Is Cutting Calories The Key To Healthy Long Life?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Caloric Restriction with Optimal Nutrition
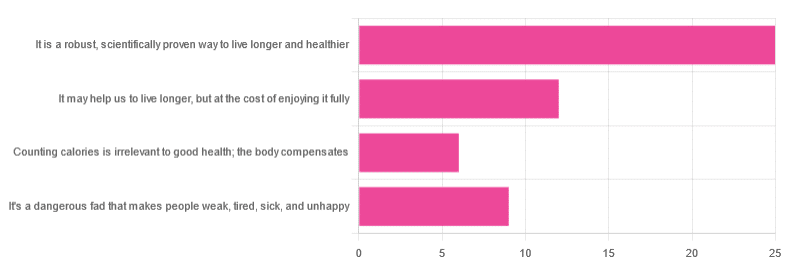
Yesterday, we asked you “What is your opinion of caloric restriction as a health practice?” and got the above-depicted, below-described spread of responses:
- 48% said “It is a robust, scientifically proven way to live longer and healthier”
- 23% said “It may help us to live longer, but at the cost of enjoying it fully”
- 17% said “It’s a dangerous fad that makes people weak, tired, sick, and unhealthy”
- 12% said “Counting calories is irrelevant to good health; the body compensates”
So… What does the science say?
A note on terms, first
“Caloric restriction” (henceforth: CR), as a term, sees scientific use to mean anything from a 25% reduction to a 50% reduction, compared to metabolic base rate.
This can also be expressed the other way around, “dropping to 60% of the metabolic base rate” (i.e., a 40% reduction).
Here we don’t have the space to go into much depth, so our policy will be: if research papers consider it CR, then so will we.
A quick spoiler, first
The above statements about CR are all to at least some degree True in one way or another.
However, there are very important distinctions, so let’s press on…
CR is a robust, scientifically proven way to live longer and healthier: True or False?
True! This has been well-studied and well-documented. There’s more science for this than we could possibly list here, but here’s a good starting point:
❝Calorie restriction (CR), a nutritional intervention of reduced energy intake but with adequate nutrition, has been shown to extend healthspan and lifespan in rodent and primate models.
Accumulating data from observational and randomized clinical trials indicate that CR in humans results in some of the same metabolic and molecular adaptations that have been shown to improve health and retard the accumulation of molecular damage in animal models of longevity.
In particular, moderate CR in humans ameliorates multiple metabolic and hormonal factors that are implicated in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer, the leading causes of morbidity, disability and mortality❞
Source: Ageing Research Reviews | Calorie restriction in humans: an update
See also: Caloric restriction in humans reveals immunometabolic regulators of health span
We could devote a whole article (or a whole book, really) to this, but the super-short version is that it lowers the metabolic “tax” on the body and allows the body to function better for longer.
CR may help us to live longer, but at the cost of enjoying it fully: True or False?
True or False, contingently, depending on what’s important to you. And that depends on psychology as much as physiology, but it’s worth noting that there is often a selection bias in the research papers; people ill-suited to CR drop out of the studies and are not counted in the final data.
Also, relevant for a lot of our readers, most (human-based) studies recruit people over 18 and under 60. So while it is reasonable to assume the same benefits will be carried over that age, there is not nearly as much data for it.
Studies into CR and Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) have been promising, and/but have caveats:
❝In non-obese adults, CR had some positive effects and no negative effects on HRQoL.❞
❝We do not know what degree of CR is needed to achieve improvements in HRQoL, but we do know it requires an extraordinary amount of support.
Therefore, the incentive to offer this intervention to a low-risk, normal or overweight individual is lacking and likely not sustainable in practice.❞
CR a dangerous fad that makes people weak, tired, sick, and unhealthy: True or False?
True if it is undertaken improperly, and/or without sufficient support. Many people will try CR and forget that the idea is to reduce metabolic load while still getting good nutrition, and focus solely on the calorie-counting.
So for example, if a person “saves” their calories for the day to have a night out in a bar where they drink their calories as alcohol, then this is going to be abysmal for their health.
That’s an extreme example, but lesser versions are seen a lot. If you save your calories for a pizza instead of a night of alcoholic drinks, then it’s not quite so woeful, but for example the nutrition-to-calorie ratio of pizza is typically not great. Multiply that by doing it as often as not, and yes, someone’s health is going to be in ruins quite soon.
Counting calories is irrelevant to good health; the body compensates: True or False?
True if by “good health” you mean weight loss—which is rarely, if ever, what we mean by “good health” here at 10almonds (unless we clarify such), but it’s a very common association and indeed, for some people it’s a health goal. You cannot sustainably and healthily lose weight by CR alone, especially if you’re not getting optimal nutrition.
Your body will notice that you are starving, and try to save you by storing as much fat as it can, amongst other measures that will similarly backfire (cortisol running high, energy running low, etc).
For short term weight loss though, yes, it’ll work. At a cost. That we don’t recommend.
❝By itself, decreasing calorie intake will have a limited short-term influence.❞
Source: Reducing Calorie Intake May Not Help You Lose Body Weight
See also…
❝Caloric restriction is a commonly recommended weight-loss method, yet it may result in short-term weight loss and subsequent weight regain, known as “weight cycling”, which has recently been shown to be associated with both poor sleep and worse cardiovascular health❞
Source: Dieting Behavior Characterized by Caloric Restriction
In summary…
Caloric restriction is a well-studied area of health science. We know:
- Practised well, it can extend not only lifespan, but also healthspan
- Practised well, it can improve mood, energy, sexual function, and the other things people fear losing
- Practised badly, it can be ruinous to the health—it is critical to practise caloric restriction with optimal nutrition.
- Practised badly, it can lead to unhealthy weight loss and weight regain
One final note…
If you’ve tried CR and hated it, and you practised it well (e.g., with optimal nutrition), then we recommend just not doing it.
You could also try intermittent fasting instead, for similar potential benefits. If that doesn’t work out either, then don’t do that either!
Sometimes, we’re just weird. It can often be because of a genetic or epigenetic quirk. There are usually workarounds, and/but not everything that’s right for most people will be right for all of us.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Unchaste Berry
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A Chasteberry, By Any Other Name…
Vitex agnus castus, literally “chaste lamb vine”, hence its modern common English name “chasteberry”, gets its name from its traditional use as an anaphrodisiac for monks (indeed, it’s also called “monk’s pepper”), which traditional use is not in the slightest backed up by modern science.
Nor is its second most popular traditional use (the increase in production of milk) well-supported by science either:
❝Its traditional use as a galactagogue (i.e., a substance that enhances breast milk production) is not well supported in the literature and should be discouraged. There are no clinical data to support the use of chasteberry for reducing sexual desire, which has been a traditional application❞
Source: American Family Physician | Chasteberry
Both of those supposed effects of the chasteberry go against the fact that it has a prolactin-lowering effect:
❝It appears that [chasteberry] may represent a potentially useful and safe phytotherapic option for the management of selected patients with mild hyperprolactinaemia who wish to be treated with phytotherapy.❞
Source: Vitex agnus castus effects on hyperprolactinaemia
Prolactin, by the way, is the hormone that (as the name suggests) stimulates milk production, and also reduces sexual desire (and motivation in general)
- In most women, it spikes during breastfeeding
- In most men, it spikes after orgasm
- In both, it can promote anhedonic depression, as it antagonizes dopamine
In other words, the actual pharmacological effect of chasteberry, when it comes to prolactin, is the opposite of what we would expect from its traditional use.
Ok, so it’s an unchaste berry after all…. Does it have any other claims to examine?
Yes! It genuinely does help relieve PMS, for those who have it, and reduce menopause symptoms, for those who have those, for example:
❝Dry extract of agnus castus fruit is an effective and well tolerated treatment for the relief of symptoms of the premenstrual syndrome.❞
❝That [Vitex agnus castus] trial indicated strong symptomatic relief of common menopausal symptoms❞
Source: Vitex agnus castus essential oil and menopausal balance: a research update
Is it safe?
Generally speaking, yes. It has been described as “well-tolerated” in the studies we mentioned above, which means it has a good safety profile.
However, it may interfere with some antipsychotic medications, certain kinds of hormone replacement therapy, or hormonal birth control.
As ever, speak with your doctor/pharmacist if unsure!
Where can I get some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
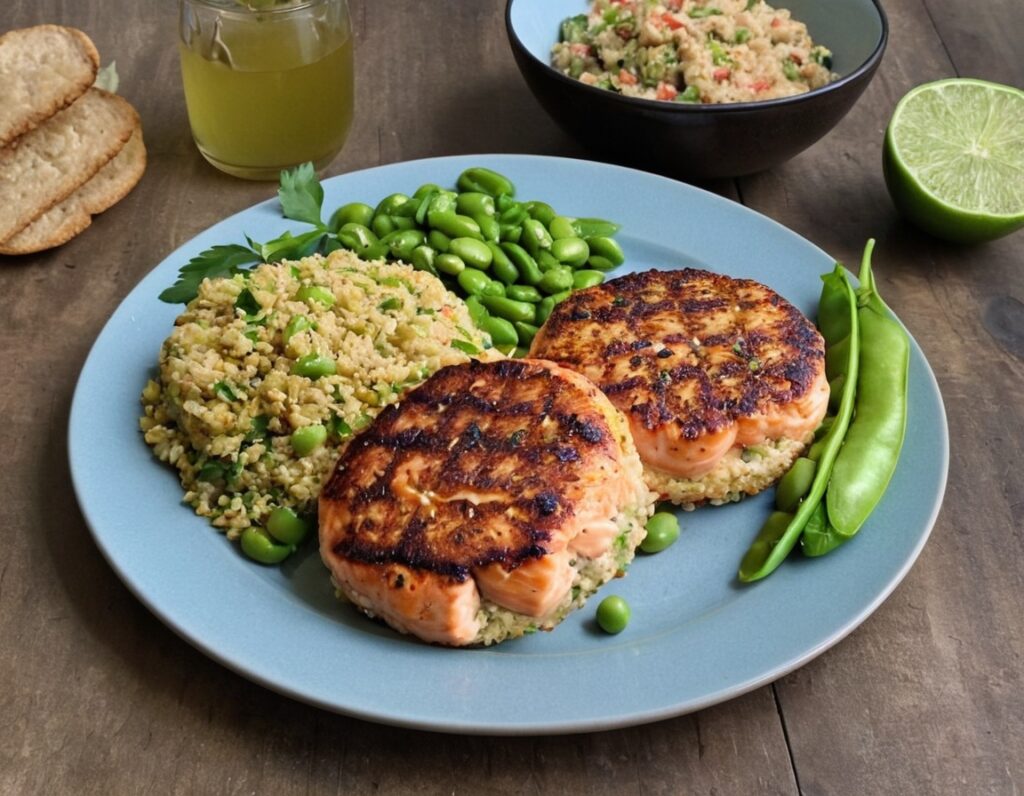
Green Curry Salmon Burgers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
These lean and healthy burgers are as quick and easy to make as they are good for entertaining. The serving-bed has its nutritional secrets too! All in all, an especially heart-healthy and brain-healthy dish.
You will need
- 4 skinless salmon fillets, cubed (Vegetarian/Vegan? Consider this Plant-Based Salmon Recipe or, since they are getting blended, simply substitute 1½ cups cooked chickpeas instead with 1 tbsp tahini)
- 2 cloves garlic, chopped
- 2 tbsp thai green curry paste
- juice of two limes, plus wedges to serve
- 1 cup quinoa
- ½ cup edamame beans, thawed if they were frozen
- large bunch fresh cilantro (or parsley if you have the “soap “cilantro tastes like soap” gene), chopped
- extra virgin olive oil, for frying
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Put the salmon, garlic, curry paste, nutritional yeast, and half the lime juice into a food processor, and blend until smooth.
2) Remove, divide into four parts, and shape into burger patty shapes. Put them in the fridge where they can firm up while we do the next bit.
3) Cook the quinoa with the tablespoon of chia seeds added (which means boiling water and then letting it simmer for 10–15 minutes; when the quinoa is tender and unfurled a little, it’s done).
4) Drain the quinoa with a sieve, and stir in the edamame beans, the rest of the lime juice, the cilantro, and the black pepper. Set aside.
5) Using the olive oil, fry the salmon burgers for about 5 minutes on each side.
6) Serve; we recommend putting the burgers atop the rest, and adding a dash of lime at the table.
(it can also be served this way!)
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Farmed Fish vs Wild–Caught
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Miss Diagnosis: Anxiety, ADHD, & Women
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Why is ADHD so often misdiagnosed as anxiety in women?❞
A great question! A short and slightly flippant answer could be “it’s the medical misogyny”:
Women and Minorities Bear the Brunt of Medical Misdiagnosis
…and if you’d like to learn more in-depth about this, we recommend this excellent book:
Unwell Women: Misdiagnosis and Myth in a Man-Made World – by Dr. Elinor Cleghorn ← you can read our review here
However, in this case there is more going on too!
Part of this is because ADHD is, like many psychiatric issues, a collection of symptoms that may or may not all always be present. Since clinical definitions are decided by clinicians, rather than some special natural law of the universe, sometimes this results in “several small conditions in a trenchcoat”, and if one symptom is or isn’t present, it can make things look quite different:
What’s The Difference Between ADD and ADHD?
There are two things at hand here: as in the above example, there’s the presence or absence of hyperactivity, but also, that “attention deficit”?
It’s often not really a deficit of attention, so much as the attention is going somewhere else—an example of naming psychiatric disorders for how they affect other people, rather than the person in question.
Sidenote: personality disorders really get the worst of this!
“You have a deep insecurity about never being good enough, and you constantly mess up in your attempt to overcompensate? You may have Evil Bastard Disorder!”
“You have a crippling fear of abandonment and that you are fundamentally unloveable, so you do all you can to try to keep people close? You must have Manipulative Bitch Disorder!”
etc
See also: Why Everyone You Don’t Like Is A Narcissist
In the case of ADHD and anxiety and women, a lot of this comes down to how the redirection of focus is perceived:
❝For some time, it has been held that women with ADHD are more likely to internalize symptoms and become anxious and depressed and to suffer emotional dysregulation❞
This internalization of symptoms, vs the externalization more generally perceived in boys and men, is more likely to be seen as anxiety.
Double standards also abound for social reasons, e.g:
- He is someone who thinks ten steps ahead and covers all bases
- She is anxious and indecisive and unable to settle on one outcome
Here’s a very good overview of how this double-standard makes its way into diagnostic processes, along with other built-in biases:
Miss. Diagnosis: A Systematic Review of ADHD in Adult Women
Want to learn more?
We’ve reviewed quite a few books about ADHD, but if we had to pick one to spotlight, we’d recommend this one:
The Silent Struggle: Taking Charge of ADHD in Adults – by L. William Ross-Child, MLC
Enjoy! And while we have your attention… Would you like this section to be bigger? If so, send us more questions!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A spoonful of pepper makes the… Hang on, no, that’s not right…
We know that spices are the spice of life, and many have great health-giving qualities. But…
- How much is the right amount?
- What’s the minimum to get health benefits?
- What’s the maximum to avoid toxicity?
That last one always seems like a scary question, but please bear in mind: everything is toxic at a certain dose. Oxygen, water, you-name-it.
On the other hand, many things have a toxicity so low that one could not physically consume it sufficiently faster than the body eliminates it, to get a toxic build-up.
Consider, for example, the €50 banknote that was nearly withdrawn from circulation because one of the dyes used in it was found to be toxic. However, the note remained in circulation after scientists patiently explained that a person would have to eat many thousands of them to get a lethal dose.
So, let’s address these questions in reverse order:
What’s the maximum to avoid toxicity?
In the case of the spices we’ll look at today, the human body generally* has high tolerance for them if eaten at levels that we find comfortable eating.
*IMPORTANT NOTE: If you have (or may have) a medical condition that may be triggered by spices, go easier on them (or if appropriate, abstain completely) after you learn about that.
Check with your own physician if unsure, because not only are we not doctors, we’re specifically not your doctors, and cannot offer personalized health advice.
We’re going to be talking in averages and generalizations here. Caveat consumator.
For most people, unless you are taking the spice in such quantities that you are folding space and seeing the future, or eating them as the main constituents of your meal rather than an embellishment, you should be fine. Please don’t enter a chilli-eating contest and sue us.
What is the minimum to get health benefits and how much should we eat?
The science of physiology generally involves continuous rather than discrete data, so there’s not so much a hard threshold, as a point at which the benefits become significant. The usefulness of most nutrients we consume, be they macro- or micro-, will tend to have a bell curve.
In other words, a tiny amount won’t do much, the right amount will have a good result, and usefulness will tail off after that point. To that end, we’re going to look at the “sweet spot” of peaking on the graph.
Also note: the clinical dose is the dose of the compound, not the amount of the food that one will need to eat to get that dose. For example, food x containing compound y will not usually contain that compound at 100% rate and nothing else. We mention this so that you’re not surprised when we say “the recommended dose is 5mg of compound, so take a teaspoon of this spice”, for example.
Further note: we only have so much room here, so we’re going to list only the top benefits, and not delve into the science of them. You can see the related main features for more details, though!
The “big 5” health-giving spices, with their relevant active compound:
- Black pepper (piperine)
- Hot pepper* (capsaicin)
- Garlic (allicin)
- Ginger (gingerol)
- Turmeric (curcumin**)
*Cayenne pepper is very high in capsaicin; chilli peppers are also great
**not the same thing as cumin, which is a completely different plant. Cumin does have some health benefits of its own, but not in the same league as the spices above, and there’s only so much we have room to cover today.
Black pepper
- Benefits: antioxidant, anti-cancer, boosts bioavailability of other nutrients, aids digestion
- Dosage: 5–20mg for benefits
- Suggestion: ½ teaspoon of black pepper is sufficient for benefits. However, this writer’s kitchen dictum in this case is “if you can’t see the black pepper in/on the food, add more”—but that’s more about taste!
- Related main feature: Black Pepper’s Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
Hot Pepper
- Benefits: anti-inflammatory, metabolism accelerator
- Dosage: 6mg gives benefits, 500mg is a common dose in capsules
- Suggestion: if not making a spicy dish, consider using a teaspoon of cayenne as part of the seasoning for rice or potatoes
- Related main feature: Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
Garlic
- Benefits: heart health, blood sugar balancing, anti-cancer
- Dosage: 4–8µg for benefits
- Suggestion: 1–2 cloves daily is generally good. However, cooking reduces allicin content (and so does oxidation after cutting/crushing), so you may want to adjust accordingly if doing those things.
- Related main feature: The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
Ginger
- Benefits: anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-nausea
- Dosage: 3–4g for benefits
- Suggestion: 1 teaspoon grated raw ginger or ½ a teaspoon powdered ginger, can be used in baking or as part of the seasoning for a stir-fry
- Related main feature: Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
Turmeric
- Benefits: anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer
- Dosage: 500–2000mg for benefits
- Suggestion: ¼ teaspoon per day is sufficient for benefits; ½ teaspoon dropped into the water when cooking rice will infuse the rice with turmeric (which is very water-soluble), turn the rice a pretty golden color, and not affect the flavor. Throw in some black pepper as it increases the bioavailability of curcumin up to 2000%
- Related main feature: Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
Closing notes
The above five spices are very healthful for most people. Personal physiology can and will vary, so if in doubt, a) check with your doctor b) start at lowest doses and establish your tolerance (or lack thereof).
Enjoy, and stay well!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Seven Things To Do For Good Lung Health!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
YouTube Channel Wellness Check is challenging us all to do the following things. They’re framing it as a 30-day challenge, but honestly, there’s nothing here that isn’t worth doing for life
Here’s the list:
- Stop smoking (of course, smoking is bad for everything, but the lungs are one of its main areas of destruction)
- Good posture (a scrunched up chest is not the lungs’ best operating conditions!)
- Regular exercise (exercising your body in different ways exercises your lungs in different ways!)
- Monitor air quality (some environments are much better/worse than others, but don’t underestimate household air quality threats either)
- Avoid respiratory infections (shockingly, COVID is not great for your lungs, nor are the various other respiratory infections available)
- Check your O2 saturation levels (pulse oximeters like this one are very cheap to buy and easy to use)
- Prevent mucus and phlegm from accumulating (these things are there for reasons; the top reason is trapping pathogens, allergens, and general pollutants/dust etc; once those things are trapped, we don’t want that mucus there any more!)
Check out the video itself for more detail on each of these items:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to know more?
You might like our article about COPD:
Why Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Is More Likely Than You Think
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Elderly loss of energy
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Please please give some information on elderly loss of energy and how it can be corrected. Please!❞
A lot of that is the metabolic slump described above! While we certainly wouldn’t describe 60 as elderly, and the health impacts from those changes at 45–55 get a gentler curve from 60 onwards… that curve is only going in one direction if we don’t take exceptionally good care of ourselves.
And of course, there’s also a degree of genetic lottery, and external factors we can’t entirely control (e.g. injuries etc).
One factor that gets overlooked a lot, though, is really easy to fix: B-vitamins.
In particular, vitamins B1, B5, B6, and B12. Of those, especially vitamins B1 and B12.
(Vitamins B5 and B6 are critical to health too, but relatively few people are deficient in those, while many are deficient in B1 and/or B12, especially as we get older)
Without going so detailed as to make this a main feature: these vitamins are essential for energy conversion from food, and they will make a big big difference.
You might especially want to consider taking sulbutiamine, which is a synthetic version of thiamin (vitamin B1), and instead of being water-soluble, it’s fat-soluble, and it easily crosses the blood-brain barrier, which is a big deal.
As ever, always check with your doctor because your needs/risks may be different. Also, there can be a lot of reasons for fatigue and you wouldn’t want to overlook something important.
You might also want to check out yesterday’s sponsor, as they offer personalized at-home health testing to check exactly this sort of thing.
❝What are natural ways to lose weight after 60? Taking into account bad knees or ankles, walking may be out as an exercise, running certainly is.❞
Losing weight is generally something that comes more from the kitchen than the gym, as most forms of exercise (except HIIT; see below) cause the metabolism to slow afterwards to compensate.
However, exercise is still very important, and swimming is a fine option if that’s available to you.
A word to the wise: people will often say “gentle activities, like tai chi or yoga”, and… These things are not the same.
Tai chi and yoga both focus on stability and suppleness, which are great, but:
- Yoga is based around mostly static self-support, often on the floor
- Tai chi will have you very often putting most of your weight on one slowly-increasingly bent knee at a time, and if you have bad knees, we’ll bet you winced while reading that.
So, maybe skip tai chi, or at least keep it to standing meditations and the like, not dynamic routines. Qigong, the same breathing exercises used in tai chi, is also an excellent way to improve your metabolism, by the way.
Ok, back onto HIIT:
You might like our previous article: How To Do HIIT* (Without Wrecking Your Body)
*High-Intensity Interval Training (the article also explains what this is and why you want to do it)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: