Artichoke vs Cabbage – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing artichoke to cabbage, we picked the artichoke.
Why?
Looking at the macros first of all, artichoke has more than 2x the protein; it also has nearly 2x the carbs, but to more than counterbalance that, it has more than 2x the fiber. An easy win for artichoke in the macros category.
In the category of vitamins, both are very respectable; artichoke has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B9, E, and choline, while cabbage has more of vitamins A, C, and K. Superficially, that’s a 7:3 win for artichoke, but the margins of difference for artichoke’s vitamins are very small (meaning cabbage is hot on its heels for those vitamins), whereas cabbage’s A, C, and K are with big margins of difference (3–7x more), and arguably those vitamins are higher priority in the sense that B-vitamins of various kinds are found in most foods, whereas A, C, and K aren’t, and while E isn’t either, artichoke had a tiny margin of difference for that. All in all, we’re calling this category a tie, as an equally fair argument could be made for either vegetable here.
When it comes to minerals, there’s a much clearer winner: artichoke has a lot more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while cabbage has a tiny bit more selenium. The two vegetables are equal on calcium.
Adding up two clear artichoke wins and a tie, makes for an overall clear win for artichoke. Of course, enjoy both though; diversity is almost always best of all!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Much Can Hypnotherapy Really Do?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sit Back, Relax, And…
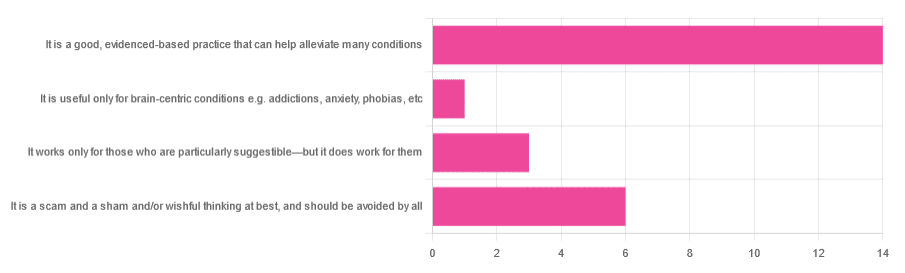
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinions of hypnotherapy, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 58% said “It is a good, evidenced-based practice that can help alleviate many conditions”
- Exactly 25% said “It is a scam and sham and/or wishful thinking at best, and should be avoided by all”
- About 13% said “It works only for those who are particularly suggestible—but it does work for them”
- One (1) person said “It is useful only for brain-centric conditions e.g. addictions, anxiety, phobias, etc”
So what does the science say?
Hypnotherapy is all in the patient’s head: True or False?
True! But guess which part of your body controls much of the rest of it.
So while hypnotherapy may be “all in the head”, its effects are not.
Since placebo effect, nocebo effect, and psychosomatic effect in general are well-documented, it’s quite safe to say at the very least that hypnotherapy thus “may be useful”.
Which prompts the question…
Hypnotherapy is just placebo: True or False?
False, probably. At the very least, if it’s placebo, it’s an unusually effective placebo.
And yes, even though testing against placebo is considered a good method of doing randomized controlled trials, some placebos are definitely better than others. If a placebo starts giving results much better than other placebos, is it still a placebo? Possibly a philosophical question whose answer may be rooted in semantics, but happily we do have a more useful answer…
Here’s an interesting paper which: a) begins its abstract with the strong, unequivocal statement “Hypnosis has proven clinical utility”, and b) goes on to examine the changes in neural activity during hypnosis:
Brain Activity and Functional Connectivity Associated with Hypnosis
It works only for the very suggestible: True or False?
False, broadly. As with any medical and/or therapeutic procedure, a patient’s expectations can affect the treatment outcome.
And, especially worthy of note, a patient’s level of engagement will vastly affect it treatment that has patient involvement. So for example, if a doctor prescribes a patient pills, which the patient does not think will work, so the patient takes them intermittently, because they’re slow to get the prescription refilled, etc, then surprise, the pills won’t get as good results (since they’re often not being taken).
How this plays out in hypnotherapy: because hypnotherapy is a guided process, part of its efficacy relies on the patient following instructions. If the hypnotherapist guides the patient’s mind, and internally the patient is just going “nope nope nope, what a lot of rubbish” then of course it will not work, just like if you ask for directions in the street and then ignore them, you won’t get to where you want to be.
For those who didn’t click on the above link by the way, you might want to go back and have a look at it, because it included groups of individuals with “high/low hypnotizability” per several ways of scoring such.
It works only for brain-centric things, e.g. addictions, anxieties, phobias, etc: True or False?
False—but it is better at those. Here for example is the UK’s Royal College of Psychiatrists’ information page, and if you go to “What conditions can hypnotherapy help to treat”, you’ll see two broad categories; the first is almost entirely brain-stuff; the second is more varied, and includes pain relief of various kinds, burn care, cancer treatment side effects, and even menopause symptoms. Finally, warts and other various skin conditions get their own (positive) mention, per “this is possible through the positive effects hypnosis has on the immune system”:
RCPsych | Hypnosis And Hypnotherapy
Wondering how much psychosomatic effect can do?
You might like this previous article; it’s not about hypnotherapy, but it is about the difference the mind can make on physical markers of aging:
Aging, Counterclockwise: When Age Is A Flexible Number
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Dancing vs Parkinson’s Depression
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a fun study, and the results are/were very predictable, and/but not necessarily something that people might think of in advance. First, let’s look at how some things work:
Parkinson’s disease & depression
Parkinson’s disease is a degenerative neurological disease that, amongst other things, is characterized by low dopamine levels.
For the general signs and symptoms, see: Recognize The Early Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
Dopamine is the neurotransmitter responsible for feelings of reward, is involved in our language faculties and the capacity to form plans (even simple plans such as “make a cup of coffee”) as well as being critical for motor functions.
See also: Neurotransmitter Cheatsheet ← for demystifying some of “what does what” for commonly-conflated chemicals
You can see, therefore, why Parkinson’s disease will often have depression as a comorbidity—there may be influencing social factors as well (many Parkinson’s disease sufferers are quite socially isolated, which certainly does not help), but a clear neurochemical factor that we can point to is “a person with low dopamine levels will feel joyless, bored, and unmotivated”.
Let movement be thy medicine
Parkinson’s disease medications, therefore, tend to involve increasing dopamine levels and/or the brain’s ability to use dopamine.
Antidepressant medications, however, are more commonly focused on serotonin, as serotonin is another neurotransmitter associated with happiness—it’s the one we get when we look at open green spaces with occasional trees and a blue sky ← we get it in other ways too, but for evolutionary reasons, it seems our brains still yearn the most for landscapes that look like the Serengeti, even if we have never even been there personally.
There are other kinds of antidepressants too, and (because depression can have different causes) what works for one person won’t necessarily work for another. See: Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
In the case of Parkinson’s disease, because the associated depression is mostly dopamine-related, those green spaces and blue skies and SSRIs won’t help much. But you know what does?
Dance!
A recent (published last month, at time of writing) study by Dr. Karolina Bearss et al. did an interventional study that found that dance classes significantly improved both subjective experience of depression, and objective brain markers of depression, across people with (68%) and without (32%) Parkinson’s disease.
The paper is quite short and it has diagrams, and discusses the longer-term effect as well as the per-session effect:
Dance is thought to have a double-effect, improving both cognitive factors and motor control factors, for obvious reasons, and all related to dopamine response (dancing is an activity we are hardwired to find rewarding*, plus it is exercise which also triggers various chemicals to be made, plus it is social, which also improves many mental health factors).
*You may have heard the expression that “dancing is a vertical expression of a horizontal desire”, and while that may not be true for everyone on an individual level, on a species level it is a very reasonable hypothesis for why we do it and why it is the way it is.
Want to learn more?
We wrote previously about battling depression (of any kind) here:
The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Pinto Beans vs Fava Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pinto beans to fava beans, we picked the pinto beans.
Why?
It wasn’t close!
In terms of macros, pinto beans have more protein and carbs, and much more fiber, resulting in a much lower glycemic index. We mention this, because while often the GI of two similar foods is similar, in this case pinto beans have a GI of 39 (low), while fava beans have a GI of 79 (high). In other words, not at all close, and pinto beans are the clear winner.
When it comes to vitamins, pinto beans have more of vitamins B1, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while fava beans have more of vitamins B2 and B3. Once again, not close, and that’s before we take into account the margins of difference for those vitamins; the margins of difference are much greater on the pinto beans’ side of the scale, for example pinto beans having 47x more vitamin E, while fava beans have only 43% more vitamin B2. So, orders of magnitude less. A clear win for pinto beans in all respects.
In the category of minerals, pinto beans have more calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while fava beans have more copper and zinc. This time, the margins of difference were quite moderate across the board, and/but pinto beans win on clear strength of numbers.
All in all, three clear wins for pinto beans add up to one big clear win for pinto beans.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What Matters Most For Your Heart? Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Black Olives vs Green Olives – Which is Healthier
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing black olives to green olives, we picked the black olives.
Why?
First know this: they are the same plant, just at different stages of ripening (green olives are, as you might expect, less ripe).
Next: the nutritional values of both, from macros down to the phytochemicals, are mostly very similar, but there are a few things that stand out:
• Black olives usually have more calories per serving, average about 25% more. But these are from healthy fats, so unless you’re on a calorie-restricted diet, this is probably not a consideration.
• Green olives are almost always “cured” for longer, which results in a much higher sodium content often around 200% that of black olives. Black olives are often not “cured” at all.Hence, we chose the black olives!
You may be wondering: do green olives have anything going for them that black olives don’t?
And the answer has a clue in the taste: green olives generally have a stronger, more bitter/pungent taste. And remember what we said about things that have a stronger, more bitter/pungent taste:
Tasty Polyphenols: Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
That’s right, green olives are a little higher in polyphenols than black olives.
But! If you want to enjoy the polyphenol content of green olives without the sodium content, the best way to do that is not olives, but olive oil—which is usually made from green olives.
For more about olive oil, check out:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hot And Sour Shiitake Soup
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a popular, easy, and delicious soup that nonetheless is not found in many western kitchens, despite being enjoyed in restaurants/take-out. Best of all, making it at home means that you know all the ingredients, can account for quality, and also can customize it per your preferences (i.e. how much heat/sourness you like).
You will need
- 3 cups shiitake mushrooms, sliced
- 3 cups bok choy, chopped
- 2 cups cherry tomatoes, quartered
- 1 cup carrot, grated
- 3 spring onions, chopped
- 2 shallots, sliced lengthways
- 2 serrano chilis (or similar), sliced thinly
- 2 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- 1 tbsp fresh ginger, sliced into 1″ strips
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 6 cups low-sodium vegetable stock. Ideally you will have made it yourself from vegetable cuttings that you saved in the freezer until you had enough to make stock from, but if that’s not an option, then low-sodium vegetable stock cubes can be purchased and used.
- Garnish: ¼ cup (or 4 tbsp) cilantro, chopped, or if you have the soap gene, then this time we recommend chopped basil as the subsitution
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Put the ginger in a big pot with the stock; cover and simmer for about 20 minutes (otherwise the ginger flavor will remain mostly concentrated in the ginger strips).
2) Bring it to a boil and add the bok choy, mushrooms, shallots, chili peppers, and the carrot; simmer for another 5 minutes
3) Add the remaining ingredients except for the garnish, and simmer for another 5 minutes
4) Serve, adding the garnish
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The (Longevity) Magic of Mushrooms
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
- Enjoy Bitter/Hot/Sour/Pungent Foods For Your Heart & Brain
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
- Some Surprising Truths About Hunger And Satiety
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Mindfulness – by Olivia Telford
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Olivia Telford takes us on a tour of mindfulness, meditation, mindfulness meditation, and how each of these things impacts stress, anxiety, and depression—as well as less obvious things too, like productivity and relationships.
In the category of how much this is a “how-to-” guide… It’s quite a “how-to” guide. We’re taught how to meditate, we’re taught assorted mindfulness exercises, and we’re taught specific mindfulness interventions such as beating various life traps (e.g. procrastination, executive dysfunction, etc) with mindfulness.
The writing style is simple and to the point, explanatory and very readable. References are made to pop-science and hard science alike, and all in all, is not too far from the kind of writing you might expect to find here at 10almonds.
Bottom line: if you’d like to practice mindfulness meditation and want an easy “in”, or perhaps you’re curious and wonder what mindfulness could tangibly do for you and how, then this book is a great choice for that.
Click here to check out Mindfulness, and enjoy being more present in life!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: