Do You Need to Wear Sunscreen Indoors? An Analysis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Michelle Wong—chemist, science educator, and cosmetician—explains the science:
Factors to take into account
UVA and UVB aren’t entirely interchangeable, so it’s important to know what you’re up against.
Sunscreen is rated by SPF, which indicates UVB protection—guarding against burning, skin cancer, and premature aging. Broad spectrum or UVA ratings measure protection against UVA rays, which cause tanning, contribute to melanoma, and can lead to skin aging and hyperpigmentation. However, most UV studies are based on white skin, which may not apply universally.
The need for sunscreen indoors depends on how much UV exposure you receive there:
- Direct exposure occurs when sunlight shines directly on you, such as when sitting by a window.
- Diffuse exposure happens when UV rays are scattered by air molecules or reflected off surfaces, which can still occur in shaded areas.
Indoors, walls and barriers do reduce UV exposure significantly. However, factors like window size, distance from windows, and the type of glass (which blocks UVB but not all UVA) play important roles in determining exposure.
The UV index (your phone’s weather app will probably have this) indicates the level of sunburn-causing UV in a specific area at a particular time. In Sydney, for example (where Dr. Wong is), the UV index can vary from 12 in summer to 2 in winter. Although UVA levels fluctuate less dramatically than UVB, they still peak during midday and in summer. Health guidelines in countries like Australia recommend wearing sunscreen when the UV index is 3 or above, but not necessarily every day.
Personal factors also influence the need for sunscreen indoors. People with darker skin, who have more melanin, may need less protection from incidental UV exposure but might still require UVA protection to prevent pigmentation. Those using skincare products that increase UV sensitivity, like alpha hydroxy acids, or those with specific medical conditions, such as photosensitivity or a family history of skin cancer, may also get particular benefit from wearing sunscreen indoors.
As to the downsides? There are some drawbacks to wearing sunscreen indoors, including cost, the effort required for application, and the risk of clogged pores. Though health concerns related to sunscreen are generally minor, they may tip the balance against wearing it if UV exposure is minimal.
For more on all of this plus visual teaching aids, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Do We Need Sunscreen In Winter, Really? ← we tackle the science behind the answer to this similar* question
*But different, because now we need to take into account such things as axial tilt, the sun’s trajectory through the atmosphere (and thus how much gets reflected, refracted, diffused, etc—or not, as the case may be).
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What you need to know about xylazine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Xylazine is a non-opioid tranquilizer designed for veterinary use in animals. The sedative is not approved for use in people, yet it’s becoming more prevalent in the illicit drug supply.
Sometimes called “tranq,” it’s often mixed with other drugs, such as fentanyl, a potent opioid responsible for a growing number of overdose deaths. Last year, the White House Office of National Drug Control Policy declared fentanyl mixed with xylazine an “emerging threat.”
Read on to learn more about xylazine: what happens when people take it, what to do if an overdose is suspected, and how harm reduction tools can prevent overdose deaths.
How are people who use drugs exposed to xylazine?
Studies show people are exposed to xylazine—knowingly or unknowingly—when it’s mixed with other drugs like heroin, cocaine, meth, and, most frequently, fentanyl. When combined with opioids or other drugs, it increases the risk of a drug overdose.
What happens if someone takes xylazine?
Taking xylazine can cause drowsiness, amnesia, slow breathing, slow heart rate, dangerously low blood pressure, wounds that can become infected, and death, especially when taken in combination with other drugs.
Why does xylazine increase the risk of overdose?
Xylazine is a central nervous system depressant, which means that it slows down the body’s heart rate and breathing. It can also enhance the effects of other depressants, such as opioids, which may lead to suffocation.
What are the signs of a xylazine-related overdose?
Xylazine-related overdoses look like opioid overdoses. A person who has overdosed may exhibit a slow pulse, slow breathing, blurry vision, disorientation, drowsiness, confusion, blue skin, and loss of consciousness.
How many people die from xylazine-related overdoses in the U.S.?
Xylazine-related overdose deaths in the U.S. rose from 102 deaths in 2018 to 3,468 deaths in 2021. Most occurred in Delaware, the District of Columbia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, Virginia, and West Virginia. Fentanyl was the most frequently co-occurring drug involved in those deaths.
What should I do if an overdose is suspected?
If you suspect that a person has overdosed on any drug, call 911 and give them naloxone—sometimes sold under the brand name Narcan—a medication that can reverse an opioid overdose. You should also stay with the person who has overdosed until first responders arrive. Most states have Good Samaritan laws, which protect people who have overdosed and those assisting them from certain criminal penalties.
While naloxone cannot reverse the effects of xylazine alone, experts recommend administering naloxone if an overdose is suspected because it’s often mixed with opioids.
You can get naloxone for free from some nonprofit organizations and government-run programs. You can also purchase over-the-counter naloxone at pharmacies, grocery and convenience stores, and other retailers.
Learn how to use naloxone in this short training video from the American Medical Association, or sign up for a free online training.
How can people prevent xylazine-related overdoses?
Harm reduction programs are community programs that prevent drug overdoses, reduce the spread of infectious diseases, and connect people to medical care. These programs provide lifesaving tools like naloxone, as well as fentanyl and xylazine test strips, which can detect the presence of these drugs in a substance and prevent overdoses. Drug test strips can also be ordered online.
However, test strips are considered “drug paraphernalia” in some states and are not legal everywhere. Learn more about state laws around drug checking equipment from the Network for Public Health Law.
Learn more about harm reduction from the CDC.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Meditation That You’ll Actually Enjoy
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Meditation That You’ll Actually Enjoy
We previously wrote about…
No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
this is a great primer, by the way, for the science and simplicity of mindfulness, along with the simplest mindfulness meditation to get you going.
Today, we’re going to have some fun with meditation.
First: The Problem
Once the usefulness and health benefits of meditation have been established, often people want to meditate, but complain they don’t have the time.
But that’s not the real reason, though, is it?
Let’s face it, a basic meditation can give benefits within two minutes. Or within two breaths, for that matter. So, it’s not really for a lack of time.
The real reason is because it doesn’t feel productive, and it’s not fun. For us to feel motivated to do a thing, usually we need at least one or the other. And even if we know it really is productive, it not feeling that way will hobble us.
So instead, let us make things a little more fun, with…
Meditation games!
As it turns out, there are good kinds of meditation with which one can have a little fun.
Catch the next thought
A common feature of many meditative practices is the experience of having fewer, or ideally no, thoughts.
But it’s hard to enact a negative, and thoughts keep coming.
So instead, make yourself comfortable, settle in, and lie in wait for thoughts. When one comes along, pounce on it in your mind. And then release it, and wait for the next.
At first, your thoughts may be coming thick and fast, but soon, you’ll find the pauses between them lengthening, and you have moments of contented not-knowing of what the next thought will be before it comes along.
This state of relaxed, ready alertness, calm and receptive, is exactly what we’re hoping to find here. But don’t worry about that while you’re busy lying in wait for the next wild thought to come along
Counting breaths
Many meditative practices involve focus on one’s breath. But it’s easy for attention to wander!
This game is a simple one. Count your breaths, not trying to change your rate of breathing at all, just letting it be, and see how high you can get before you lose count.
Breathing in and out, once, counts as one breath, by the way.
You may find that your rate of breathing naturally slows while you’re doing this. That’s fine; let it. It’ll add to the challenge of the game, because before long there will be lengthy pauses between each number.
If you lose count, just start again, and see if you can beat your high score.
This meditation game is an excellent exercise to build for sustained focus, while also improving the quality of breathing (as a side-effect of merely paying attention to it).
Hot spot, cold spot
The above two meditation games were drawn from Japanese and Chinese meditative practices, zen and qigong respectively; this one’s from an Indian meditative practice, yoga nidra. But for now, just approach it with a sense of playful curiosity, for best results.
Make yourself comfortable, lying on your back, arms by your sides.
Take a moment first to pay attention to each part of your body from head to toe, and release any tension that you may be holding along the way.
First part: mentally scan your body for where it feels warmest, or most active, or most wanting of attention (for example if there is pain, or an itch, or some other sensation); that’s your “hot spot” for the moment.
Second part: mentally scan your body for where it feels coolest, or most inert, or almost like it’s not a part of your body at all; that’s your “cold spot” for the moment.
Now, see if you can flip them. Whether you can or can’t, notice if your “hot spot” or “cold spot” moves, or if you can move them consciously.
This meditation game is a great exercise to strengthen interoception and somatic awareness in general—essential for being able to “listen to your body”!
Closing thoughts
All three practices above have very serious reasons and great benefits, but make sure you don’t skip enjoyment of the fun aspects!
Being “young at heart” is, in part, to do with the ability to enjoy—literally, to take joy in—the little things in life.
With that in mind, all we have left to say here is…
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Ice Cream vs Fruit Sorbet – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing ice cream to fruit sorbet, we picked the ice cream.
Why?
Well, neither are great!
But the deciding factor is simple: ice cream has more nutrients to go with its sugar.
While “fruit is good” is a very reliable truism in and of itself, sorbet tends to be made with fruit juice (or at best, purée, which for these purposes is more or less the same) and sugar. The small vitamin content is nowhere near enough to make up for this. The fiber having been removed by juicing or puréeing, the fruit juice with added sugar is basically shooting glucose and fructose into your veins while doing little else.
Fruit juice (even freshly-pressed) is nowhere near in the same league of healthiness as actual fruit!
See also: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Ice cream, meanwhile, is also not exactly a health food. But it has at least some minerals worth speaking of (mostly: calcium, potassium, phosphorus), and some fat that a) can be used b) helps slightly slow the absorption of the sugars.
In short: please do not consider either of these things to be a health food. But if you’re going to choose one or the other (and are not lactose-intolerant), then ice cream has some small positives to go with its negatives.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Five Flavors & Five Benefits
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Five Flavors Of Good Health
Schisandra chinensis, henceforth Schisandra, is also called the “five flavor fruit”, for covering the culinary bases of sweet, salt, bitter, sour, and pungent.
It can be eaten as a fruit (small red berries), juiced from the fruit, or otherwise extracted into supplements (dried powder of the fruit being a common one).
It has long enjoyed usage in various traditional medicines, especially in China and Siberia.
So, what are its health claims, and how does the science stack up?
Menopause
Most of the studies are mouse studies, and we prefer studies on humans, so here’s a small (n=36) randomized clinical trial that concluded…
❝Schisandra chinensis can be a safe and effective complementary medicine for menopausal symptoms, especially for hot flushes, sweating, and heart palpitations❞
~ Dr. Joon Young Park & Dr. Kye Hyun Kim
Read more: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of Schisandra chinensis for menopausal symptoms
Antioxidant (and perhaps more)
Like many berries, it’s a good source of lignans offering antioxidant effects:
Antioxidant Effects of Schisandra chinensis Fruits and Their Active Constituents
Lignans usually have anticancer effects too (which is reasonably, given what is antioxidant is usually anticancer and anti-inflammatory as well, by the same mechanism) but those have not yet been studied in schisandra specifically.
Antihepatotoxicity
In other words, it’s good for your liver. At least, so animal studies tell us, because human studies haven’t been done yet for this one. The effect is largely due to its antioxidant properties, but it seems especially effective for the liver—which is not surprising, giving the liver’s regeneration mechanism.
Anyway, here’s a fascinating study that didn’t even need to use the fruit itself, just the pollen from the plant, it was that potent:
Athletics enhancer
While it’s not yet filling the shelves of sports nutrition stores, we found a small (n=45) study with healthy post-menopausal women who took either 1g of schisandra (experimental group) or 1g of starch (placebo group), measured quadriceps muscle strength and resting lactate levels over the course of a 12 week intervention period, and found:
❝Supplementation of Schisandra chinensis extract can help to improve quadriceps muscle strength as well as decrease lactate level at rest in adult women ❞
Anti-Alzheimers & Anti-Parkinsons
The studies for this are all in vitro, but that’s because it’s hard to find volunteers willing to have their brains sliced and looked at under a microscope while they’re still alive.
Nevertheless, the results are compelling, and it seems uncontroversial to say that schisandra, or specifically Schisandrin B, a compound it contains, has not only anti-inflammatory properties, but also neuroprotective properties, and specifically blocks the formation of excess amyloid-β peptides in the brain (which are critical for the formation of amyloid plaque, as found in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients):
Is it safe?
For most people, yes! Some caveats:
- As it can stimulate the uterus, it’s not recommended if you’re pregant.
- Taking more than the recommended amount can worsen symptoms of heartburn, GERD, ulcers, or other illnesses like that.
And as ever, do speak with our own doctor/pharmacist if unsure, as your circumstances may vary and we cannot cover all possibilities here.
Where can I get some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eating on the Wild Side: – by Jo Robinson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author is an investigative journalist, and it shows here, as she leaves no stone unturned in her quest for the truth in the face of many food myths.
She covers a lot of “popular wisdom” things that are varyingly true or false, or sometimes even both—in the case of food lore that’s a good rule of thumb, but has notable exceptions (e.g. “more colorful and/or darker-colored fruits/vegetables contain more nutrients”, which is a very good rule of thumb until one meets a cauliflower, for example).
She also covers food preparation myths, and how, to give one example, in spite of the popularity of “less cooked is better”, in some cases certain cooking methods will indeed destroy nutrients; in others, certain cooking methods will improve nutritional availability. Either by destroying an adjacent antinutrient (e.g. phytates), or by breaking something down into a more manageable form that our body can absorb. Knowing which is which, is important.
The book is organized by kinds of food, and does exclusively cover plants, but there’s more than enough material for any omnivore to enjoy.
The style is… Journalistic, it would be fair to say. Which is not surprising, given the author. But it means that it is written in a fairly narrative way, to draw the reader in and make it an enjoyable read while still being informative in all parts (there is no padding). In terms of science, the in-the-prose science is as minimal as possible to still convey what needs to be conveyed, while 25 pages of bibliography stack up at the end to show that indeed, this journalist cites sources.
Bottom line: this is a really enjoyable book, packed with a wealth of knowledge, and is perfect to uplift your cooking by knowing your ingredients a little more intimately!
Click here to check out Eating On The Wild Side, and, enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Saturated Fat: What’s The Truth?
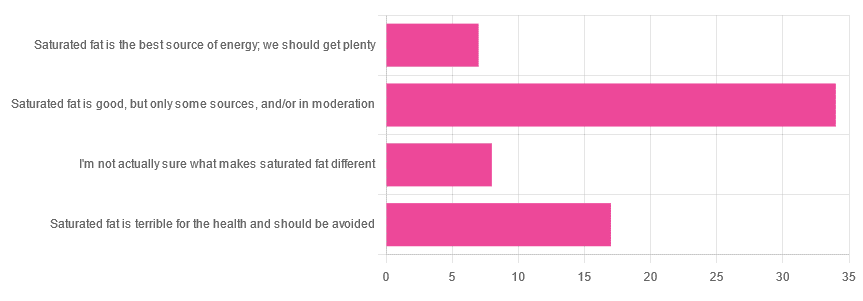
We asked you for your health-related opinion of saturated fat, and got the above-pictured, below-described, set of results.
- Most recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation”
- This is an easy one to vote for, because of the “and/or in moderation” part, which tends to be a “safe bet” for most things.
- Next most popular was “Saturated fat is terrible for the health and should be avoided”
- About half as many recorded votes were for “I’m not actually sure what makes saturated fat different”, which is a very laudable option to click. Admitting when we don’t know things (and none of us know everything) is a very good first step to learning about them!
- Fewest recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is the best source of energy; we should get plenty”.
So, what does the science say?
First, a bit of physics, chemistry, and biology
You may be wondering what, exactly, saturated fats are “saturated” with. That’s a fair question, so…
All fats have a molecular structure made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Saturated fats are saturated with hydrogen, and thus have only single bonds between carbon atoms (unsaturated fats have at least one double-bond between carbon atoms).
The observable effect this has on them, is that fats that are saturated with hydrogen are solid at room temperature, whereas unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature. Their different properties also make for different interactions inside the human body, including how likely or not they are to (for example) clog arteries.
See also: Could fat in your bloodstream cause blood clots?
Saturated fat is the best source of energy; we should get plenty: True or False?
False, in any reasonable interpretation, anyway. That is to say, if your idea of “plenty” is under 13g (e.g: two tablespoons of butter, and no saturated fat from other sources, e.g. meat) per day, then yes, by all means feel free to eat plenty. More than that, though, and you might want to consider trimming it down a bit.
The American Heart Association has this to say:
❝When you hear about the latest “diet of the day” or a new or odd-sounding theory about food, consider the source.
The American Heart Association recommends limiting saturated fats, which are found in butter, cheese, red meat and other animal-based foods, and tropical oils.
Decades of sound science has proven it can raise your “bad” cholesterol and put you at higher risk for heart disease.❞
Source: The American Heart Association Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations on Saturated Fat
The British Heart Foundation has a similar statement:
❝Despite what you read in the media, our advice is clear: replace saturated fats with unsaturated fats and avoid trans fats. Saturated fat is the kind of fat found in butter, lard, ghee, fatty meats and cheese. This is linked to an increased risk of heart and circulatory disease❞
Source: British Heart Foundation: What does fat do and what is saturated fat?
As for the World Health Organization:
❝1. WHO strongly recommends that adults and children reduce saturated fatty acid intake to 10% of total energy intake
2. WHO suggests further reducing saturated fatty acid intake to less than 10% of total energy intake
3. WHO strongly recommends replacing saturated fatty acids in the diet with polyunsaturated fatty acids; monounsaturated fatty acids from plant sources; or carbohydrates from foods containing naturally occurring dietary fibre, such as whole grains, vegetables, fruits and pulses.❞
Source: Saturated fatty acid and trans-fatty acid intake for adults and children: WHO guideline
Please note, organizations such as the AHA, the BHF, and the WHO are not trying to sell us anything, and just would like us to not die of heart disease, the world’s #1 killer.
As for “the best source of energy”…
We evolved to eat (much like our nearest primate cousins) a diet consisting mostly of fruits and other edible plants, with a small supplementary amount of animal-source protein and fats.
That’s not to say that because we evolved that way we have to eat that way—we are versatile omnivores. But for example, we are certainly not complete carnivores, and would quickly sicken and die if we tried to live on only meat and animal fat (we need more fiber, more carbohydrates, and many micronutrients that we usually get from plants)
The closest that humans tend to come to doing such is the ketogenic diet, which focuses on a high fat, low carbohydrate imbalance, to promote ketosis, in which the body burns fat for energy.
The ketogenic diet does work, and/but can cause a lot of health problems if a lot of care is not taken to avoid them.
See for example: 7 Keto Risks To Keep In Mind
Saturated fat is terrible for the health and should be avoided: True or False?
False, if we are talking about “completely”.
Firstly, it’s practically impossible to cut out all saturated fats, given that most dietary sources of fat are a mix of saturated, unsaturated (mono- and poly-), and trans fats (which are by far the worst, but beyond the scope of today’s main feature).
Secondly, a lot of research has been conducted and found insignificant or inconclusive results, in cases where saturated fat intake was already within acceptable levels (per the recommendations we mentioned earlier), and then cut down further.
Rather than fill up the newsletter with individual studies of this kind here’s a high-quality research review, looking at 19 meta-analyses, each of those meta-analyses having looked at many studies:
Dietary saturated fat and heart disease: a narrative review
Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation: True or False?
True! The moderation part is easy to guess, so let’s take a look at the “but only some sources”.
We were not able to find any convincing science to argue for health-based reasons to favor plant- or animal-sourced saturated fat. However…
Not all saturated fats are created equal (there are many kinds), and also many of the foods containing them have additional nutrients, or harmful compounds, that make a big difference to overall health, when compared gram-for-gram in terms of containing the same amount of saturated fat.
For example:
- Palm oil’s saturated fat contains a disproportionate amount of palmitic acid, which raises LDL (“bad” cholesterol) without affecting HDL (“good” cholesterol), thus having an overall heart-harmful effect.
- Most animal fats contain a disproportionate amount of stearic acid, which has statistically insignificant effects on LDL and HDL levels, and thus is broadly considered “heart neutral” (in moderation!)
- Coconut oil’s saturated fat contains a disproportionate amount of lauric acid, which raises total cholesterol, but mostly HDL without affecting LDL, thus having an overall heart-beneficial effect (in moderation!)
Do you know what’s in the food you eat?
Test your knowledge with the BHF’s saturated fat quiz!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Most recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation”