Breast Milk’s Benefits That Are (So Far) Not Replicable
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Simply The Breast 🎶
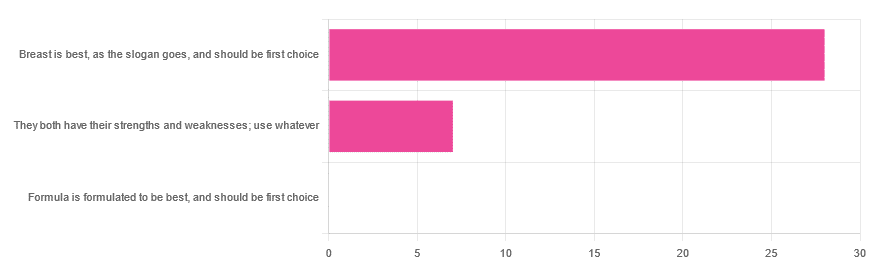
In Wednesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion on breast vs formula milk (for babies!), and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- 80% said “Breast is best, as the slogan goes, and should be first choice”
- 20% said “They both have their strengths and weaknesses; use whatever”
- 0% said “Formula is formulated to be best, and should be first choice”
That’s the first time we’ve ever had a possible poll option come back with zero votes whatsoever! It seems this topic is relatively uncontentious amongst our readership, so we’ll keep things brief today, but there is still a little mythbusting to be done.
So, what does the science say?
[Breast milk should be the first choice] at least for the few few weeks and months for the benefit of baby’s health as breast milk has protective factors formula does not: True or False?
True! The wording here was taken from one of our readers’ responses, by the way (thank you, Robin). There are a good number of those protective factors, the most well-known of which is passing on immune cells and cell-like things; in other words, immune-related information being passed from parent* to child.
*usually the mother, though in principle it could be someone else and in practice sometimes it is; the only real requirements are that the other person be healthy, lactating, and willing.
As for immune benefits, see for example:
Perspectives on Immunoglobulins in Colostrum and Milk
And for that matter, also:
(Colostrum is simply the milk that is produced for a short period after giving birth; the composition of milk will tend to change later)
In any case, immunoglobulin A is a very important component in breast milk (colostrum and later), as well as lactoferrin (has an important antimicrobial effect and is good for the newborn’s gut), and a plethora of cytokines:
As for that about the gut, lactoferrin isn’t the only breast milk component that benefits this, by far, and there’s a lot that can’t be replicated yet:
Human Breast Milk and the Gastrointestinal Innate Immune System
As long as your infant/child is nutritiously fed, it shouldn’t matter if it comes from breast or formula: True or False?
False! Formula milk will not convey those immune benefits.
This doesn’t mean that formula-feeding is neglectful; as several people who commented mentioned*, there are many reasons a person may not be able to breastfeed, and they certainly should not be shamed for that.
*(including the reader whose words we borrowed for this True/False item; the words we quoted above were prefaced with: “Not everyone is able to breastfeed for many different reasons”)
But, while formula milk is a very good second choice, and absolutely a respectable choice if breast milk isn’t an option (or an acceptable option) for whatever reason, it still does not convey all the health benefits of breast milk—yet! The day may come when they’ll find a way to replicate the immune benefits, but today is not that day.
They both have their strengths and weaknesses: True or False?
True! But formula’s strengths are only in the category of convenience and sometimes necessity—formula conveys no health benefits that breast milk could not do better, if available.
For many babies, formula means they get to eat, when without it they would starve due to non-availability of breast milk. That’s a pretty important role!
Note also: this is a health science publication, not a philosophical publication, but we’d be remiss not to mention one thing; let’s bring it in under the umbrella of sociology:
The right to bodily autonomy continues to be the right to bodily autonomy even if somebody else wants/needs something from your body.
Therefore, while there are indeed many good reasons for not being able to breastfeed, or even just not being safely* able to breastfeed, it is at the very least this writer’s opinion that nobody should be pressed to give their reason for not breastfeeding; “no” is already a sufficient answer.
*Writer’s example re safety: when I was born, my mother was on such drugs that it would have been a very bad idea for her to breastfeed me. There are plenty of other possible reasons why it might be unsafe for someone one way or another, but “on drugs that have a clear ‘do not take while pregnant or nursing’ warning” is a relatively common one.
All that said, for those who are willing and safely able, the science is clear: breast is best.
Want to read more?
The World Health Organization has a wealth of information (including explanations of its recommendations of, where possible, exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months, ideally continuing some breastfeeding for the first 2 years), here:
World Health Organization | Breastfeeding
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Spiced Fruit & Nut Chutney
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
‘Tis the season to make the chutney that will then be aged chutney when you want it later! And unlike supermarket varieties with their ingredients list that goes “Sugar, spirit vinegar, inverted glucose-fructose syrup,” this one has an array of health-giving fruits and nuts (just omit the nuts if you or someone you may want to give this to has an allergy), and really nothing bad in here at all. And of course, tasty healthful spices!
You will need
- 2 red onions, chopped
- 1½ cups dried apricots, chopped
- 1½ cups dried figs, chopped
- 1 cup raisins
- ½ cup apple cider vinegar
- ½ cup slivered almonds
- ½ lime, chopped and deseeded
- ¼ bulb garlic, chopped
- 1 hot pepper, chopped (your choice what kind; omit if you don’t like heat at all; multiply if you want more heat)
- 2 tablespoons honey or maple syrup (omit for a less sweet chutney; there is sweetness in the dried fruits already, after all)
- 1 tbsp freshly grated ginger
- 2 tsp sweet cinnamon
- 1 tsp nutmeg
- 1 tsp black pepper
- ½ teaspoon allspice
- ½ MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat some oil in a heavy-based pan that will be large enough for all ingredients to go into eventually. Fry the onions on a gentle heat for around 15 minutes. We don’t need to caramelize them yet (this will happen with time), but we do want them soft and sweet already.
2) Add the ginger, garlic, and chili, and stir in well.
3) When the onions start to brown, add the fruit and stir well to mix thoroughly.
4) Add the honey or maple syrup (if using), and the vinegar; add the remaining spices/seasonings, so everything is in there now except the almonds.
5) Cook gently for another 30 minutes while stirring. At some point it’ll become thick and sticky; add a little water as necessary. You don’t want to drown it, but you do want it to stay moist. It’ll probably take only a few tablespoons of added water in total, but add them one at a time and stir in before judging whether more is needed. By the end of the 30 minutes, it should be more solid, to the point it can stand up by itself.
6) Add the almonds, stir to combine, and leave to cool. Put it in jars until you need it (or perhaps give it as gifts).
Alternative method: if you don’t want to be standing at a stove stirring for about an hour in total, you can use a slow cooker / crock pot instead. Put the same ingredients in the same order, but don’t stir them, just leave them in layers (this is because of the pattern of heat distribution; it’ll be hotter at the bottom, so the things that need to be more cooked should be there, and the design means they won’t burn) for about two hours, then stir well to mix thoroughly, and leave it for another hour or two, before turning it off to let it cool. Put it in jars until you need it (or perhaps give it as gifts).
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← figs and apricots appear here
- Apricots vs Peaches – Which is Healthier? ← have a guess
- Almonds vs Walnuts – Which is Healthier? ← almonds won, but walnuts were close and would also work in this recipe
- Pistachios vs Almonds – Which is Healthier? ← almonds won, but pistachios were close and would also work in this recipe
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we scored 4/5 today!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Limitless Expanded Edition – by Jim Kwik
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a little flashier in presentation than we usually go for here, but the content is actually very good. Indeed, we’ve featured Jim Kwik before, with different, but also good content—in that case, physical exercises that strengthen the brain.
This time, Kwik (interspersed with motivational speeches that you may or may not benefit from, but they are there) offers a step-by-step course in improving various metrics of cognitive ability. His methods were produced by trial and error, and now have been refined and enjoyed by man. If it sounds like a sales gimmick, it is a bit, but the good news is that everything you need to benefit is in the book; it’s not about upselling to a course or “advanced” books or whatnot.
The style is enthusiastically conversational, and instructions when given (which is often) are direct and clear.
Bottom line: one of the most critical abilities a brain can have is the ability to improve itself, so whatever level your various cognitive abilities are at right now, if you apply this book, you will almost certainly improve in one or more areas, which will make it worth the price of the book.
Click here to check out Limitless, and find out what you can do!
Share This Post
-
Who you are and where you live shouldn’t determine your ability to survive cancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In Canada, nearly everyone has a cancer story to share. It affects one in every two people, and despite improvements in cancer survivorship, one out of every four people affected by cancer still will die from it.
As a scientist dedicated to cancer care, I work directly with patients to reimagine a system that was never designed for them in the first place – a system in which your quality of care depends on social drivers like your appearance, your bank statements and your postal code.
We know that poverty, poor nutrition, housing instability and limited access to education and employment can contribute to both the development and progression of cancer. Quality nutrition and regular exercise reduce cancer risk but are contingent on affordable food options and the ability to stay active in safe, walkable neighbourhoods. Environmental hazards like air pollution and toxic waste elevate the risk of specific cancers, but are contingent on the built environment, laws safeguarding workers and the availability of affordable housing.
On a health-system level, we face implicit biases among care providers, a lack of health workforce competence in addressing the social determinants of health, and services that do not cater to the needs of marginalized individuals.
Indigenous peoples, racialized communities, those with low income and gender diverse individuals face the most discrimination in health care, resulting in inadequate experiences, missed diagnosis and avoidance of care. One patient living in subsidized housing told me, “You get treated like a piece of garbage – you come out and feel twice as bad.”
As Canadians, we benefit from a taxpayer funded health-care system that encompasses cancer care services. The average Canadian enjoys a life expectancy of more than 80 years and Canada boasts high cancer survival rates. While we have made incredible strides in cancer care, we must work together to ensure these benefits are equally shared amongst all people in Canada. We need to redesign systems of care so that they are:
- Anti-oppressive. We must begin by understanding and responding to historical and systemic racism that shapes cancer risk, access to care and quality of life for individuals facing marginalizing conditions. Without tackling the root causes, we will never be able to fully close the cancer care gap. This commitment involves undoing intergenerational trauma and harm through public policies that elevate the living and working conditions of all people.
- Patient-centric. We need to prioritize patient needs, preferences and values in all aspects of their health-care experience. This means tailoring treatments and services to individual patient needs. In policymaking, it involves creating policies that are informed by and responsive to the real-life experiences of patients. In research, it involves engaging patients in the research process and ensuring studies are relevant to and respectful of their unique perspectives and needs. This holistic approach ensures that patients’ perspectives are central to all aspects of health care.
- Socially just. We must strive for a society in which everyone has equal access to resources, opportunities and rights, and systemic inequalities and injustices are actively challenged and addressed. When redesigning the cancer care system, this involves proactive practices that create opportunities for all people, particularly those experiencing the most marginalization, to become involved in systemic health-care decision-making. A system that is responsive to the needs of the most marginalized will ultimately work better for all people.
Who you are, how you look, where you live and how much money you make should never be the difference between life and death. Let us commit to a future in which all people have the resources and support to prevent and treat cancer so that no one is left behind.
This article is republished from HealthyDebate under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Thai Green Curry With Crispy Tofu Balls
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Diversity is key here, with a wide range of mostly plants, offering an even wider range of phytochemical benefits:
You will need
- 7 oz firm tofu
- 1 oz cashew nuts (don’t soak them)
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp turmeric
- 4 scallions, sliced
- 7 oz mangetout
- 7 oz fermented red cabbage (i.e., from a jar)
- 1 cup coconut milk
- Juice of ½ lime
- 2 tsp light soy sauce
- 1 handful fresh cilantro, or if you have the “cilantro tastes like soap” gene, then parsley
- 1 handful fresh basil
- 1 green chili, chopped (multiply per heat preference)
- 1″ piece fresh ginger, roughly chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic, crushed
- 1 tsp red chili flakes
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Avocado oil for frying
- Recommended, to serve: lime wedges
- Recommended, to serve: your carbohydrate of choice, such as soba noodles or perhaps our Tasty Versatile Rice.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat the oven to 350℉ / 180℃, and bake the cashews on a baking tray for about 8 minutes until lightly toasted. Remove from the oven and allow to cool a little.
2) Combine the nuts, tofu, nutritional yeast, turmeric, and scallions in a food processor, and process until the ingredients begin to clump together. Shape into about 20 small balls.
3) Heat some oil in a skillet and fry the tofu balls, jiggling frequently to get all sides; it should take about 5 minutes to see them lightly browned. Set aside.
4) Combine the coconut milk, lime juice, soy sauce, cilantro/parsley, basil, scallions, green chili, ginger, garlic, and MSG/salt in a high-speed blender, and blend until a smooth liquid.
5) Transfer the liquid to a saucepan, and bring to the boil. Reduce the heat, add the mangetout, and simmer for about 5 minutes to reduce slightly. Stir in the red chili flakes and black pepper.
6) Serve with your preferred carbohydrate, adding the fermented red cabbage and the crispy tofu balls you set aside, along with any garnish you might like to add.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
- Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- What’s Your Plant Diversity Score? ← a score of 8.25 for this dish, not counting whatever carbs you might add. Remember, herbs/spices* count for ¼ of a point each!
*but not MSG or salt, as while they may in culinary terms get lumped in with spices, they are of course not plants. Nor is nutritional yeast (nor any other yeast, for that matter). However, mushrooms (not seen in this recipe, though to be honest they would be a respectable addition) would get included for a whole point per mushroom type, since while they are not technically plants but fungi, the nutritional profile is plantlike.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Life-Changing Manga Of Tidying Up – by Marie Kondo
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Everyone knows the slogan “does this spark joy?”, but there’s a whole method to the magic that goes far beyond that. It spans all manner of things from the over-arching strategy of taking on a house-sized tidying project, to practical little tips like “store these things this way instead; now they’re safe, tidy and accessible—and look good too!”.
You may be wondering: why are we reviewing this book instead of the much more famous “The Life-Changing Magic of Tidying Up”?
It’s simple: here at 10almonds, we like things to be super simple and easy to digest.
This book is smaller, simpler, and more digestible than her more famous book, without sacrificing content. And you know what? We held it in our hands and it sparked joy
Bottom line is: it’s useful, it’s beautiful, it will change your life (and your underwear drawer).
PS: this 10almonds team-member gifted a copy to her 12-year-old son. He implemented it the same day, unbidden. Magic indeed!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Tech Bliss – by Clo S., MSc.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The popular idea of a “digital detox” is simple enough, “just unplug!”, they say.
But here in the real world, not only is that often not practical for many of us, it may not always even be entirely desirable. The Internet (and our devices with all their bells and whistles) can be a source of education, joy, and connection!
So, how to find out what’s good for us and what’s not, in our daily digital practices? Clo. S. has answers… Or rather, experiments for us to do and find out for ourselves.
These experiments range from the purely practical “try this to streamline your experience” to the more personal “how does this thing make you feel?”. A lot of the experiments will be performed via your digital devices—some, without! Others are about online interpersonal dynamics, be they one-on-one or navigating a world in which it seems everyone is out to get us, our outrage, and/or our money. Still yet others are about optimizing what you do get from the parts of your digital experience that are enriching for you.
As the title suggests, there are 30 experiments, and it’s not a stretch to do them one per day for a month. But, as the author notes, it’s by no means necessary to do them like that; it’s a workbook and reference guide, not a to-do list!
(On the topic of it being a reference guide…There’s also an extensive tools directory towards the end!)
In short: this is a great book for optimizing your online experience—whatever that might mean for you personally; you can decide for yourself along the way!
Click here to get a copy of Tech Bliss: 30 Experiments For Your Digital Wellness today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: