Accidental falls in the older adult population: What academic research shows
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Accidental falls are among the leading causes of injury and death among adults 65 years and older worldwide. As the aging population grows, researchers expect to see an increase in the number of fall injuries and related health spending.
Falls aren’t unique to older adults. Nealy 684,000 people die from falls each year globally. Another 37.3 million people each year require medical attention after a fall, according to the World Health Organization. But adults 65 and older account for the greatest number of falls.
In the United States, more than 1 in 4 older adults fall each year, according to the National Institute on Aging. One in 10 report a fall injury. And the risk of falling increases with age.
In 2022, health care spending for nonfatal falls among older adults was $80 billion, according to a 2024 study published in the journal Injury Prevention.
Meanwhile, the fall death rate in this population increased by 41% between 2012 and 2021, according to the latest CDC data.
“Unfortunately, fall-related deaths are increasing and we’re not sure why that is,” says Dr. Jennifer L. Vincenzo, an associate professor at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences in the department of physical therapy and the Center for Implementation Research. “So, we’re trying to work more on prevention.”
Vincenzo advises journalists to write about how accidental falls can be prevented. Remind your audiences that accidental falls are not an inevitable consequence of aging, and that while we do decline in many areas with age, there are things we can do to minimize the risk of falls, she says. And expand your coverage beyond the national Falls Prevention Awareness Week, which is always during the first week of fall — Sept. 23 to 27 this year.
Below, we explore falls among older people from different angles, including injury costs, prevention strategies and various disparities. We have paired each angle with data and research studies to inform your reporting.
Falls in older adults
In 2020, 14 million older adults in the U.S. reported falling during the previous year. In 2021, more than 38,700 older adults died due to unintentional falls, according to the CDC.
A fall could be immediately fatal for an older adult, but many times it’s the complications from a fall that lead to death.
The majority of hip fractures in older adults are caused by falls, Vincenzo says, and “it could be that people aren’t able to recover [from the injury], losing function, maybe getting pneumonia because they’re not moving around, or getting pressure injuries,” she says.
In addition, “sometimes people restrict their movement and activities after a fall, which they think is protective, but leads to further functional declines and increases in fall risk,” she adds.
Factors that can cause a fall include:
- Poor eyesight, reflexes and hearing. “If you cannot hear as well, anytime you’re doing something in your environment and there’s a noise, it will be really hard for you to focus on hearing what that noise is and what it means and also moving at the same time,” Vincenzo says.
- Loss of strength, balance, and mobility with age, which can lessen one’s ability to prevent a fall when slipping or tripping.
- Fear of falling, which usually indicates decreased balance.
- Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or problems with nerves or feet that can affect balance.
- Conditions like incontinence that cause rushed movement to the bathroom.
- Cognitive impairment or certain types of dementia.
- Unsafe footwear such as backless shoes or high heels.
- Medications or medication interactions that can cause dizziness or confusion.
- Safety hazards in the home or outdoors, such as poor lighting, steps and slippery surfaces.
Related Research
Nonfatal and Fatal Falls Among Adults Aged ≥65 Years — United States, 2020–2021
Ramakrishna Kakara, Gwen Bergen, Elizabeth Burns and Mark Stevens. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, September 2023.
Summary: Researchers analyzed data from the 2020 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System — a landline and mobile phone survey conducted each year in all 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia — and data from the 2021 National Vital Statistics System to identify patterns of injury and death due to falls in the U.S. by sex and state for adults 65 years and older. Among the findings:
- The percentage of women who reported falling was 28.9%, compared with 26.1% of men.
- Death rates from falls were higher among white and American Indian or Alaska Native older adults than among older adults from other racial and ethnic groups.
- In 2020, the percentage of older adults who reported falling during the past year ranged from 19.9% in Illinois to 38.0% in Alaska. The national estimate for 18 states was 27.6%.
- In 2021, the unintentional fall-related death rate among older adults ranged from 30.7 per 100,000 older adults in Alabama to 176.5 in Wisconsin. The national estimate for 26 states was 78.
“Although common, falls among older adults are preventable,” the authors write. “Health care providers can talk with patients about their fall risk and how falls can be prevented.”
Trends in Nonfatal Falls and Fall-Related Injuries Among Adults Aged ≥65 Years — United States, 2012-2018
Briana Moreland, Ramakrishna Kakara and Ankita Henry. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, July 2020.
Summary: Researchers compared data from the 2018 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. Among the findings:
- The percentage of older adults reporting a fall increased from 2012 to 2016, then slightly decreased from 2016 to 2018.
- Even with this decrease in 2018, older adults reported 35.6 million falls. Among those falls, 8.4 million resulted in an injury that limited regular activities for at least one day or resulted in a medical visit.
“Despite no significant changes in the rate of fall-related injuries from 2012 to 2018, the number of fall-related injuries and health care costs can be expected to increase as the proportion of older adults in the United States grows,” the authors write.
Understanding Modifiable and Unmodifiable Older Adult Fall Risk Factors to Create Effective Prevention Strategies
Gwen Bergen, et al. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, October 2019.
Summary: Researchers used data from the 2016 U.S. Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System to better understand the association between falls and fall injuries in older adults and factors such as health, state and demographic characteristics. Among the findings:
- Depression had the strongest association with falls and fall injuries. About 40% of older adults who reported depression also reported at least one fall; 15% reported at least one fall injury.
- Falls and depression have several factors in common, including cognitive impairment, slow walking speed, poor balance, slow reaction time, weakness, low energy and low levels of activity.
- Other factors associated with an increased risk of falling include diabetes, vision problems and arthritis.
“The multiple characteristics associated with falls suggest that a comprehensive approach to reducing fall risk, which includes screening and assessing older adult patients to determine their unique, modifiable risk factors and then prescribing tailored care plans that include evidence-based interventions, is needed,” the authors write.
Health care use and cost
In addition to being the leading cause of injury, falls are the leading cause of hospitalization in older adults. Each year, about 3 million older adults visit the emergency department due to falls. More than 1 million get hospitalized.
In 2021, falls led to more than 38,000 deaths in adults 65 and older, according to the CDC.
The annual financial medical toll of falls among adults 65 years and older is expected to be more than $101 billion by 2030, according to the National Council on Aging, an organization advocating for older Americans.
Related research
Healthcare Spending for Non-Fatal Falls Among Older Adults, USA
Yara K. Haddad, et al. Injury Prevention, July 2024.
Summary: In 2015, health care spending related to falls among older adults was roughly $50 billion. This study aims to update the estimate, using the 2017, 2019 and 2021 Medicare Current Beneficiary Survey, the most comprehensive and complete survey available on the Medicare population. Among the findings:
- In 2020, health care spending for non-fatal falls among older adults was $80 billion.
- Medicare paid $53.3 billion of the $80 billion, followed by $23.2 billion paid by private insurance or patients and $3.5 billion by Medicaid.
“The burden of falls on healthcare systems and healthcare spending will continue to rise if the risk of falls among the aging population is not properly addressed,” the authors write. “Many older adult falls can be prevented by addressing modifiable fall risk factors, including health and functional characteristics.”
Cost of Emergency Department and Inpatient Visits for Fall Injuries in Older Adults Lisa Reider, et al. Injury, February 2024.
Summary: The researchers analyzed data from the 2016-2018 National Inpatient Sample and National Emergency Department Sample, which are large, publicly available patient databases in the U.S. that include all insurance payers such as Medicare and private insurance. Among the findings:
- During 2016-2018, more than 920,000 older adults were admitted to the hospital and 2.3 million visited the emergency department due to falls. The combined annual cost was $19.2 billion.
- More than half of hospital admissions were due to bone fractures. About 14% of these admissions were due to multiple fractures and cost $2.5 billion.
“The $20 billion in annual acute treatment costs attributed to fall injury indicate an urgent need to implement evidence-based fall prevention interventions and underscores the importance of newly launched [emergency department]-based fall prevention efforts and investments in geriatric emergency departments,” the authors write.
Hip Fracture-Related Emergency Department Visits, Hospitalizations and Deaths by Mechanism of Injury Among Adults Aged 65 and Older, United States 2019
Briana L. Moreland, Jaswinder K. Legha, Karen E. Thomas and Elizabeth R. Burns. Journal of Aging and Health, June 2024.
Summary: The researchers calculated hip fracture-related U.S. emergency department visits, hospitalizations and deaths among older adults, using data from the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project and the National Vital Statistics System. Among the findings:
- In 2019, there were 318,797 emergency department visits, 290,130 hospitalizations and 7,731 deaths related to hip fractures among older adults.
- Nearly 88% of emergency department visits and hospitalizations and 83% of deaths related to hip fractures were caused by falls.
- These rates were highest among those living in rural areas and among adults 85 and older. More specifically, among adults 85 and older, the rate of hip fracture-related emergency department visits was nine times higher than among adults between 65 and 74 years old.
“Falls are common among older adults, but many are preventable,” the authors write. “Primary care providers can prevent falls among their older patients by screening for fall risk annually or after a fall, assessing modifiable risk factors such as strength and balance issues, and offering evidence-based interventions to reduce older adults’ risk of falls.”
Fall prevention
Several factors, including exercising, managing medication, checking vision and making homes safer can help prevent falls among older adults.
“Exercise is one of the best interventions we know of to prevent falls,” Vincenzo says. But “walking in and of itself will not help people to prevent falls and may even increase their risk of falling if they are at high risk of falls.”
The National Council on Aging also has a list of evidence-based fall prevention programs, including activities and exercises that are shown to be effective.
The National Institute on Aging has a room-by-room guide on preventing falls at home. Some examples include installing grab bars near toilets and on the inside and outside of the tub and shower, sitting down while preparing food to prevent fatigue, and keeping electrical cords near walls and away from walking paths.
There are also national and international initiatives to help prevent falls.
Stopping Elderly Accidents, Deaths and Injuries, or STEADI, is an initiative by the CDC’s Injury Center to help health care providers who treat older adults. It helps providers screen patients for fall risk, assess their fall risk factors and reduce their risk by using strategies that research has shown to be effective. STEADI’s guidelines are in line with the American and British Geriatric Societies’ Clinical Practice Guidelines for fall prevention.
“We’re making some iterations right now to STEADI that will come out in the next couple of years based on the World Falls Guidelines, as well as based on clinical providers’ feedback on how to make [STEADI] more feasible,” Vincenzo says.
The World Falls Guidelines is an international initiative to prevent falls in older adults. The guidelines are the result of the work of 14 international experts who came together in 2019 to consider whether new guidelines on fall prevention were needed. The task force then brought together 96 experts from 39 countries across five continents to create the guidelines.
The CDC’s STEADI initiative has a screening questionnaire for consumers to check their risk of falls, as does the National Council on Aging.
On the policy side, U.S. Rep. Carol Miller, R-W.V., and Melanie Stansbury, D-N.M., introduced the Stopping Addiction and Falls for the Elderly (SAFE) Act in March 2024. The bill would allow occupational and physical therapists to assess fall risks in older adults as part of the Medicare Annual Wellness Benefit. The bill was sent to the House Subcommittee on Health in the same month.
Meanwhile, older adults’ attitudes toward falls and fall prevention are also pivotal. For many, coming to terms with being at risk of falls and making changes such as using a cane, installing railings at home or changing medications isn’t easy for all older adults, studies show.
“Fall is a four-letter F-word in a way to older adults,” says Vincenzo, who started her career as a physical therapist. “It makes them feel ‘old.’ So, it’s a challenge on multiple fronts: U.S. health care infrastructure, clinical and community resources and facilitating health behavior change.”
Related research
Environmental Interventions for Preventing Falls in Older People Living in the Community
Lindy Clemson, et al. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, March 2023.
Summary: This review includes 22 studies from 10 countries involving a total of 8,463 older adults who live in the community, which includes their own home, a retirement facility or an assisted living facility, but not a hospital or nursing home. Among the findings:
- Removing fall hazards at home reduced the number of falls by 38% among older adults at a high risk of having a fall, including those who have had a fall in the past year, have been hospitalized or need support with daily activities. Examples of fall hazards at home include a stairway without railings, a slippery pathway or poor lighting.
- It’s unclear whether checking prescriptions for eyeglasses, wearing special footwear or installing bed alarm systems reduces the rate of falls.
- It’s also not clear whether educating older adults about fall risks reduces their fall risk.
The Influence of Older Adults’ Beliefs and Attitudes on Adopting Fall Prevention Behaviors
Judy A. Stevens, David A. Sleet and Laurence Z. Rubenstein. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. January 2017.
Summary: Persuading older adults to adopt interventions that reduce their fall risk is challenging. Their attitudes and beliefs about falls play a large role in how well they accept and adopt fall prevention strategies, the authors write. Among the common attitudes and beliefs:
- Many older adults believe that falls “just happen,” are a normal result of aging or are simply due to bad luck.
- Many don’t acknowledge or recognize their fall risk.
- For many, falls are considered to be relevant only for frail or very old people.
- Many believe that their home environment or daily activities can be a risk for fall, but do not consider biological factors such as dizziness or muscle weakness.
- For many, fall prevention simply consists of “being careful” or holding on to things when moving about the house.
“To reduce falls, health care practitioners have to help patients understand and acknowledge their fall risk while emphasizing the positive benefits of fall prevention,” the authors write. “They should offer patients individualized fall prevention interventions as well as provide ongoing support to help patients adopt and maintain fall prevention strategies and behaviors to reduce their fall risk. Implementing prevention programs such as CDC’s STEADI can help providers discuss the importance of falls and fall prevention with their older patients.”
Reframing Fall Prevention and Risk Management as a Chronic Condition Through the Lens of the Expanded Chronic Care Model: Will Integrating Clinical Care and Public Health Improve Outcomes?
Jennifer L. Vincenzo, Gwen Bergen, Colleen M. Casey and Elizabeth Eckstrom. The Gerontologist, June 2024.
Summary: The authors recommend approaching fall prevention from the lens of chronic disease management programs because falls and fall risk are chronic issues for many older adults.
“Policymakers, health systems, and community partners can consider aligning fall risk management with the [Expanded Chronic Care Model], as has been done for diabetes,” the authors write. “This can help translate high-quality research on the effectiveness of fall prevention interventions into daily practice for older adults to alter the trajectory of older adult falls and fall-related injuries.”
Disparities
Older adults face several barriers to reducing their fall risk. Accessing health care services and paying for services such as physical therapy is not feasible for everyone. Some may lack transportation resources to go to and from medical appointments. Social isolation can increase the risk of death from falls. In addition, physicians may not have the time to fit in a fall risk screening while treating older patients for other health concerns.
Moreover, implementing fall risk screening, assessment and intervention in the current U.S. health care structure remains a challenge, Vincenzo says.
Related research
Mortality Due to Falls by County, Age Group, Race, and Ethnicity in the USA, 2000-19: A Systematic Analysis of Health Disparities
Parkes Kendrick, et al. The Lancet Public Health, August 2024.
Summary: Researchers analyzed death registration data from the U.S. National Vital Statistics System and population data from the U.S. National Center for Health Statistics to estimate annual fall-related mortality. The data spanned from 2000 to 2019 and includes all age groups. Among the findings:
- The disparities between racial and ethnic populations varied widely by age group. Deaths from falls among younger adults were highest for the American Indian/Alaska Native population, while among older adults it was highest for the white population.
- For older adults, deaths from falls were particularly high in the white population within clusters of counties across states including Florida, Minnesota and Wisconsin.
- One factor that could contribute to higher death rates among white older adults is social isolation, the authors write. “Studies suggest that older Black and Latino adults are more likely to have close social support compared with older white adults, while AIAN and Asian individuals might be more likely to live in multigenerational households,” they write.
“Among older adults, current prevention techniques might need to be restructured to reduce frailty by implementing early prevention and emphasizing particularly successful interventions. Improving social isolation and evaluating the effectiveness of prevention programs among minoritized populations are also key,” the authors write.
Demographic Comparisons of Self-Reported Fall Risk Factors Among Older Adults Attending Outpatient Rehabilitation
Mariana Wingood, et al. Clinical Interventions in Aging, February 2024.
Summary: Researchers analyzed the electronic health record data of 108,751 older adults attending outpatient rehabilitation within a large U.S. health care system across seven states, between 2018 and 2022. Among the findings:
- More than 44% of the older adults were at risk of falls; nearly 35% had a history of falls.
- The most common risk factors for falls were diminished strength, gait and balance.
- Compared to white older adults, Native American/Alaska Natives had the highest prevalence of fall history (43.8%) and Hispanics had the highest prevalence of falls with injury (56.1%).
“Findings indicate that rehabilitation providers should perform screenings for these impairments, including incontinence and medication among females, loss of feeling in the feet among males, and all Stay Independent Questionnaire-related fall risk factors among Native American/Alaska Natives, Hispanics, and Blacks,” the authors write.
Resources and articles
- National Institute on Aging
- National Council on Aging
- Gerontological Society of America
- Home Health Agencies Failed To Report Over Half of Falls With Major Injury and Hospitalization Among Their Medicare Patients, a 2023 report from the U.S Department of Health and Human Services’ Office of Inspector General.
- 6 tips for improving new coverage of older people, a tip sheet from The Journalist’s Resource.
- Crosswalk and pedestrian safety: What you need to know from recent research, from The Journalist’s Resource.
- Aging-in-place technology challenges and trends, a resource from the Association of Health Care Journalists.
- Successful aging at home: what reporters should know, a resource from the Association of Health Care Journalists.
This article first appeared on The Journalist’s Resource and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Tempeh vs Tofu – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing tempeh to tofu, we picked the tempeh.
Why?
Per 100g, tempeh has about 1.5x as many calories, about 2x as much protein, about 3x as much fiber, and about 4x the carbohydrates.
Which latter sounds like a lot, but really, the amounts here are small—tempeh is under 12% carbohydrates, and most of that is treated by the body as fiber (e.g. it’s a resistant starch).
Both have no sugar, and both have more or less the same (tiny) amount of fat.
Micronutrients, you ask? As they’re both made from soybeans, the micronutrient profiles are similar, but exact amounts will depend on the method used, so by all means check labels if comparing products in store. By and large, there’s usually not much difference, though.
You can see sample stats here:
In summary
Both are great, and/but tempeh is the more nutrient-dense of the two.
Therefore, tempeh is the healthier option, unless you are on a very strictly calorie-controlled diet, in which case, tofu will give you more quantity per calorie.
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Currants vs Grapes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing currants to grapes, we picked the currants.
Why?
First, a note on nomenclature: when we say “currants”, we are talking about actual currants, of the Ribes genus, and in this case (as per the image) red ones. We are not talking about “currants” that are secretly tiny grapes that also get called currants in the US. So, there are important botanical differences here, beyond how they have been cultivated; they are literally entirely different plants.
So, about those differences…
In terms of macros, currants have nearly 5x the fiber, while grapes are slightly higher in carbs. So there’s an easy choice here in terms of fiber and on the glycemic index front; currants win easily.
In the category of vitamins, currants have more of vitamins B5, B9, C, and choline, while grapes have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, E, and K. So, a win for grapes in this round.
When it comes to minerals, currants have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while grapes have more manganese. A win, therefore, for currants again this time.
In terms of polyphenols, currants have a lot more in terms of total polyphenols, including (as a matter of interest) approximately 5x the resveratrol content compared to grapes—and that’s compared to black grapes, which are the “best” kind of grapes for such. Grapes really aren’t a very good source of resveratrol; people just really like the idea of red wine being a health food, so it has been talked up a lot and got a popular reputation despite its extreme paucity of nutritional value.
In any case, adding up the sections makes for a clear overall win for currants, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
21 Most Beneficial Polyphenols & What Foods Have Them
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Fisetin: The Anti-Aging Assassin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Out With The Old…
Fisetin is a flavonoid (specifically, a flavonol), but it’s a little different than most. While it has the usual antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties you might reasonably expect from flavonoids, it has an extra anti-aging trick up its sleeve that most don’t.
❝Fisetin is a flavonol that shares distinct antioxidant properties with a plethora of other plant polyphenols. Additionally, it exhibits a specific biological activity of considerable interest as regards the protection of functional macromolecules against stress which results in the sustenance of normal cells cytoprotection. Moreover, it shows potential as an anti-inflammatory, chemopreventive, chemotherapeutic and recently also senotherapeutic agent❞
~ Dr. Grynkiewicz & Dr. Demchuk
Let’s briefly do some due diligence on its expected properties, and then we’ll take a look at its bonus anti-aging effects.
The flavonol that does-it-ol
Because of the similar mechanisms involved, there are three things that often come together, which are:
- Antioxidant
- Anti-inflammatory
- Anticancer
This list often gets expanded to also include:
- Anti-aging
…although that is usually the last thing to get tested out of that list.
In today’s case, let’s kick it off with…
❝Fisetin (3,3′,4′,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) is a dietary flavonoid found in various fruits (strawberries, apples, mangoes, persimmons, kiwis, and grapes), vegetables (tomatoes, onions, and cucumbers), nuts, and wine that has shown strong anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-tumorigenic, anti-invasive, anti-angiogenic, anti-diabetic, neuroprotective, and cardioprotective effects❞
Read more: Fisetin and Its Role in Chronic Diseases
Understanding its anticancer mechanisms
The way that fisetin fights cancer is basically “all the ways”, and this will be important when we get to its special abilities shortly:
❝Being a potent anticancer agent, fisetin has been used to inhibit stages in the cancer cells (proliferation, invasion),prevent cell cycle progression, inhibit cell growth, induce apoptosis, cause polymerase (PARP) cleavage, and modulate the expressions of Bcl‐2 family proteins in different cancer cell lines (HT‐29, U266, MDA‐MB‐231, BT549, and PC‐3M‐luc‐6), respectively. Further, fisetin also suppresses the activation of the PKCα/ROS/ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways, reduces the NF‐κB activation, and down‐regulates the level of the oncoprotein securin. Fisetin also inhibited cell division and proliferation and invasion as well as lowered the TET1 expression levels. ❞
Read more: Fisetin: An anticancer perspective
There’s also more about it than we even have room to quote, here:
Now For What’s New And Exciting: Senolysis
All that selectivity that fisetin exhibits when it comes to “this cell gets to live, and this one doesn’t” actions?
It makes a difference when it comes to aging, too. Because aging and cancer happen by quite similar mechanisms; they’re both DNA-copying errors that get copied forward, to our detriment.
- In the case of cancer, it’s a cell line that accidentally became immortal and so we end up with too many of them multiplying in one place (a tumor)
- In the case of aging, it’s the cellular equivalent of “a photocopy of a photocopy of a photocopy” gradually losing information as it goes
In both cases…
The cell must die if we want to live
Critically, and which quality differentiates it from a lot of other flavonoids, fisetin has the ability to selectively kill senescent cells.
To labor the photocopying metaphor, this means there’s an office worker whose job it is to say “this photocopy is barely legible, I’m going to toss this, and then copy directly from the clearest copy we have instead”, thus keeping the documents (your DNA) in pristine condition.
In fisetin’s case, this was first tested in mouse (in vivo) studies, and in human tissue (in vitro) studies, before moving to human clinical studies:
❝Of the 10 flavonoids tested, fisetin was the most potent senolytic.
The natural product fisetin has senotherapeutic activity in mice and in human tissues. Late life intervention was sufficient to yield a potent health benefit.❞
~ Dr. Matthew Yousefzadeh et al.
Read in full: Fisetin is a senotherapeutic that extends health and lifespan
There’s lots more science that’s been done to it since that first groundbreaking study though; here’s a more recent example:
Want some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
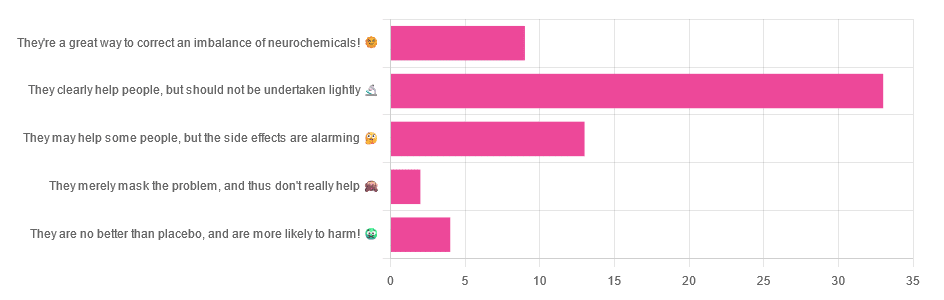
Yesterday, we asked you for your opinions on antidepressants, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- Just over half of respondents said “They clearly help people, but should not be undertaken lightly”
- Just over a fifth of respondents said “They may help some people, but the side effects are alarming”
- Just under a sixth of respondents said “They’re a great way to correct an imbalance of neurochemicals”
- Four respondents said “They are no better than placebo, and are more likely to harm”
- Two respondents said “They merely mask the problem, and thus don’t really help”
So what does the science say?
❝They are no better than placebo, and are more likely to harm? True or False?❞
True or False depending on who you are and what you’re taking. Different antidepressants can work on many different systems with different mechanisms of action. This means if and only if you’re not taking the “right” antidepressant for you, then yes, you will get only placebo benefits:
- Placebo Effect in the Treatment of Depression and Anxiety ← randomly assigned antidepressants are, shockingly, luck of the draw in usefulness
- Antidepressants versus placebo in major depression: an overview ← “wow this science is messy”
- Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs: a systematic review and network meta-analysis ← “oh look, it makes a difference which antidepressant we give to people”
Rather than dismissing antidepressants as worthless, therefore, it is a good idea to find out (by examination or trial and error) what kind of antidepressant you need, if you indeed do need such.
Otherwise it is like getting a flu shot and being surprised when you still catch a cold!
❝They merely mask the problem, and thus don’t really help: True or False?❞
False, categorically.
The problem in depressed people is the depressed mood. This may be influenced by other factors, and antidepressants indeed won’t help directly with those, but they can enable the person to better tackle them (more on this later).
❝They may help some people, but the side-effects are alarming: True or False?❞
True or False depending on more factors than we can cover here.
Side-effects vary from drug to drug and person to person, of course. As does tolerability and acceptability, since to some extent these things are subjective.
One person’s dealbreaker may be another person’s shrugworthy minor inconvenience at most.
❝They’re a great way to correct an imbalance of neurochemicals: True or False?❞
True! Contingently.
That is to say: they’re a great way to correct an imbalance of neurochemicals if and only if your problem is (at least partly) an imbalance of neurochemicals. If it’s not, then your brain can have all the neurotransmitters it needs, and you will still be depressed, because (for example) the other factors* influencing your depression have not changed.
*common examples include low self-esteem, poor physical health, socioeconomic adversity, and ostensibly bleak prospects for the future.
For those for whom the problem is/was partly a neurochemical imbalance and partly other factors, the greatest help the antidepressants give is getting the brain into sufficient working order to be able to tackle those other factors.
Want to know more about the different kinds?
Here’s a helpful side-by-side comparison of common antidepressants, what type they are, and other considerations:
Mind | Comparing Antidepressants
Want a drug-free approach?
You might like our previous main feature:
The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Gentler Hair Health Options
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hair, Gently
We have previously talked about the medicinal options for combatting the thinning hair that comes with age especially for men, but also for a lot of women. You can read about those medicinal options here:
Hair-Loss Remedies, By Science
We also did a whole supplement spotlight research review for saw palmetto! You can read about how that might help you keep your hair present and correct, here:
One Man’s Saw Palmetto Is Another Woman’s Serenoa Repens
Today we’re going to talk options that are less “heavy guns”, and/but still very useful.
Supplementation
First, the obvious. Taking vitamins and minerals, especially biotin, can help a lot. This writer takes 10,000µg (that’s micrograms, not milligrams!) biotin gummies, similar to this example product on Amazon (except mine also has other vitamins and minerals in, but the exact product doesn’t seem to be available on Amazon).
When thinking “what vitamins and minerals help hair?”, honestly, it’s most of them. So, focus on the ones that count for the most (usually: biotin and zinc), and then cover your bases for the rest with good diet and additional supplementation if you wish.
Caffeine (topical)
It may feel silly, giving one’s hair a stimulant, but topical caffeine application really does work to stimulate hair growth. And not “just a little help”, either:
❝Specifically, 0.2% topical caffeine-based solutions are typically safe with very minimal adverse effects for long-term treatment of AGA, and they are not inferior to topical 5% minoxidil therapy❞
(AGA = Androgenic Alopecia)
Argan oil
As with coconut oil, argan oil is great on hair. It won’t do a thing to improve hair growth or decrease hair shedding, but it will help you hair stay moisturized and thus reduce breakage—thus, may not be relevant for everyone, but for those of us with hair long enough to brush, it’s important.
Bonus: get an argan oil based hair serum that also contains keratin (the protein used to make hair), as this helps strengthen the hair too.
Here’s an example product on Amazon
Silk pillowcases
Or a silk hair bonnet to sleep in! They both do the same thing, which is prevent damaging the hair in one’s sleep by reducing the friction that it may have when moving/turning against the pillow in one’s sleep.
- Pros of the bonnet: if you have lots of hair and a partner in bed with you, your hair need not be in their face, and you also won’t get it caught under you or them.
- Pros of the pillowcase: you don’t have to wear a bonnet
Both are also used widely by people without hair loss issues, but with easily damaged and/or tangled hair—Black people especially with 3C or tighter curls in particular often benefit from this. Other people whose hair is curly and/or gray also stand to gain a lot.
Here are Amazon example products of a silk pillowcase (it’s expensive, but worth it) and a silk bonnet, respectively
Want to read more?
You might like this article:
From straight to curly, thick to thin: here’s how hormones and chemotherapy can change your hair
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Do Probiotics Work For Weight Loss?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Can you talk about using probiotics for weight loss? Thanks❞
Great question! First, a quick catch-up:
How Much Difference Do Probiotic Supplements Make, Really?
Our above-linked article covers a number of important benefits of probiotic supplements, but we didn’t talk about weight loss at all. So let’s examine whether probiotics are useful for weight loss.
Up-front summary: the science is unclear
This 2021 systematic review found that they are indeed very effective:
❝The intake of probiotics or synbiotics could lead to significant weight reductions, either maintaining habitual lifestyle habits or in combination with energy restriction and/or increased physical activity for an average of 12 weeks.
Specific strains belonging to the genus Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium were the most used and those that showed the best results in reducing body weight.
Both probiotics and synbiotics have the potential to help in weight loss in overweight and obese populations.❞
This slightly older (2015) systematic review and meta-analysis found the opposite:
❝Collectively, the RCTs examined in this meta-analysis indicated that probiotics have limited efficacy in terms of decreasing body weight and BMI and were not effective for weight loss.❞
Source: Probiotics for weight loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis
And in case that’s not balanced enough, this 2020 randomized controlled trial got mixed results:
❝Regression analysis performed to correlate abundance of species following supplementation with body composition parameters and biomarkers of obesity found an association between a decrease over time in blood glucose and an increase in Lactobacillus abundance, particularly in the synbiotic group.
However, the decrease over time in body mass, BMI, waist circumstance, and body fat mass was associated with a decrease in Bifidobacterium abundance.❞
Source: Effects of Synbiotic Supplement on Human Gut Microbiota, Body Composition and Weight Loss in Obesity
Summary
Probiotics may or may not work for weight loss.
In all likelihood, it depends on the blend of cultures contained in the supplement. It’s possible that Lactobacillus is more beneficial for weight loss than Bifidobacterium, which latter may actually reduce weight loss.
Or it might not, because that was just one study and correlation ≠ causation!
We’d love to give you a hard-and-fast answer, but if the data doesn’t support a hard-and-fast answer, we’re not going to lie to you.
What we can say for sure though is that probiotics come with very many health benefits, so whether or not weight loss is one of them, they’re a good thing to have for most people.
Some further articles that may interest you:
- How Much Difference Do Probiotic Supplements Make, Really? ← the aforementioned article
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later) ← gut health 101
- Burn! How To Boost Your Metabolism ← these things can help change your metabolic base rate, which is highly relevant to weight loss
- How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body) ←unlike most forms of exercise, which cause the body to slow the metabolism afterwards to compensate, high-intensity interval training results in an increased metabolic rate (so generally: fat-burning) for several hours after training.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: