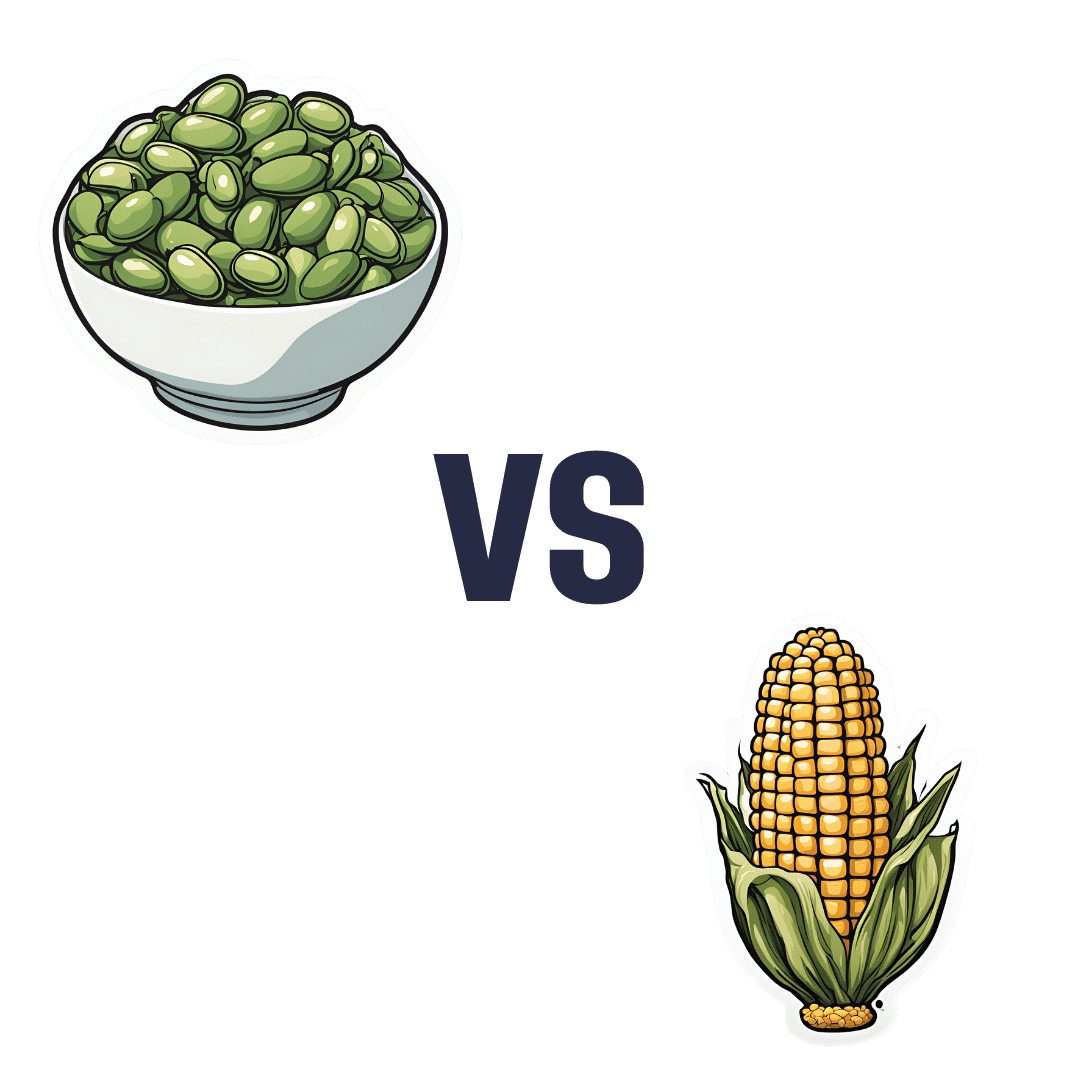
Broad Beans vs Sweetcorn – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing broad beans to sweetcorn, we picked the broad beans.
Why?
Firstly, you may be wondering: “aren’t broad beans fava beans?”, and yes, yes they are, but by convention, broad beans are the young green beans, while fava beans are the mature beans of the plant. Similar situation to the relationship between edamame and soybeans. And, in both cases, you’re more likely to put the young green beans in a salad, thus making the broad beans the more reasonable vegetable to compare to the sweetcorn. On which note…
In terms of macros, the broad beans have more protein and fiber, while the sweetcorn has more carbs. We call that a win for the beans.
Looking at the vitamins, the broad beans have (barely) more vitamin B6, while the sweetcorn has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B5, B9, E, and choline. An easy win for the corn this time.
In the category of minerals, the situation is reversed: broad beans have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while sweetcorn is not higher in any minerals. So, a clear win for the beans.
Adding up the sections gives a 2:1 win for the beans over the corn, but by all means enjoy either or both—together is great, and diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Air Purifiers & Sleep
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I’ve read that air pollution has a negative effect on sleep quality and duration. Since I live next to a busy road, I was wondering whether I should invest in an air purifier. What are 10Almonds’s views?❞
Going straight to the science, there are two questions here:
- Does air pollution negatively affect sleep quality and duration?
- Does the use of an air purify actually improve the air quality in the way(s) necessary to make a difference?
We thought we’d have to tackle these questions separately, but we did find one study that addressed your question directly. It was a small study (n=30 if you believe the abstract; n=29 if you read the paper itself—one person dropped out); the results were modest but clear:
❝The purifier filter was associated with increased total sleep time for an average of 12 min per night, and increased total time in bed for an average of 19 min per night relative to the placebo.
There were several sleep and mood outcomes for which no changes were observed, and time awake after sleep onset was higher for the purifier filter. Air quality was better during the high-efficiency particulate air filter condition.
These findings offer positive indications that environmental interventions that improve air quality can have benefits for sleep outcomes in healthy populations who are not exhibiting clinical sleep disturbances.❞
In the above-linked paper’s introduction, it does establish the deleterious effect of air pollution on a wide variety of health metrics, including sleep, this latter evidenced per Caddick et al. (2018): A review of the environmental parameters necessary for an optimal sleep environment
Now, you may be wondering: is an extra 12 minutes per night worth it?
That’s your choice to make, but we would argue that it is. We can make many choices in our lives that affect our health slightly for the better or the worse. If we make a stack of choices in a particular direction, the effects will also stack, if not outright compound.
So in the case of sleep, it might be (arbitrary numbers for the sake of illustration):
- Get good exercise earlier in the day (+3%)
- Get good food earlier in the day (+2.5%)
- Practice mindfulness/meditation before bed (+2.5%)
- Have a nice dark room (+5%)
- Have fresh bedding (+2.5%)
- Have an air purifier running (+3%)
Now, those numbers are, as we said, arbitrary*, but remember that percentages don’t add up; they compound. So that “+3%” starts being a lot more meaningful than if it were just by itself.
*Confession: the figure of 3% for the air purifier wasn’t entirely arbitrary; it was based on 100(12/405) = 80/27 ≈ 3, wherein the 405 figure was an approximation of the average total time (in minutes) spent sleeping with placebo, based on a peep at their results graph. There are several ways the average could be reasonably calculated, but 6h45 (i.e., 405 minutes) was an approximate average of those reasonable approximate averages.
So, 12 minutes is a 3% improvement on that.
Don’t have an air purifier and want one?
We don’t sell them, but here’s an example on Amazon, for your convenience
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The voice in your head may help you recall and process words. But what if you don’t have one?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Can you imagine hearing yourself speak? A voice inside your head – perhaps reciting a shopping list or a phone number? What would life be like if you couldn’t?
Some people, including me, cannot have imagined visual experiences. We cannot close our eyes and conjure an experience of seeing a loved one’s face, or imagine our lounge room layout – to consider if a new piece of furniture might fit in it. This is called “aphantasia”, from a Greek phrase where the “a” means without, and “phantasia” refers to an image. Colloquially, people like myself are often referred to as having a “blind mind”.
While most attention has been given to the inability to have imagined visual sensations, aphantasics can lack other imagined experiences. We might be unable to experience imagined tastes or smells. Some people cannot imagine hearing themselves speak.
A recent study has advanced our understanding of people who cannot imagine hearing their own internal monologue. Importantly, the authors have identified some tasks that such people are more likely to find challenging.
fizkes/Shutterstock What the study found
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark and at the University of Wisconsin-Madison in the United States recruited 93 volunteers. They included 46 adults who reported low levels of inner speech and 47 who reported high levels.
Both groups were given challenging tasks: judging if the names of objects they had seen would rhyme and recalling words. The group without an inner monologue performed worse. But differences disappeared when everyone could say words aloud.
Importantly, people who reported less inner speech were not worse at all tasks. They could recall similar numbers of words when the words had a different appearance to one another. This negates any suggestion that aphants (people with aphantasia) simply weren’t trying or were less capable.
Hearing our own imagined voice may play an important role in word processing. sutadimages/Shutterstock A welcome validation
The study provides some welcome evidence for the lived experiences of some aphants, who are still often told their experiences are not different, but rather that they cannot describe their imagined experiences. Some people feel anxiety when they realise other people can have imagined experiences that they cannot. These feelings may be deepened when others assert they are merely confused or inarticulate.
In my own aphantasia research I have often quizzed crowds of people on their capacity to have imagined experiences.
Questions about the capacity to have imagined visual or audio sensations tend to be excitedly endorsed by a vast majority, but questions about imagined experiences of taste or smell seem to cause more confusion. Some people are adamant they can do this, including a colleague who says he can imagine what combinations of ingredients will taste like when cooked together. But other responses suggest subtypes of aphantasia may prove to be more common than we realise.
The authors of the recent study suggest the inability to imagine hearing yourself speak should be referred to as “anendophasia”, meaning without inner speech. Other authors had suggested anauralia (meaning without auditory imagery). Still other researchers have referred to all types of imagined sensation as being different types of “imagery”.
Having consistent names is important. It can help scientists “talk” to one another to compare findings. If different authors use different names, important evidence can be missed.
We’re starting to broaden our understanding of the senses and how we imagine them. Napat Chaichanasiri/Shutterstock We have more than 5 senses
Debate continues about how many senses humans have, but some scientists reasonably argue for a number greater than 20.
In addition to the five senses of sight, smell, taste, touch and hearing, lesser known senses include thermoception (our sense of heat) and proprioception (awareness of the positions of our body parts). Thanks to proprioception, most of us can close our eyes and touch the tip of our index finger to our nose. Thanks to our vestibular sense, we typically have a good idea of which way is up and can maintain balance.
It may be tempting to give a new name to each inability to have a given type of imagined sensation. But this could lead to confusion. Another approach would be to adapt phrases that are already widely used. People who are unable to have imagined sensations commonly refer to ourselves as “aphants”. This could be adapted with a prefix, such as “audio aphant”. Time will tell which approach is adopted by most researchers.
Why we should keep investigating
Regardless of the names we use, the study of multiple types of inability to have an imagined sensation is important. These investigations could reveal the essential processes in human brains that bring about a conscious experience of an imagined sensation.
In time, this will not only lead to a better understanding of the diversity of humans, but may help uncover how human brains can create any conscious sensation. This question – how and where our conscious feelings are generated – remains one of the great mysteries of science.
Derek Arnold, Professor, School of Psychology, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
You Are the One You’ve Been Waiting For – by Dr. Richard Schwartz
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As self-therapy approaches go, the title here could be read two ways: as pop-psychology fluff, or a suggestion of something deeper. And, while written in a way to make it accessible to all, we’re happy to report the content consists of serious therapeutic ideas, presented clearly.
Internal Family Systems (IFS) is a large, internationally recognized, and popular therapeutic approach. It’s also an approach that lends itself quite well to self-therapy, as this book illustrates.
Dr. Schwartz kicks off by explaining not IFS, but the problem that it solves… We (most of us, anyway) have over the course of our lives tried to plug the gaps in our own unmet psychological needs. And, that can cause resentment, strain, and can even be taken out on others if we’re not careful.
The real meat of the book, however, is in its illustrative explanations of how IFS works, and can be applied by an individual. The goal is to recognize all the parts that make us who we are, understand what they need in order to be at peace, and give them that. Spoiler: most what they will need is just being adequately heard, rather than locked in a box untended.
One of the benefits of using this book for self-therapy, of course, is that it requires a lot less vulnerability with a third party.
But, speaking of which, what of these intimate relationships the subtitle of the book referenced? Mostly the benefits to such come from a “put your own oxygen mask on first” angle… but the book does also cover discussions between intimate partners, and approaches to love, including what the author calls “courageous love”.
Bottom line: this is a great book if you want to do some “spring-cleaning of the soul” and live a little more lightly as a result.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How Your Exercise Today Gives A Brain Boost Tomorrow
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Regular 10almonds readers may remember we not long back wrote about a study that showed how daily activity levels, in aggregate, make a difference to brain health over the course of 1–2 weeks (in fact, it was a 9-day study):
Daily Activity Levels & The Measurable Difference They Make To Brain Health
Today, we’re going to talk about a new (published today, at time of writing) study that shows the associations between daily exercise levels (amongst other things) and how well people performed in cognitive tests the next day.
By this we mean: they recorded exercise vs sedentary behavior vs sleep on a daily basis (using wearable tech to track it), and tested them daily with cognitive tests, and looked at how the previous day’s activities (or lack thereof) impacted the next day’s test results.
Notably, the sample was of older adults (aged 50–83). The sample size wasn’t huge but was statistically significant (n=76) and the researchers are of course calling for more studies to be done with more people.
What they found
To put their findings into few words:
- Consistent light exercise boosts general cognitive performance not just for hours (which was already known) but through the next day.
- More moderate or vigorous activity than usual in particular led to better working memory and episodic memory the next day.
- More sleep (especially slow-wave deep sleep) improved episodic memory and psychomotor speed.
- Sedentary behavior was associated with poorer working memory.
Let’s define some terms:
- general cognitive performance = average of scores across the different tests
- working memory = very short term memory, such as remembering what you came into this room for, or (as an example of a test format) being able to take down a multi-digit number in one go without it being broken down (and then, testing with longer lengths of number until failure)
- episodic memory = memory of events in a narrative context, where and when they happened, etc
- psychomotor speed = the speed of connection between perception and reaction in quick-response tests
These are, of course, all useful things to have, which means the general advice here is to:
- move more, generally
- exercise more, specifically
- sit less, whenever reasonably possible
- sleep well
You can read the study itself here:
Want to know the best kind of exercise for brain health?
Check out our article about neuroscientist Dr. Suzuki, and what she has to say about it:
The Exercise That Protects Your Brain
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Natto, Taurine + Black Pepper, And Other Game-Changers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Loved the info on nuts; of course I always eat pecans, which didn’t make the list of healthy nuts!❞
Dear subscriber, pardon the paraphrase of your comment—somehow it got deleted and now exists only in this writer’s memory. However, to address it:
Pecans are great too! We can’t include everything in every article (indeed, we got another feedback the same day saying the article was too long), but we love when you come to us with stuff for us to look at and write about (seriously, writer here: the more you ask, the easier it makes my job), so let’s talk pecans for a moment:
Pecans would have been number six on our list if we’d have written more!
Like many nuts, they’ve an abundance of healthy fats, fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
They’re particularly good for zinc, which is vital for immune function, healing (including normal recovery after normal exercise), and DNA synthesis (so: anti-aging).
Pecans are also great for reducing LDL (“bad” cholesterol) and triglycerides (which are also bad for heart health); check it out:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Body Image Dissatisfaction/Appreciation Across The Ages
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Every second news article about body image issues is talking about teens and social media use, but science tells a different story.
A large (n=1,327) study of people of mixed genders aged 16–88 examined matters relating to people’s body image, expecting…
❝We hypothesized that body dissatisfaction and importance of appearance would be higher in women than in men, that body dissatisfaction would remain stable across age in women, and that importance of appearance would be lower in older women compared to younger women. Body appreciation was predicted to be higher in men than in women.❞
As they discovered, only half of that turned out to be true:
❝In line with our hypotheses, body dissatisfaction was higher in women than in men and was unaffected by age in women, and importance of appearance was higher in women than in men.
However, only in men did age predict a lower level of the importance of appearance. Compared to men, women stated that they would invest more hours of their lives to achieve their ideal appearance.
Contrary to our assumption, body appreciation improved and was higher in women across all ages than in men.❞
You can read the study in full here:
That’s a lot of information, and we don’t have the space to go into all parts of it here, fascinating as that would be. So we’re going to put two pieces of information (from the above) next to each other:
- body dissatisfaction was higher in women than in men and was unaffected by age in women
- body appreciation improved and was higher in women across all ages than in men
…and resolve this apparent paradox.
Dissatisfied appreciation
How is it that women are both more dissatisfied with, and yet also more appreciative of, their bodies?
The answer is that we can have positive and negative feelings about the same thing, without them cancelling each other out. In short, simply, feeling more feelings about it.
Whether the gender-related disparity in this case comes more from hormones or society could be vigorously debated, but chances are, it’s both. And, for our gentleman-readers, note that the principle still applies to you, even if scaled down on average.
Call to action:
- be aware of the negative feelings of body dissatisfaction
- focus on the positive feelings of body appreciation
While in theory both could motivate us to action, in reality, the former will tend to inform us (about what we might wish to change), while the latter will actually motivate us in a useful way (to do something positive about it).
This is because the negative feelings about body image tend to be largely based in shame, and shame is a useless motivator (i.e., it simply doesn’t work) when it comes to taking positive actions:
Why Shame Only Works Negatively
You can’t hate yourself into a body you love
That may sound like a wishy-washy platitude, but given the evidence on how shame works (and doesn’t), it’s true.
Instead, once you’ve identified the things about your body with which you’re dissatisfied, you can then assess:
- what can reasonably be changed
- whether it is important enough to you to change it
- how to go about usefully changing it
While weight issues are perhaps the most commonly-discussed body image consideration, to the point that often all others get forgotten, let’s look at something that’s generally more specific to adults, and also a very common cause of distress for women and men alike: hair loss/thinning.
If your hair is just starting to thin and fall, then if this bothers you, there’s a lot that can be done about it quite easily, but (and this is important) you have to love yourself enough to actually do it. Merely feeling miserable about it, and perhaps like you don’t deserve better, or that it is somehow a personal failing on your part, will not help.
If your hair has been gone for years, then chances are you’ve made your peace with this by now, and might not even take it back if a fairy godmother came along and offered to restore it magically. On the other hand, let’s say that you’re just coming out the other end of a 10-year-long depression, and perhaps you let a lot of things go that you now wish you hadn’t, and maybe your hair is one of them. In this case, now you need to decide whether getting implants (likely the only solution at this late stage) is worth it.
Note that in both cases, whatever the starting point and whether the path ahead is easy or hard, the person who has dissatisfaction and/but still values themself and their body will get what they need.
In contrast, the person who has dissatisfaction and does not value themself and their body, will languish.
The person without dissatisfaction, of course, probably already has what they need.
In short: identification of dissatisfaction + love and appreciation of oneself and one’s body → motivation to usefully take action (out of love, not hate)
Now, dear reader, apply the same thinking to whatever body image issues you may have, and take it from there!
Embodiment
A quick note in closing: if you are a person with no body dissatisfactions, there are two main possible reasons:
- You are genuinely happy with your body in all respects. Congratulations!
- You have disassociated from your body to such an extent that it’s become a mere vehicle to you and you don’t care about it.
This latter may seem like a Zen-level win, but in fact it’s a warning sign for depression, so please do examine that even if you don’t “feel” depressed (depression is often characterized by a lack of feelings), perhaps by taking the (very quick) free PHQ9 Test ← under 2 minutes; immediate results; industry-standard diagnostic tool
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: