2 minutes daily for 7 days. It doesn’t have to be a dedicated exercise session; you can do it while you’re waiting for the water to boil in the kitchen, or things like that.
For more on these exercises plus visual demonstrations (it’s very simple), enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Fascia: Why (And How) You Should Take Care Of Yours
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Green Tea Allergies and Capsules
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Hey Sheila – As always, your articles are superb !! So, I have a topic that I’d love you guys to discuss: green tea. I used to try + drink it years ago but I always got an allergic reaction to it. So the question I’d like answered is: Will I still get the same allergic reaction if I take the capsules ? Also, because it’s caffeinated, will taking it interfere with iron pills, other vitamins + meds ? I read that the health benefits of the decaffeinated tea/capsules are not as great as the caffeinated. Any info would be greatly appreciated !! Thanks much !!❞
Hi! I’m not Sheila, but I’ll answer this one in the first person as I’ve had a similar issue:
I found long ago that taking any kind of tea (not herbal infusions, but true teas, e.g. green tea, black tea, red tea, etc) on an empty stomach made me want to throw up. The feeling would subside within about half an hour, but I learned it was far better to circumvent it by just not taking tea on an empty stomach.
However! I take an l-theanine supplement when I wake up, to complement my morning coffee, and have never had a problem with that. Of course, my physiology is not your physiology, and this “shouldn’t” be happening to either of us in the first place, so it’s not something there’s a lot of scientific literature about, and we just have to figure out what works for us.
This last Monday I wrote (inspired in part by your query) about l-theanine supplementation, and how it doesn’t require caffeine to unlock its benefits after all, by the way. So that’s that part in order.
I can’t speak for interactions with your other supplements or medications without knowing what they are, but I’m not aware of any known issue, beyond that l-theanine will tend to give a gentler curve to the expression of some neurotransmitters. So, if for example you’re talking anything that affects that (e.g. antidepressants, antipsychotics, ADHD meds, sleepy/wakefulness meds, etc) then checking with your doctor is best.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The FDA Just Redefined “Healthy”—But How?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In the ongoing war of labelling regulations (usually with advertisers on one side and regulators on the other), the FDA has updated what’s required in order to label a food as “healthy”.
Here’s what they’re now* requiring:
To bear the “healthy” claim, a food product needs to:
- Contain a certain amount of food (food group equivalent) from at least one of the food groups or subgroups (such as fruits, vegetables, fat-free and low-fat dairy etc.) recommended by the Dietary Guidelines.
- Adhere to specified limits for the following nutrients: saturated fat, sodium, and added sugars.
Source: FDA | Press Releases | FDA Finalizes Updated “Healthy” Nutrient Content Claim
*however, manufacturers have 3 years to conform, which if we’re being cynical about it, looks suspiciously like just short of a US presidential election cycle so that actual enforcement will be someone else’s problem.
Will it help?
Maybe! It’s not too dissimilar to the “traffic light system” already in use in Europe, although that currently emphasizes the absence/presence of “bad things” e.g. saturated fat, sodium, and added sugars.
It has its faults, because for example…
- not all saturated fat is bad, and a jar of coconut oil is now definitely going to get labelled as very unhealthy
- low-sodium salt is, ironically, going to to get flagged as being very high in sodium and therefore unhealthy
This latter is because on a g/100g basis, a product that’s ⅓ sodium chloride is going to have a lot of sodium, even if it’s approaching ⅔ less sodium than the product it’s (healthily!) replacing.
However, on a large scale, these kinds of problems are surely going to be small next to (hopefully) manufacturers scrambling to find ways to cut down on the saturated fats, sodium, and added sugars.
You may be wondering…
What will they replace them with?
Sometimes, companies trying to make something healthier will mess up, like when the health risks of smoking hit public consciousness, one cigarette company had the bright idea of putting asbestos in their filter tips, to market them as healthier. So, could something similar happen here?
- Saturated fat: definitely could; because the health benefits/risks of different kinds of fats and their constituent fatty acids are a lot more nuanced than just “saturated” vs “mono-/polyunsaturated”, it is definitely possible that companies may replace healthier saturated-heavy fats with less healthy unsaturated fats, depending on what is cheaper.
- See also: Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
- Sodium: probably not; likely go-to replacements for sodium chloride will be potassium chloride (healthier than sodium chloride) and MSG (has an unearned bad reputation in the US, but is healthier than sodium chloride).
- Added sugars: probably—things get very complicated very quickly when it comes to artificial sweeteners, and also the crux will definitely lie in what gets defined as an “added sugar”; watch out for a rise in the use of things that slide by the definition of added sugar while still being chemically (and, which is important, metabolically) the same thing.
Well that doesn’t sound great
It doesn’t, but on the flipside, the positive inclusions will probably be mostly good.
For example, the only way to get a “healthy” labelling in including fiber is to include more fiber, same with vitamins and minerals.
The low-fat dairy thing could possibly get abused (much like with the general “low-fat” trend of the 80s).
The “portion of fruit” thing will need to be carefully defined to avoid running straight back into the “this is just added sugar by another name” problem; mostly that it’ll need to still include the same amount of fiber as was in the whole fruit, gram for gram.
See also: What Matters Most For Your Heart? ← it’s about fiber, not salt or saturated fats!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to Read a Book – by Mortimer J. Adler and Charles Van Doren
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are you a cover-to-cover person, or a dip-in-and-out person?
Mortimer Adler and Charles van Doren have made a science out of getting the most from reading books.
They help you find what you’re looking for (Maybe you want to find a better understanding of PCOS… maybe you want to find the definition of “heuristics”… maybe you want to find a new business strategy… maybe you want to find a romantic escape… maybe you want to find a deeper appreciation of 19th century poetry, maybe you want to find… etc).
They then help you retain what you read, and make sure that you don’t miss a trick.
Whether you read books so often that optimizing this is of huge value for you, or so rarely that when you do, you want to make it count, this book could make a real difference to your reading experience forever after.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Discipline is Destiny – by Ryan Holiday
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed another of Holiday’s books, The Daily Stoic, and here is another excellent work from the same author.
We’re not a philosophy newsletter, but there are some things that make a big difference to physical and mental health, the habits we build, and the path we take in life for better or for worse.
Self-discipline is one of those things. A lot of the time, we know what we need to do, but knowing isn’t the problem. We need to actually do it! This applies to diet, exercise, sleep, and more.
Holiday gives us, in a casual easy-reading style, timeless principles to lock in strong discipline and good habits for life.
The book’s many small chapters, by the way, are excellent for reading a chapter-per-day as a healthy dose of motivation each morning, if you’re so inclined.
Bottom line: if you’ve noticed that one of the biggest barriers between you and your goals is actually doing the necessary things in a disciplined fashion, then this book will help you become more efficient, and actually get there.
Click here to check out Discipline is Destiny, and upgrade yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: