Blood, urine and other bodily fluids: how your leftover pathology samples can be used for medical research
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A doctor’s visit often ends with you leaving with a pathology request form in hand. The request form soon has you filling a sample pot, having blood drawn, or perhaps even a tissue biopsy taken.
After that, your sample goes to a clinical pathology lab to be analysed, in whichever manner the doctor requested. All this is done with the goal of getting to the bottom of the health issue you’re experiencing.
But after all the tests are done, what happens with the leftover sample? In most cases, leftover samples go in the waste bin, destined for incineration. Sometimes though, they may be used again for other purposes, including research.

Who can use my leftover samples?
The samples we’re talking about here cover the range of samples clinical labs receive in the normal course of their testing work. These include blood and its various components (including plasma and serum), urine, faeces, joint and spinal fluids, swabs (such as from the nose or a wound), and tissue samples from biopsies, among others.
Clinical pathology labs often use leftover samples to practise or check their testing methods and help ensure test accuracy. This type of use is a vital part of the quality assurance processes labs need to perform, and is not considered research.
Leftover samples can also be used by researchers from a range of agencies such as universities, research institutes or private companies.
They may use leftover samples for research activities such as trying out new ideas or conducting small-scale studies (more on this later). Companies that develop new or improved medical diagnostic tests can also use leftover samples to assess the efficacy of their test, generating data needed for regulatory approval.
What about informed consent?
If you’ve ever participated in a medical research project such as a clinical trial, you may be familiar with the concept of informed consent. In this process, you have the opportunity to learn about the study and what your participation involves, before you decide whether or not to participate.
So you may be surprised to learn using leftover samples for research purposes without your consent is permitted in most parts of Australia, and elsewhere. However, it’s only allowed under certain conditions.
In Australia, the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) offers guidance around the use of leftover pathology samples.
One of the conditions for using leftover samples without consent for research is that they were received and retained by an accredited pathology service. This helps ensure the samples were collected safely and properly, for a legitimate clinical reason, and that no additional burdens or risk of harm to the person who provided the sample will be created with their further use.
Another condition is anonymity: the leftover samples must be deidentified, and not easily able to be reidentified. This means they can only be used in research if the identity of the donor is not needed.

The decision to allow a particular research project to use leftover pathology samples is made by an independent human research ethics committee which includes consumers and independent experts. The committee evaluates the project and weighs up the risks and potential benefits before permitting an exemption to the need for informed consent.
Similar frameworks exist in the United States, the United Kingdom, India and elsewhere.
What research might be done on my leftover samples?
You might wonder how useful leftover samples are, particularly when they’re not linked to a person and their medical history. But these samples can still be a valuable resource, particularly for early-stage “discovery” research.
Research using leftover samples has helped our understanding of antibiotic resistance in a bacterium that causes stomach ulcers, Helicobacter pylori. It has helped us understand how malaria parasites, Plasmodium falciparum, damage red blood cells.
Leftover samples are also helping researchers identify better, less invasive ways to detect chronic diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis. And they’re allowing scientists to assess the prevalence of a variant in haemoglobin that can interfere with widely used diagnostic blood tests.
All of this can be done without your permission. The kinds of tests researchers do on leftover samples will not harm the person they were taken from in any way. However, using what would otherwise be discarded allows researchers to test a new method or treatment and avoid burdening people with providing fresh samples specifically for the research.
When considering questions of ethics, it could be argued not using these samples to derive maximum benefit is in fact unethical, because their potential is wasted. Using leftover samples also minimises the cost of preliminary studies, which are often funded by taxpayers.
Inconsistencies in policy
Despite NHMRC guidance, certain states and territories have their own legislation and guidelines which differ in important ways. For instance, in New South Wales, only pathology services may use leftover specimens for certain types of internal work. In all other cases consent must be obtained.
Ethical standards and their application in research are not static, and they evolve over time. As medical research continues to advance, so too will the frameworks that govern the use of leftover samples. Nonetheless, developing a nationally consistent approach on this issue would be ideal.
Striking a balance between ensuring ethical integrity and fostering scientific discovery is essential. With ongoing dialogue and oversight, leftover pathology samples will continue to play a crucial role in driving innovation and advances in health care, while respecting the privacy and rights of individuals.
Christine Carson, Senior Research Fellow, School of Medicine, The University of Western Australia and Nikolajs Zeps, Professor, School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Neuropsychologist Explains What She’s Got Out Of 6 Years Taking L-Theanine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Inka Land, MSc neuropsychology, PgDip(c) Nutrition and Disease, talks about her use of l-theanine and the biochemistry behind it:
So, what’s the tea?
While she’s tested over 60 supplements, she regularly uses only a few. L-theanine made the cut, and has been a staple for over six years due to its noticeable effects on her brain, nervous system in general, and gut. Some notes from the video:
- L-theanine was discovered during university studies as a way to enhance focus and reduce stress. Initially, 50mg doses combined with coffee showed no effect, but increasing to 150mg, paired with 100mg of caffeine, produced significant nootropic benefits.
- L-theanine enhances sustained focus, enabling prolonged attention on repetitive tasks while avoiding distractions. It’s particularly effective for maintaining concentration during monotonous activities.
- L-theanine alleviates gut inflammation by boosting antioxidant activity and supporting glutamine metabolism. Combined with l-glutamine, it is more effective for reducing gut inflammation, and she mentions anecdotally that it seemed to help her personally recover quickly from food poisoning.
- Known for its calming effects, L-theanine reduces anxiety and regulates the nervous system. It is beneficial before stressful or crowded events and has anecdotal support for alleviating social anxiety specifically, though that’s not been formally tested in RCTs (yet). That said, since it has been tested against anxiety in the lab (usually combined with stress tests), it would be strange if it didn’t help alleviate social anxiety too, since what’s required for the nervous system is the same.
- Studies suggest 100–200mg twice daily, but she personally takes 250mg in the morning with coffee or 200–250mg PRN.
Want to try some? Here’s an example product on Amazon 😎
For more on all of this, enjoy (and kindly disregard that she clearly is holding a jar of curcumin in the thumbnail):
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
L-Theanine Against Stress, Anxiety, Inflammation, & More
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Better Sex Through Mindfulness – by Dr. Lori Brotto
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Female sexuality is such a taboo topic that, if one searches for (ob/gyn professor, women’s health research director, and psychologist) Dr. Brotto’s book on Google or Amazon, it suggests only “lori brotto mindfulness book”. So, for those brave enough to read a book that would have shocked Victorians, what does this one contain?
The focus is on, as the title suggests, better sex, by and for women. That said, it’s mostly because typically women are more likely to experience the problems described in the book; it’s nothing actually intrinsic to womanhood. A man with the same problems could read this book and benefit just the same.
While the book covers many possible problems between the sheets, the overarching theme is problems of the mind, such as:
- Not getting into the mood in the first place
- Losing the mood quickly and easily, such as by becoming distracted
- Difficulty achieving orgasm even when mechanically everything’s delightful
- Physical discomfort creating a barrier to enjoyment
…and yes, that last one is in part mind-stuff too! Though Dr. Brotto isn’t arguing that mindfulness is a panacea, just an incredibly useful tool. And, it’s one she not only explains very well, but also explains from the position of a wealth of scientific evidence… Enough so, that we see a one-star Amazon reviewer from Canada complained that it was too well-referenced! For us, though, it’s what we like to see.
Good science, presented clearly and usefully, giving practical tips that improve people’s lives.
Bottom line: if you’ve ever lost the mood because you got distracted into thinking about taxes or that meeting on Tuesday, this is the book for you.
Click here to check out Better Sex Through Mindfulness—you can thank us later!
Share This Post
-
Healthy Living in a Contaminated World – by Dr. Donald Hoernschemeyer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s a lot going on here, as this book tackles very many kinds of common contaminants, from waste products and industrial chemicals (such as from fracking), pesticides that are banned in most places but not the US, smog and soot from coal and oil power, mercury and other heavy metals, dioxins, Teflon and its close relatives, phthalates, BPA, and other things again regulated out of use in many countries but not entirely in the US (which bans them only in some things, like baby bottles), drinking water issues of various kinds, and much more.
Indeed, there’s a whole chapter on the US and international regulation of toxic substances; the problem is often that on a political level, the same people who are against nebulous “chemicals” are also against environmentalist regulations that would ban them. This is mostly not a political book though, and rather is chiefly a book of chemistry (the author’s field).
It does also cover the medical maladies associated with various contaminants, while the bulk of the data is on the chemistry side of such things as “elimination times for toxic chemicals”, “amounts of pesticides in fruit and vegetables”, “antibiotics and hormones used in animal agriculture”, and so forth.
The style is dense, and/but it is clear the author has made an effort to not be too dry. Still, this is not a fun read; it’s depressing in content and the style is more suited to academia. There are appendices containing glossaries and acronym tables, but reading front-to-back, there’s a lot that’s not explained so unless you also are a PhD chemist, chances are you’ll be needing to leaf forwards and backwards a lot.
Bottom line: this book is not thrilling, but what you don’t know, can kill you.
Click here to check out Healthy Living In A Contaminated World, and improve your odds!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
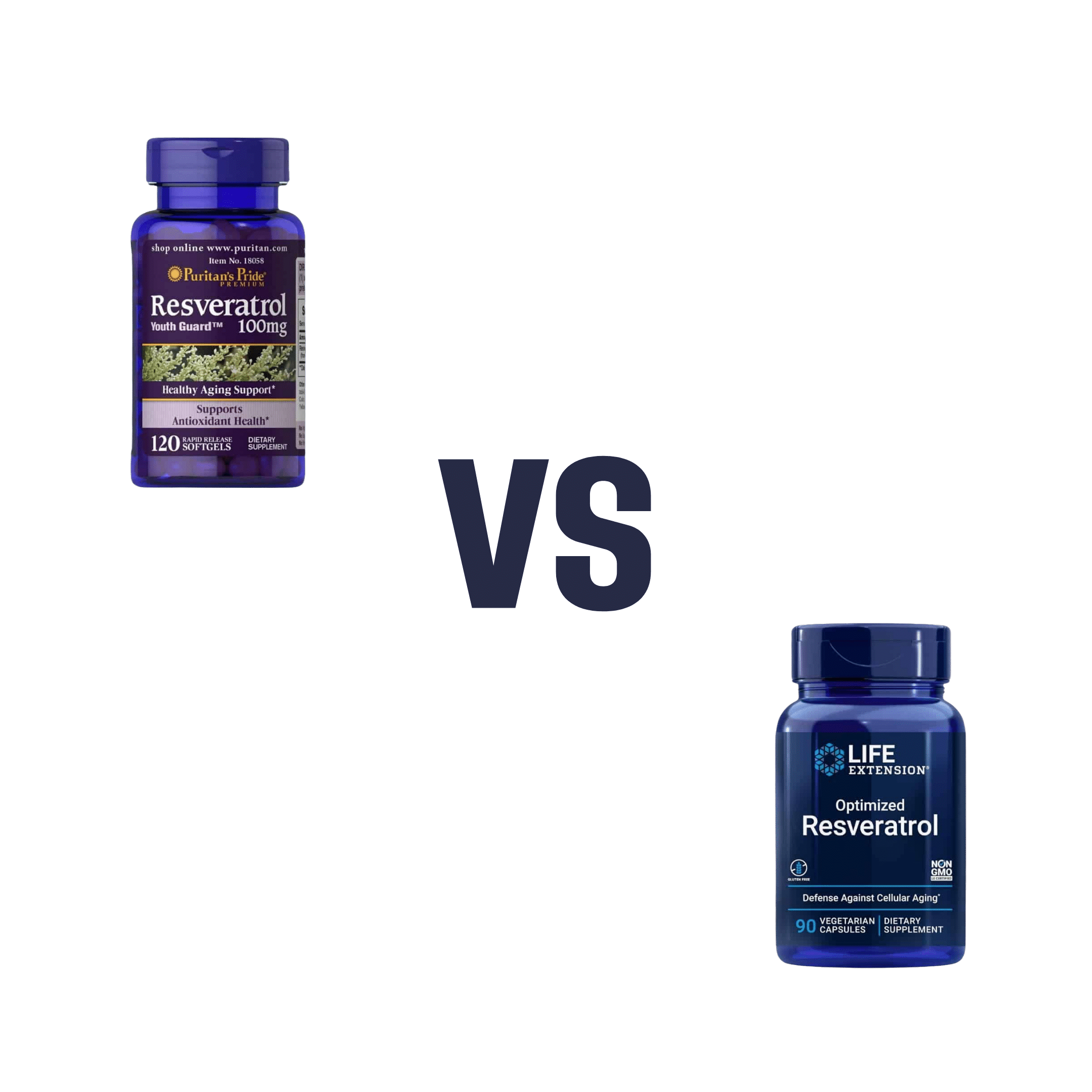
Puritans Pride Resveratrol vs Life Extension Resveratrol – Which is Healthier
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Puritan’s Pride Resveratrol to Life Extension Resveratrol, we picked the Life Extension Resveratrol.
Why?
It contains not only more resveratrol per serving (250mg compared to Puritan’s Pride’s 100mg), but also contains other goodies too. Specifically, each capsule also contains:
- Quercetin (150mg)
- Grape & berry blend (85mg)
- Fisetin (10mg)
Whereas the Puritan’s Pride softgels? The other top ingredients are soybean oil and gelatin.
Want to check out the products for yourself? Here they are:
Puritan’s Pride Resveratrol | Life Extension Resveratrol
Want to know more about these supplements? Check out:
Resveratrol & Healthy Aging
Fight Inflammation & Protect Your Brain, With Quercetin
Berries & Other Polyphenol-rich Foods
Fisetin: The Anti-Aging AssassinEnjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Doesn’t Lycopene Do?
Lycopene is an antioxidant carotenoid famously found in tomatoes; it actually appears in even higher levels in watermelon, though. If you are going to get it from tomato, know that cooking improves the lycopene content rather than removing it (watermelon, on the other hand, can be enjoyed as-is and already has the higher lycopene content).
Antioxidant properties
Let’s reiterate the obvious first, for the sake of being methodical and adding a source. Lycopene is a potent antioxidant with multiple health benefits:
Lycopene: A Potent Antioxidant with Multiple Health Benefits
…and as such, it does all the things you might reasonably expect and antioxidant to do. For example…
Anti-inflammatory properties
In particular, it regulates macrophage activity, reducing inflammation while improving immune response:
Lycopene Regulates Macrophage Immune Response through the Autophagy Pathway Mediated by RIPK1
As can be expected of most antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents, it also has…
Anticancer properties
Scientific papers tend to be “per cancer type”, so we’re just going to give one example, but there’s pretty much evidence for its utility against most if not all types of cancer. We’re picking prostate cancer though, as it’s one that’s been studied the most in the context of lycopene intake—in this study, for example, it was found that men who enjoyed at least two servings of lycopene-rich tomato sauce per week were 30% less likely to develop prostate cancer than those who didn’t:
Dietary lycopene intake and risk of prostate cancer defined by ERG protein expression
If you’d like to see something more general, however, then check out:
Potential Use of Tomato Peel, a Rich Source of Lycopene, for Cancer Treatment
It also fights Candida albicans
Ok, this is not (usually) so life-and-death as cancer, but reducing our C. albicans content (specifically: in our gut) has a lot of knock-on effects for other aspects of our health, so this isn’t one to overlook:
The title does not make this clear, but yes: this does mean it has an antifungal effect. We mention this because often cellular apoptosis is good for an overall organism, but in this case, it simply kills the Candida.
It’s good for the heart
A lot of studies focus just on triglyceride markers (which lycopene improves), but more tellingly, here’s a 10-year observational study in which diets rich in lycopene were associated to a 17–26% lower risk of heart disease:
Relationship of lycopene intake and consumption of tomato products to incident CVD
…and a 39% overall reduced mortality in, well, we’ll let the study title tell it:
…which means also:
It’s good for the brain
As a general rule of thumb, what’s good for the heart is good for the brain (because the brain needs healthy blood flow to stay healthy, and is especially vulnerable when it doesn’t get that), and in this case that rule of thumb is also borne out by the post hoc evidence, specifically yielding a 31% decreased incidence of stroke:
Dietary and circulating lycopene and stroke risk: a meta-analysis of prospective studies
Is it safe?
As a common food product, it is considered very safe.
If you drink nothing but tomato juice all day for a long time, your skin will take on a reddish hue, which will go away if you stop getting all your daily water intake in tomato juice.
In all likelihood, even if you went to extremes, you would get sick from the excess of vitamin A (generally present in the same foods) sooner than you’d get sick from the excess of lycopene.
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, and also we recommend simply enjoying tomatoes, watermelons, etc, but if you do want a supplement, here’s an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Best Menopause Advice You Don’t Want To Hear About
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Nutritionist and perimenopause coach Claudia Canu, whom we’ve featured before in our Expert Insights segment, has advice:
Here’s to good health
When it comes to alcohol, the advice is: don’t.
Or at least, cut back, and manage the effects by ensuring good hydration, having an “alcohol curfew” and so forth.
What’s the relation to menopause? Well, alcohol’s not good for anyone at any time of life, but there are some special considerations when it comes to alcohol and estrogenic hormonal health:
- The liver works hard to process the alcohol as a matter of urgency, delaying estrogen processing, which can increase the risk of breast and uterine cancer.
- Alcohol has no positive health effects and is also linked to higher risks of breast and colorectal cancer.
- Alcohol can also trigger some menopausal symptoms, such as night sweats and hot flashes. So, maybe reaching for that “cooling drink” isn’t the remedy it might seem.
- During menopause, the body becomes more insulin-resistant, making it more susceptible to blood sugar spikes caused by alcohol. Also not good.
Common reasons women turn to alcohol include stress, frustration, the need for reward, and social pressure, and all of these can be heightened when undergoing hormonal changes. Yet, alcohol will ultimately only worsen each of those things.
For more on the science of some of the above, plus tips on how to make positive changes with minimum discomfort, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
- How To Reduce The Harm Of Drinking (Without Abstaining)
- Where Nutrition Meets Habits! ← our “Expert Insights” spotlight on Canu
- How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk Early ← particularly important at this life stage
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:







