Bacopa Monnieri: A Well-Evidenced Cognitive Enhancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Bacopa monnieri: a powerful nootropic
Bacopa monnieri is one of those “from traditional use” herbs that has made its way into science.
It’s been used for at least 1,400 years in Ayurvedic medicine, for cognitive enhancement, against anxiety, and some disease-specific treatments.
See: Pharmacological attributes of Bacopa monnieri extract: current updates and clinical manifestation
What are its claimed health benefits?
Bacopa monnieri is these days mostly sold and bought as a nootropic, and that’s what the science supports best.
Nootropic benefits claimed:
- Improves attention, learning, and memory
- Reduces depression, anxiety, and stress
- Reduces restlessness and impulsivity
Other benefits claimed:
- Antioxidant properties
- Anti-inflammatory properties
- Anticancer properties
What does the science say?
Those last three, the antioxidant / anti-inflammatory / anticancer properties, when something has one of those qualities it often has all three, because there are overlapping systems at hand when it comes to oxidative stress, inflammation, and cellular damage.
Bacopa monnieri is no exception to this “rule of thumb”, and/but studies to support these benefits have mostly been animal studies and/or in vitro studies (i.e., cell cultures in a petri dish in lab conditions).
For example:
- Inhibition of lipoxygenases and cyclooxygenase-2 enzymes by extracts isolated from Bacopa monnieri
- Assessing the anti-inflammatory effects of Bacopa-derived bioactive compounds using network pharmacology and in vitro studies
- The evolving roles of Bacopa monnieri as potential anticancer agent: a review
In the category of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in the brain, sometimes results differ depending on the test population, for example:
- Neuroprotective effects of Bacopa monnieri in experimental model of dementia (it worked for rats)
- Use of Bacopa monnieri in the treatment of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: systematic review of randomized controlled trials (it didn’t work for humans)
Anything more promising than that?
Yes! The nootropic effects have been much better-studied in humans, and with much better results.
For example, in this 12-week study in healthy adults, taking 300mg/day significantly improved visual information processing, learning, and memory (tested against placebo):
The chronic effects of an extract of Bacopa monnieri on cognitive function in healthy human subjects
Another 12-week study showed older adults enjoyed the same cognitive enhancement benefits as their younger peers:
Children taking 225mg/day, meanwhile, saw a significant reduction in ADHD symptoms, such as restlessness and impulsivity:
And as for the mood benefits, 300mg/day significantly reduced anxiety and depression in elderly adults:
In summary
Bacopa monnieri, taken at 300mg/day (studies ranged from 225mg/day to 600mg/day, but 300mg is most common) has well-evidenced cognitive benefits, including:
- Improved attention, learning, and memory
- Reduced depression, anxiety, and stress
- Reduced restlessness and impulsivity
It may also have other benefits, including against oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer, but the research is thinner and/or not as conclusive for those.
Where to get it
As ever, we don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience, here is an example product on Amazon.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
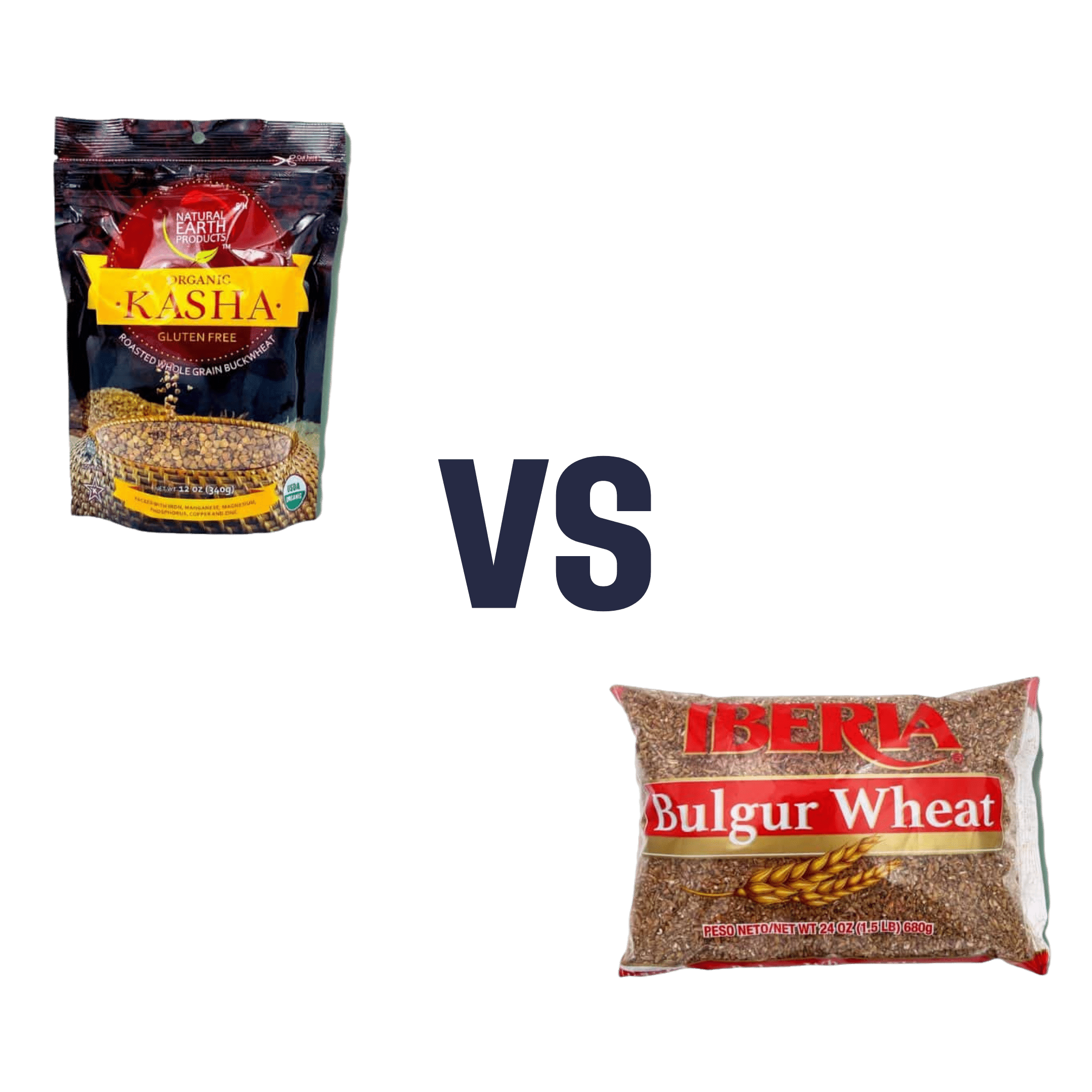
Buckwheat vs Bulgur Wheat – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing buckwheat to bulgur, we picked the buckwheat.
Why?
First, some things to know up front:
- Bulgur wheat is a kind of cracked wheat product. As such, it contains wheat, and yes, gluten.
- Buckwheat is not a wheat, nor even a grass, but a flowering plant. Buckwheat is as related to wheat as a lionfish is to a lion. It does not contain gluten.
- Buckwheat can be purchased whole or hulled. We went with whole. If you go with hulled, the percentages of vitamins and minerals will be relatively higher, and/but this will be because you lost the fibrous husk, so they’ll be commensurately lower in fiber. If you were to go with hulled, we’d still pick it over bulgur wheat though, just for a different reason (as in that case, the vitamin and mineral contents would be more overwhelmingly in buckwheat’s favor, even though it’d have less fiber).
Ok, now that those things are covered…
Looking at the macronutrients, there’s not a lot between them, except that buckwheat has the much lower glycemic index (this is only the case if you got whole, not hulled—if you got hulled, the glycemic index would be about the same).
In terms of vitamins, buckwheat has more of vitamins B2, B5, B9, E, K, and choline, while bulgur wheat technically has more vitamin A, but the numbers are tiny; a cup of bulgur wheat will give you 0.12% of the RDA. So, an easy win (functionally: 5:0) for buckwheat.
When it comes to minerals, buckwheat has more copper, magnesium, potassium, and selenium, while bulgur wheat has more calcium and manganese. They’re equal on iron and phosphorus, making this a 4:2 win for buckwheat.
Adding up the categories makes this a clear win for buckwheat!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Myth of Normal – by Dr. Gabor Maté and Daniel Maté
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of popular beliefs (and books!) start with the assumption that everyone is, broadly speaking, “normal”. That major diversions from “normal” happen only to other people… And that minor diversions from “normal” are just something to suck up and get over—magically effecting a return to “normalcy”.
Dr. Maté, however, will have none of these unhelpful brush-offs, and observes that in fact most if not all of us have been battered by the fates one way or another. We just:
- note that we have more similarities than differences, and
- tend to hide our own differences (to be accepted) or overlook other people’s (to make them more acceptable).
How is this more helpful? Well, the above approach isn’t always, but Mate has an improvement to offer:
We must see flawed humans (including ourselves) as the product of our environments… and/but see this a reason to look at improving those environments!
Beyond that…
The final nine chapters of the books he devotes to “pathways to wholeness” and, in a nutshell, recovery. Recovery from whatever it was for you. And if you’ve had a life free from anything that needs recovering from, then congratulations! You doubtlessly have at least one loved one who wasn’t so lucky, though, so this book still makes for excellent reading.
Dr. Maté was awarded the Order of Canada for his medical work and writing. His work has mostly been about addiction, trauma, stress, and childhood development. He co-wrote this book with his son, Daniel.
Share This Post
-
Why scrapping the term ‘long COVID’ would be harmful for people with the condition
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The assertion from Queensland’s chief health officer John Gerrard that it’s time to stop using the term “long COVID” has made waves in Australian and international media over recent days.
Gerrard’s comments were related to new research from his team finding long-term symptoms of COVID are similar to the ongoing symptoms following other viral infections.
But there are limitations in this research, and problems with Gerrard’s argument we should drop the term “long COVID”. Here’s why.
A bit about the research
The study involved texting a survey to 5,112 Queensland adults who had experienced respiratory symptoms and had sought a PCR test in 2022. Respondents were contacted 12 months after the PCR test. Some had tested positive to COVID, while others had tested positive to influenza or had not tested positive to either disease.
Survey respondents were asked if they had experienced ongoing symptoms or any functional impairment over the previous year.
The study found people with respiratory symptoms can suffer long-term symptoms and impairment, regardless of whether they had COVID, influenza or another respiratory disease. These symptoms are often referred to as “post-viral”, as they linger after a viral infection.
Gerrard’s research will be presented in April at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. It hasn’t been published in a peer-reviewed journal.
After the research was publicised last Friday, some experts highlighted flaws in the study design. For example, Steven Faux, a long COVID clinician interviewed on ABC’s television news, said the study excluded people who were hospitalised with COVID (therefore leaving out people who had the most severe symptoms). He also noted differing levels of vaccination against COVID and influenza may have influenced the findings.
In addition, Faux pointed out the survey would have excluded many older people who may not use smartphones.
The authors of the research have acknowledged some of these and other limitations in their study.
Ditching the term ‘long COVID’
Based on the research findings, Gerrard said in a press release:
We believe it is time to stop using terms like ‘long COVID’. They wrongly imply there is something unique and exceptional about longer term symptoms associated with this virus. This terminology can cause unnecessary fear, and in some cases, hypervigilance to longer symptoms that can impede recovery.
But Gerrard and his team’s findings cannot substantiate these assertions. Their survey only documented symptoms and impairment after respiratory infections. It didn’t ask people how fearful they were, or whether a term such as long COVID made them especially vigilant, for example.
Tens of thousands of Australians, and millions of people worldwide, have long COVID.
New Africa/ShutterstockIn discussing Gerrard’s conclusions about the terminology, Faux noted that even if only 3% of people develop long COVID (the survey found 3% of people had functional limitations after a year), this would equate to some 150,000 Queenslanders with the condition. He said:
To suggest that by not calling it long COVID you would be […] somehow helping those people not to focus on their symptoms is a curious conclusion from that study.
Another clinician and researcher, Philip Britton, criticised Gerrard’s conclusion about the language as “overstated and potentially unhelpful”. He noted the term “long COVID” is recognised by the World Health Organization as a valid description of the condition.
A cruel irony
An ever-growing body of research continues to show how COVID can cause harm to the body across organ systems and cells.
We know from the experiences shared by people with long COVID that the condition can be highly disabling, preventing them from engaging in study or paid work. It can also harm relationships with their friends, family members, and even their partners.
Despite all this, people with long COVID have often felt gaslit and unheard. When seeking treatment from health-care professionals, many people with long COVID report they have been dismissed or turned away.
Last Friday – the day Gerrard’s comments were made public – was actually International Long COVID Awareness Day, organised by activists to draw attention to the condition.
The response from people with long COVID was immediate. They shared their anger on social media about Gerrard’s comments, especially their timing, on a day designed to generate greater recognition for their illness.
Since the start of the COVID pandemic, patient communities have fought for recognition of the long-term symptoms many people faced.
The term “long COVID” was in fact coined by people suffering persistent symptoms after a COVID infection, who were seeking words to describe what they were going through.
The role people with long COVID have played in defining their condition and bringing medical and public attention to it demonstrates the possibilities of patient-led expertise. For decades, people with invisible or “silent” conditions such as ME/CFS (myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome) have had to fight ignorance from health-care professionals and stigma from others in their lives. They have often been told their disabling symptoms are psychosomatic.
Gerrard’s comments, and the media’s amplification of them, repudiates the term “long COVID” that community members have chosen to give their condition an identity and support each other. This is likely to cause distress and exacerbate feelings of abandonment.
Terminology matters
The words we use to describe illnesses and conditions are incredibly powerful. Naming a new condition is a step towards better recognition of people’s suffering, and hopefully, better diagnosis, health care, treatment and acceptance by others.
The term “long COVID” provides an easily understandable label to convey patients’ experiences to others. It is well known to the public. It has been routinely used in news media reporting and and in many reputable medical journal articles.
Most importantly, scrapping the label would further marginalise a large group of people with a chronic illness who have often been left to struggle behind closed doors.
Deborah Lupton, SHARP Professor, Vitalities Lab, Centre for Social Research in Health and Social Policy Centre, and the ARC Centre of Excellence for Automated Decision-Making and Society, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Gut Health 2.0
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Gene Expression & Gut Health
This is Dr. Tim Spector. After training in medicine and becoming a consultant rheumatologist, he’s turned his attention to medical research, and is these days a specialist in twin studies, genetics, epigenetics, microbiome, and diet.
What does he want us to know?
For one thing: epigenetics are for more than just getting your grandparents’ trauma.
More usefully: there are things we can do to improve epigenetic factors in our body
DNA is often seen as the script by which our body does whatever it’s going to do, but it’s only part of the story. Thinking of DNA as some kind of “magical immutable law of reality” overlooks (to labor the metaphor) script revisions, notes made in the margins, directorial choices, and ad-lib improvizations, as well as the quality of the audience’s hearing and comprehension.
Hence the premise of one of Dr. Spector’s older books, “Identically Different: Why We Can Change Our Genes”
(*in fact, it was his first, from all the way back in 2013, when he’d only been a doctor for 34 years)
Gene expression will trump genes every time, and gene expression is something that can often be changed without getting in there with CRISPR / a big pair of scissors and some craft glue.
How this happens on the micro level is beyond the scope of today’s article; part of it has to do with enzymes that get involved in the DNA transcription process, and those enzymes in turn are despatched or not depending on hormonal messaging—in the broadest sense of “hormonal”; all the body’s hormonal chemical messengers, not just the ones people think of as hormones.
However, hormonal messaging (of many kinds) is strongly influenced by something we can control relatively easily with a little good (science-based) knowledge: the gut.
The gut, the SAD, and the easy
In broad strokes: we know what is good for the gut. We’ve written about it before at 10almonds:
Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
This is very much in contrast with what in scientific literature is often abbreviated “SAD”, the Standard American Diet, which is very bad for the gut.
However, Dr. Spector (while fully encouraging everyone to enjoy an evidence-based gut-healthy diet) wanted to do one better than just a sweeping one-size-fits-all advice, so he set up a big study with 15,000 identical twins; you can read about it here: TwinsUK
The information that came out of that was about a lot more than just gene expression and gut health, but it did provide the foundation for Dr. Spector’s next project, ZOE.
ZOE crowdsources huge amounts of data including individual metabolic responses to standardized meals in order to predict personalized food responses based on individual biology and unique microbiome profile.
In other words, it takes the guesswork out of a) knowing what your genes mean for your food responses b) tailoring your food choices with your genetic expression in mind, and c) ultimately creating a positive feedback loop to much better health on all levels.
Now, this is not an ad for ZOE, but if you so wish, you can…
- Get the free ZOE gut health guide (this is good, but generic, gut health information)
- Take the ZOE home gut health test (quiz followed by offers of lab tests)
- Browse the ZOE Health Academy, its education wing
Want to know more?
Dr. Spector has a bunch of books out, including some that we’ve reviewed previously:
- Spoon-Fed: Why Almost Everything We’ve Been Told About Food Is Wrong
- The Diet Myth: The Real Science Behind What We Eat
- Food for Life: The New Science of Eating Well
You can also check out our own previous main feature, which wasn’t about Dr. Spector’s work but was very adjacent:
The Brain-Gut Highway: A Two-Way Street
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Celeriac vs Celery – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing celeriac to celery, we picked the celeriac.
Why?
Yes, these are essentially the same plant, but there are important nutritional differences:
In terms of macros, celeriac has more than 2x the protein, and slightly more carbs and fiber. Both are very low glycemic index, so the higher protein and fiber makes celeriac the winner in this category.
In the category of vitamins, celeriac has more of vitamins B1, B3, B5, B6, C, E, K, and choline, while celery has more of vitamins A and B9. An easy win for celeriac.
When it comes to minerals, celeriac has more copper, calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while celery is not higher in any minerals. Another obvious win for celeriac.
Adding these sections up makes for a clear overall win for celeriac, but by all means enjoy either or both!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How they did it: STAT reporters expose how ailing seniors suffer when Medicare Advantage plans use algorithms to deny care
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In a call with a long-time source, what stood out most to STAT reporters Bob Herman and Casey Ross was just how viscerally frustrated and angry the source was about an algorithm used by insurance companies to decide how long patients should stay in a nursing home or rehab facility before being sent home.
The STAT stories had a far-reaching impact:
- The U.S. Senate Committee on Homeland Security and Government Affairs took a rare step of launching a formal investigation into the use of algorithms by the country’s three largest Medicare Advantage insurers.
- Thirty-two House members urged the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services to increase the oversight of algorithms that health insurers use to make coverage decisions.
- In a rare step, CMS launched its own investigation into UnitedHealth. It also stiffened its regulations on the use of proprietary algorithms and introduced plans to audit denials across Medicare Advantage plans in 2024.
- Based on STAT’s reporting, Medicare Advantage beneficiaries filed two class-action lawsuits against UnitedHealth and its NaviHealth subsidiary, the maker of the algorithm, and against Humana, another major health insurance company that was also using the algorithm.
- Amid scrutiny, UnitedHealth renamed NaviHealth.
The companies never allowed an on-the-record interview with their executives, but they acknowledged that STAT’s reporting was true, according to the news organization.
Ross and Herman spoke with The Journalist’s Resource about their project and shared the following eight tips.
1. Search public comments on proposed federal rules to find sources.
Herman and Ross knew that the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services had put out a request for public comments, asking stakeholders within the Medicare Advantage industry how the system could improve.
There are two main ways to get Medicare coverage: original Medicare, which is a fee-for-service health plan, and Medicare Advantage, which is a type of Medicare health plan offered by private insurance companies that contract with Medicare. Medicare Advantage plans have increasingly become popular in recent years.
Under the Social Security Act, the public has the opportunity to submit comments on Medicare’s proposed national coverage determinations. CMS uses public comments to inform its proposed and final decisions. It responds in detail to all public comments when issuing a final decision.
The reporters began combing through hundreds of public comments attached to a proposed Medicare Advantage rule that was undergoing federal review. NaviHealth, the UnitedHealth subsidiary and the maker of the algorithm, came up in many of the comments, which include the submitters’ information.
“These are screaming all-caps comments to federal regulators about YOU NEED TO SOMETHING ABOUT THIS BECAUSE IT’S DISGUSTING,” Ross says.
“The federal government is proposing rules and regulations all the time,” adds Herman, STAT’s business of health care reporter. “If someone’s going to take the time and effort to comment on them, they must have at least some knowledge of what’s going on. It’s just a great tool for any journalist to use to figure out more and who to contact.”
The reporters also found several attorneys who had complained in the comments. They began reaching out to them, eventually gaining access to confidential documents and intermediaries who put them in touch with patients to show the human impact of the algorithm.
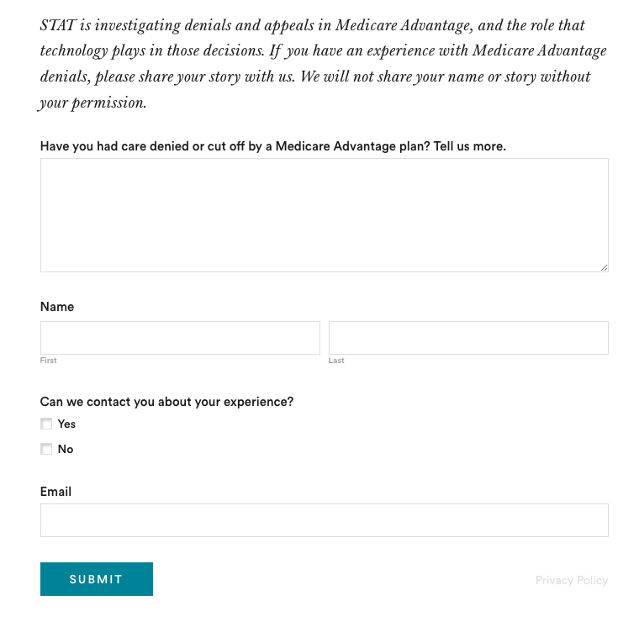
2. Harness the power of the reader submission box.
At the suggestion of an editor, the reporters added a reader submission box at the bottom of their first story, asking them to share their own experiences with Medicare Advantage denials.
The floodgates opened. Hundreds of submissions arrived.
By the end of their first story, Herman and Ross had confidential records and some patients, but they had no internal sources in the companies they were investigating, including Navihealth. The submission box led them to their first internal source.
(Screenshot of STAT’s submission box.) The journalists also combed through LinkedIn and reached out to former and current employees, but the response rate was much lower than what they received via the submission box.
The submission box “is just right there,” Herman says. “People who would want to reach out to us can do it right then and there after they read the story and it’s fresh in their minds.”
3. Mine podcasts relevant to your story.
The reporters weren’t sure if they could get interviews with some of the key figures in the story, including Tom Scully, the former head of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services who drew up the initial plans for NaviHealth years before UnitedHealth acquired it.
But Herman and another colleague had written previously about Scully’s private equity firm and they had found a podcast where he talked about his work. So Herman went back to the podcast — where he discovered Scully had also discussed NaviHealth.
The reporters also used the podcast to get Scully on the phone for an interview.
“So we knew we had a good jumping off point there to be like, ‘OK, you’ve talked about NaviHealth on a podcast, let’s talk about this,’” Herman says. “I think that helped make him more willing to speak with us.”
4. When covering AI initiatives, proceed with caution.
“A source of mine once said to me, ‘AI is not magic,’” Ross says. “People need to just ask questions about it because AI has this aura about it that it’s objective, that it’s accurate, that it’s unquestionable, that it never fails. And that is not true.”
AI is not a neutral, objective machine, Ross says. “It’s based on data that’s fed into it and people need to ask questions about that data.”
He suggests several questions to ask about the data behind AI tools:
- Where does the data come from?
- Who does it represent?
- How is this tool being applied?
- Do the people to whom the tool is being applied match the data on which it was trained? “If racial groups or genders or age of economic situations are not adequately represented in the training set, then there can be an awful lot of bias in the output of the tool and how it’s applied,” Ross says.
- How is the tool applied within the institution? Are people being forced to forsake their judgment and their own ability to do their jobs to follow the algorithm?
5. Localize the story.
More than half of all Medicare beneficiaries have Medicare Advantage and there’s a high likelihood that there are multiple Medicare Advantage plans in every county across the nation.
“So it’s worth looking to see how Medicare Advantage plans are growing in your area,” Herman says.
Finding out about AI use will most likely rely on shoe-leather reporting of speaking with providers, nursing homes and rehab facilities, attorneys and patients in your community, he says. Another source is home health agencies, which may be caring for patients who were kicked out of nursing homes and rehab facilities too soon because of a decision by an algorithm.
The anecdote that opens their first story involves a small regional health insurer in Wisconsin, which was using NaviHealth and a contractor to manage post-acute care services, Ross says.
“It’s happening to people in small communities who have no idea that this insurer they’ve signed up with is using this tool made by this other company that operates nationally,” Ross says.
There are also plenty of other companies like NaviHealth that are being used by Medicare Advantage plans, Herman says. “So it’s understanding which Medicare Advantage plans are being sold in your area and then which post-acute management companies they’re using,” he adds.
Some regional insurers have online documents that show which contractors they use to evaluate post-acute care services.
6. Get familiar with Medicare’s appeals databases
Medicare beneficiaries can contest Medicare Advantage denials through a five-stage process, which can last months to years. The appeals can be filed via the Office of Medicare Hearings and Appeals.
“Between 2020 and 2022, the number of appeals filed to contest Medicare Advantage denials shot up 58%, with nearly 150,000 requests to review a denial filed in 2022, according to a federal database,” Ross and Herman write in their first story. “Federal records show most denials for skilled nursing care are eventually overturned, either by the plan itself or an independent body that adjudicates Medicare appeals.”
There are several sources to find appeals data. Be mindful that the cases themselves are not public to protect patient privacy, but you can find the number of appeals filed and the rationale for decisions.
CMS has two quality improvement organizations, or QIOs, Livanta and Kepro, which are required to file free, publicly-available annual reports, about the cases they handle, Ross says.
Another company, Maximus, a Quality Improvement Contractor, also files reports on prior authorization cases it adjudicates for Medicare. The free annual reports include data on raw numbers of cases and basic information about the percentage denials either overturned or upheld on appeal, Ross explains.
CMS also maintains its own database on appeals for Medicare Part C (Medicare Advantage plans) and Part D, which covers prescription drugs, although the data is not complete, Ross explains.
7. Give your editor regular updates.
“Sprinkle the breadcrumbs in front of your editors,” Ross says.
“If you wrap your editors in the process, you’re more likely to be able to get to the end of [the story] before they say, ‘That’s it! Give me your copy,’” Ross says.
8. Get that first story out.
“You don’t have to know everything before you write that first story,” Ross says. “Because with that first story, if it has credibility and it resonates with people, sources will come forward and sources will continue to come forward.”
Read the stories
Denied by AI: How Medicare Advantage plans use algorithms to cut off care for seniors in need
UnitedHealth pushed employees to follow an algorithm to cut off Medicare patients’ rehab care
UnitedHealth used secret rules to restrict rehab care for seriously ill Medicare Advantage patients
This article first appeared on The Journalist’s Resource and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: