The Alzheimer’s Gene That Varies By Race & Sex
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Alzheimer’s Gene That Varies By Race & Sex
You probably know that there are important genetic factors that increase or decrease Alzheimer’s Risk. If you’d like a quick refresher before we carry on, here are two previous articles on this topic:
- Genetic Testing: Health Benefits & Methods (about personal genomics and health, including Alzheimer’s)
- The Surprising Link Between Type 2 Diabetes & Alzheimer’s (about the APOE-ε4 allele that is implicated in both)
A Tale of Two Alleles
It has generally been understood that APOE-ε2 lowers Alzheimer’s disease risk, and APOE-ε4 increases it.
However, for reasons beyond the scope of this article, research populations for genetic testing are overwhelmingly white. If you, dear reader, are white, you may be thinking “well, I’m white, so this isn’t a problem for me”, you might still want to read on…
An extensive new study, published days ago, by Dr. Belloy et al., looked at how these correlations held out per race and sex. They found:
- The “APOE-ε2 lowers; APOE-ε4 increases” dictum held out strongest for white people.
- In the case of Hispanic people, there was only a small correlation on the APOE-ε4 side of things, and none on the APOE-ε2 side of things per se.
- East Asians also saw no correlation with regard to APOE-ε2 per se.
- But! Hispanic and East Asian people had a reduced risk of Alzheimer’s if and only if they had both APOE-ε2 and APOE-ε4.
- Black people, meanwhile, saw a slight correlation with regard to the protective effect of APOE-ε2, and as for APOE-ε4, if they had any European ancestry, increased European ancestry meant a higher increased risk factor if they had APOE-ε4. African ancestry, on the other hand, had a protective effect, proportional to the overall amount of that ancestry.
And as for sex…
- Specifically for white people with the APOE-ε3/ε4 genotype, especially in the age range of 60–70, the genetic risk for Alzheimer’s was highest in women.
If you’d like to read more and examine the data for yourself:
APOE Genotype and Alzheimer Disease Risk Across Age, Sex, and Population Ancestry
Want to reduce your Alzheimer’s risk?
We have just the thing for you:
How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk: It’s Never Too Early To Do These 11 Things
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
No, sugar doesn’t make your kids hyperactive
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s a Saturday afternoon at a kids’ birthday party. Hordes of children are swarming between the spread of birthday treats and party games. Half-eaten cupcakes, biscuits and lollies litter the floor, and the kids seem to have gained superhuman speed and bounce-off-the-wall energy. But is sugar to blame?
The belief that eating sugary foods and drinks leads to hyperactivity has steadfastly persisted for decades. And parents have curtailed their children’s intake accordingly.
Balanced nutrition is critical during childhood. As a neuroscientist who has studied the negative effects of high sugar “junk food” diets on brain function, I can confidently say excessive sugar consumption does not have benefits to the young mind. In fact, neuroimaging studies show the brains of children who eat more processed snack foods are smaller in volume, particularly in the frontal cortices, than those of children who eat a more healthful diet.
But today’s scientific evidence does not support the claim sugar makes kids hyperactive.
Sharomka/Shutterstock The hyperactivity myth
Sugar is a rapid source of fuel for the body. The myth of sugar-induced hyperactivity can be traced to a handful of studies conducted in the 1970s and early 1980s. These were focused on the Feingold Diet as a treatment for what we now call Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), a neurodivergent profile where problems with inattention and/or hyperactivity and impulsivity can negatively affect school, work or relationships.
Devised by American paediatric allergist Benjamin Feingold, the diet is extremely restrictive. Artificial colours, sweeteners (including sugar) and flavourings, salicylates including aspirin, and three preservatives (butylated hydroxyanisole, butylated hydroxytoluene, and tert-Butrylhdryquinone) are eliminated.
Salicylates occur naturally in many healthy foods, including apples, berries, tomatoes, broccoli, cucumbers, capsicums, nuts, seeds, spices and some grains. So, as well as eliminating processed foods containing artificial colours, flavours, preservatives and sweeteners, the Feingold diet eliminates many nutritious foods helpful for healthy development.
However, Feingold believed avoiding these ingredients improved focus and behaviour. He conducted some small studies, which he claimed showed a large proportion of hyperactive children responded favourably to his diet.
Even it doesn’t make kids hyperactive, they shouldn’t have too much sugar. DenisMArt/Shutterstock Flawed by design
The methods used in the studies were flawed, particularly with respect to adequate control groups (who did not restrict foods) and failed to establish a causal link between sugar consumption and hyperactive behaviour.
Subsequent studies suggested less than 2% responded to restrictions rather than Feingold’s claimed 75%. But the idea still took hold in the public consciousness and was perpetuated by anecdotal experiences.
Fast forward to the present day. The scientific landscape looks vastly different. Rigorous research conducted by experts has consistently failed to find a connection between sugar and hyperactivity. Numerous placebo-controlled studies have demonstrated sugar does not significantly impact children’s behaviour or attention span.
One landmark meta-analysis study, published almost 20 years ago, compared the effects of sugar versus a placebo on children’s behaviour across multiple studies. The results were clear: in the vast majority of studies, sugar consumption did not lead to increased hyperactivity or disruptive behaviour.
Subsequent research has reinforced these findings, providing further evidence sugar does not cause hyperactivity in children, even in those diagnosed with ADHD.
While Feingold’s original claims were overstated, a small proportion of children do experience allergies to artificial food flavourings and dyes.
Pre-school aged children may be more sensitive to food additives than older children. This is potentially due to their smaller body size, or their still-developing brain and body.
Hooked on dopamine?
Although the link between sugar and hyperactivity is murky at best, there is a proven link between the neurotransmitter dopamine and increased activity.
The brain releases dopamine when a reward is encountered – such as an unexpected sweet treat. A surge of dopamine also invigorates movement – we see this increased activity after taking psychostimulant drugs like amphetamine. The excited behaviour of children towards sugary foods may be attributed to a burst of dopamine released in expectation of a reward, although the level of dopamine release is much less than that of a psychostimulant drug.
Dopamine function is also critically linked to ADHD, which is thought to be due to diminished dopamine receptor function in the brain. Some ADHD treatments such as methylphenidate (labelled Ritalin or Concerta) and lisdexamfetamine (sold as Vyvanse) are also psychostimulants. But in the ADHD brain the increased dopamine from these drugs recalibrates brain function to aid focus and behavioural control.
Maybe it’s less of a sugar rush and more of a dopamine rush? Anastasiya Tsiasemnikava/Shutterstock Why does the myth persist?
The complex interplay between diet, behaviour and societal beliefs endures. Expecting sugar to change your child’s behaviour can influence how you interpret what you see. In a study where parents were told their child had either received a sugary drink, or a placebo drink (with a non-sugar sweetener), those parents who expected their child to be hyperactive after having sugar perceived this effect, even when they’d only had the sugar-free placebo.
The allure of a simple explanation – blaming sugar for hyperactivity – can also be appealing in a world filled with many choices and conflicting voices.
Healthy foods, healthy brains
Sugar itself may not make your child hyperactive, but it can affect your child’s mental and physical health. Rather than demonising sugar, we should encourage moderation and balanced nutrition, teaching children healthy eating habits and fostering a positive relationship with food.
In both children and adults, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends limiting free sugar consumption to less than 10% of energy intake, and a reduction to 5% for further health benefits. Free sugars include sugars added to foods during manufacturing, and naturally present sugars in honey, syrups, fruit juices and fruit juice concentrates.
Treating sugary foods as rewards can result in them becoming highly valued by children. Non-sugar rewards also have this effect, so it’s a good idea to use stickers, toys or a fun activity as incentives for positive behaviour instead.
While sugar may provide a temporary energy boost, it does not turn children into hyperactive whirlwinds.
Amy Reichelt, Senior Lecturer (Adjunct), Nutritional neuroscientist, University of Adelaide
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
What Happens To Your Body When You Eat Raw Garlic Everyday
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Garlic’s benefits are not all in its most talked-about active compound, allicin (some are in other parts of the garlic), but the allicin is certainly very potent. However, allicin breaks down easily, which means that cooking reduces its value greatly, meaning that for health purposes, it is best consumed raw. Pickled garlic cloves are great, by the way, and you should try them if you haven’t already.
Garlic’s benefits (aside from being delicious)
Benefits that can be expected include:
- Boosts immunity: allicin enhances white blood cell function, helping fight off colds and flu
- Supports heart health: lowers blood pressure, reduces cholesterol, and prevents blood clots, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke
- Anti-cancer properties: it contains sulfur compounds that may inhibit cancer cell growth, particularly in the digestive system
- Improves digestion: stimulates digestive enzymes and promotes gut health, helping with better nutrient absorption and digestion
- Enhances brain function: antioxidants in garlic are neuroprotective, reducing cognitive decline
- Good for your skin: its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties can help improve skin health
- Regulates blood sugar levels: helps regulate blood sugar and improves insulin sensitivity
- Anti-inflammatory effects: contains compounds that reduce inflammation, helping to combat inflammatory diseases such as arthritis
- Supports weight loss: stimulates metabolism, suppresses appetite, and helps break down fats, aiding in weight management
- May protect against osteoporosis: increases estrogen levels in women, potentially reducing the risk of osteoporosis (no effect on estrogen levels if you don’t have ovaries)
The daily dose that this video recommends is 1–2 cloves of garlic or 3600mg of aged garlic extract as a supplement.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
Take care!
Share This Post
-
6 Daily Habits To Keep Your Brain Young & Sharp
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Without brain health, we do not have health. So here are six ways to keep it in order:
Food for thought
The six areas to focus on are as follows:
- Physical exercise: as we at 10almonds sometimes say, what’s good for the heart is good for the brain (because the brain is only as healthy as the circulation feeding it). For this reason, the recommendation here is for physical exercise that improves heart health—so, walking, running, swimming, dancing, etc.
- Healthy diet: shocking nobody, this is important too. Specifically, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy proteins and fats is important—partly for the heart benefits that give indirect benefits to the brain, and partly because the brain is built of stuff and so we have to consume that stuff in order to rebuild it (omega-3s features strongly here, for instance). Remember to hydrate, too! The body can’t do anything without water.
- Good sleep: yes, the famous 7–9 hours sleep per night, and yes, even at your age, whatever that might be. This is important for memory consolidation, cell repair, toxin removal, and more. Sleep deprivation, on the other hand, leads to cognitive decline and brain shrinkage.
- Mental stimulation: ideally, engaging those parts of the brain you most wish to protect (e.g. language, memory, or whatever is most important to you).
- Social interaction: this one gets underestimated a lot, but it’s important to have meaningful conversations (not just polite smalltalk from a small menu of stock phrases), and that these should be two-way, i.e. involving both listening/reading and speaking/writing. Ideally, all four of those, which for most people means online and offline social interactions.
- Stress management: because chronic stress damages brain cells and accelerates cognitive decline, it’s important to manage that; practices like mindfulness meditation go a very long way and make a big difference.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Physical Exercises That Build Your Brain ← this is different from just exercising for one’s heart and thus the brain by extension, and rather, is specific exercises that strengthen specific parts of the brain.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
A Statin-Free Life – by Dr. Aseem Malhotra
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Here at 10almonds, we’ve written before about the complexities of statins, and their different levels of risk/benefit for men and women, respectively. It’s a fascinating topic, and merits more than an article of the size we write here!
So, in the spirit of giving pointers of where to find a lot more information, this book is a fine choice.
Dr. Malhotra, a consultant cardiologist and professor of evidence-based medicine, talks genes and lifestyle, drugs and blood. He takes us on a tour of the very many risk factors for heart disease, and how cholesterol levels may be at best an indicator, but less likely a cause, of heart disease, especially for women. Further and even better, he discusses various more reliable indicators and potential causes, too.
Rather than be all doom and gloom, he does offer guidance on how to reduce each of one’s personal risk factors and—which is important—keep on top of the various relevant measures of heart health (including some less commonly tested ones, like the coronary calcium score).
The style is light reading andyet with a lot of reference to hard science, so it’s really the best of both worlds in that regard.
Bottom line: if you’re considering statins, or are on statins and are reconsidering that choice, then this book will (notwithstanding its own bias in its conclusion) help you make a more-informed decision.
Click here to check out A Statin-Free Life, and make the best choice for you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Oral vaccines could provide relief for people who suffer regular UTIs. Here’s how they work
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In a recent TikTok video, Australian media personality Abbie Chatfield shared she was starting a vaccine to protect against urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Huge news for the UTI girlies. I am starting a UTI vaccine tonight for the first time.
Chatfield suffers from recurrent UTIs and has turned to the Uromune vaccine, an emerging option for those seeking relief beyond antibiotics.
But Uromune is not a traditional vaccine injected to your arm. So what is it and how does it work?
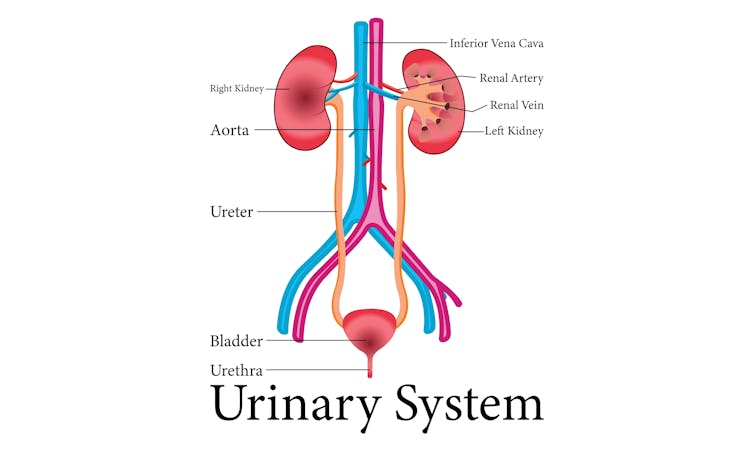
9nong/Shutterstock First, what are UTIs?
UTIs are caused by bacteria entering the urinary system. This system includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters (thin tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder), and the urethra (the tube through which urine leaves the body).
The most common culprit is Escherichia coli (E. coli), a type of bacteria normally found in the intestines.
While most types of E. coli are harmless in the gut, it can cause infection if it enters the urinary tract. UTIs are particularly prevalent in women due to their shorter urethras, which make it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder.
Roughly 50% of women will experience at least one UTI in their lifetime, and up to half of those will have a recurrence within six months.
UTIs are caused by bacteria enterning the urinary system. oxo7051/Shutterstock The symptoms of a UTI typically include a burning sensation when you wee, frequent urges to go even when the bladder is empty, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or back. If left untreated, a UTI can escalate into a kidney infection, which can require more intensive treatment.
While antibiotics are the go-to treatment for UTIs, the rise of antibiotic resistance and the fact many people experience frequent reinfections has sparked more interest in preventive options, including vaccines.
What is Uromune?
Uromune is a bit different to traditional vaccines that are injected into the muscle. It’s a sublingual spray, which means you spray it under your tongue. Uromune is generally used daily for three months.
It contains inactivated forms of four bacteria that are responsible for most UTIs, including E. coli. By introducing these bacteria in a controlled way, it helps your immune system learn to recognise and fight them off before they cause an infection. It can be classified as an immunotherapy.
A recent study involving 1,104 women found the Uromune vaccine was 91.7% effective at reducing recurrent UTIs after three months, with effectiveness dropping to 57.6% after 12 months.
These results suggest Uromune could provide significant (though time-limited) relief for women dealing with frequent UTIs, however peer-reviewed research remains limited.
Any side effects of Uromune are usually mild and may include dry mouth, slight stomach discomfort, and nausea. These side effects typically go away on their own and very few people stop treatment because of them. In rare cases, some people may experience an allergic reaction.
How can I access it?
In Australia, Uromune has not received full approval from the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), and so it’s not something you can just go and pick up from the pharmacy.
However, Uromune can be accessed via the TGA’s Special Access Scheme or the Authorised Prescriber pathway. This means a GP or specialist can apply for approval to prescribe Uromune for patients with recurrent UTIs. Once the patient has a form from their doctor documenting this approval, they can order the vaccine directly from the manufacturer.
Antibiotics are the go-to treatment for UTIs – but scientists are looking at options to prevent them in the first place. Photoroyalty/Shutterstock Uromune is not covered under the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, meaning patients must cover the full cost out-of-pocket. The cost of a treatment program is around A$320.
Uromune is similarly available through special access programs in places like the United Kingdom and Europe.
Other options in the pipeline
In addition to Uromune, scientists are exploring other promising UTI vaccines.
Uro-Vaxom is an established immunomodulator, a substance that helps regulate or modify the immune system’s response to bacteria. It’s derived from E. coli proteins and has shown success in reducing UTI recurrences in several studies. Uro-Vaxom is typically prescribed as a daily oral capsule taken for 90 days.
FimCH, another vaccine in development, targets something called the adhesin protein that helps E. coli attach to urinary tract cells. FimCH is typically administered through an injection and early clinical trials have shown promising results.
Meanwhile, StroVac, which is already approved in Germany, contains inactivated strains of bacteria such as E. coli and provides protection for up to 12 months, requiring a booster dose after that. This injection works by stimulating the immune system in the bladder, offering temporary protection against recurrent infections.
These vaccines show promise, but challenges like achieving long-term immunity remain. Research is ongoing to improve these options.
No magic bullet, but there’s reason for optimism
While vaccines such as Uromune may not be an accessible or perfect solution for everyone, they offer real hope for people tired of recurring UTIs and endless rounds of antibiotics.
Although the road to long-term relief might still be a bit bumpy, it’s exciting to see innovative treatments like these giving people more options to take control of their health.
Iris Lim, Assistant Professor in Biomedical Science, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Ultimate Booster
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Winning The Biological Arms Race
The human immune system (and indeed, other immune systems, but we are all humans here, after all) is in a constant state of war with pathogens, and that war is a constant biological arms race:
- We improve our defenses and destroy the attackers; the 1% of pathogens that survived now “know” how to counter that trick.
- The pathogens wreak havoc in our systems; the n% of us that survive now have immune systems that “know” how to counter that trick.
Vaccines are a mighty tool in our favor here, because they’re the technology that stops our n% from also being a very low number.
With vaccines, we can effectively pass on established defenses onto the population at large, as this cute video explains very well and very simply in 57 seconds:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
The problem with vaccines
The problem is that this accelerates the arms race. It’s like a chess game where we are able to respond to every move quickly (which is good for us), and/but this means passing the move over to our opponent sooner.
That problem’s hard to avoid, because the alternative has always been “let people die in much larger numbers”.
Traditional vs mRNA vaccines
A quick refresher before we continue to the big news of the day:
- Traditional vaccines use a disabled version of a pathogen to trigger an immune response that will teach the body to recognize the pathogen ready for when the full version shows up
- mRNA vaccines use a custom-made bit of genetic information to tell the body to make its own harmless fake pathogen and then respond to the harmless fake pathogen it made.
Note: this happens independently of the host’s DNA, so no, it does not change your DNA
See also: The Truth About Vaccines
Here’s a more detailed explainer (with a helpful diagram) using the COVID mRNA vaccine as an example:
Genome.gov | How does an mRNA vaccine work?
However, this still leaves us “chasing strains”, because as the pathogen (in this case, a virus) adapts, the vaccine has to be updated too, hence all the boosters.
This is a lot like a security update for your computer’s antivirus software. They’re annoying, but they do an important job.
No more “chasing strains”
The press conference soundbite on this sums it up well:
❝Scientists at UC Riverside have demonstrated a new, RNA-based vaccine strategy that is effective against any strain of a virus and can be used safely even by babies or the immunocompromised.❞
Read in full: Vaccine breakthrough means no more chasing strains
You may be wondering: what makes this one effective against any strain?
❝What I want to emphasize about this vaccine strategy is that it is broad.
It is broadly applicable to any number of viruses, broadly effective against any variant of a virus, and safe for a broad spectrum of people. This could be the universal vaccine that we have been looking for.
Viruses may mutate in regions not targeted by traditional vaccines. However, we are targeting their whole genome with thousands of small RNAs. They cannot escape this.❞
Importantly, this means it can be applied not just to one disease, let alone just one strain of COVID. Rather, it can be used for a wide variety of viruses that have similar viral functions—COVID / SARS in general, including influenza, and even viruses such as dengue.
How it does this: the above article explains in more detail, but in few words: it targets tiny strings of the genome that are present in all strains of the virus.
Illustrative example: if you wanted to block 10almonds (please don’t), you could block our email address.
But if we were malicious (we’re not) we could be sneaky and change it, so you’d have to block the new one, and the cycle repeats.
But if you were block all emails containing the tiny string of characters “10almonds”, changing our email address would no longer penetrate your defenses.
Now imagine also blocking strings such as “One-Minute Book Review” and “Today’s almonds have been activated by” and other strings we use in every email.
Now multiply this by thousands of strings (because genomes are much larger than our little newsletter), and you see its effectiveness!
Great! How can I get this?
It’s still in the testing stages for now; this is “breaking news” science, after all.
The study itself
…is paywalled for now, sadly, but if you happen to have institutional access, here it is:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: