Reading At Night: Good Or Bad For Sleep? And Other Questions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Would be interested in your views about “reading yourself to sleep”. I find that current affairs magazines and even modern novels do exactly the opposite. But Dickens – ones like David Copperfield and Great Expectations – I find wonderfully effective. It’s like entering a parallel universe where none of your own concerns matter. Any thoughts on the science that may explain this?!❞
Anecdotally: this writer is (like most writers) a prolific reader, and finds reading some fiction last thing at night is a good way to create a buffer between the affairs of the day and the dreams of night—but I could never fall asleep that way, unless I were truly sleep-deprived. The only danger is if I “one more chapter” my way deep into the night! For what it’s worth, bedtime reading for me means a Kindle self-backlit with low, soft lighting.
Scientifically: this hasn’t been a hugely researched area, but there are studies to work from. But there are two questions at hand (at least) here:
- one is about reading, and
- the other is about reading from electronic devices with or without blue light filters.
Here’s a study that didn’t ask the medium of the book, and concluded that reading a book in bed before going to sleep improved sleep quality, compared to not reading a book in bed:
Here’s a study that concluded that reading on an iPad (with no blue light filter) that found no difference in any metrics except EEG (so, there was no difference on time spent in different sleep states or sleep onset latency), but advised against it anyway because of the EEG readings (which showed slow wave activity being delayed by approximately 30 minutes, which is consistent with melatonin production mechanics):
Here’s another study that didn’t take EEG readings, and/but otherwise confirmed no differences being found:
We’re aware this goes against general “sleep hygiene” advice in two different ways:
- General advice is to avoid electronic devices before bedtime
- General advice is to not do activities besides sleep (and sex) in bed
…but, we’re committed to reporting the science as we find it!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Tartar Removal At Home & How To Prevent Tartar
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Three things to bear in mind:
- Tartar is hardened plaque.
- Plaque is an infected biofilm that expands the natural thin film on teeth.
- Healthy biofilm resists plaque and tartar formation.
Therefore, the recommended approach is a multistep program:
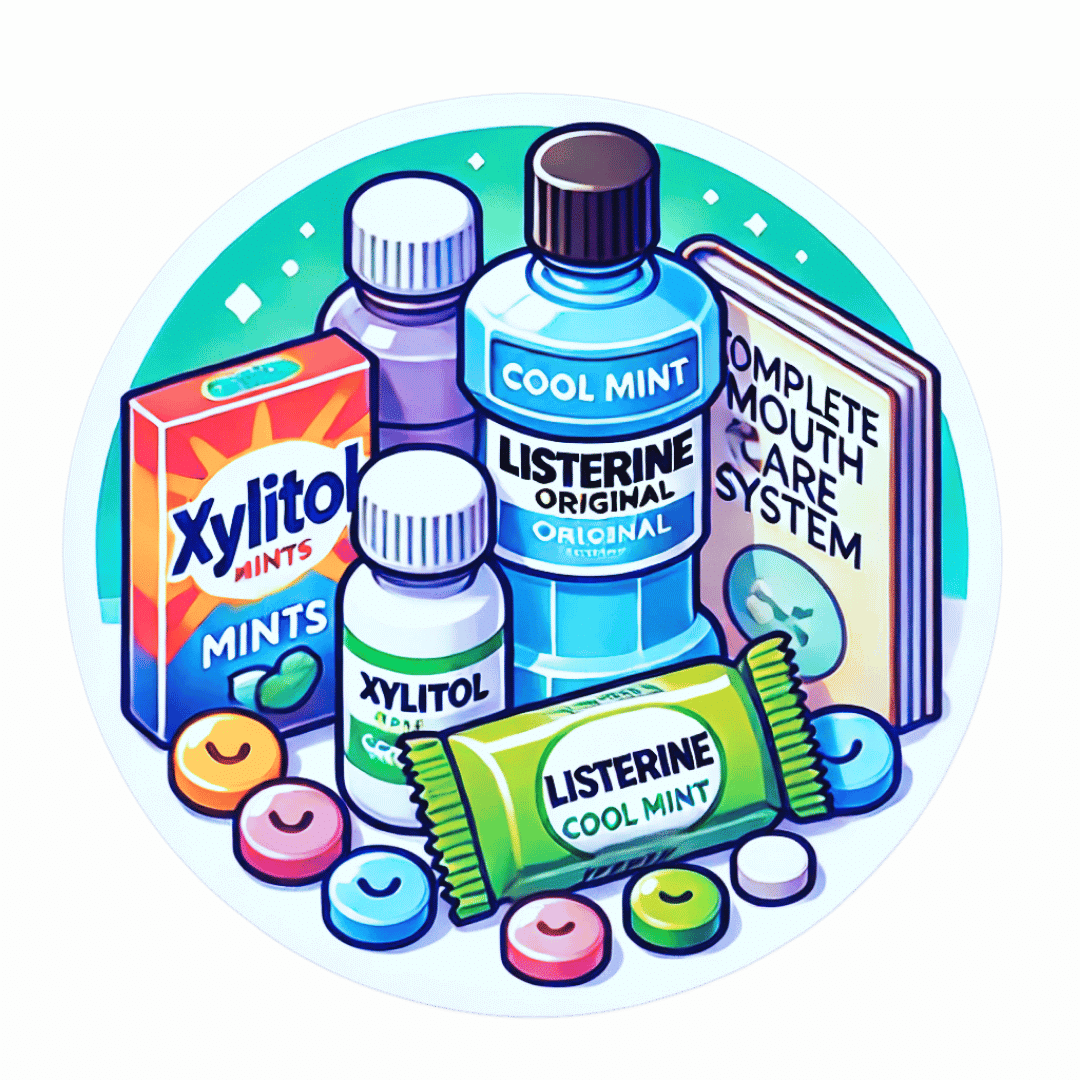
The Complete Mouth Care System
Dr. Phillips recommends to use these five products in this order twice daily:
- Zellie’s Mints & Gum: having 6–10 grams of xylitol daily will help to loosen plaque on teeth so that the following program is more effective. Xylitol protects from mouth acidity and help to remineralize teeth.
- CloSYS Prerinse: CloSYS will prepare your teeth for brushing. This pH neutral rinse ensures that brushing teeth does not occur in an acidic mouth and therefore easily damage teeth.
- Crest Cavity Protection Regular Paste: has an active ingredient of sodium fluoride at optimal concentration (not stannous fluoride). This paste has the proper abrasion and no glycerine.
- Listerine: is an effective rinse that targets the bacteria that cause plaque build up and gingivitis with three active ingredients: eucalyptus essential oil, menthol essential oil, and thymol essential oil. As such, unlike many mouthwashes, listerine does not harm the mouth’s diversity of good bacteria or the mouth’s production of nitric oxide.
- ACT Anticavity Rinse: ACT is a very dilute but extremely effective sodium fluoride solution. It helps prevent and reverse cavities, strengthen teeth, reduce sensitivity, and leaves your breath fresh.
She advises us that by doing this twice-daily over 6 months, we can expect significant tartar reduction, and indeed, that dental appointments may reveal minimal or no need for tartar removal.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read our own three-part series:
- Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
- Flossing Without Flossing?
- Less Common Oral Hygiene Options ← we recommend the miswak! Not only does it clean the teeth as well as or better than traditional brushing, but also it changes the composition of saliva to improve the oral microbiome, effectively turning your saliva into a biological mouthwash that kills unwanted microbes and is comfortable for the ones that should be there.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Total Fitness After 40 – by Nick Swettenham
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Time may march relentlessly on, but can we retain our youthful good health?
The answer is that we can… to a degree. And where we can’t, we can and should adapt what we do as we age.
The key, as Swettenham illustrates, is that there are lifestyle factors that will help us to age more slowly, thus retaining our youthful good health for longer. At the same time, there are factors of which we must simply be mindful, and take care of ourselves a little differently now than perhaps we did when we were younger. Here, Swettenham acts guide and instructor.
A limitation of the book is that it was written with the assumption that the reader is a man. This does mean that anything relating to hormones is assuming that we have less testosterone as we’re getting older and would like to have more, which is obviously not the case for everyone. However, happily, the actual advice remains applicable regardless.
Swettenham covers the full spread of what he believes everyone should take into account as we age:
- Mindset changes (accepting that physical changes are happening, without throwing our hands in the air and giving up)
- Focus on important aspects such as:
- strength
- flexibility
- mobility
- agility
- endurance
- Some attention is also given to diet—nothing you won’t have read elsewhere, but it’s a worthy mention.
All in all, this is a fine book if you’re thinking of taking up or maintaining an exercise routine that doesn’t stick its head in the sand about your aging body, but doesn’t just roll over and give up either. A worthy addition to anyone’s bookshelf!
Check Out Fitness After 40 On Amazon Today!
Looking for a more women-centric equivalent book? Vonda Wright M.D. has you covered (and her bio is very impressive)!
Share This Post
-
‘Noisy’ autistic brains seem better at certain tasks. Here’s why neuroaffirmative research matters
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pratik Raul, University of Canberra; Jeroen van Boxtel, University of Canberra, and Jovana Acevska, University of Canberra
Autism is a neurodevelopmental difference associated with specific experiences and characteristics.
For decades, autism research has focused on behavioural, cognitive, social and communication difficulties. These studies highlighted how autistic people face issues with everyday tasks that allistic (meaning non-autistic) people do not. Some difficulties may include recognising emotions or social cues.
But some research, including our own study, has explored specific advantages in autism. Studies have shown that in some cognitive tasks, autistic people perform better than allistic people. Autistic people may have greater success in identifying a simple shape embedded within a more complex design, arranging blocks of different shapes and colours, or spotting an object within a cluttered visual environment (similar to Where’s Wally?). Such enhanced performance has been recorded in babies as young as nine months who show emerging signs of autism.
How and why do autistic individuals do so well on these tasks? The answer may be surprising: more “neural noise”.
What is neural noise?
Generally, when you think of noise, you probably think of auditory noise, the ups and downs in the amplitude of sound frequencies we hear.
A similar thing happens in the brain with random fluctuations in neural activity. This is called neural noise.
This noise is always present, and comes on top of any brain activity caused by things we see, hear, smell and touch. This means that in the brain, an identical stimulus that is presented multiple times won’t cause exactly the same activity. Sometimes the brain is more active, sometimes less. In fact, even the response to a single stimulus or event will fluctuate continuously.
Neural noise in autism
There are many sources of neural noise in the brain. These include how the neurons become excited and calm again, changes in attention and arousal levels, and biochemical processes at the cellular level, among others. An allistic brain has mechanisms to manage and use this noise. For instance, cells in the hippocampus (the brain’s memory system) can make use of neural noise to enhance memory encoding and recall.
Evidence for high neural noise in autism can be seen in electroencephalography (EEG) recordings, where increased levels of neural fluctuations were observed in autistic children. This means their neural activity is less predictable, showing a wider range of activity (higher ups and downs) in response to the same stimulus.
In simple terms, if we imagine the EEG responses like a sound wave, we would expect to see small ups and downs (amplitude) in allistic brains each time they encounter a stimulus. But autistic brains seem to show bigger ups and downs, demonstrating greater amplitude of neural noise.
Many studies have linked this noisy autistic brain with cognitive, social and behavioural difficulties.
But could noise be a bonus?
The diagnosis of autism has a long clinical history. A shift from the medical to a more social model has also seen advocacy for it to be reframed as a difference, rather than a disorder or deficit. This change has also entered autism research. Neuroaffirming research can examine the uniqueness and strengths of neurodivergence.
Psychology and perception researcher David Simmons and colleagues at the University of Glasgow were the first to suggest that while high neural noise is generally a disadvantage in autism, it can sometimes provide benefits due to a phenomenon called stochastic resonance. This is where optimal amounts of noise can enhance performance. In line with this theory, high neural noise in the autistic brain might enhance performance for some cognitive tasks.
Our 2023 research explores this idea. We recruited participants from the general population and investigated their performance on letter-detection tasks. At the same time, we measured their level of autistic traits.
We performed two letter-detection experiments (one in a lab and one online) where participants had to identify a letter when displayed among background visual static of various intensities.
By using the static, we added additional visual noise to the neural noise already present in our participants’ brains. We hypothesised the visual noise would push participants with low internal brain noise (or low autistic traits) to perform better (as suggested by previous research on stochastic resonance). The more interesting prediction was that noise would not help individuals who already had a lot of brain noise (that is, those with high autistic traits), because their own neural noise already ensured optimal performance.
Indeed, one of our experiments showed people with high neural noise (high autistic traits) did not benefit from additional noise. Moreover, they showed superior performance (greater accuracy) relative to people with low neural noise when the added visual static was low. This suggests their own neural noise already caused a natural stochastic resonance effect, resulting in better performance.
It is important to note we did not include clinically diagnosed autistic participants, but overall, we showed the theory of enhanced performance due to stochastic resonance in autism has merits.
Why this is important?
Autistic people face ignorance, prejudice and discrimination that can harm wellbeing. Poor mental and physical health, reduced social connections and increased “camouflaging” of autistic traits are some of the negative impacts that autistic people face.
So, research underlining and investigating the strengths inherent in autism can help reduce stigma, allow autistic people to be themselves and acknowledge autistic people do not require “fixing”.
The autistic brain is different. It comes with limitations, but it also has its strengths.
Pratik Raul, PhD candidiate, University of Canberra; Jeroen van Boxtel, Associate professor, University of Canberra, and Jovana Acevska, Honours Graduate Student, University of Canberra
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It
We’ve talked before about how waist circumference is a much more useful indicator of metabolic health than BMI.
So, let’s say you’ve a bit more around the middle than you’d like, but it stubbornly stays there. What’s going on underneath what you can see, why is it going on, and how can you get it to change?
What is visceral fat?
First, let’s talk about subcutaneous fat. That’s the fat directly under your skin. Women usually have more than men, and that’s perfectly healthy (up to a point); it’s supposed to be that way. We (women) will tend to accumulate this mostly in places such as our breasts, hips, and butt, and work outwards from there. Men will tend to put it on more to the belly and face.
Side-note: if you’re undergoing (untreated) menopause, the changes in your hormone levels will tend to result in more subcutaneous fat to the belly and face too. That’s normal, and/but normal is not always good, and treatment options are great (with hormone replacement therapy, HRT, topping the list).
Visceral fat (also called visceral adipose tissue), on the other hand, is the fat of the viscera—the internal organs of the abdomen.
So, this is fat that goes under your abdominal muscles—you can’t squeeze this (directly).
So what can we do?
Famously “you can’t do spot reduction” (lose fat from a particular part of your body by focusing exercises on that area), but that’s about subcutaneous fat. There are things you can do that will reduce your visceral fat in particular.
Some of these advices you may think “that’s just good advice for losing fat in general” and it is, yes. But these are things that have the biggest impact on visceral fat.
Cut alcohol use
This is the biggie. By numerous mechanisms, some of which we’ve talked about before, alcohol causes weight gain in general yes, but especially for visceral fat.
Get better sleep
You might think that hitting the gym is most important, but this one ranks higher. Yes, you can trim visceral fat without leaving your bed (and even without getting athletic in bed, for that matter). Not convinced?
- Here’s a study of 101 people looking at sleep quality and abdominal adiposity
- Oh, and here’s a meta-analysis with 56,000 people (finding the same thing), in case that one study didn’t convince you.
So, the verdict is clear: you snooze, you lose (visceral fat)!
Tweak your diet
You don’t have to do a complete overhaul (unless you want to), but a few changes can make a big difference, especially:
- Getting more fiber (this is the biggie when it comes to diet)
- Eating less sugar (not really a surprise, but relevant to mention)
- Eat whole foods (skip the highly processed stuff)
If you’d like to learn more and enjoy videos, here’s an informative one to get you going!
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically! Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
This Book May Save Your Life – by Dr. Karan Rajan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The title is a bold sell, but the book does include a lot of information about what can go wrong in your body, and how those things can be avoided.
What it’s not: a reiteration of Dr. Michael Greger’s “How Not To Die“. It’s not dense medical information, and it doesn’t cite papers at a rate of ten per page.
What it is: an easy-reading tour guide of the human body and its many quirks and foibles, and how we can leverage those to our benefit. On which note…
Hopefully, your insides will never see the light of day, but this author is a general surgeon and as such, is an experienced and well-qualified tour guide. Here, we learn about everything from the long and interesting journey through our gut, to the unique anatomical features and liabilities of the brain. From the bizarre oddities of the genitals, to things most people don’t know about the process of death.
The style of the book is very casual, with lots of short sections (almost mini chapters-within-chapters, really) making for very light reading—and certainly enjoyable reading too, unless you are inclined to squeamishness.
Bottom line: in honesty, the book is more informative than it is instructional, though it does contain the promised health tips too. With that in mind, it’s a very enjoyable and educational read, and we do recommend it.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Red Cabbage vs White Cabbage – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing red cabbage to white cabbage, we picked the red.
Why?
Perhaps you guessed this one, based on the “darker and/or more colorful foods are usually more nutritionally dense” dictum. That’s not always true, by the way, but it is a good rule of thumb and it is correct here. In the case of cabbages, each type is a nutritional powerhouse, but red does beat white:
In terms of macros, they’re quite comparable. They’re both >90% water with just enough other stuff (carbs, fiber, protein) to hold them together, and the “other stuff” in question is quite similarly proportioned in both cases. Within the carbs, even the sugar breakdown is similar. There are slight differences, but the differences are not only tiny, but also they balance out in any case.
When it comes to vitamins, as you might expect, the colorful red cabbage does better with more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, C, and choline, while white has more of vitamins B5, B9, E, and K. So, a 7:4 win for red.
In the category of minerals, it’s even more polarized; red cabbage has more calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. On the other hand, white contains a tiny amount more copper.
In short, both are great (red just makes white look bad by standing next to it, but honestly, white has lots of all those same things too, just not quite as much as red), and this writer will continue to use white when making her favorite shchi, but if you’re looking for the most nutritionally dense option, it’s red.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: