Ayurveda’s Contributions To Science
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ayurveda’s Contributions To Science (Without Being Itself Rooted in Scientific Method)
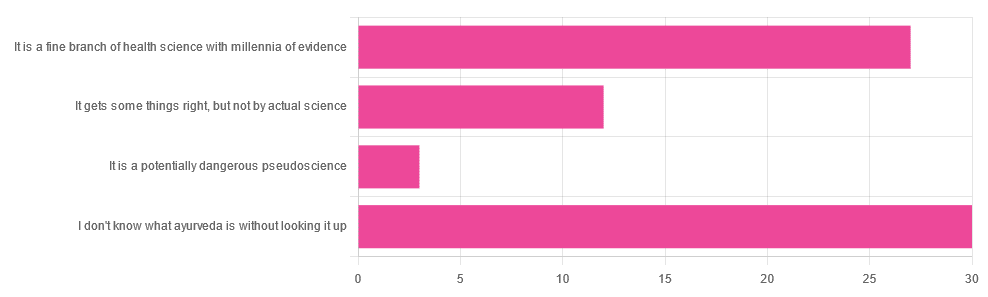
Yesterday, we asked you for your opinions on ayurveda, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses. Of those who responded…
- A little over 41% said “I don’t know what ayurveda is without looking it up”
- A little over 37% said “It is a fine branch of health science with millennia of evidence”
- A little over 16% said “It gets some things right, but not by actual science”
- A little over 4% said “It is a potentially dangerous pseudoscience”
So, what does the science say?
Ayurveda is scientific: True or False?
False, simply. Let’s just rip the band-aid off in this case. That doesn’t mean it’s necessarily without merit, though!
Let’s put it this way:
- If you drink coffee to feel more awake because scientific method has discerned that caffeine has vasoconstrictive and adenosine-blocking effects while also promoting dopaminergic activity, then your consumption of coffee is evidence-based and scientific. Great!
- If you drink coffee to feel more awake because somebody told you that that somebody told them that it energizes you by balancing the elements fire (the heat of the coffee), air (the little bubbles on top), earth (the coffee grinds), water (the water), and ether (steam), then that is neither evidence-based nor scientific, but it will still work exactly the same.
Ayurveda is a little like that. It’s an ancient traditional Indian medicine, based on a combination of anecdotal evidence and supposition.
- The anecdotal evidence from ayurveda has often resulted in herbal remedies that, in modern scientific trials, have been found to have merit.
- Ayurvedic meditative practices also have a large overlap with modern mindfulness practices, and have also been found to have merit
- Ayurveda also promotes the practice of yoga, which is indeed a very healthful activity
- The supposition from ayurveda is based largely in those five elements we mentioned above, as well as a “balancing of humors” comparable to medieval European medicine, and from a scientific perspective, is simply a hypothesis with no evidence to support it.
Note: while ayurveda is commonly described as a science by its practitioners in the modern age, it did not originally claim to be scientific, but rather, wisdom handed down directly by the god Dhanvantari.
Ayurveda gets some things right: True or False?
True! Indeed, we covered some before in 10almonds; you may remember:
Bacopa Monnieri: A Well-Evidenced Cognitive Enhancer
(Bacopa monnieri is also known by its name in ayurveda, brahmi)
There are many other herbs that have made their way from ayurveda into modern science, but the above is a stand-out example. Others include:
- Ashwagandha: The Root of All Even-Mindedness?
- Boswellia serrata (Frankincense) Against Pain and Depression/Anxiety
Yoga and meditation are also great, and not only that, but great by science, for example:
- NCCIH | Yoga for Health: Clinical Guidelines, Scientific Literature, Info for Patients
- The Neuroscience of Mindfulness: How Mindfulness Alters the Brain and Facilitates Emotion Regulation
Ayurveda is a potentially dangerous pseudoscience: True or False?
Also True! We covered why it’s a pseudoscience above, but that doesn’t make it potentially dangerous, per se (you’ll remember our coffee example).
What does, however, make it potentially dangerous (dose-dependent) is its use of heavy metals such as lead, mercury, and arsenic:
Heavy Metal Content of Ayurvedic Herbal Medicine Products
Some final thoughts…
Want to learn more about the sometimes beneficial, sometimes uneasy relationship between ayurveda and modern science?
A lot of scholarly articles trying to bridge (or further separate) the two were very biased one way or the other.
Instead, here’s one that’s reasonably optimistic with regard to ayurveda’s potential for good, while being realistic about how it currently stands:
Development of Ayurveda—Tradition to trend
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Beautiful Cure – by Dr. Daniel Davis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This one is not just a book about the history of immunology and a primer on how the immune system works. It is those things too, but it’s more:
Dr. Daniel Davis, a professor of immunology and celebrated researcher in his own right, bids us look at not just what we can do, but also what else we might.
This is not to say that the book is speculative; Dr. Davis deals in data rather than imaginings. He also cautions us against falling prey to sensationalization of the “beautiful cures” that the field of immunology is working towards. What, then, are these “beautiful cures”?
Just like our immune systems (in the plural; by Dr. Davis’ count, primarily talking about our innate and adaptive immune systems) can in principle deal with any biological threat, but in practice don’t always get it right, the same goes for our medicine.
He argues that in principle, we categorically can cure any immune-related disease (including autoimmune diseases, and tangentially, cancer). The theoretical existence of such cures is a mathematically known truth. The practical, contingent existence of them? That’s what takes the actual work.
The style of the book is accessible pop science, with a hard science backbone from start to finish.
Bottom line: if you’d like to know more about immunology, and be inspired with hope and wonder without getting carried away, this is the book for you.
Click here to check out The Beautiful Cure, and learn about these medical marvels!
Share This Post
-
Turmeric (Curcumin) Dos and Don’ts With Dr. Kim
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Turmeric is a fabulous spice, most well-known for its anti-inflammatory powers; its antioxidant effects benefit all of the body, including the brain. While it fights seemingly everything from arthritis to atherosclerosis to Alzheimer’s and more, it also boosts brain-derived neurotrophic factor, looks after your cardiovascular health, holds back diabetes, reduces the risk of cancer, fights depression, slows aging, and basically does everything short of making you sing well too.
Dr. Leonid Kim goes over the scientific evidence for these, and also talks about some of the practicalities of taking turmeric, and safety considerations.
For the most part, turmeric is very safe even at high doses (up to 8g at least); indeed, at smaller doses (e.g. 500mg) it largely does the same job as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, with fewer problems.
It also does the job of several antidiabetic medications, by increasing uptake of glucose (thus reducing blood sugar levels) while simultaneously decreasing the glucose secretion from the liver. It does this by regulating the AMPK signalling pathway, just like metformin—while again, being safer.
Dr. Kim also looks at the (good!) evidence for turmeric in managing PCOS and undoing NAFLD; so far, so good.
Dosage: he bids us pay attention whether we’re taking it as turmeric itself or as curcumin standardized extract. The latter is the active compound, and in principle more powerful, but in practice it can get metabolized too quickly and easily—before it can have its desired effect. So, turmeric itself is a very good choice.
Absorption: since we do want it to be absorbed well, though, he does recommend taking it with piperine (as in black pepper).
You may be thinking: isn’t this going to cause the same problem you were just talking about, and cause it to be metabolized too quickly? And the answer is: no! How piperine works is almost the opposite; it protects the curcumin in the turmeric from our digestive enzymes, and thus allows them to get absorbed without being broken down too quickly—thus increasing the bioavailability by slowing the process down.
Lipophilia: no, that’s not a disease (or a fetish), rather it means that curcumin is soluble in fats, so we should take it near in time to a meal that contains at least a tablespoon of oil in total (so if you’re cooking a curry with your turmeric, this need is covered already, for example).
Supplement provenance: he recommends picking a supplement that’s been tested by a reputable 3rd party, as otherwise turmeric can be quite prone to impurities (which can include lead and arsenic, so, not great).
Contraindications: for some people, curcumin can cause gastrointestinal issues (less likely if taking with meals), and also, it can interact with blood-thinners. While taking aspirin or curcumin alone might help avoid circulatory problems, taking both could increase the bleeding risk for some people, for example. Similarly, if taking curcumin and metformin while diabetic, one must watch out for the combination being too effective at lowering blood sugar levels, and thus causing hypoglycemia instead. Similar deal with blood pressure medications.
There’s more in the video though (yes really; we know we wrote a lot but it’s information-dense), so do check it out:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
Want to know more?
You can also check out our related articles:
Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)Share This Post
-
How much time should you spend sitting versus standing? New research reveals the perfect mix for optimal health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
People have a pretty intuitive sense of what is healthy – standing is better than sitting, exercise is great for overall health and getting good sleep is imperative.
However, if exercise in the evening may disrupt our sleep, or make us feel the need to be more sedentary to recover, a key question emerges – what is the best way to balance our 24 hours to optimise our health?
Our research attempted to answer this for risk factors for heart disease, stroke and diabetes. We found the optimal amount of sleep was 8.3 hours, while for light activity and moderate to vigorous activity, it was best to get 2.2 hours each.
Finding the right balance
Current health guidelines recommend you stick to a sensible regime of moderate-to vigorous-intensity physical activity 2.5–5 hours per week.
However mounting evidence now suggests how you spend your day can have meaningful ramifications for your health. In addition to moderate-to vigorous-intensity physical activity, this means the time you spend sitting, standing, doing light physical activity (such as walking around your house or office) and sleeping.
Our research looked at more than 2,000 adults who wore body sensors that could interpret their physical behaviours, for seven days. This gave us a sense of how they spent their average 24 hours.
At the start of the study participants had their waist circumference, blood sugar and insulin sensitivity measured. The body sensor and assessment data was matched and analysed then tested against health risk markers — such as a heart disease and stroke risk score — to create a model.
Using this model, we fed through thousands of permutations of 24 hours and found the ones with the estimated lowest associations with heart disease risk and blood-glucose levels. This created many optimal mixes of sitting, standing, light and moderate intensity activity.
When we looked at waist circumference, blood sugar, insulin sensitivity and a heart disease and stroke risk score, we noted differing optimal time zones. Where those zones mutually overlapped was ascribed the optimal zone for heart disease and diabetes risk.
You’re doing more physical activity than you think
We found light-intensity physical activity (defined as walking less than 100 steps per minute) – such as walking to the water cooler, the bathroom, or strolling casually with friends – had strong associations with glucose control, and especially in people with type 2 diabetes. This light-intensity physical activity is likely accumulated intermittently throughout the day rather than being a purposeful bout of light exercise.
Our experimental evidence shows that interrupting our sitting regularly with light-physical activity (such as taking a 3–5 minute walk every hour) can improve our metabolism, especially so after lunch.
While the moderate-to-vigorous physical activity time might seem a quite high, at more than 2 hours a day, we defined it as more than 100 steps per minute. This equates to a brisk walk.
It should be noted that these findings are preliminary. This is the first study of heart disease and diabetes risk and the “optimal” 24 hours, and the results will need further confirmation with longer prospective studies.
The data is also cross-sectional. This means that the estimates of time use are correlated with the disease risk factors, meaning it’s unclear whether how participants spent their time influences their risk factors or whether those risk factors influence how someone spends their time.
Australia’s adult physical activity guidelines need updating
Australia’s physical activity guidelines currently only recommend exercise intensity and time. A new set of guidelines are being developed to incorporate 24-hour movement. Soon Australians will be able to use these guidelines to examine their 24 hours and understand where they can make improvements.
While our new research can inform the upcoming guidelines, we should keep in mind that the recommendations are like a north star: something to head towards to improve your health. In principle this means reducing sitting time where possible, increasing standing and light-intensity physical activity, increasing more vigorous intensity physical activity, and aiming for a healthy sleep of 7.5–9 hours per night.
Beneficial changes could come in the form of reducing screen time in the evening or opting for an active commute over driving commute, or prioritising an earlier bed time over watching television in the evening.
It’s also important to acknowledge these are recommendations for an able adult. We all have different considerations, and above all, movement should be fun.
Christian Brakenridge, Postdoctoral research fellow at Swinburne University Centre for Urban Transitions, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Truth About Vaccines
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Truth About Vaccines
Yesterday we asked your views on vaccines, and we got an interesting spread of answers. Of those who responded to the poll, most were in favour of vaccines. We got quite a lot of comments this time too; we can’t feature them all, but we’ll include extracts from a few in our article today, as they raised interesting points!
Vaccines contain dangerous ingredients that will harm us more than the disease would: True or False?
False, contextually.
Many people are very understandably wary of things they know full well to be toxic, being injected into them.
One subscriber who voted for “Vaccines are poison, and/or are some manner of conspiracy ” wrote:
❝I think vaccines from 50–60 years ago are true vaccines and were safer than vaccines today. I have not had a vaccine for many, many years, and I never plan to have any kind of vaccine/shot again.❞
They didn’t say why they personally felt this way, but the notion that “things were simpler back in the day” is a common (and often correct!) observation regards health, especially when it comes to unwanted additives and ultraprocessing of food.
Things like aluminum or mercury in vaccines are much like sodium and chlorine in table salt. Sodium and chlorine are indeed both toxic to us. But in the form of sodium chloride, it’s a normal part of our diet, provided we don’t overdo it.
Additionally, the amount of unwanted metals (e.g. aluminum, mercury) in vaccines is orders of magnitude smaller than the amount in dietary sources—even if you’re a baby and your “dietary sources” are breast milk and/or formula milk.
In the case of formaldehyde (an inactivating agent), it’s also the dose that makes the poison (and the quantity in vaccines is truly miniscule).
This academic paper alone cites more sources than we could here without making today’s newsletter longer than it already is:
Vaccine Safety: Myths and Misinformation
I have a perfectly good immune system, it can handle the disease: True or False?
True! Contingently.
In fact, our immune system is so good at defending against disease, that the best thing we can do to protect ourselves is show our immune system a dead or deactivated version of a pathogen, so that when the real pathogen comes along, our immune system knows exactly what it is and what to do about it.
In other words, a vaccine.
One subscriber who voted for “Vaccines are important but in some cases the side effects can be worse ” wrote:
❝In some ways I’m vacd out. I got COVid a few months ago and had no symptoms except a cough. I have asthma and it didn’t trigger a lot of congestion. No issues. I am fully vaccinated but not sure I’ll get one in fall.❞
We’re glad this subscriber didn’t get too ill! A testimony to their robust immune system doing what it’s supposed to, after being shown a recent-ish edition of the pathogen, in deactivated form.
It’s very reasonable to start wondering: “surely I’m vaccinated enough by now”
And, hopefully, you are! But, as any given pathogen mutates over time, we eventually need to show our immune system what the new version looks like, or else it won’t recognize it.
See also: Why Experts Think You’ll Need a COVID-19 Booster Shot in the Future
So why don’t we need booster shots for everything? Often, it’s because a pathogen has stopped mutating at any meaningful rate. Polio is an example of this—no booster is needed for most people in most places.
Others, like flu, require annual boosters to keep up with the pathogens.
Herd immunity will keep us safe: True or False?
True! Ish.
But it doesn’t mean what a lot of people think it means. For example, in the UK, “herd immunity” was the strategy promoted by Prime Minister of the hour, Boris Johnson. But he misunderstood what it meant:
- What he thought it meant: everyone gets the disease, then everyone who doesn’t die is now immune
- What it actually means: if most people are immune to the disease (for example: due to having been vaccinated), it can’t easily get to the people who aren’t immune
One subscriber who voted for “Vaccines are critical for our health; vax to the max! ” wrote:
❝I had a chiropractor a few years ago, who explained to me that if the general public took vaccines, then she would not have to vaccinate her children and take a risk of having side effects❞
Obviously, we can’t speak for this subscriber’s chiropractor’s children, but this raises a good example: some people can’t safely have a given vaccine, due to underlying medical conditions—or perhaps it is not available to them, for example if they are under a certain age.
In such cases, herd immunity—other people around having been vaccinated and thus not passing on the disease—is what will keep them safe.
Here’s a useful guide from the US Dept of Health and Human Services:
How does community immunity (a.k.a. herd immunity) work?
And, for those who are more visually inclined, here’s a graphical representation of a mathematical model of how herd immunity works (you can run a simulation)!
Stay safe!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Pine Bark’s Next-Level Antioxidant Properties
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pine Bark’s Next-Level Antioxidant Properties
Pine bark extract has been used by the indigenous peoples of N. America for a very long time, to treat a variety of ailments.
This one falls into the category of “things from traditional medicine that eventually got investigated and their scientific worth noticed by people from outside of those cultures”.
Not all pine trees!
If you happen to have pine trees near you, be aware that without sufficient botanical knowledge, you could find yourself bark-harvesting from the wrong tree—but many species of pine do have these qualities.
Useful (for this purpose) pine trees include, but are not limited to:
- Pinus banksiana
- Pinus massoniana
- Pinus pinaster
- Pinus radiata
- Pinus resinosa
- Pinus strobus
…which is already a fair list, but there are dozens more that have not been studied, and/or found lacking in medicinal qualities, and/or just didn’t make our list here today.
What does it do & How does it work?
We sneakily put those two questions together today because it’s easiest to explain in one:
The Pinus family in general has powerful antioxidant qualities, and not just like blueberries or coffee (wonderful as those are).
Rather, it has:
- Phenolic acids: these are the polyphenols found in many plant foods rich in antioxidants. These are great, but they aren’t the exciting part here.
- Catechins: these aren’t classified as antioxidants, but they are flavonoids that do the same job in a slightly different way
- Procyanidins: another class of flavonoids, and this is where pine bark really comes into its own
And yes, as ever, “those three things that always seem to come together”, it having these antioxidant properties means it is also anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer:
…and anti-aging:
Pleiotropic Effects of French Maritime Pine Bark Extract to Promote Healthy Aging
…which does of course mean that it almost certainly fights age-related cognitive decline, though studies for that have been animal studies so far, such as:
- Pine Bark Polyphenolic Extract Attenuates Amyloid-β and Tau Misfolding in a Model System of Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropathology
- Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Pinus densiflora Bark Extract in Gerbil Hippocampus Following Transient Forebrain Ischemia
- Neuroprotective Effects of Korean Red Pine ( Pinus densiflora) Bark Extract and Its Phenolics
- Pine bark treatment decelerates plaque development and improves spatial memory in Alzheimer’s disease mice
Where to get it?
As ever, we don’t sell it, but here’s an example product on Amazon for your convenience; we recommend shopping around though, as prices vary a lot!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Turmeric: Raw Root, Powder, Tea, Or…?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Is turmeric infused water better or chewing half an inch of raw turmeric better? I am trying to work on my immunity as this year I have suffered the most with my allergies in the last 20 years. In case you can guide me, I will be thankful.❞
Great question! First of all, a quick recap of the properties of turmeric (and its relevant active compound, curcumin)
Let’s do a quick run-down:
- It fights inflammation, and thus helps fight many diseases where inflammation is a factor (ranging from atherosclerosis to arthritis to Alzheimer’s and more)
- It has powerful antioxidant effects too
- It boosts brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) and thus improves memory and attention
- It helps protect against heart disease…
- …and can give a 65% decreased risk of experiencing a heart attack
- It can help prevent cancer, and reduce cancerous lesions by 40%
- It’s also good against depression
- It even slows aging
If you take curcumin with black pepper, it allows your body to use the curcumin around 2,000% better. This goes whether you’re cooking with both, or take them as a supplement (they’re commonly sold as a combo-capsule for this reason).
Note: you mentioned an infusion or chewing the root, so perhaps you are not having black pepper with either of those. That’s fine, but try to have it near to black pepper (for example, perhaps while cooking a meal in which you use black pepper, so you take the turmeric and then you eat the meal).
Extra note: in fact, that’s ideal, because curcumin is fat-soluble, so having it with (or near in time to) consuming fats (such as perhaps used in cooking) is a great way to do it.
Curcumin vs allergies, specifically
For any thinking “that wasn’t on the list”… It was hidden! It comes with curcumin’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant powers.
See for example:
- Modulation of the Immune Response to Allergies Using Alternative Functional Foods ← turmeric is one of the functional foods discussed
- Turmeric extract alleviates airway inflammation via oxidative stress-driven MAPKs/MMPs pathway ← this is important to dial down an inappropriate immune response, e.g. an allergy
- Dietary Polyphenols, Plant Metabolites, and Allergic Disorders: A Comprehensive Review ← again, turmeric is a key player
- Development of fast-dissolving sublingual nanofibers containing allergen and curcumin for immune response modulation in a mouse model of allergic rhinitis ← allergic rhinitis = “seasonal allergies” and similar respiratory allergic responses
- DES/O microemulsion for solubilizing and delivering curcumin via the nasal administration to treat acute asthma ← similar mechanism of action
food vs supplement
You didn’t ask this, but it’ll be helpful for understanding if we quickly cover this first.
- Turmeric root is just that: a root, which contains abundant phytochemicals, and/but is not at all standardized in dosage
- Curcumin extract, on the other hand, have been standardized, optimized, and are metabolized much more quickly
…which latter can be a problem, because it’s been taken apart and used for scrap metabolites faster than the body could actually make use of the curcumin as-is.
The black pepper hack fixes this, by the way, because of how it improves absorption.
You may be thinking: isn’t this going to cause the same problem you were just talking about, and cause it to be metabolized too quickly? And the answer is: no! How piperine works is almost the opposite; it protects the curcumin in the turmeric from our digestive enzymes, and thus allows them to get absorbed without being broken down too quickly—thus increasing the bioavailability by slowing the process down.
In short: food is best, but supplements are fine for anyone whose local supermarkets don’t sell turmeric root. Make sure to get it from a vendor who has transparency about their processes and has reputable certifications against heavy metal contamination though, because that’s especially common in cheap turmeric/curcumin supplements.
The different ways of taking it
There are a few more options than those you mentioned, so let’s quickly note:
- Infusion: the chopped/grated root is steeped in hot water, and then we drink the hot water (sometimes called “turmeric tea”) and discard the solids
- Suspension: the dried, powdered root is mixed in water, which we then drink in its entirety
- Decoction: the finely chopped/grated root is steeped in hot water, and then we consume this in its entirety, which most people don’t find pleasant
- Mastication only: chewing the root, spitting out the fibrous remnants
- Solid ingestion: eating the root
All of these will allow you to gain the benefits of curcumin (wherever that yellow-red pigment goes, so goes the curcumin), but only those which include consuming the solids will give you the full benefit (as otherwise, you are discarding a large amount of the curcumin with the solids that you discard).
So, we can remove both of the methods that you mentioned (infusion and chewing, assuming you meant chewing only, and not eating).
Things tend to lose potency with drying and grinding processes, not to mention long-term storage, so we can also remove suspension from the list.
That leaves decoction and solid ingestion. Since solid ingestion is not comfortable for most people without cooking the root, that leaves decoction as the superior method unless you personally are happy to just eat raw turmeric root.
However!
Out of the two you presented, infusion can be improved if a) you make the infusion very strong, by grating the root before steeping, and letting it steep for a good while, and b) if practical, throw the grated root (after pouring the tea) into a dish where its flavor will be appropriate. If this seems strange, like throwing a waste product into your meal, then remember that that’s only a matter of convention: physically, what it is is cooked (boiling is cooking!) grated turmeric, nothing more nor less.
At the end of the day though, the way that works best will be the way that you enjoy most (or if that’s not an option, dislike least), and thus will do more often.
Want to know more?
Check out:
Turmeric (Curcumin) Dos and Don’ts With Dr. Kim
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: