Eat To Beat Chronic Fatigue!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Eat To Beat Chronic Fatigue
Chronic fatigue is on the rise, and it can make life a living Hell. Days blur into one, and you try to take each day as it comes, but sometimes several days gang up on you at once.
You probably know some lifestyle changes that might help—if only you had the energy to implement them.
You’d like to eat well, but you need to…
- Buy the fresh produce (and take a little rest after)
- Put the groceries away (and take a little rest after)
- Wash the vegetables (and take a little rest after)
- Chop the things as necessary (and take a little rest after)
- Cook dinner (and take a little rest after)
…and now you’re too exhausted to eat it.
So, what can be done?
First, avoid things that cause inflammation, as this is a major contributor to chronic fatigue. You might like our previous main feature:
Next up, really do stay hydrated. It’s less about quantity, and more about ubiquity. Hydrate often.
Best is if you always have some (hydrating) drink on the go.
Do experiment with your diet, and/but keep a food journal of what you eat and how you feel 30–60 minutes after eating it. Only make one change at a time, otherwise you won’t know which change made the difference.
Notice what patterns emerge over time, and adjust your ingredients accordingly.
Limit your caffeine intake. We know that sometimes it seems like the only way to get through the day, but you will always crash later, because it was only ever taxing your adrenal system (thus: making you more tired in the long run) and pulling the wool over the eyes of your adenosine receptors (blocking you from feeling how tired you are, but not actually reducing your body’s tiredness).
Put simply, caffeine is the “payday loan” of energy.
Eat more non-starchy vegetables, and enjoy healthy fats. Those healthy fats can come from nuts and seeds, avocado, or fish (not fried, though!).
The non-starchy vegetables will boost your vitamins and fiber while being easy on your beleaguered metabolism, while the healthy fats will perk up your energy levels without spiking insulin like sugars would.
Pay the fatigue tax up front. What this means is… Instead of throwing away vegetables that didn’t get used because it would take too much effort and you just need an easier dinner today, buy ready-chopped vegetables, for example.
And if you buy vegetables frozen, they’re also often not only cheaper, but also (counterintuitively) contain more nutrients.
A note of distinction:
Many more people have chronic fatigue (the symptom: being exhausted all the time) than have chronic fatigue syndrome (the illness: myalgic encephalomyelitis).
This is because fatigue can be a symptom of many, many other conditions, and can be heavily influenced by lifestyle factors too.
A lot of the advice for dealing with chronic fatigue is often the same in both cases, but some will be different, because for example:
- If your fatigue is from some other condition, that condition probably impacts what lifestyle factors you are (and are not) able to change, too
- If your fatigue is from lifestyle factors, that hopefully means you can change those and enjoy less fatigue…
- But if it’s not from lifestyle factors, as in ME/CFS, then advice to “exercise more” etc is not going to help so much.
There are ways to know the difference though:
Check out: Do You Have Chronic Fatigue Syndrome?
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How we can prepare for future public health emergencies
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The U.S. is experiencing an increasing number of disease outbreaks and extreme weather events. While state and national preparedness for public health emergencies has improved in some areas, dangerous gaps remain, says a recent report from Trust for America’s Health.
Titled, “Ready or Not 2024: Protecting the Public’s Health from Diseases, Disasters, and Bioterrorism,” the report identifies gaps in national and state preparedness for public health emergencies and provides recommendations for improvement.
Using nine key indicators, the report categorizes all U.S. states and the District of Columbia into three readiness levels: high, medium, and low. The writers hope the report will help policymakers in under-performing states improve public health infrastructure.
Read on to learn more about what the research found and how we can individually prepare for future public health emergencies.
There’s work to be done
The report highlights areas with strong performance as well as those that need improvement.
Some areas with strong performance:
- State public health funding: Most states and the District of Columbia either maintained or increased their public health funding during the 2023 fiscal year.
- Health care labor force preparedness: Most states have started expanding the health care labor force for improved emergency response. As of 2023, 39 states participated in the Nurse Licensure Compact, which allows nurses to work in multiple member states without the need for additional state licenses.
Some areas that need improvement:
- Hospital safety scores: Only 25 percent of acute care hospitals earned the highest patient safety grade in fall 2023. These scores measure health care-associated infection rates, intensive care unit capacity, and other metrics. More high-scoring hospitals would improve preparedness for future public health emergencies.
- Access to paid time off: From March 2018 to March 2023, only 55 percent of U.S. workers used paid time off. Access to paid time off is important for reducing the spread of infectious diseases.
We can all do our part by staying up to date on vaccines
While the report focuses on policy changes that would improve emergency preparedness, Trust for America’s Health’s research identifies one way that we can individually prepare for future public health emergencies: staying up to date on vaccines.
The report found that during the 2022-2023 flu season, only 49 percent of those eligible for the flu vaccine received it. Public health experts are concerned that false claims about COVID-19 vaccines have resulted in overall vaccine hesitancy.
A decline in vaccination rates has led to an uptick in life-threatening, vaccine-preventable diseases, such as measles. Increasing vaccine uptake would prevent the spread of vaccine-preventable diseases and reduce strain on hospital systems during public health crises.
Make sure that you and your children have received all recommended vaccines to prevent severe illness, hospitalization, and death. Learn more about recommended vaccines for adults and children from the CDC.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
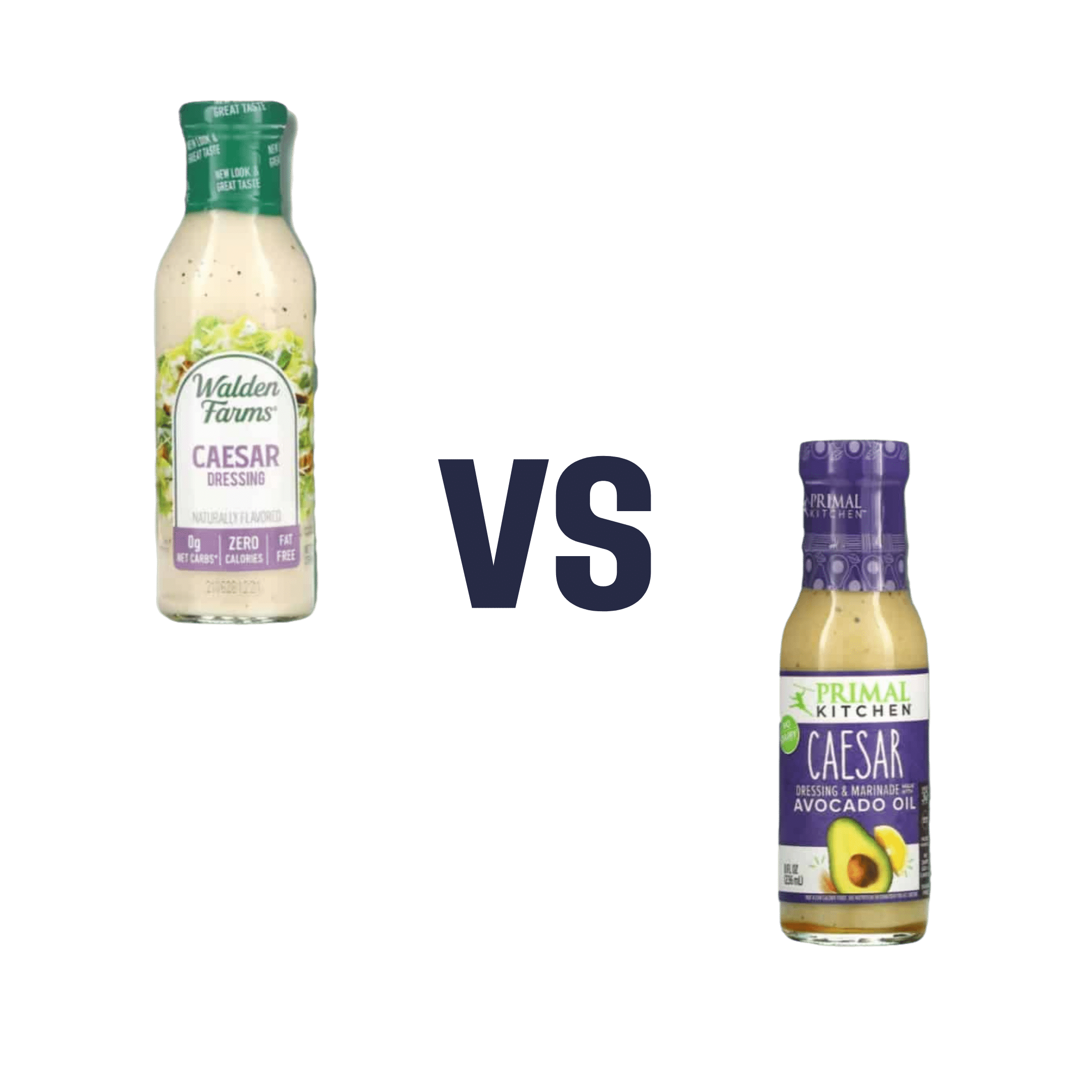
Walden Farms Caesar Dressing vs. Primal Kitchen Caesar Dressing – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Walden Farms Caesar Dressing to Primal Kitchen Caesar Dressing, we picked the Primal Kitchen.
Why?
As you can see from the front label, the Walden Farms product has 0 net carbs, 0 calories, and 0 fat. In fact, its ingredients list begins:
Water, white distilled vinegar, erythritol, corn fiber, salt, microcrystalline cellulose, xanthan gum, titanium dioxide (color)
…before it gets to something interesting (garlic purée), by which point the amount must be miniscule.
The Primal Kitchen product, meanwhile, has 140 calories per serving and 15g fat (of which, 1.5g is saturated). However! The ingredients list this time begins:
Avocado oil, water, organic coconut aminos (organic coconut sap, sea salt), organic apple cider vinegar, organic distilled vinegar, mushroom extract, organic gum acacia, organic guar gum
…before it too gets to garlic, which this time, by the way, is organic roasted garlic.
In case you’re wondering about the salt content in both, they add up to 190mg for the Walden Farms product, and 240mg for the Primal Kitchen product. We don’t think that the extra 50mg (out of a daily allowance of 2300–5000mg, depending on whom you ask) is worthy of note.
In short, the Walden Farms product is made of mostly additives of various kinds, whereas the Primal Kitchen product is made of mostly healthful ingredients.
So, the calories and fat are nothing to fear.
For this reason, we chose the product with more healthful ingredients—but we acknowledge that if you are specifically trying to keep your calories down, then the Walden Farms product may be a valid choice.
Read more:
• Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
• Caloric Restriction with Optimal NutritionShare This Post
-
Sarah Raven’s Garden Cookbook – by Sarah Raven
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Note: the US Amazon site currently (incorrectly) lists the author as “Jonathan Buckley”. The Canadian, British, and Australian sites all list the author correctly as Sarah Raven, and some (correctly) credit Jonathan Buckley as the photographer she used.
First, what it’s not: a gardening book. Beyond a few helpful tips, pointers, and “plant here, harvest here” instructions, this book assumes you are already capable of growing your own vegetables.
She does assume you are in a temperate climate, so if you are not, this might not be the book for you. Although! The recipes are still great; it’s just you’d have to shop for the ingredients and they probably won’t be fresh local produce for the exact same reason that you didn’t grow them.
If you are in a temperate climate though, this will take you through the year of seasonal produce (if you’re in a temperate climate but it’s in for example Australia, you’ll need to make a six-month adjustment for being in the S. Hemisphere), with many recipes to use not just one ingredient from your garden at a time, but a whole assortment, consistent with the season.
About the recipes: they (which are 450 in number) are (as you might imagine) very plant-forward, but they’re generally not vegan and often not vegetarian. So, don’t expect that you’ll produce everything yourself—just most of the ingredients!
Bottom line: if you like cooking, and are excited by the idea of growing your own food but are unsure how regularly you can integrate that, this book will keep you happily busy for a very long time.
Click here to check out Sarah Raven’s Garden Cookbook, and level-up your home cooking!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Anti-Stress Herb That Also Fights Cancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What does Rhodiola rosea actually do, anyway?
Rhodiola rosea (henceforth, “rhodiola”) is a flowering herb whose roots have adaptogenic properties.
In the cold, mountainous regions of Europe and Asia where it grows, it has been used in herbal medicine for centuries to alleviate anxiety, fatigue, and depression.
What does the science say?
Well, let’s just say the science is more advanced than the traditional use:
❝In addition to its multiplex stress-protective activity, Rhodiola rosea extracts have recently demonstrated its anti-aging, anti-inflammation, immunostimulating, DNA repair and anti-cancer effects in different model systems❞
Nor is how it works a mystery, as the same paper explains:
❝Molecular mechanisms of Rhodiola rosea extracts’s action have been studied mainly along with one of its bioactive compounds, salidroside. Both Rhodiola rosea extracts and salidroside have contrasting molecular mechanisms on cancer and normal physiological functions.
For cancer, Rhodiola rosea extracts and salidroside inhibit the mTOR pathway and reduce angiogenesis through down-regulation of the expression of HIF-1α/HIF-2α.
For normal physiological functions, Rhodiola rosea extracts and salidroside activate the mTOR pathway, stimulate paracrine function and promote neovascularization by inhibiting PHD3 and stabilizing HIF-1α proteins in skeletal muscles❞
~ Ibid.
And, as for the question of “do the supplements work?”,
❝In contrast to many natural compounds, salidroside is water-soluble and highly bioavailable via oral administration❞
~ Ibid.
And as to how good it is:
❝Rhodiola rosea extracts and salidroside can impose cellular and systemic benefits similar to the effect of positive lifestyle interventions to normal physiological functions and for anti-cancer❞
~ Ibid.
Source: Rhodiola rosea: anti-stress, anti-aging, and immunostimulating properties for cancer chemoprevention
But that’s not all…
We can’t claim this as a research review if we only cite one paper (even if that paper has 144 citations of its own), and besides, it didn’t cover all the benefits yet!
Let’s first look at the science for the “traditional use” trio of benefits:
When you read those, what are your first thoughts?
Please don’t just take our word for things! Reading even just the abstracts (summaries) at the top of papers is a very good habit to get into, if you don’t have time (or easy access) to read the full text.
Reading the abstracts is also a very good way to know whether to take the time to read the whole paper, or whether it’s better to skip onto a different one.
- Perhaps you noticed that the paper we cited for anxiety was quite a small study.
- The fact is, while we found mountains of evidence for rhodiola’s anxiolytic (antianxiety) effects, they were all small and/or animal studies. So we picked a human study and went with it as illustrative.
- Perhaps you noticed that the paper we cited for fatigue pertained mostly to stress-related fatigue.
- This, we think, is a feature not a bug. After all, most of us experience fatigue because of the general everything of life, not because we just ran a literal marathon.
- Perhaps you noticed that the paper we cited for depression said it didn’t work as well as sertraline (a very common pharmaceutical SSRI antidepressant).
- But, it worked almost as well and it had far fewer adverse effects reported. Bear in mind, the side effects of antidepressants are the reason many people avoid them, or desist in taking them. So rhodiola working almost as well as sertraline for far fewer adverse effects, is quite a big deal!
Bonus features
Rhodiola also putatively offers protection against Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and cerebrovascular disease in general:
Rosenroot (Rhodiola): Potential Applications in Aging-related Diseases
It may also be useful in the management of diabetes (types 1 and 2), but studies so far have only been animal studies, and/or in vitro studies. Here are two examples:
- Antihyperglycemic action of rhodiola-aqeous extract in type 1 diabetic rats
- Evaluation of Rhodiola crenulata and Rhodiola rosea for management of type 2 diabetes and hypertension
How much to take?
Dosages have varied a lot in studies. However, 120mg/day seems to cover most bases. It also depends on which of rhodiola’s 140 active compounds a particular benefit depends on, though salidroside and rosavin are the top performers.
Where to get it?
As ever, we don’t sell it (or anything else) but here’s an example product on Amazon.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Perhaps you noticed that the paper we cited for anxiety was quite a small study.
-
Undoing Creatine’s Puffiness Side Effect
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Creatine is known to increase “puffiness”, especially in my face. Are there any supplements that do the opposite?!❞
So first, let’s examine why this happens: creatine is most often taken to boost muscle size and performance. Your muscles are, of course, mostly water by mass, and so building your muscles requires extra water, which triggers systemic water retention.
In other words: you take creatine, exercise, and as the muscles start growing, the body goes “oh heck, we are running out of water, better save as much as possible in order to keep hydrating the muscles without running out” and starts putting it anywhere it can that’s not your bladder, so this will largely be the soft tissues of your body.
So, this results in classic water retentions symptoms including bloating and, yes, facial puffiness.
How much this happens, and how long the effects last, depend on three main things:
- What daily dose of creatine you are taking
- What kind of exercise you are doing
- What your hydration is like
The dose is relevant as it’s most common to get this puffiness during the “loading” phase, i.e. if you’re taking an increased dose to start with.
The exercise is relevant as it affects how much your body is actually using the water to build muscles.
The hydration is relevant because the less water you are taking, the more the body will try to retain whatever you do have.
This means, of course, that the supplement you are looking for to undo the facial puffiness is, in fact, water (even, nay, especially, if you feel bloated too):
Water For Everything? Water’s Counterintuitive Properties
Additionally, you could scale back the dose of creatine you’re taking, if you’re not currently doing heavy muscle-building exercise.
That said, the recommended dose for cognitive benefits is 5g/day, which is a very standard main-phase (i.e., post-loading) bodybuilding dose, so do with that information what you will.
See also: Creatine’s Brain Benefits Increase With Age
On which note: whether or not you want to take creatine for brain benefits, however, may depend on your age:
Creatine: Very Different For Young & Old People
Most research on creatine’s effects on humans has usually been either collegiate athletes or seniors, which leaves quite a research gap in the middle—so it’s unclear at what age the muscle-building effects begin to taper off, and at what age the cognitive benefits begin to take off.
Want a quicker fix?
If you want to reduce your facial puffiness acutely (e.g., you have a date in an hour and would like to not have a puffy face), then there are two things you can do that will help immediately, and/but only have short-term effects, meaning you’d have to do them daily to enjoy the results every day:
The first is an ice bath; simply fill a large bowl with water and ice cubes, give it a couple of minutes to get down to temperature, hold your breath and plunge your face in for as long as you can comfortably hold your breath. Repeat a few times, and towel off.
This helps by waking up the vasculature in your face, helping it to reduce puffiness naturally.
The second is facial yoga or guā shā, which is the practice of physically manipulating the soft tissues of your face to put them where you want them, rather than where you don’t want them. This will work against water retention puffiness, as well as cortisol puffiness, lymphatic puffiness, and more:
7-Minute Face Fitness For Lymphatic Drainage & Youthful Jawline
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cooking for Longevity – by Nisha Melvani
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Before it gets to the recipes, this book kicks off with a lot of science (much more than is usual for even healthy-eating recipe books), demystifying more nutrients than most people think of on a daily basis, what they do and where to get them, and even how to enhance nutrient absorption.
As well as an up-front ingredients list, we additionally get not just meal planning advice in the usual sense of the word, but also advice on timing various aspects of nutrition in order to enjoy the best metabolic benefits.
The recipes themselves are varied and good. It’s rare to find a recipe book that doesn’t include some redundant recipes, and this one’s no exception, but it’s better to have too much information than too little, so it’s perhaps no bad thing that all potentially necessary bases are covered.
In terms of how well it delivers on the title’s promised “cooking for longevity” and the subtitle’s promised “boosting healthspan”, the science is good; very consistent with what we write here at 10almonds, and well-referenced too.
Bottom line: if you’d like recipes to help you live longer and more healthily, then this book has exactly that.
Click here to check out Cooking For Longevity, and cook for longevity!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: